======================= **基础知识** =======================
1. FILO(先入后出) : 出栈 更多意义上是指 指针移动(与队列出队类似,都是指针的移动);
2. 括号匹配问题引出 思路进阶过程:记录左右括号个数 -> 影响的其实左右括号差 -> 本质是 ( 等价 发生,) 等价 结束,()才是一件事情完整;
( ( ) ) 可以看作 是事件与事件之间的完全包含关系: 等价于: funcA{ funcB; funcC}; 二叉树: 一个节点,包含两个子结点, 前序遍历);
注意: 完全包含关系中,隐含了顺序要求(具体例子看下面经典问题1);
3. 所以对于 完全包含关系 问题,都可以考虑用栈来解决:表达式求值,递归问题,二叉树遍历 ...
4. C++ STL 中stack 采用deque 实现(adaptor), 但是没有将iterator 封装出来,所以没法进行不改变式遍历;
注意: 有时候为了实现随即访问要求,可以通过vector,deque... 等容器实现stack 理念,但是还是满足随即访问需求,只要注意要FILO 即可;(具体例子见先面经典问题4)
======================= **代码演示** =======================
stack 实现:

1 class Stack { 2 public: 3 Stack(int s = 100): size(s) { 4 pos = -1; //通常栈0 指针设为-1, 防止没有分配内存时候,指针溢出? 5 ps = (int*) malloc(sizeof(int) * s); 6 } 7 bool isEmpty() { 8 return pos == -1; 9 } 10 bool isFull(){ 11 return pos == size - 1; 12 } 13 int len(){ 14 return pos + 1; 15 } 16 bool push(int val) { 17 if(isFull()) return false; 18 pos += 1; 19 *(ps + pos) = val; 20 return true; 21 } 22 bool pop() { 23 if(isEmpty()) return false; 24 pos -= 1; 25 return true; 26 } 27 int top() { 28 return *(ps + pos); 29 } 30 void output(){ 31 if(isEmpty()) { 32 cout << "stack is empty;\n"; 33 return; 34 } 35 for(int i = pos; i >= 0; --i) cout << *(i + ps) << " " ; 36 cout << endl; 37 return; 38 } 39 40 private: 41 int size; 42 int pos; 43 int *ps; 44 45 };
模拟 简单计算器(leetcode227): ( 如果考虑括号,可以把 '(' 强制入op,到了')' 强制 出到第一个‘(';

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 4 string removeSpace(string s) { 5 string ret = ""; 6 for(auto x : s) { 7 if(' ' == x) continue; 8 ret += x; 9 } 10 return ret; 11 } 12 13 int priority(char op) { 14 switch (op) { 15 case '+' : 16 case '-' : return 1; 17 case '*' : 18 case '/' : return 2; 19 default : cout << "error op : " << op << endl; 20 } 21 return -1; 22 } 23 24 int basicCal(int a, int b, char op) { 25 switch (op) { 26 case '+' : return a + b; 27 case '-' : return a - b; 28 case '*' : return a * b; 29 case '/' : return a / b; 30 default: cout << "error op : " << op << endl; 31 } 32 return 0; 33 } 34 35 36 int calculate(string s) { 37 stack<int> nums; 38 stack<char> op; 39 int temp = 0; 40 41 s = removeSpace(s); 42 43 for(auto x : s) { 44 if(x >= '0' && x <= '9') { 45 temp = temp * 10 + (x - '0'); 46 continue; 47 } 48 49 nums.push(temp); 50 temp = 0; 51 while(op.size() && priority(op.top()) >= priority(x)) { 52 int b = nums.top(); nums.pop(); 53 int a = nums.top(); nums.pop(); 54 nums.push( basicCal(a, b, op.top())); 55 op.pop(); 56 } 57 op.push(x); 58 } 59 nums.push(temp); 60 61 while(op.size()) { 62 int b = nums.top(); nums.pop(); 63 int a = nums.top(); nums.pop(); 64 nums.push( basicCal(a, b, op.top())); 65 op.pop(); 66 } 67 return nums.top(); 68 } 69 };
======================= **经典问题** =======================
1.括号匹配(leetcode20): 不仅有左右括号数目相等,还有顺序要求;这也是完全包含中包含的意思;

