编写汽车类,其功能有启动(start),停止(stop),加速(speedup)和减速(slowDown),启动和停止可以改变汽车的状态(on/off),初始时状态为off,速度为0,speedUp和slowDown可以调整汽车的速度,每调用一次汽车速度改变10(加速增10,减速减10),汽车启动后才能加减速,加速上限为160,减速下限为0,汽车速度减为0后才能停止,给出汽车类的定义。 Main函数中构造一个汽车对象,并对该对象进行操作,各个操作的编号为:
- start
- stop
- speedup
- slowdown 操作完成后打印出汽车的状态和速度。
输入描述:
操作
输出描述:
汽车的状态和速度
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = s.nextInt();
Car c = new Car();
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) {
int a = s.nextInt();
switch (a) {
case 1: c.start(); break;
case 2: c.stop(); break;
case 3: c.speedUp(); break;
case 4: c.slowDown(); break;
}
}
System.out.print(c.status + " ");
System.out.println(c.speed);
}
}
/* 你的代码被嵌在这里 */输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
8
1 3 3 4 3 4 4 2输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
off 0
1 class Car 2 { 3 public String status; 4 public int speed = 0; 5 public void start() 6 { 7 8 status = "on"; 9 speed = 0; 10 } 11 public void stop() 12 { 13 if(speed == 0) 14 { 15 status = "off"; 16 } 17 } 18 public void speedUp() 19 { 20 if(speed<160) 21 { 22 speed += 10; 23 } 24 } 25 public void slowDown() 26 { 27 if(speed >= 10) 28 { 29 speed -= 10; 30 } 31 } 32 33 34 }
两点可以确定一条直线,请设计一个直线类Line,需要通过两个点Point对象来确定。
设计类Point,包含两个坐标值,提供必要的构造函数和其他辅助函数
设计类Line,包含两个点,提供必要的构造函数和其他辅助函数
为Line提供一个getLength方法返回直线的长度
在Main类的main方法中,读入2对Point的坐标,输出2对Point所表示的直线的长度,保留两位小数(可用System.out.printf)
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Point p1 = new Point(sc.nextDouble(),sc.nextDouble());
Point p2 = new Point(sc.nextDouble(),sc.nextDouble());
Line l = new Line(p1,p2);
System.out.printf("%.2f",l.getLength());
}
}
/* 请在这里填写答案 */输入样例:
23.2 22.1 12.2 3.2输出样例:
21.87
class Point { public double x; public double y; public Point(double x, double y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } } class Line { public Point p1; public Point p2; public Line(Point p1, Point p2) { this.p1 = p1; this.p2 = p2; } public double getLength() { return Math.pow((p1.x-p2.x)*(p1.x-p2.x)+(p1.y-p2.y)*(p1.y-p2.y), 0.5); //return Math.sqrt((p1.x-p2.x)*(p1.x-p2.x)+(p1.y-p2.y)*(p1.y-p2.y)); } }
构造类Student,包含姓名,性别,年龄。提供必要的构造函数和其他成员函数。
提供静态函数getMaleCount,getFemaleCount,能够获得所有在main函数中构造的Student对象中男生和女生的数量。
main函数中先读取学生个数n,而后构造n个学生对象,最后分别打印其中男生和女生的人数。(输入的三个字段用空格分开,名字内部没有空格,性别用数字表示,1为男生,0为女生)
裁判测试程序样例:
在这里给出函数被调用进行测试的例子。例如:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
Student s = new Student(sc.next(),sc.nextInt(), sc.nextInt());
}
System.out.println("number of male students:" + Student.getMaleCount() );
System.out.println("number of female students:" + Student.getFemaleCount() );
}
}
/* 请在这里填写答案 */输入样例:
5
LiuMing 0 20
FangDa 1 19
DaShan 0 20
ChenHuang 0 21
DeLi 0 20输出样例:
number of male students:1 number of female students:4
class Student { public String name; public static int sex; public int age; public static int MaleCount = 0; public static int FeMaleCount = 0; public Student(String name, int sex, int age) { this.name = name; this.sex = sex; this.age = age; if(sex == 1) { this.MaleCount++; } if(sex == 0) { this.FeMaleCount++; } } public static int getMaleCount() { return MaleCount; } public static int getFemaleCount() { return FeMaleCount; } }
构造Person类。包括姓名(name),性别(sex)和年龄(age)。提供所有属性的set和get函数,提供print函数打印其信息
输入描述:
姓名(name),性别(sex)和年龄(age)
输出描述:
用户信息
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = scan.next();
String sex = scan.next();
int age = scan.nextInt();
Person p = new Person();
p.setName(name);
p.setSex(sex);
p.setAge(age);
p.print();
scan.close();
}
}
