mybatis批量插入优化(ExecutorType.BATCH/BatchInsert/executeBatch)
最新更新
2023.1.26 感谢大家的反馈和支持,对于文中设计到的一些内容进行更正和修补,请看文末附加部分。
总结
-
Mybatis内置的
ExecutorType有3种,默认的是simple单句模式,该模式下它为每个语句的执行创建一个新的预处理语句,单句提交sql;batch模式重复使用已经预处理的语句,并且批量执行所有语句,大批量模式下性能更优。- 请注意
batch模式在Insert操作时事务没有提交之前,是没有办法获取到自增的id,所以请根据业务情况使用。 - 使用simple模式提交10000条数据,时间为19s,batch模式为6s ,大致情况如此,优化的具体还要看提交的语句情况。
- 请注意
-
如果需要使用
foreach来优化数据插入的话,需要将每次插入的记录控制在 10-100 左右是比较快的,建议每次100来分割数据,也就是分而治之思想。
普通插入
默认的插入方式是遍历insert语句,单条执行,效率肯定低下,如果成堆插入,更是性能有问题。
INSERT INTO `table1` (`field1`, `field2`) VALUES ("data1", "data2");
INSERT INTO `table1` (`field1`, `field2`) VALUES ("data1", "data2");
INSERT INTO `table1` (`field1`, `field2`) VALUES ("data1", "data2");
INSERT INTO `table1` (`field1`, `field2`) VALUES ("data1", "data2");
INSERT INTO `table1` (`field1`, `field2`) VALUES ("data1", "data2");foreach 优化插入
如果要优化插入速度时,可以将许多小型操作组合到一个大型操作中。理想情况下,这样可以在单个连接中一次性发送许多新行的数据,并将所有索引更新和一致性检查延迟到最后才进行。
<insert id="batchInsert" parameterType="java.util.List">
insert into table1 (field1, field2) values
<foreach collection="list" item="t" index="index" separator=",">
(#{t.field1}, #{t.field2})
</foreach>
</insert>翻译成sql语句也就是
INSERT INTO `table1` (`field1`, `field2`)
VALUES ("data1", "data2"),
("data1", "data2"),
("data1", "data2"),
("data1", "data2"),
("data1", "data2");foreach 遇到数量大,性能瓶颈
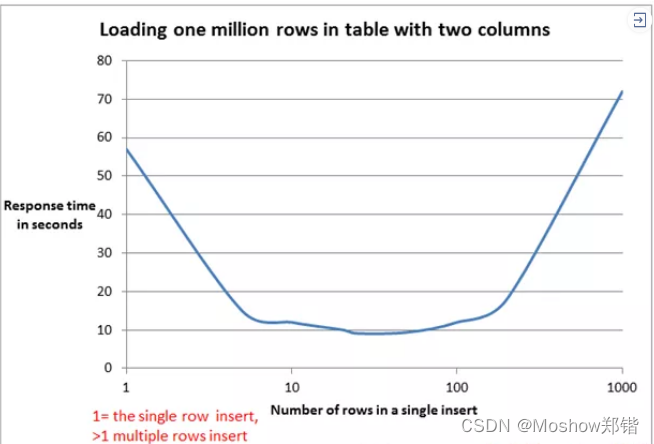
项目实践发现,当表的列数较多(超过20),以及一次性插入的行数较多(上万条)时,插入性能非常差,通常需要20分钟以上
这个时候就需要观察曲线了,10-100个来讲是很快的,当然也要根据项目请来看,总之建议100个就ok了,不要太高。
executeBatch方法
批量执行的一种方式,使用PreparedStatement预编译进行优化。
int insertNum = 100;
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/xxx?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useServerPrepStmts=false&rewriteBatchedStatements=true","root","root123");
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(
"insert into table1(field1) values(?)");
for (int i = 0; i < insertNum; i++) {
ps.setString(1,"大狼狗"+insertNum);
ps.addBatch();
}
ps.executeBatch();
connection.commit();
connection.close();开启ExecutorType.BATCH模式
简单的讲就是openSession的时候带上参数ExecutorType.BATCH,可以几乎无损优化你的代码性能。
SqlSession session = sessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.BATCH);
for (Model model : list) {
session.insert("insertStatement", model);
}
session.flushStatements();BatchInsert模式
也是官方针对批量数据插入优化的方法之一
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.BATCH);
try {
TableMapper mapper = session.getMapper(TableMapper.class);
//自定义你的方法来获取需要插入的数据
List<TableRecord> records = getRecordsToInsert();
//BatchInsert
BatchInsert<TableRecord> batchInsert = insert(records)
.into(table)
.map(id).toProperty("id")
.map(field1).toProperty("field1")
.map(field2).toProperty("field2")
.build()
.render(RenderingStrategy.MYBATIS3);
batchInsert.insertStatements().stream().forEach(mapper::insert);
session.commit();
} finally {
session.close();
}附加2023.1.26新年更新
感谢大家的反馈,这里有些方法确实过时了,现更新以下内容:
BatchInsert应该更新为MultiRowInsertStatementProvider,- 带来
mybatis-plus批量插入方法,
更多详情欢迎移步官方文档 Mybatis Insert Statements
by zhengkai.blog.csdn.net
附加1.1 BatchInsert 应该更新为 MultiRowInsertStatementProvider :
// 单条插入模式
//...