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 bool isValid(string s) { 4 stack<char> s1; 5 for(auto x : s) { 6 switch (x) { 7 case '(' : { 8 s1.push('('); 9 } break; 10 case '[' : { 11 s1.push('['); 12 } break; 13 case '{' : { 14 s1.push('{'); 15 } break; 16 case ')' : { 17 if(s1.empty() || s1.top() != '(') return false; 18 s1.pop(); 19 } break; 20 case ']' : { 21 if(s1.empty() || s1.top() != '[') return false; 22 s1.pop(); 23 } break; 24 case '}' : { 25 if(s1.empty() || s1.top() != '{') return false; 26 s1.pop(); 27 } break; 28 default: cout << "error" << endl; break; 29 } 30 } 31 return s1.empty(); 32 33 //下面方式无法保证先入括号类型一定会后出 34 // int cnt[3] = {0}; 35 // for(auto x : s) { 36 // switch (x) { 37 // case '(' : cnt[0] += 1; break; 38 // case '[' : cnt[1] += 1; break; 39 // case '{' : cnt[2] += 1; break; 40 // case ')' : cnt[0] -= 1; break; 41 // case ']' : cnt[1] -= 1; break; 42 // case '}' : cnt[2] -= 1; break; 43 // default: break; 44 // } 45 // for(int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) { 46 // if(cnt[i] < 0) return false; 47 // continue; 48 // } 49 // } 50 // for(int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) { 51 // if(cnt[i] != 0) return false; 52 // continue; 53 // } 54 // return true; 55 } 56 };
2. 递归;
引申:如何将递归程序通过迭代算法实现:(leetcode145):
注意点:a.保存当前递归层中参数,通过stack 实现,如果对应多个参数,就需要多个栈 依次操作;
b. 迭代过程,如何记录每个递归层做到哪一步骤(对于单个递归层有多个操作程序,返回递归结果时,是返回到当前递归层中调用函数位置的,知道执行的位置的);

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 class Solution { 13 public: 14 vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { 15 if(!root) return vector<int>(); 16 vector<int> ans; 17 stack<TreeNode*> s1; 18 stack<int> pri; //(0: left, 1: right, 2:root) 19 s1.push(root), pri.push(0); 20 21 while(s1.size()) { 22 int status = pri.top(); 23 pri.pop(); 24 if(status == 0) { 25 pri.push(1); 26 if(s1.top()->left) { 27 pri.push(0); 28 s1.push(s1.top()->left); 29 } 30 continue; 31 } 32 if(status == 1) { 33 pri.push(2); 34 if(s1.top()->right){ 35 pri.push(0); 36 s1.push(s1.top()->right); 37 } 38 continue; 39 } 40 if(status == 2) { 41 ans.push_back(s1.top()->val); 42 s1.pop(); 43 } 44 } 45 return ans; 46 } 47 };
3. 对于问题处理中,完整性问题体现:(leetcode636)

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 vector<int> exclusiveTime(int n, vector<string>& logs) { 4 stack<int> s1; //记录前一次id 5 vector<int> ans(n, 0); 6 for(int i = 0, pre = -1, I = logs.size(); i < I; ++i) { 7 int i1 = logs[i].find_first_of(":"), i2 = logs[i].find_last_of(":"); 8 int id = stoi(logs[i].substr(0, i1)), num = stoi(logs[i].substr(i2 + 1)); 9 if('s' == logs[i][i1 + 1]) { 10 if(s1.size()) ans[s1.top()] += (num - pre - 1); 11 pre = num - 1; //如何定义pre 也是归纳各种情况结果,优化后的方法; 12 s1.push(id); 13 } else { 14 ans[id] += (num - pre); 15 pre = num; 16 s1.pop(); 17 } 18 } 19 return ans; 20 } 21 // 这里对题意理解有偏差,所以存储的数据不够,这里就需要考虑一个问题完整性, 完全包含性,用栈来实现会更方便; 22 // void process(string &s, int *op) { 23 // int ind = 0, i = 0, len = s.size(); 24 // while(i < len) { 25 // if(1 == ind) { 26 // op[ind] = ('s' != s[i]); // start: 0; end : 1; 27 // 28 // while(':' != s[i]) i += 1; 29 // ind += 1; 30 // i += 1; 31 // continue; 32 // } 33 // 34 // int temp = 0; 35 // while(i < len && ':' != s[i]) { 36 // temp = temp * 10 + (s[i] - '0'); 37 // i += 1; 38 // } 39 // op[ind++] = temp; 40 // i += 1; 41 // } 42 // return ; 43 // } 44 // 45 // vector<int> exclusiveTime(int n, vector<string>& logs) { 46 // vector<int> ans(n, 0); 47 // int pre[2][3]; 48 // process(logs[0], pre[0]); 49 // 50 // cout << pre[0][0] << " ," << pre[0][1] << " ," << pre[0][2] << " ," << endl; 51 // 52 // for(int i = 1, I = logs.size(); i < I; ++i){ 53 // int ind = i % 2, p_ind = (i + 1) % 2; 54 // process(logs[i], pre[ind]); 55 // 56 // if(pre[ind][0] == pre[p_ind][0] && pre[p_ind][1] == 0 && pre[ind][1] == 1) { 57 // ans[pre[ind][0]] += (pre[ind][2] - pre[p_ind][2] + 1); 58 // } else if(!pre[ind][1] && !pre[p_ind][1]) { //now is start, pre is start; 59 // ans[pre[p_ind][0]] += (pre[ind][2] - pre[p_ind][2]); 60 // } else if(pre[ind][1] && pre[p_ind][1]){ //now is end, pre is endl; 61 // ans[pre[ind][0]] += (pre[ind][2] - pre[p_ind][2]); 62 // } 63 // } 64 // 65 // return ans; 66 // } 67 };
4. 使用其他容器,但是利用FILO 思想,同时又能实现随机访问的需求;(leetcode331)