/* 你的代码被嵌在这里 */输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
Lucy male 23输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
name:Lucy; sex:male; age:23
class Person { private String name; private String sex; private int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public void print() { System.out.println("name:"+this.name+"; sex:"+this.sex+"; age:"+this.age); } }
有一个学生类的结构如下:
class Student {
private int no;
private String name;
private int score;
public Student(int _no, String _name, int _score) {
no = _no;
name = _name;
score = _score;
}
public int getNo() {return no;}
public String getName() {return name;}
public int getScore() {return score;}
public void print(){
System.out.println(no + " "+name+" "+score);
}
}请构造main函数完成如下功能: 从键盘中读入三个学生的信息,比较他们的成绩,按照成绩由高到低排列输出
输入描述:
三个学生的学号、姓名、成绩
输出描述:
由高到低排列输出的三个学生信息
裁判测试程序样例:
/*你的代码被嵌在这里*/
class Student {
private int no;
private String name;
private int score;
public Student(int _no, String _name, int _score) {
no = _no;
name = _name;
score = _score;
}
public int getNo() {return no;}
public String getName() {return name;}
public int getScore() {return score;}
public void print(){
System.out.println(no + " "+name+" "+score);
}
}输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 wang 89
2 liu 78
3 ma 90输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
3 ma 90 1 wang 89 2 liu 78
import java.util.*; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); Student stu[] = new Student [3]; for(int i = 0; i < 3 ;i++) { stu[i] = new Student(s.nextInt(),s.next(),s.nextInt()); } for(int i = 0; i < stu.length-1; i++) { for(int j = i+1; j < stu.length; j++) { Student t = new Student(0,null,0); if(stu[i].getScore() < stu[j].getScore()) { t = stu[i]; stu[i] = stu[j]; stu[j] = t; } } } for(int i = 0 ; i < stu.length; i++) { stu[i].print(); } s.close(); } }
或者
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); Map<Integer, Student> map = new HashMap<>(); for(int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i++) { int no = s.nextInt(); String name = s.next(); int score = s.nextInt(); map.put(score, new Student(no,name,score)); } for(int i = 100 ; i > 0 ; i--) { if(map.get(i) == null) { continue; } map.get(i).print(); } s.close(); } }
构建家具类Furniture,包括长、宽、高,均为整数(cm)。提供相应的构造函数和get、set函数。 Main函数里构造家具对象,并调用相应的函数。
输入描述:
家具对象的长宽高
输出描述:
家具对象的相关属性
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Furniture f = new Furniture(sc.nextInt(),sc.nextInt(),sc.nextInt());
System.out.println(f.getHeight());
System.out.println(f.getLength());
System.out.println(f.getWidth());
}
}
/* 你的代码被嵌在这里*/输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
50 60 100输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
100 50 60
class Furniture { public int length; public int width; public int height; public Furniture(int length, int width, int height) { super(); this.length = length; this.width = width; this.height = height; } public int getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(int length) { this.length = length; } public int getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(int width) { this.width = width; } public int getHeight() { return height; } public void setHeight(int height) { this.height = height; } }
定义一个形状类Shape,提供计算周长getPerimeter()和面积getArea()的函数 定义一个子类正方形类Square继承自Shape类,拥有边长属性,提供构造函数,能够计算周长getPerimeter()和面积getArea() 定义一个子类长方形类Rectangle继承自Square类,拥有长、宽属性,提供构造函数,能够计算周长getPerimeter()和面积getArea() 定义一个子类圆形类Circle继承自Shape,拥有半径属性,提供构造函数,能够计算周长getPerimeter()和面积getArea()
