Spring入门学习---01
Spring
1、Spring的介绍
spring是一个轻量级的开源框架,为解决企业级应用开发的一些复杂问题而创建。
spring的创始人:Rod Johnson(曾是一位悉尼大学的音乐学博士)
spring拥有的两个最大特性:IOC(控制反转)、AOP(面向切面编程)
是现代化java的开发(构建一切、协调一切、连接一切)
2、Spring的组成
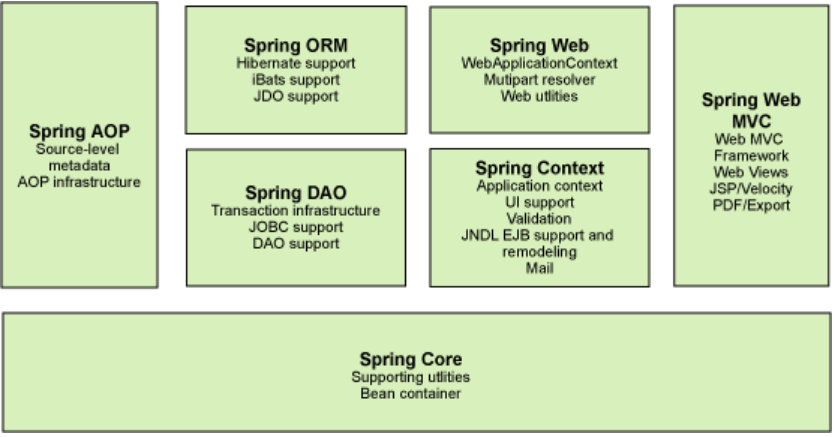
3、IOC控制反转
最先,实现一个业务的步骤是
编写dao层接口和实现类 ---> 编写业务层接口和实现类
但是在这个业务中,我们的业务只由程序员主导,一旦要根据用户的需求来修改,则需要大量的修改成本,因此我们可以利用set进行动态注入,这个时候,程序变成了被动的接受对象。这种思想,从本质上解决了问题,我们程序员不用再去管理对象的创建了,系统的耦合性大大降低。可以更加专注在业务的实现上。这是IOC的原型。
3.1、IOC的介绍
控制反转(Inversion of Control,缩写为IoC),是面向对象编程中的一种设计原则,可以用来减低计算机代码之间的耦合度。其中最常见的方式叫做依赖注入(Dependency Injection,简称DI),还有一种方式叫“依赖查找”(Dependency Lookup)。通过控制反转,对象在被创建的时候,由一个调控系统内所有对象的外界实体将其所依赖的对象的引用传递给它。也可以说,依赖被注入到对象中。
------源自百度百科
3.2、IOC的展示
首先,,搭建一个pojo类
package com.charles.pojo; public class HelloSpring { private Integer id; private String username; public HelloSpring(){} public HelloSpring(Integer id, String username) { this.id = id; this.username = username; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } @Override public String toString() { return "HelloSpring{" + "id=" + id + ", username='" + username + '\'' + '}'; } }
接着,搭建一个Spring的配置文件 applicationContext.xml 来作为容器,并向其中进行注入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 使用Spring来创建对象,在Spring这些都称为Bean 通常在JAVA语法中,创建对象的方法 类型 变量名 = new 类型(); Hello hello = new Hello(); 在这行代码中: id = 变量名 class = new 的对象 property 相当于给对象中的属性赋值 ref与value ref:引用Spring容器中创建好的对象 value:具体值,基本数据类型或String --> <bean id="hello" class="com.charles.pojo.HelloSpring"> <property name="username" value="dasdas"/> <property name="id" value="111"/> </bean> </beans>
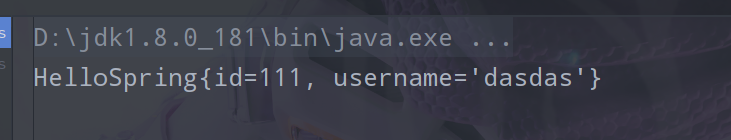
最后,在测试类中进行测试
@Test public void test1(){ ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); // 我们的对象现在都在Spring中管理了,我们要使用直接去里面取出来即可。 System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("hello").toString()); }
结果展示



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号