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 bool isValidSerialization(string preorder) { 4 deque<string> process; 5 for(int i = 0, pre = 0, I = preorder.size(); i < I; ++i) { 6 pre = i; 7 if(',' == preorder[i]) continue; 8 while(i < I && preorder[i] >= '0' && preorder[i] <= '9') ++i; 9 if(pre != i) process.push_back(preorder.substr(pre, i - pre)); 10 else process.push_back("#"); 11 12 13 while(process.size() >= 3 && "#" == *process.rbegin() 14 && "#" == *(++process.rbegin()) && "#" != *(++++process.rbegin())) { 15 process.pop_back(); 16 process.pop_back(); 17 process.pop_back(); 18 process.push_back("#"); 19 } 20 } 21 22 return process.size() == 1 && process[0] == "#"; 23 } 24 };
======================= **应用场景** =======================
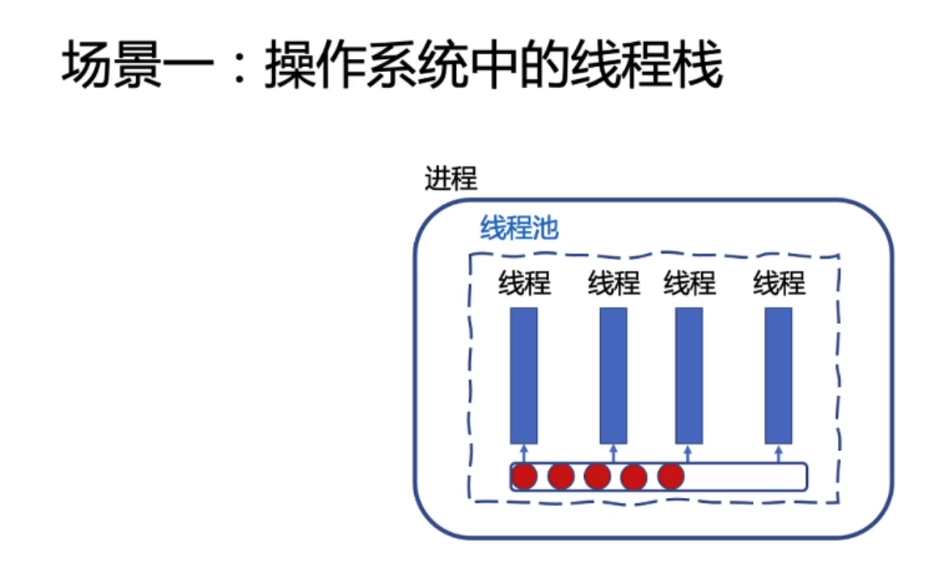
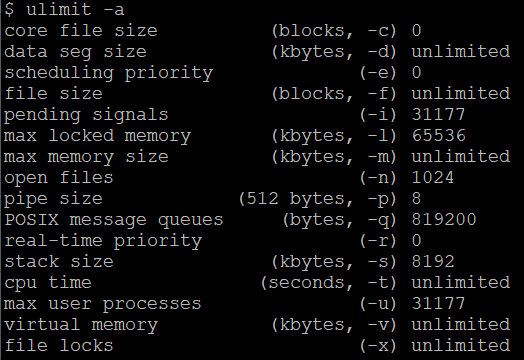
1. 操作系统中的线程栈; 当前系统中每个stack size : 8192;
所以在多线程编程中,每个线程都会占用8M 内存,需要注意对硬件的需求;
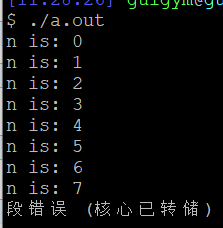
爆栈概念: 当递归函数调用过深,导致当前线程栈超出系统上限,就会引起爆栈;结果如下图中运行爆栈程序时候的结果:

1 using namespace std; 2 #define MAX_N 1000000 3 void funcA(int n) { 4 if(n > 10) return; 5 cout << "n is: " << n << endl; 6 char num[MAX_N]; 7 8 funcA(n + 1); 9 return; 10 } 11 12 int main() 13 { 14 funcA(0); 15 return 0; 16 }
 ---------->
----------> 
2. 这里的二叉树表达形式, 再想想 trie tree(在实现的理念上类似);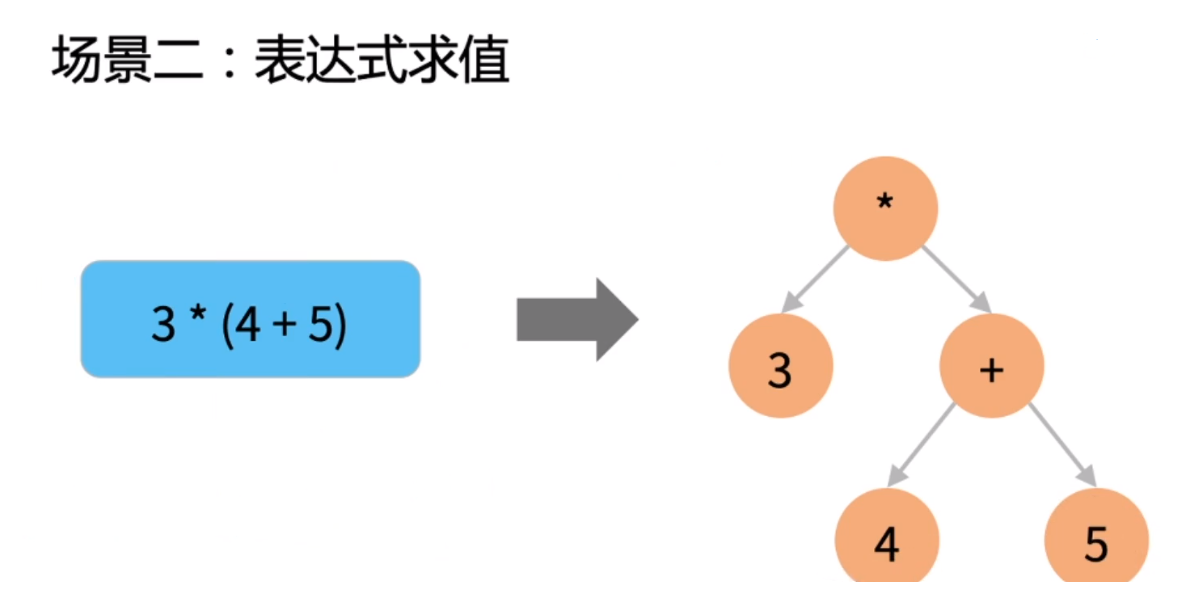
3. 自动机中的状态设定思维(还涉及到广义表);

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 class Codec { 11 public: 12 13 // Encodes a tree to a single string. 14 string serialize(TreeNode* root) { 15 if(!root) return ""; 16 string ret = ""; 17 stringstream ss; 18 ss << root->val; 19 ss >> ret; 20 21 if(!root->left && !root->right) return ret; 22 ret += "("; 23 if(root->left) ret += serialize(root->left); 24 ret += ","; 25 if(root->right) ret += serialize(root->right); 26 ret += ")"; 27 return ret; 28 } 29 30 // Decodes your encoded data to tree. 31 TreeNode* deserialize(string data) { 32 stack<TreeNode*> s; 33 int opcode = 0, idx = 0, LR_flag = 0; 34 TreeNode *p = nullptr, *root = nullptr; 35 36 while(idx < data.size()) { 37 switch (opcode) { 38 case 0: { 39 if(data[idx] >= '0' && data[idx] <= '9') opcode = 1; 40 else if(data[idx] == '(') opcode = 2; 41 else if(data[idx] == ',') opcode = 3; 42 else if(data[idx] == ')') opcode = 4; 43 } break; 44 case 1: { //num 45 int val = 0; 46 while(data[idx] >= '0' && data[idx] <= '9') val = val * 10 + (data[idx++] - '0'); 47 p = new TreeNode(val); 48 if(!root) root = p; 49 if(LR_flag == 1) s.top()->left = p; 50 else if(LR_flag == 2) s.top()->right = p; 51 opcode = 0; 52 } break; 53 case 2: { //"(" 54 s.push(p); 55 LR_flag = 1, idx++, opcode = 0; 56 } break; 57 case 3: { //"," 58 LR_flag = 2, idx++, opcode = 0; 59 } break; 60 case 4: { //")" 61 s.pop(), idx++, opcode = 0; 62 } break; 63 } 64 } 65 return root; 66 } 67 }; 68 69 // Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such: 70 // Codec* ser = new Codec(); 71 // Codec* deser = new Codec(); 72 // string tree = ser->serialize(root); 73 // TreeNode* ans = deser->deserialize(tree); 74 // return ans;




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号