在main函数中,分别构造三个子类的对象,并输出他们的周长、面积. 提示:用System.out.printf("%.2f",d)进行格式化输出
输入描述:
正方形类的边长 长方形类的长宽 圆类的半径
输出描述:
正方形的周长、面积 长方形的周长、面积
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
double length = scan.nextDouble();
Square s = new Square(length);
System.out.printf("%.2f ",s.getPerimeter());
System.out.printf("%.2f\n",s.getArea());
length = scan.nextDouble();
double wide = scan.nextDouble();
Rectangle r = new Rectangle(length,wide);
System.out.printf("%.2f ",r.getPerimeter());
System.out.printf("%.2f\n",r.getArea());
double radius = scan.nextDouble();
Circle c = new Circle(radius);
System.out.printf("%.2f ",c.getPerimeter());
System.out.printf("%.2f\n",c.getArea());
scan.close();
}
}
/* 你的代码被嵌在这里 */输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1
1 2
2输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
4.00 1.00 6.00 2.00 12.57 12.57
class Shape { public double length; public Shape(double length) { super(); this.length = length; } public double getPerimeter() { return 4*length; } public double getArea() { return length*length; } } class Square extends Shape { public Square(double length) { super(length); } } class Rectangle extends Shape { public double width; public Rectangle(double length, double width) { super(length); this.width = width; } public double getPerimeter() { return 2*width+2*length; } public double getArea() { return width*length; } } class Circle extends Shape { public Circle(double length) { super(length); } public double getPerimeter() { return 2*3.14159*length; } public double getArea() { return 3.14159*length*length; } }
定义Student学生类,拥有学号、姓名、性别属性,提供构造函数,以及相应属性的get set函数,提供函数attendClass(String className)表示上课。 定义CollegeStudent大学生类继承自Student类,拥有新增属性专业,提供构造函数,提供新增属性的get和set函数 定义GraduateStudent研究生类继承自CollegeStudent类,拥有新增属性导师,提供构造函数,提供新增属性的get和set函数,提供函数doResearch() 表示做研究(打印xx is doing research)。
main函数中对构造的类进行测试
输入描述:
学生类信息,学号、姓名、性别 大学生类信息,学号、姓名、性别、专业 研究生类信息,学号、姓名、性别、专业、导师
输出描述:
学生类信息 大学生类信息 研究生类信息
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int no = scan.nextInt();
String name = scan.next();
String sex = scan.next();
Student s = new Student(no, name, sex);
s.print();
no = scan.nextInt();
name = scan.next();
sex = scan.next();
String major = scan.next();
CollegeStudent c = new CollegeStudent(no, name, sex, major);
c.print();
no = scan.nextInt();
name = scan.next();
sex = scan.next();
major = scan.next();
String supervisor = scan.next();
GraduateStudent g = new GraduateStudent(no, name, sex, major, supervisor );
g.print();
g.doResearch();
scan.close();
}
}
/* 你的代码被嵌在这里*/输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 liu female
2 chen female cs
3 li male sc wang输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
no: 1 name: liu sex: female no: 2 name: chen sex: female major: cs no: 3 name: li sex: male major: sc supervisor: wang li is doing research
class Student { public int no; public String name; public String sex; public Student(int no, String name, String sex) { super(); this.no = no; this.name = name; this.sex = sex; } public void attendClass(String className) { } public void print() { System.out.println("no: "+no); System.out.println("name: "+name); System.out.println("sex: "+sex); } } class CollegeStudent extends Student { public String major; public CollegeStudent(int no, String name, String sex, String major) { super(no, name, sex); this.major = major; } @Override public void print() { super.print(); System.out.println("major: "+major); } } class GraduateStudent extends CollegeStudent { public String supervisor; public GraduateStudent(int no, String name, String sex, String major, String supervisor) { super(no, name, sex, major); this.supervisor = supervisor; } public void doResearch() { System.out.println(name+" is doing research"); } @Override public void print() { super.print(); System.out.println("supervisor: "+supervisor); } }
