leetcode 001 - 003
leetcode 001
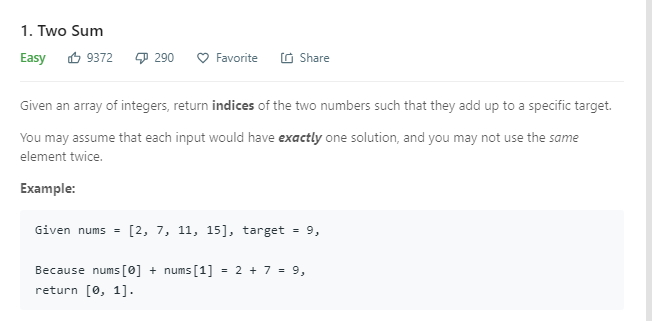
代码实现
暴力求解行不通,第一次运行成功是用首尾递归法。时间复杂度其实也不差,有O(nlogn)。
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
sNums = sorted(nums)
i = 0
j = len(sNums) - 1
while i < j:
if sNums[i] + sNums[j] > target:
j = j - 1
elif sNums[i] + sNums[j] < target:
i = i + 1
else:
m = nums.index(sNums[i])
n = nums.index(sNums[j])
if m == n:
nums.remove(nums[m])
n = nums.index(sNums[j]) + 1
return [m, n]
上面的代码其实太啰嗦了,用索引来循环查找形式上会更简洁:
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
sorted_id = sorted(range(len(nums)), key=lambda k: nums[k])
head = 0
tail = len(nums) - 1
sum_result = nums[sorted_id[head]] + nums[sorted_id[tail]]
while sum_result != target:
if sum_result > target:
tail -= 1
elif sum_result < target:
head += 1
sum_result = nums[sorted_id[head]] + nums[sorted_id[tail]]
return [sorted_id[head], sorted_id[tail]]
这是答案上的最佳实践,时间复杂度O(n)。
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
hashmap = {}
for index, num in enumerate(nums):
another_num = target - num
if another_num in hashmap:
return [hashmap[another_num], index]
hashmap[num] = index
return None
leetcode 002
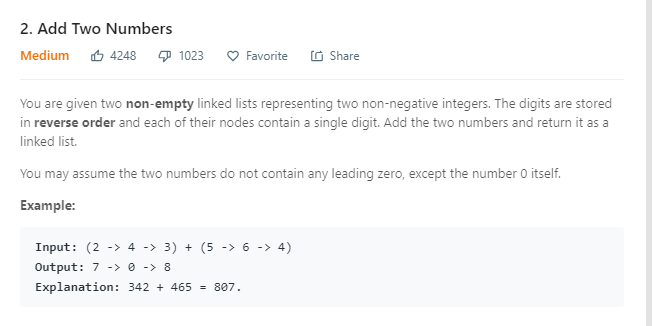
代码实现
没什么好说的,虽然想了挺久,但是弄明白后就是一次过,这里贴上最后一次优化结构提交的:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def nextNode(self, node, val):
"""
:type val: int
:rtpe: ListNode
"""
nextNode = ListNode(val)
node.next = nextNode
return nextNode
def plus(self, node1, node2, carry):
"""
:type node1: ListNode
:type node2: ListNode
:type carry: int
:rtype: int, int
"""
v1 = node1.val if node1 else 0
v2 = node2.val if node2 else 0
val = v1 + v2 + carry
return val % 10 , val // 10
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1, l2):
"""
:type l1: ListNode
:type l2: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
node = head = ListNode(0)
carry = 0
while l1 or l2 or carry:
val, carry = self.plus(l1, l2, carry)
node = self.nextNode(node, val)
l1 = l1.next if l1 else None
l2 = l2.next if l2 else None
return head.next
leetcode 003
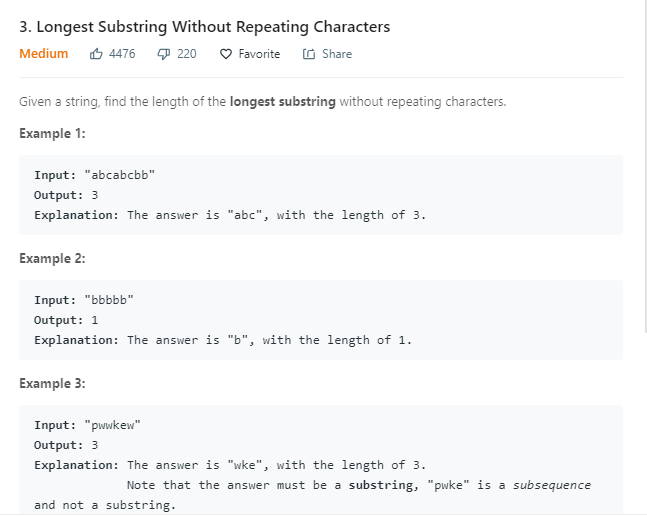
代码实现
有点用到队列的思想,但又不一样。
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: int
"""
lst = []
length = 0
for i in s:
if i in lst:
while True:
if lst[0] != i:
lst.pop(0)
else:
lst.pop(0)
break
lst.append(i)
length = len(lst) if len(lst) > length else length
return length
上面代码有一部分可以优化得非常简单:
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: int
"""
lst = []
length = 0
for i in s:
if i in lst:
lst = lst[lst.index(i) + 1:] ## 巧妙运用切片
lst.append(i)
length = len(lst) if len(lst) > length else length
return length



