======================= **基础知识** =======================
1. 应用 完全二叉树 结构,通过连续数组空间储存( 左子树:2 * n, 右子树 : 2 * n + 1; root = 1) , 实现一个完全二叉树;
要学会 数组(表现形式) 与 完全二叉树 (思维结构)之间的转换!
数据结构:本质就是定义一种性质,并在所有操作中都要维护这种性质的;
也就意味这数据结构中包含 数据定义 + 结构操作(增删改查)两部分,对于这段的理解,结合下面 2& 3 部分仔细理解;
2. 任意 三元组中,顶点节点 是最大节点: 大顶堆;下一大节点,在第一大节点下一层; 下下大节点,是在下一层或下下一层中;所以兄弟节点之间大小没有直接关系;
顶点节点 是最小节点: 小顶堆; 同样性质类似大顶堆;
3. 增操作,结尾插入新元素, 然后将堆进行满足性质的位置调整(上浮调整);
删操作,弹出堆定元素,然后将数组中最后一个元素调整到堆顶(保证是完全二叉树),然后做弹出后为满足性质的位置调整(下沉调整);
4. 堆排序(如下图):

参考下面示意图:使用大顶堆,然后每次将弹出的最大值放到数组末尾,弹出所有元素以后,数组的值就是从小到排序!
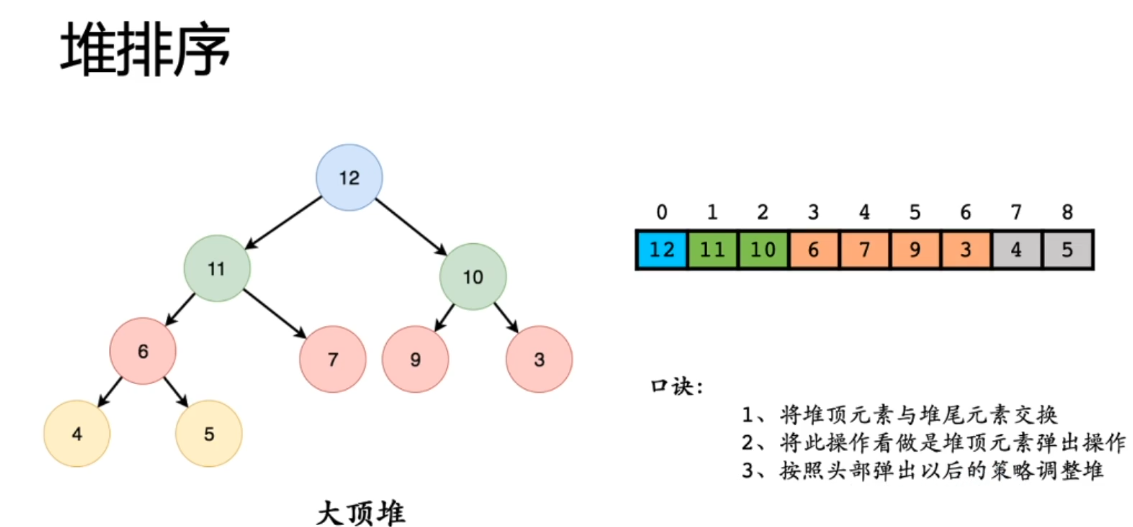
5. 堆 为什么 又叫优先队列?
比较下面的性质,会发现下面很多类似的地方;所以堆是优先队列的实现方式;
| 普通队列 | 优先队列 |
| 尾部入队 |
尾部插入数据 |
| 头部出队 | 头部弹出数据 |
| 先进先出(FIFO) | 每次出队权值(最大/小元素) |
| 数组实现 | 数组实现,逻辑上是一个堆 |
======================= **代码演示** =======================
1. 实现一个大顶堆(顺带实现堆排序);