某租车公司提供租车服务,针对不同的车辆类型,日租金的计算方式不同,具体地,对于货车而言,根据载重量load(单位是吨)计算,公式为loadx 1000;对于大型客车而言,根据车内座位数seats计算,公式为seatsx50;对于小型汽车而言,根据车辆等级和折旧年数计算,公式为200*level/sqrt(year),其中sqrt表示平方根。设计合适的类继承结构实现上述功能,构造租车公司类CarRentCompany,提供静态函数rentVehicles,能够给定一组待租车辆,计算日租金总额。 在main函数中,读入多个车辆数据,并计算总的日租金。
输入描述:
汽车数量 汽车种类 该类汽车相关属性 其中1表示货车,2表示大型客车,3表示小型汽车
输出描述:
总的日租金,保留两位小数
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int c = sc.nextInt();
Vehicle[] vs = new Vehicle[c];
for (int i=0;i<c;i++) {
int type = sc.nextInt();
Vehicle v = null;
if (type == 1) {//货车
vs[i] = new Truck (sc.nextDouble());
} else if (type == 2) {
vs[i] = new Keche(sc.nextInt());
} else if (type == 3) {
vs[i] = new Car(sc.nextInt(), sc.nextInt());
}
}
System.out.printf("%.2f",CarRentCompany.rentVehicles(vs));
}
}
/* 你的代码被嵌在这里 */输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3
1 3
2 50
3 5 5输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
5947.21
abstract class Vehicle { public abstract double getRank(); } class Truck extends Vehicle { public double load; public Truck(double load) { this.load = load; } public double getRank() { return load*1000; } } class Keche extends Vehicle { public int seat; public Keche(int seat) { this.seat = seat; } public double getRank() { return seat*50; } } class Car extends Vehicle { public int level; public int year; public Car(int level,int year) { this.level = level; this.year = year; } public double getRank() { return 200*level/Math.sqrt(year); } } class CarRentCompany { public static double rentVehicles(Vehicle[] vs) { double sum = 0; for(Vehicle v : vs) { sum += v.getRank(); }
//for(int i = 0 ; i < vs.length ; i++)
//{
//flag += vs[i].getFee();
//}
return sum; } }
从键盘录入表示矩形个数的数字n,然后录入n个矩形的长和宽,然后对这n个矩形按照面积从大到小排序,并输出排序后的每个矩形的面积。要求:请设计Rectangle类,包含相应的构造函数和成员函数,实现Comparable接口
输入描述:
矩形个数,每个矩形的长和宽
输出描述:
由大到小排序的每个矩形的面积
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*你的代码被嵌在这里*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
//输入矩形个数
int num_rectangle = scan.nextInt();
Rectangle[] recs = new Rectangle[num_rectangle];
//输入每个矩形的长和宽
for(int i=0;i<num_rectangle;i++){
int length = scan.nextInt();
int width = scan.nextInt();
Rectangle rec = new Rectangle(length,width);
recs[i] = rec;
}
//按照面积由大到小排序
Arrays.sort(recs);
//打印前n-1个矩形的面积
for(int i=0;i<recs.length-1;i++){
System.out.print(recs[i].getArea()+",");
}
//打印最后一个矩形的面积
System.out.print(recs[recs.length-1].getArea());
scan.close();
}
}输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3 1 2 3 4 2 3输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
12,6,2
import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Scanner; class Rectangle implements Comparable<Rectangle> { public int length; public int width; public int getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(int length) { this.length = length; } public int getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(int width) { this.width = width; } public Rectangle(int length, int width) { super(); this.length = length; this.width = width; } public int getArea() { return length*width; } @Override public int compareTo(Rectangle o) { return o.getArea() - this.getArea(); } }
请设计如下相关接口和类:
1) 接口IntegerGroup表示以某种方式定义的一组整数,称为数群,它可以为空,也可以包含一到多个整数。该接口包含唯一的函数boolean contains(int),返回某个整数参数是否在这个IntegerGroup对象里。如group1是IntegerGroup类型的一个对象,包含两个数字-5和3,那么group1.contains(-5)返回true,group1.contains(2)返回false。请定义接口IntegerGroup
2) 类Range是IntegerGroup的实现类,表示包含在最小值和最大值之间的所有连续整数(最小和最大值包含在内)。例如new Range(-3, 2)表示数群-3,-2,-1,0,1,2。请写出完整的Range类,包括必要的成员数据、构造函数、成员函数。假定最小值小于等于最大值。
3) 类Enum也是IntegerGroup的实现类,表示多个分散整数构成的数群。例如new Enum(new int[]{1,3,5,2,-1})表示构造一个包含整数1,3,5, 2,-1的Enum对象,以整数数组作为参数。请完成类Enum,包含必要的成员数据、构造函数、成员函数。
4) 类MultipleGroups表示一组IntegerGroup对象,并用一个列表来存储多个IntegerGroup对象,MultipleGroups类有函数add,用于添加IntegerGroup对象,有函数contains,该函数以一个整数作为参数,当且仅当该IntegerGroup对象中的一个或者多个IntegerGroup对象包含这个整数时返回true。例如MultipleGroups对象multiple1包含三个对象 new Range(5, 8), new Range(10, 12), new Enum(new int[]{1, 6}),那么对multiple1.contains的调用应当返回的值如下表所示,请完成类MultipleGroup,包含必要的成员数据、构造函数、成员函数。
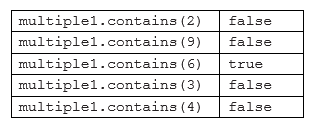
Main函数已经提供,其中构造了一个MultipleGroup对象,然后读入整数n,表示构造的IntegerGroup对象的个数,接着每行表示一个IntegerGroup对象,第一个整数表示对象类型,1为Range对象,2为Enum对象。对于Range对象来说,读入最小值和最大值,对于Enum对象来说,读入包含整数的个数,然后读入各个整数并构造为一个数组传入Enum的构造函数中。最后跟着5个测试数据,调用多个MultipleGroup对象的contains方法进行测试并输出结果。
裁判测试程序样例:
/* 请在这里填写答案 */
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
MultipleGroups mg = new MultipleGroups();
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) {
int t = sc.nextInt();
IntegerGroup ng = null;
if (t==1) {//Range
ng = new Range(sc.nextInt(), sc.nextInt());
} else {//Enum
int len = sc.nextInt();
int arr[] = new int[len];
for (int j=0;j<len;j++)
arr[j] = sc.nextInt();
ng = new Enum(arr);
}
mg.add(ng);
}
for (int i=0;i<5;i++)
System.out.println(mg.contains(sc.nextInt()));
}
}
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3
1 5 8
1 10 12
2 2 1 6
2 9 6 3 4输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
false false true false false
import java.util.*; interface IntegerGroup { boolean contains(int a); } class Range implements IntegerGroup { public int min; public int max; public Range(int min, int max) { this.min = min; this.max = max; } @Override public boolean contains(int a) { if(a >= min && a<= max) { return true; } return false; } } class Enum implements IntegerGroup { public int []nu; public Enum(int[] nu) { this.nu = nu; } @Override public boolean contains(int a) { for(int i = 0 ; i < nu.length ; i++) { if(nu[i] == a) { return true; } } return false; } } class MultipleGroups implements IntegerGroup { LinkedList<IntegerGroup> mu = new LinkedList<IntegerGroup>(); public MultipleGroups(LinkedList<IntegerGroup> mu) { super(); this.mu = mu; } public MultipleGroups() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public void add(IntegerGroup ng) { mu.add(ng); } @Override public boolean contains(int a) { for(int i = 0 ; i < mu.size() ; i++) { if(mu.get(i).contains(a)) { return true; } } return false; } }
图书和音像店提供出租服务,包括图书和DVD的出租。图书包括书名(String,一个词表示)和价格(double),DVD包括片名(String,一个词表示)。它们都是按天出租,但租金计算方式却不同,图书的日租金为图书价格的1%,DVD的日租金为固定的1元。构造图书和DVD类的继承体系,它们均继承自Media类,且提供方法getDailyRent()返回日租金,构造音像店类MediaShop,提供静态函数double calculateRent(Media[] medias, int days)。 在main函数中构造了Media数组,包含图书和DVD的对象,调用calculateRent方法得到并输出租金,保留小数点两位
输入描述:
待租图书和DVD的数量
图书和DVD的详细信息
租借天数
输出描述:
总的租金
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
Media[] ms = new Media[n];
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
String type = sc.next();
if (type.equals("book")) {
ms[i] = new Book(sc.next(), sc.nextDouble());
}else {
ms[i] = new DVD(sc.next());
}
}
double rent = MediaShop.calculateRent(ms, sc.nextInt());
System.out.printf("%.2f", rent);
}
}
/* 请在这里填写答案 */输入样例:
5
book Earth 25.3
book Insights 34
dvd AI
dvd Transformer
book Sun 45.6
20输出样例:
60.98
abstract class Media { public abstract double getDailyRent(); } class Book extends Media { public String name; public double price; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } public Book(String name, double price) { this.name = name; this.price = price; } @Override public double getDailyRent() { return price/100; } } class DVD extends Media { public String name; public DVD(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public double getDailyRent() { return 1; } } class MediaShop { static double rent = 0; public static double calculateRent(Media[] medias, int days) { for(int i = 0 ; i < medias.length ; i++) { rent += medias[i].getDailyRent(); } return rent * days; } }
基于继承关系编写一个动物体系,具体的动物包含小狗和小猫。每只动物都有名字和颜色,都能够做自我介绍(introduce)。此外,小狗有智商属性(整数),能接飞盘(catchFrisbee(),方法体内输出一行“catch frisbee”即可),小猫有眼睛颜色属性,能抓老鼠(catchMouse(),方法体内输出一行“catch mouse”即可)。各种小动物自我介绍时均介绍自己的姓名和颜色,此外,小狗应介绍自己的智商,小猫应介绍自己的眼睛颜色。小狗介绍时输出”My name is xxx, my color is xxx, my IQ is xxx”, 小猫介绍时输出“My name is xxx, my color is xxx, my eyecolor is xxx” 构造类TestAnimal,提供静态函数introduce(Animal),对参数动物自我介绍。提供静态函数action(Animal),根据参数对象的实际类型进行活动,如果是小狗,则让其接飞盘,如果是小猫,则让其抓老鼠。 Main函数中,根据动物类型构造动物,并调用TestAnimal中的方法进行自我介绍(introduce)和活动(action)
输入描述:
动物类型 动物名称 动物颜色 动物其他属性 如 1 猫名称 猫颜色 猫眼睛颜色 2 狗名称 狗颜色 狗的智商
输出描述:
自我介绍 活动
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Scanner;
/*你的代码被嵌在这里 */
public class Main{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner s = new Scanner (System.in);
int i = s.nextInt();
Animal a = null;
if (i==1) {
a = new Cat(s.next(), s.next(), s.next());
} else if (i==2) {
a = new Dog(s.next(), s.next(), s.nextInt());
}
TestAnimal.introduce(a);
TestAnimal.action(a);
}
}输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 Mikey white blue输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
My name is Mikey, my color is white, my eyecolor is blue catch mouse
class Animal { public String name; public String color; public Animal(String name, String color) { this.name = name; this.color = color; } public void introduce() {}; public void action() {}; } class Cat extends Animal { public String eyecolor; public Cat(String name, String color, String eyecolor) { super(name, color); this.eyecolor = eyecolor; } public void introduce() { System.out.println("My name is "+name+", my color is "+color+", my eyecolor is "+eyecolor); } public void action() { System.out.print("catch mouse"); } } class Dog extends Animal { public int IQ; public Dog(String name, String color, int iQ) { super(name, color); IQ = iQ; } public void introduce() { System.out.println("My name is "+name+", my color is "+color+", my IQ is "+IQ); } public void action() { System.out.print("catch frisbee"); } } class TestAnimal { public static void introduce(Animal a) { a.introduce(); } public static void action(Animal a) { a.action(); } }
设计一个Duck类和它的两个子类RedheadDuck和MallardDuck。裁判测试程序中的Main类会自动提交。
类的定义:
//Duck类的定义
class Duck { }
//RedheadDuck类的定义
class RedheadDuck extends Duck { }
//MallardDuck类的定义
class MallardDuck extends Duck { }裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
Duck rduck = new RedheadDuck();
rduck.display();
rduck.quack();
rduck.swim();
rduck.fly();
Duck gduck = new MallardDuck();
gduck.display();
gduck.quack();
gduck.swim();
gduck.fly();
}
}
/* 请在这里填写答案 */输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
无
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
我是一只红头鸭 我会呱呱呱 我会游泳 我会飞 我是一只绿头鸭 我会呱呱呱 我会游泳 我会飞
