@Transactional注解失效的场景总结
一、引言
有朋友面试被问到了@Transactional注解失效的场景,自己也想了一下发现并不是很全面,就去找了一下相关的资料,在这里进行总结,希望对大家有所帮助。
@Transactional 注解相信大家并不陌生,平时开发中很常用的一个注解,它能保证方法内多个数据库操作要么同时成功、要么同时失败。使用@Transactional注解时需要注意许多的细节,不然你会发现@Transactional总是莫名其妙的就失效了。
二、spring的事务
事务是项目中不可缺少的操作,spring提供了很好的事务处理机制,主要分为编程式事务和声明式事务。
1、编程式事务
编程式事务是指在代码中手动的进行事务的提交和回滚操作,代码入侵性比较强。如我们经常进行入下操作。
try { //TODO something transactionManager.commit(status); } catch (Exception e) { transactionManager.rollback(status); throw new InvoiceApplyException("异常失败"); }
2、声明式事务
基于AOP面向切面的,它将具体业务与事务处理部分解耦,代码侵入性很低,所以在实际开发中声明式事务用的比较多。声明式事务也有两种实现方式,一是基于TX和AOP的xml配置文件方式,二种就是基于@Transactional注解了。
基于TX和AOP的xml配置文件方式:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.2.xsd"> <!-- 事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <!-- 数据源 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> </bean> <!-- 通知 --> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <!-- 传播行为 --> <tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED" /> <tx:method name="insert*" propagation="REQUIRED" /> <tx:method name="add*" propagation="REQUIRED" /> <tx:method name="create*" propagation="REQUIRED" /> <tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED" /> <tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED" /> <tx:method name="find*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true" /> <tx:method name="select*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true" /> <tx:method name="get*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true" /> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 切面 --> <aop:config> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* com.jeenotes.ssm.service.*.*(..))" /> </aop:config> </beans>
基于@Transactional注解:
<!-- 3、定义事务 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> </bean> <!-- 4、开启事务控制的注解支持,配置 Annotation 驱动,扫描@Transactional注解的类定义事务 --> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" proxy-target-class="true"/>
三、@Transactional注解的属性
@AliasFor("transactionManager")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String transactionManager() default "";
Propagation propagation() default Propagation.REQUIRED; //事务的传播行为,已说过
Isolation isolation() default Isolation.DEFAULT; //事务的隔离级别,默认的使用数据库的隔离级别
int timeout() default -1; //事务的超时时间,超过一丁的时间事务未完成,则进行回滚
boolean readOnly() default false; //是否是只读事务
Class<? extends Throwable>[] rollbackFor() default {}; //指定接收什么异常类型进行回滚
String[] rollbackForClassName() default {};
Class<? extends Throwable>[] noRollbackFor() default {}; //指定特定的异常类型不回滚事务
String[] noRollbackForClassName() default {};
四、事务的失效场景
1、事务注解应用在非public方法上。
之所以会失效是因为在Spring AOP 代理时,如上图所示 TransactionInterceptor (事务拦截器)在目标方法执行前后进行拦截,DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(CglibAopProxy 的内部类)的 intercept 方法或 JdkDynamicAopProxy 的 invoke 方法会间接调用 AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource的 computeTransactionAttribute 方法,获取Transactional 注解的事务配置信息。
protected TransactionAttribute computeTransactionAttribute(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) { // Don't allow no-public methods as required. if (allowPublicMethodsOnly() && !Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) { returnnull; }
2、@Transactional 注解属性 propagation 设置错误
这种失效是由于配置错误,若是错误的配置以下三种 propagation,事务将不会发生回滚。
TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS:如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务;如果当前没有事务,则以非事务的方式继续运行。
TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,则把当前事务挂起。
TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER:以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。
3、@Transactional 注解属性 rollbackFor 设置错误
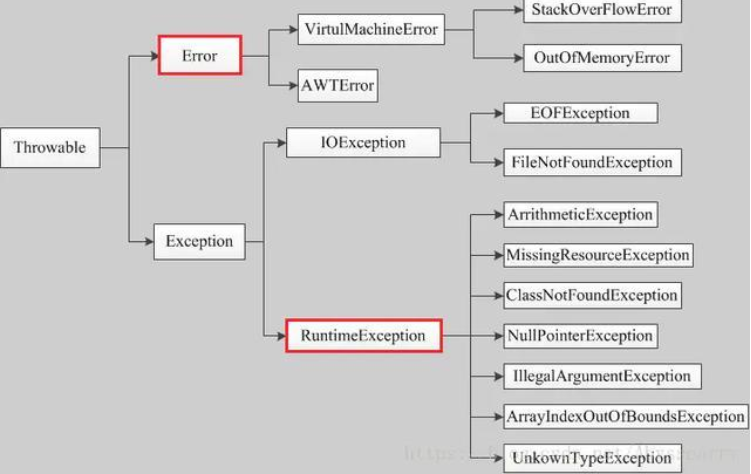
rollbackFor 可以指定能够触发事务回滚的异常类型。Spring默认抛出了未检查unchecked异常(继承自 RuntimeException 的异常)或者 Error才回滚事务;其他异常不会触发回滚事务。如果在事务中抛出其他类型的异常,但却期望 Spring 能够回滚事务,就需要指定 rollbackFor属性。
4、同一个类中方法调用,导致@Transactional失效
开发中避免不了会对同一个类里面的方法调用,比如有一个类Test,它的一个方法A,A再调用本类的方法B(不论方法B是用public还是private修饰),但方法A没有声明注解事务,而B方法有。则外部调用方法A之后,方法B的事务是不会起作用的。这也是经常犯错误的一个地方。
那为啥会出现这种情况?其实这还是由于使用Spring AOP代理造成的,因为只有当事务方法被当前类以外的代码调用时,才会由Spring生成的代理对象来管理。
5、异常被你的 catch“吃了”导致@Transactional失效
6、数据库引擎不支持事务
这种情况出现的概率并不高,事务能否生效数据库引擎是否支持事务是关键。常用的MySQL数据库默认使用支持事务的innodb引擎。一旦数据库引擎切换成不支持事务的myisam,那事务就从根本上失效了。