1 //#include "heap.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <cstring> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 //定义大顶堆 8 9 struct my_heap{ 10 #define MAX_N 1000 11 int h[MAX_N + 5], len; 12 my_heap(): len(0) { 13 memset(h, 0, sizeof(int) * (MAX_N + 5)); 14 } 15 bool empty(){ 16 return len == 0; 17 } 18 19 int size() { 20 return len; 21 } 22 23 int top() { 24 if(empty()) return -1; 25 return h[0]; 26 } 27 void push(int val) { 28 int next = (len - 1) / 2, cur = len; 29 h[len++] = val; 30 while(cur && h[next] < h[cur]) { 31 swap(h[next], h[cur]); 32 cur = next; 33 next = (cur - 1) / 2; 34 } 35 return ; 36 } 37 38 void pop() { 39 if(empty()) return; 40 swap(h[0], h[--len]); 41 int cur = 0, next = 2 * cur + 1; 42 while(next < len){ 43 if(next + 1 < len && h[next] < h[next + 1]) next += 1; 44 if(h[cur] > h[next]) break; 45 swap(h[cur], h[next]); 46 cur = next; 47 next = 2 * cur + 1; 48 } 49 return; 50 } 51 52 void output(int cnt) { 53 cout << "now heap: " ; 54 for(int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) cout << h[i] << " "; 55 cout << endl; 56 return; 57 } 58 59 }; 60 61 62 int main() 63 { 64 my_heap h1; 65 int op, val, max_cnt = 0; 66 cout << "Pls input op & val.\n 0: stop;\n 1: push;\n 2: pop;\n 3: size;\n 4: output;\n" << endl; 67 while(cin >> op) { 68 if(!op) break; // 0: stop; 69 switch (op) { 70 case 1: { //push 71 cin >> val; 72 h1.push(val); 73 cout << "after push ," ; 74 max_cnt = max(max_cnt, h1.size()); 75 h1.output(h1.size()); 76 } break; 77 case 2: { 78 h1.pop(); 79 cout << "after pop ,"; 80 h1.output(h1.size()); 81 } break; 82 case 3: cout << h1.size() << endl; break; 83 case 4: h1.output(h1.size()); break; 84 default : cout << "error op code\n"; 85 } 86 } 87 88 cout << "the seq:" ; 89 h1.output(max_cnt); //输出一个升序数组,必须是先都push, 后面都pop 90 return 0; 91 }
下面用C++ 实现heap, 泛型编程,继承,STL, 仿函数,const;
C++ 中有很多实现了的方法,这些方法 怎样在实际工作复用,并针对异常等处理, 存在很多细节...

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <functional> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 template<typename T> 9 class heap_cpp : public vector<T> { 10 private: 11 function<bool(T, T)> cmp; 12 int _size; 13 public: 14 template<typename Func_T> 15 heap_cpp(Func_T fn) : cmp(fn), _size(0){} 16 bool empty() { 17 return this->empty(); 18 } 19 int size() const{ 20 return _size; 21 } 22 T top() const{ 23 return this->at(0); 24 } 25 void push(T t){ 26 this->push_back(t); 27 push_heap(this->begin(), this->end(), cmp); 28 _size += 1; 29 return; 30 } 31 void pop() { 32 pop_heap(this->begin(), this->end(), cmp); 33 this->pop_back(); 34 _size -= 1; 35 return; 36 } 37 }; 38 39 template<typename T> 40 void output(T t1) { 41 for(auto &x : t1) cout << x << " "; 42 cout << endl; 43 } 44 45 int main() 46 { 47 heap_cpp<int> h1{less<int>()}; 48 int val; 49 while(cin >> val) { 50 h1.push(val); 51 cout << "after push :"; 52 output(h1); 53 } 54 55 while(h1.size()) { 56 cout << h1.top() << endl; 57 h1.pop(); 58 } 59 60 return 0; 61 }
======================= **经典问题** =======================
堆适合维护: 集合最值!!
(所以针对一个数组,要不断取得其中最值,用堆来处理这个数组);
1. 最小/大 的k个数(leetcode:offer40)