//Duck类的定义 class Duck { public void display() { } public void quack() { System.out.println("我会呱呱呱"); } public void swim() { System.out.println("我会游泳"); } public void fly() { System.out.println("我会飞"); } } //RedheadDuck类的定义 class RedheadDuck extends Duck { public void display() { System.out.println("我是一只红头鸭"); } } //MallardDuck类的定义 class MallardDuck extends Duck { public void display() { System.out.println("我是一只绿头鸭"); } }
构建一个书类Book,包括名称(字符串),价格(整型),作者(字符串,多个作者当做一个字符串处理),版本号(整型),提供带参数的构造函数Book(String name, int price, String author, int edition),提供该类的toString()和equals()方法,toString方法返回所有成员属性的值的字符串形式,形如“name: xxx, price: xxx, author: xxx, edition: xxx”,当两个Book对象的名称(不关心大小写,无空格)、作者(不关心大小写,无空格)、版本号相同时,认为两者表示同一本书。 Main函数中,读入两本书,输出他们是否相等,打印两本书的信息。
输入描述:
两本书信息
输出描述:
两本书的打印信息 两本书是否相等
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
Book b1 = new Book(s.next(),
s.nextInt(),
s.next(),
s.nextInt());
Book b2 = new Book(s.next(),s.nextInt(),s.next(),s.nextInt());
System.out.println(b1);
System.out.println(b2);
System.out.println(b1.equals(b2));
}
}
/* 你的代码被嵌在这里 */
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
ThinkingInJava
86
BruceEckel
4
CoreJava
95
CayS.Horstmann
10输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
name: ThinkingInJava, price: 86, author: BruceEckel, edition: 4 name: CoreJava, price: 95, author: CayS.Horstmann, edition: 10 false
class Book { public String name; public int price; public String author; public int edition; public Book() { super(); } public Book(String name, int price, String author, int edition) { super(); this.name = name; this.price = price; this.author = author; this.edition = edition; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(int price) { this.price = price; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } public int getEdition() { return edition; } public void setEdition(int edition) { this.edition = edition; } @Override public String toString() { return "name: "+name+", "+ "price: "+price+", "+ "author: "+author+", "+ "edition: "+edition; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { Book b = (Book)o; if(b.name.equalsIgnoreCase(this.name) && b.author.equalsIgnoreCase(this.author) && b.edition == this.edition) { return true; } return false; } }
构造一个成绩管理系统CourseManagementSystem,该系统包括如下几个方法:void add(int no, int grade)添加该学号的成绩,如果系统已有该学生成绩,则输出"the student already exists";void delete(int no)删除某学号成绩,如果不存在此学生则输出"no such student";int query(int no)查询并返回该学号的成绩;统计成绩void statistics( )统计[0-59]、[60-69]、[70-79]、[80-89]、[90-100]各成绩段的学生个数并打印。请选择合适的容器实现上述功能。(题目假设不会重复添加相同学号的学生成绩) main函数中读入操作类型及相关参数,并调用statictic函数输出学生成绩统计信息。
输入描述:
操作个数 操作名 操作参数
输出描述:
查询学生的成绩 各成绩段的学生个数
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
CourseManagementSystem cms = new CourseManagementSystem();
int ops = sc.nextInt();
for (int i=0;i<ops;i++) {
String op = sc.next();
if (op.equals("add"))
cms.add(sc.nextInt(), sc.nextInt());
else if (op.equals("delete"))
cms.delete(sc.nextInt());
else if (op.equals("query")) {
int no = sc.nextInt();
int s = cms.query(no);
System.out.println("the score for "+no+" is : "+s);
}
}
cms.statistic();
}
}
/* 你的代码被嵌在这里*/输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
8
add 1 63
add 2 78
add 3 74
delete 3
add 2 20
delete 5
query 1
add 4 90输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
the student already exists no such student the score for 1 is : 63 [0-59] : 0 [60-69] : 1 [70-79] : 1 [80-89] : 0 [90-100] : 1