SimpleTableRecord row = new SimpleTableRecord();
row.setId(100);
row.setFirstName("Joe");
row.setLastName("Jones");
row.setBirthDate(new Date());
row.setEmployed(true);
row.setOccupation("Developer");
InsertStatementProvider<SimpleTableRecord> insertStatement = insert(row)
.into(simpleTable)
.map(id).toProperty("id")
.map(firstName).toProperty("firstName")
.map(lastName).toProperty("lastName")
.map(birthDate).toProperty("birthDate")
.map(employed).toProperty("employed")
.map(occupation).toProperty("occupation")
.build()
.render(RenderingStrategies.MYBATIS3);
int rows = mapper.insert(insertStatement);
//...//批量插入对比
try (SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
GeneratedAlwaysAnnotatedMapper mapper = session.getMapper(GeneratedAlwaysAnnotatedMapper.class);
List<GeneratedAlwaysRecord> records = getRecordsToInsert(); // not shown
MultiRowInsertStatementProvider<GeneratedAlwaysRecord> multiRowInsert = insertMultiple(records)
.into(generatedAlways)
.map(id).toProperty("id")
.map(firstName).toProperty("firstName")
.map(lastName).toProperty("lastName")
.build()
.render(RenderingStrategies.MYBATIS3);
int rows = mapper.insertMultiple(multiRowInsert);
}附加1.2 Mybatis-Plus为service层提供了ServiceImpl的实现类,可以直接 extends ServiceImpl<mapper,object>进行调用
@Service
public class ObjectServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ObjectMapper, MyObject> implements ObjectService{
}而后就可以使用以下的实现方法了:
public boolean saveBatch(Collection<T> entityList, int batchSize) {
String sqlStatement = this.getSqlStatement(SqlMethod.INSERT_ONE);
return this.executeBatch(entityList, batchSize, (sqlSession, entity) -> {
sqlSession.insert(sqlStatement, entity);
});
}
protected <E> boolean executeBatch(Collection<E> list, int batchSize, BiConsumer<SqlSession, E> consumer) {
return SqlHelper.executeBatch(this.entityClass, this.log, list, batchSize, consumer);
}SqlHelper.executeBatch的具体的实现如下
public static <E> boolean executeBatch(Class<?> entityClass, Log log, Collection<E> list, int batchSize, BiConsumer<SqlSession, E> consumer) {
Assert.isFalse(batchSize < 1, "batchSize must not be less than one", new Object[0]);
return !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(list) && executeBatch(entityClass, log, (sqlSession) -> {
int size = list.size();
int idxLimit = Math.min(batchSize, size);
int i = 1;
for(Iterator var7 = list.iterator(); var7.hasNext(); ++i) {
E element = var7.next();
consumer.accept(sqlSession, element);
if (i == idxLimit) {
sqlSession.flushStatements();
idxLimit = Math.min(idxLimit + batchSize, size);
}
}
});
}
public static boolean executeBatch(Class<?> entityClass, Log log, Consumer<SqlSession> consumer) {
try {
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory(entityClass);
SqlSessionHolder sqlSessionHolder = (SqlSessionHolder)TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sqlSessionFactory);
boolean transaction = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive();
SqlSession sqlSession;
if (sqlSessionHolder != null) {
sqlSession = sqlSessionHolder.getSqlSession();
sqlSession.commit(!transaction);
}
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.BATCH);
if (!transaction) {
log.warn("SqlSession [" + sqlSession + "] Transaction not enabled");
}
boolean var7;
try {
consumer.accept(sqlSession);
sqlSession.commit(!transaction);
var7 = true;
} catch (Throwable var15) {
sqlSession.rollback();
Throwable unwrapped = ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(var15);
if (unwrapped instanceof PersistenceException) {
MyBatisExceptionTranslator myBatisExceptionTranslator = new MyBatisExceptionTranslator(sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getEnvironment().getDataSource(), true);
Throwable throwable = myBatisExceptionTranslator.translateExceptionIfPossible((PersistenceException)unwrapped);
if (throwable != null) {
throw throwable;
}
}
throw ExceptionUtils.mpe(unwrapped);
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
return var7;
} catch (Throwable var17) {
throw var17;
}
}
摘抄自网络,便于检索查找。





