来自学长的馈赠7
关于我没带脑子这件事——这是我第N+1次在考场上因为不看数据范围没开够数组RE挂分了……
另一个题: .修改操作数M<=160000,询问数Q<=10000,W<=2000000. 所以数组开了一个1e4+10??? 还有一些没有任何坑的数据范围……Cat的RE日常……Cat再也不想RE了
A. count
对,上文说的就是这个题,,,wait……数据被加强之后我T了

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int maxn = 1e6 + 12; const ll mod = 1e9 + 7; const int INF = 2147483647; const int lim = 1e4 + 1; int n, ans=2, siz[maxn], dgs[maxn], b[maxn], lazy[maxn]; bool tag; inline int read() { int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(ch > '9' || ch < '0') { if(ch == '-') { f = -1; } ch = getchar(); } while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') { x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch^48); ch = getchar(); } return x * f; } struct node { int next, to; }a[maxn<<1]; int head[maxn], len; void add(int x, int y) { a[++len].to = y; a[len].next = head[x]; head[x] = len; } void dfs1(int u, int fa) { siz[u] = 1; for(int i=head[u]; i; i=a[i].next) { int v = a[i].to; if(v == fa) continue; dfs1(v, u); siz[u] += siz[v]; } } bool dfs2(int u, int fa, int size) { for(int i=head[u]; i; i=a[i].next) { int v = a[i].to; if(v == fa) continue; if(siz[v] < size) continue; dfs2(v, u, size); if(siz[v] == size) { siz[u] -= size; lazy[fa] += size; } } if(lazy[u]) { siz[u] -= lazy[u]; lazy[fa] += lazy[u]; } if(u == 1) { if(siz[1] == 0 || siz[1] == size) return 1; else return 0; } else return 1; } int main() { n = read(); for(int i=1; i<n; i++) { int x = read(), y = read(); add(x, y); add(y, x); } dfs1(1, 1); for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) { b[i] = siz[i]; } for(int i=2; i<n; i++) { if(n % i == 0) { memset(dgs, 0, (n+3)*sizeof(int)); memset(lazy, 0, (n+3)*sizeof(int)); for(int j=1; j<=n; j++) siz[j] = b[j]; if(dfs2(1, 1, i)) ans++; } } printf("%d\n", ans); return 0; }

B. 序列
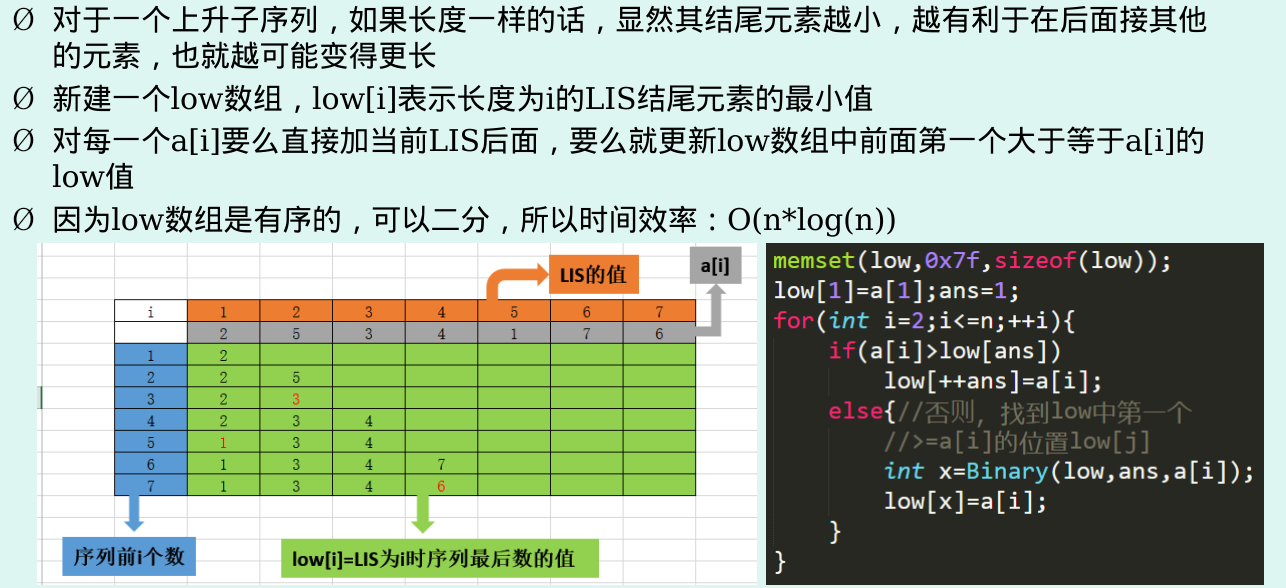
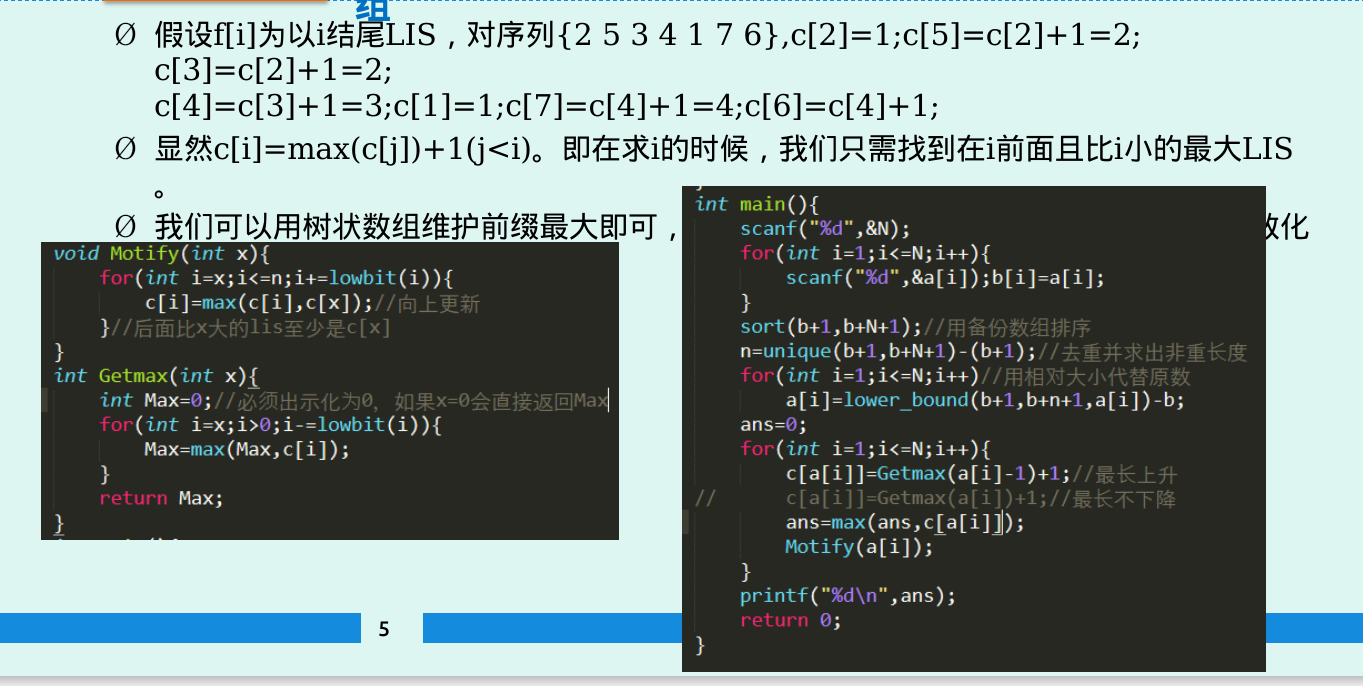
我做好了TLE的准备,判断了一个if(a[i]-a[i]>=j-i) f[i]=f[j]+1,结果发现它是以特定值为结尾的,所以不取max的话水了10分还算多的……(取max的话TLE50)
其实把每个a[i]-i就可以简化上面的问题,还需要用到优化,二分或树状数组都可以,然后我发现我都忘了,果然不长记性体现在方方面面……

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int maxn = 1e6 + 2; const ll mod = 1e9 + 7; const int INF = 2147483647; const int lim = 1e4 + 1; int n, a[maxn], low[maxn], ans; inline int read() { int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(ch > '9' || ch < '0') { if(ch == '-') { f = -1; } ch = getchar(); } while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') { x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch^48); ch = getchar(); } return x * f; } int