class CourseManagementSystem { int[][] A = new int[101][2]; int n = 0; int a=0,b=0,c=0,d=0,e=0; public void add(int no,int grade) { if(A[no][1] != 0) { System.out.println("the student already exists"); } else { A[no][1] = grade; n++; if(grade >= 90 && grade <=100) { a++; } if(grade <=89 && grade >=80) { b++; } if(grade <=79 && grade >=70) { c++; } if(grade <=69 && grade >=60) { d++; } if(grade <= 59 && grade>=0) { e++; } } } public void delete(int no) { if(A[no][1] == 0) { System.out.println("no such student"); } else { int x = A[no][1]; A[no][1] = 0; n--; if(x >= 90 && x <= 100) { a--; } if(x <=89 && x >=80) { b--; } if(x <=79 && x >=70) { c--; } if(x <=69 && x >=60) { d--; } if(x <= 59 && x>=0) { e--; } } } public int query(int no) { return A[no][1]; } public void statistic() { System.out.println("[0-59] : "+e); System.out.println("[60-69] : "+d); System.out.println("[70-79] : "+c); System.out.println("[80-89] : "+b); System.out.println("[90-100] : "+a); } }
根据Main类中main方法中的代码,设计满足要求的Student(学生)类:1)包含属性:int no(学号)、String name(姓名);2)满足Main类中main方法代码的说明要求。 Main类中main方法代码的说明:1)首先,从键盘接收形如“3 cuizhenyu 2 tiangang 1 dingchangqing 4 zhangfeng”的字符串,该字符串中包含了4个学生的学号和姓名(各学生以及学生的学号和姓名之间都用一个空格分隔,姓名中只包含英文字母),然后将该字符串内容中的前3个学生的学号及其姓名放到到Student数组stus中;2)将stus中的3个Student放入到HashSet stuSet中(注意:如果学生的学号相同,则认为是相同对象,不放入stuSet中);3)将第4个学生对象放入到stuSet中,如果第4个学生对象的学号与stuSet中已有学生对象的学号相同则不能放入。然后,打印出当前stuSet中学生对象的个数;4)用Arrays.sort方法对数组stus按照学生姓名的字母顺序排序(先比较首字母,首字母相同的比较第二个字母,以此类推),输出排序后的stus中3个学生对象的内容,每个学生对象的输出格式为“no=XX&name=YY”。
输入描述:
键盘录入的包含4个学生的学号、姓名的字符串(格式如上述题目描述)
输出描述:
stuSet放入第4个学生对象后的所包含的对象个数,数组stus中包含的前3个学生对象学号、姓名(格式如上述题目描述)
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
Student[] stus = new Student[3];
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
int no = scan.nextInt();
String name = scan.next();
Student s = new Student(no,name);
stus[i] =s;
}
//将stus中的3个学生对象,放入到HashSet中
HashSet<Student> stuSet = new HashSet<Student>();
for(Student s: stus){
stuSet.add(s);
}
//要放入的第4个Student
Student fourth = new Student(scan.nextInt(),scan.next());
stuSet.add(fourth);//如果fourth的学号(no)与stuSet中的已有学生的no重复则无法放入
System.out.println(stuSet.size());
Arrays.sort(stus);//对stus中的3个原有对象,按照姓名首字符有小到大排序
for(int i=0;i<stus.length;i++){
System.out.println(stus[i]);//输出的格式为:no=XX&name=YY
}
scan.close();
}
}
/*你的代码被嵌在这里*/输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3 cuizhenyu 2 tiangang 1 dingchangqing 4 zhangfeng输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
4 no=3&name=cuizhenyu no=1&name=dingchangqing no=2&name=tiangang
class Student implements Comparable<Student> { public int no; public String name; public Student(int no, String name) { super(); this.no = no; this.name = name; } public int getNo() { return no; } public void setNo(int no) { this.no = no; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if(this == null || obj == null) { return false; } if(this.getClass() != obj.getClass()) { return false; } Student s = (Student)obj; if(s.getNo() != this.getNo()) { return false; } return true; } public int compareTo(Student o) { return this.getName().compareTo(o.getName()); } @Override public int hashCode() { return this.no; } @Override public String toString() { return "no="+no+"&name="+name; } }




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 智能桌面机器人:用.NET IoT库控制舵机并多方法播放表情
· Linux glibc自带哈希表的用例及性能测试
· 深入理解 Mybatis 分库分表执行原理
· 如何打造一个高并发系统?
· .NET Core GC压缩(compact_phase)底层原理浅谈
· 手把手教你在本地部署DeepSeek R1,搭建web-ui ,建议收藏!
· 新年开篇:在本地部署DeepSeek大模型实现联网增强的AI应用
· 程序员常用高效实用工具推荐,办公效率提升利器!
· Janus Pro:DeepSeek 开源革新,多模态 AI 的未来
· 【译】WinForms:分析一下(我用 Visual Basic 写的)