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 vector<int> getLeastNumbers(vector<int>& arr, int k) { 4 priority_queue<int,vector<int>, greater<int>> pq; 5 for(auto x : arr) pq.push(x); 6 vector<int> ans; 7 while(k--) { 8 ans.push_back(pq.top()); 9 pq.pop(); 10 } 11 return ans; 12 } 13 };
2. 数据流中第K 大元素:(leetcode703)
数据不断变化中,然后要求第K 大值,要不断对新增加数据排序,所以堆最优;
(set/multiset 也可以实现排序,但是指定位置值返回不方便,更适合寻找特定的值是否存在;vector 等线性结构不具备排序功能,每次都要重新排序,费时);
 不断变化中的第K大
不断变化中的第K大固定数组的话,直接排序,然后求值即可;(leetcode215)

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) { 4 sort(nums.begin(), nums.end(), greater<int>()); 5 return nums[k - 1]; 6 } 7 };
3. 查找和最小的K 对数字(leetcode373): 这里有个比较有意思的点,求的是小的值,实现的却是大顶堆(限制k个数);
通过超出就有目的性的删除或跳出循环,来实现最小k 组;这也是heap 数据结构自身的特性决定的;
set 这里也可以用来取代heap;

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 4 template<typename T> 5 class heap : public vector<T> { 6 public: 7 8 template<typename Func_T> 9 heap(Func_T fun):cmp(fun){} 10 T& top() { return this->at(0);} 11 void pop(){ 12 pop_heap(this->begin(),this->end(),cmp); 13 this->pop_back(); 14 return ; 15 } 16 void push(const T& a){ 17 this->push_back(a); 18 push_heap(this->begin(),this->end(),cmp); 19 return ; 20 } 21 22 private: 23 function<bool(T,T)> cmp; 24 25 }; 26 27 struct CMP { 28 bool operator()(vector<int> a, vector<int> b){ 29 return a[0]+a[1] < b[0]+b[1] ; 30 } 31 }; 32 vector<vector<int>> kSmallestPairs(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, int k) { 33 CMP less_than; 34 heap<vector<int>> h{less_than}; 35 vector<int> temp(2) ; 36 for (auto i : nums1) { 37 for(auto j : nums2) { 38 temp[0] = i, temp[1] = j; 39 if (h.size() < k || less_than(temp,h.top())) { 40 h.push(temp); 41 if (h.size() > k) h.pop(); 42 } else { 43 break; 44 } 45 } 46 } 47 return h; 48 } 49 };
4. 数据流中的中位数 (leetcode295)

1 class MedianFinder { 2 public: 3 priority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int>> front; 4 priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> back; 5 6 MedianFinder(){} 7 8 void addNum(int num) { 9 if(front.size() == 0 || num <= front.top()) front.push(num); 10 else back.push(num); 11 12 if(back.size() > front.size()) { 13 int temp = back.top(); 14 back.pop(); 15 front.push(temp); 16 } 17 if(front.size() > back.size() + 1) { 18 int temp = front.top(); 19 front.pop(); 20 back.push(temp); 21 } 22 23 return; 24 } 25 26 double findMedian() { 27 int len = front.size() + back.size(); 28 if(len % 2) return front.top(); 29 return (double(front.top() + back.top()) / 2.0); 30 } 31 }; 32 33 /** 34 * Your MedianFinder object will be instantiated and called as such: 35 * MedianFinder* obj = new MedianFinder(); 36 * obj->addNum(num); 37 * double param_2 = obj->findMedian(); 38 */
5. 丑数(leetcode264) : 这题解法中包含了Euler 素数筛概念,每一个合数必定由 最小质数 * 最大因子 ,因此对于每一个合数,都可以由最小素因子标定;
至于这里的heap,则是用来决定顺序的;
(如果能找到某个数对应的具体位置(没找到算法),也可以用二分来找);

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int nthUglyNumber(int n) { 4 priority_queue<long long, vector<long long>, greater<long long>> pq; 5 int factor[3] = {2, 3, 5}; 6 pq.push(1); 7 while(--n) { 8 long long temp = pq.top(); 9 pq.pop(); 10 for(int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) { 11 pq.push(temp * factor[i]); 12 if(0 == temp % factor[i]) break; 13 } 14 } 15 return pq.top(); 16 } 17 };
======================= **应用场景** =======================
基本 前K 个大/小的值问题,
不断变化(插入/删除) 的数组,寻找一个某个有序情况下的值, 大都适合heap 来处理




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号