main() { n = read(); for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) { a[i] = read(); } for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) { a[i] -= i; } memset(low, 0x7f, sizeof(low)); low[1] = a[1]; ans = 1; for(int i=2; i<=n; i++) { if(a[i] >= low[ans]) { low[++ans] = a[i]; } else { int x = lower_bound(low+1, low+ans+1, a[i])-low; low[x] = a[i]; } } printf("%d\n", n-ans); return 0; }
C. 最远点对

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int maxn = 1e5 + 2; const ll mod = 1e9 + 7; const int INF = 2147483647; const int lim = 1e4 + 1; int n, siz[maxn], dep[maxn], fa[maxn]; int son[maxn], top[maxn], m, du[maxn]; ll ans, dis[maxn]; inline int read() { int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(ch > '9' || ch < '0') { if(ch == '-') { f = -1; } ch = getchar(); } while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') { x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch^48); ch = getchar(); } return x * f; } struct node { int next, to, w; }a[maxn<<1]; int head[maxn], len; void add(int x, int y, int w) { a[++len].to = y; a[len].next = head[x]; a[len].w = w; head[x] = len; } void find_heavy_edge(int u, int fat, int depth) { //printf("u = %d\n", u); fa[u] = fat; dep[u] = depth; siz[u] = 1; son[u] = 0; int maxsize = 0; for(int i=head[u]; i; i=a[i].next) { int v = a[i].to; if(dep[v]) continue; dis[v] = dis[u] + a[i].w; //printf("dis[%d] = %d\n", v, dis[v]); find_heavy_edge(v, u, depth+1); du[u]++; //dis[v] = dis[u] + a[i].w; //printf("dis[%d] = %d\n", v, dis[v]); siz[u] += siz[v]; if(siz[v] > maxsize) { maxsize = siz[v]; son[u] = v; } } } void connect_heavy_dege(int u, int ancestor) { //dfn[u] = ++ntime; top[u] = ancestor; //rnk[ntime] = u; if(son[u]) { connect_heavy_dege(son[u], ancestor); } for(int i=head[u]; i; i=a[i].next) { int v = a[i].to; if(v == son[u] || v == fa[u]) continue; connect_heavy_dege(v, v); } } int LCA(int x, int y) { while(top[x] != top[y]) { if(dep[top[x]] < dep[top[y]]) swap(x, y); x = fa[top[x]]; } if(dep[x] > dep[y]) swap(x, y); return x; } bool isLine() { for(int i=1; i<n; i++) { if(du[i] != 1) return 0; } return 1; } int main() { n = read(); for(int i=1; i<n; i++) { int x = read(), y = read(), w = read(); add(x, y, w); add(y, x, w); } find_heavy_edge(1, 1, 1); connect_heavy_dege(1, 1); m = read(); if(isLine()) { //printf("111\n"); while(m--) { int l1 = read(), r1 = read(), l2 = read(), r2 = read(); int mi = min(l1, l2), mx = max(r1, r2); printf("%lld\n", dis[mx]-dis[mi]); } exit(0); } while(m--) { int l1 = read(), r1 = read(), l2 = read(), r2 = read(); ans = 0; for(int i=l1; i<=r1; i++) { for(int j=l2; j<=r2; j++) { int lca = LCA(i, j); ll res = dis[i]+dis[j]-2*dis[lca]; ans = max(ans, res); } } printf("%lld\n", ans); } return 0; }
