Codeforces 999E(强连通分量缩点)
题面:
E. Reachability from the Capital
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
There are nn cities and mm roads in Berland. Each road connects a pair of cities. The roads in Berland are one-way.
What is the minimum number of new roads that need to be built to make all the cities reachable from the capital?
New roads will also be one-way.
Input
The first line of input consists of three integers nn, mm and ss (1≤n≤5000,0≤m≤5000,1≤s≤n1≤n≤5000,0≤m≤5000,1≤s≤n) — the number of cities, the number of roads and the index of the capital. Cities are indexed from 11 to nn.
The following mm lines contain roads: road ii is given as a pair of cities uiui, vivi (1≤ui,vi≤n1≤ui,vi≤n, ui≠viui≠vi). For each pair of cities (u,v)(u,v), there can be at most one road from uu to vv. Roads in opposite directions between a pair of cities are allowed (i.e. from uu to vv and from vv to uu).
Output
Print one integer — the minimum number of extra roads needed to make all the cities reachable from city ss. If all the cities are already reachable from ss, print 0.
Examples
input
Copy
9 9 1
1 2
1 3
2 3
1 5
5 6
6 1
1 8
9 8
7 1
output
Copy
3
input
Copy
5 4 5
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 1
output
Copy
1
Note
The first example is illustrated by the following:
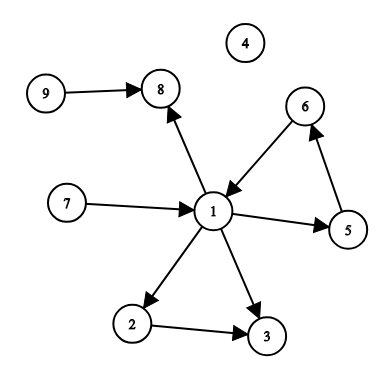
For example, you can add roads (6,46,4), (7,97,9), (1,71,7) to make all the cities reachable from s=1s=1.
The second example is illustrated by the following:
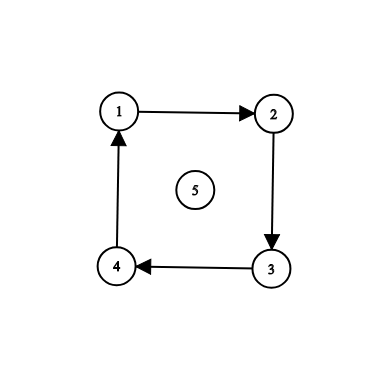
In this example, you can add any one of the roads (5,15,1), (5,25,2), (5,35,3), (5,45,4) to make all the cities reachable from s=5s=5.
题目描述:
给你n个点,m条边,以及一个初始点s,问你至少还需要增加多少条边,使得初始点s与剩下其他的所有点都连通。
题目分析:
因为要讨论连通性,而题目所要讨论的有向图,因此我们可以首先统计强连通分量,并通过Tarjin缩点,并重新构图。将图重构之后,我们会发现,倘若除了s结点所在的连通分量,如果其他连通分量所构成的新点的入度为0,则使这个连通分量与s连通的最优的方案是将这个点与s结点相连。
因此,对于这个问题,我们只需要在缩点之后统计一下入读为0的新点即是答案。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define maxn 200005
using namespace std;
struct edge{
int next,to;
}q[maxn];
int head[maxn],dfn[maxn],low[maxn],cnt,tot;
int vis[maxn],belong[maxn],index,belong_num[maxn],num_index;
int indegree[maxn],outdegree[maxn];
void add_edge(int from,int to){
q[cnt].next=head[from];
q[cnt].to=to;
head[from]=cnt++;
}
void init(){//初始化
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
memset(dfn,0,sizeof(dfn));
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
memset(low,0,sizeof(low));
memset(belong_num,0,sizeof(belong_num));//在某个连通块中有多少个结点
memset(indegree,0,sizeof(indegree));//新图的入度
memset(outdegree,0,sizeof(outdegree));
index=num_index=cnt=tot=0;
}
stack<int>st;
void tarjin(int x){//Tarjin的主体
dfn[x]=low[x]=++tot;
vis[x]=1;
st.push(x);
for(int i=head[x];i!=-1;i=q[i].next){
edge e=q[i];
if(!dfn[e.to]){
tarjin(e.to);
low[x]=min(low[e.to],low[x]);
}
else if(vis[e.to]==1){
low[x]=min(low[x],dfn[e.to]);
}
}
if(dfn[x]==low[x]){
int v;
index=index+1;
do{
v=st.top();
st.pop();
belong[v]=index;
belong_num[index]++;
vis[v]=0;
}while(v!=x);
}
}
void solve(int n,int m,int root){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){//对图进行Tarjin
if(!dfn[i]){
tarjin(i);
}
}
//如果连通分量只有一个,则直接输出0
if(index==1){
puts("0");
return ;
}
indegree[belong[root]]=1;//确保初始点root所在的连通分量入度不为0
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){//重构图的过程
for(int j=head[i];j!=-1;j=q[j].next){
edge e=q[j];
if(belong[i]==belong[e.to]) continue;
indegree[belong[e.to]]++;
outdegree[belong[i]]++;
}
}
int cnt=0;//统计入度为0的点
for(int i=1;i<=index;i++){
if(indegree[i]==0){
cnt++;
}
}
cout<<cnt<<endl;
}
int main()
{
int n,m,s;
cin>>n>>m>>s;
init();
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
add_edge(a,b);
}
solve(n,m,s);
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号