emmm……非常暴力的循环……
所以正解说两个区间中能够成最远距离的两(其实是2*2=4)个答案点其实可以合并,所以把区间的边界作为初始值放进线段树,叶子节点当然是确定了的,而由叶子可以得到扩大区间的答案,听起来……还是题解比较友好***感谢Vocanda

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int maxn = 1e5 + 2; const ll mod = 1e9 + 7; const int INF = 2147483647; const int lim = 1e4 + 1; int n, siz[maxn], dep[maxn], fa[maxn]; int son[maxn], top[maxn], m, du[maxn]; ll ans, dis[maxn]; inline int read() { int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(ch > '9' || ch < '0') { if(ch == '-') { f = -1; } ch = getchar(); } while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') { x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch^48); ch = getchar(); } return x * f; } struct node { int next, to, w; }a[maxn<<1]; int head[maxn], len; void add(int x, int y, int w) { a[++len].to = y; a[len].next = head[x]; a[len].w = w; head[x] = len; } void find_heavy_edge(int u, int fat, int depth) { //printf("u = %d\n", u); fa[u] = fat; dep[u] = depth; siz[u] = 1; son[u] = 0; int maxsize = 0; for(int i=head[u]; i; i=a[i].next) { int v = a[i].to; if(dep[v]) continue; dis[v] = dis[u] + a[i].w; //printf("dis[%d] = %d\n", v, dis[v]); find_heavy_edge(v, u, depth+1); du[u]++; //dis[v] = dis[u] + a[i].w; //printf("dis[%d] = %d\n", v, dis[v]); siz[u] += siz[v]; if(siz[v] > maxsize) { maxsize = siz[v]; son[u] = v; } } } void connect_heavy_dege(int u, int ancestor) { //dfn[u] = ++ntime; top[u] = ancestor; //rnk[ntime] = u; if(son[u]) { connect_heavy_dege(son[u], ancestor); } for(int i=head[u]; i; i=a[i].next) { int v = a[i].to; if(v == son[u] || v == fa[u]) continue; connect_heavy_dege(v, v); } } int LCA(int x, int y) { while(top[x] != top[y]) { if(dep[top[x]] < dep[top[y]]) swap(x, y); x = fa[top[x]]; } if(dep[x] > dep[y]) swap(x, y); return x; } ll get_dis(int x, int y) { int lca = LCA(x, y); ll ans = dis[x]+dis[y]-2*dis[lca]; return ans; } #define lson (rt<<1) #define rson (rt<<1|1) struct node2 { int l, r, L, R; }tree[maxn<<2]; void IWantToUseALongNameOnlyForHappiness(int a1, int a2, int b1, int b2, int &c1, int &c2) { ll ans = 0; ll a = get_dis(a1, a2); ll b = get_dis(a1, b1); ll c = get_dis(a1, b2); ll d = get_dis(a2, b1); ll e = get_dis(a2, b2); ll f = get_dis(b1, b2); if(a > ans) ans = a, c1 = a1, c2 = a2; if(b > ans) ans = b, c1 = a1, c2 = b1; if(c > ans) ans = c, c1 = a1, c2 = b2; if(d > ans) ans = d, c1 = a2, c2 = b1; if(e > ans) ans = e, c1 = a2, c2 = b2; if(f > ans) ans = f, c1 = b1, c2 = b2; } void pushup(int rt) { IWantToUseALongNameOnlyForHappiness(tree[lson].L, tree[lson].R, tree[rson].L, tree[rson].R, tree[rt].L, tree[rt].R); } void build(int rt, int l, int r) { tree[rt].l = l; tree[rt].r = r; if(l == r) { tree[rt].L = tree[rt].R = l; return; } int mid = (l + r) >> 1; build(lson, l, mid); build(rson, mid+1, r); pushup(rt); } void query(int rt, int l, int r, int &L, int &R) { //printf("rt = %d\n", rt); if(l <= tree[rt].l && tree[rt].r <= r) { IWantToUseALongNameOnlyForHappiness(L, R, tree[rt].L, tree[rt].R, L, R); return; } int mid = (tree[rt].l + tree[rt].r) >> 1; if(l <= mid) query(lson, l, r, L, R); if(r > mid) query(rson, l, r, L, R); } int main() { n = read(); for(int i=1; i<n; i++) { int x = read(), y = read(), w = read(); add(x, y, w); add(y, x, w); } find_heavy_edge(1, 1, 1); connect_heavy_dege(1, 1); build(1, 1, n); //printf("111\n"); m = read(); while(m--) { int a = read(), b = read(), c = read(), d = read(); int e = a, f = b, g = c, h = d; query(1, a, b, e, f); //printf("222\n"); query(1, c, d, g, h); ans = max(get_dis(e, g), get_dis(e, h)); ans = max(ans, max(get_dis(f, g), get_dis(f, h))); printf("%lld\n", ans); } return 0; }
D. 春节十二响
一条链的情况下那个结论我算是想到了吗?反正我写了个sort(p+dfn[x],p+dfn[x]+siz[x])再用while循环和双指针从右往左指一下……搞的挺复杂结果连部分分都没拿到,随便乱搞却水了10分(就是按深度分段,每段拿一个最大的,想想就不对)
启发式合并里的交换只对交换时有效,最后还是都得合并到根上,至于合并的应该是不包括根的子链的问题,最后再把根的数放进去就好了。(我居然才知道vector还有pop_back的用法)

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int maxn = 2e5 + 2; const ll mod = 1e9 + 7; const int INF = 2147483647; const int lim = 1e4 + 1; int n, a[maxn], f; vector<int> e[maxn], o; priority_queue<int> q[maxn]; ll ans; inline int read() { int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(ch > '9' || ch < '0') { if(ch == '-') { f = -1; } ch = getchar(); } while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') { x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch^48); ch = getchar(); } return x * f; } void merge(int x, int y) { if(q[x].size() < q[y].size()) swap(q[x], q[y]); while(q[y].size()) { o.push_back(max(q[x].top(), q[y].top())); q[x].pop(); q[y].pop(); } while(o.size()) { q[x].push(o.back()); o.pop_back(); } } void dfs(int u) { for(int i=0; i<e[u].size(); i++) { dfs(e[u][i]); merge(u, e[u][i]); } q[u].push(a[u]); } int main() { n = read(); for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) { a[i] = read(); } for(int i=2; i<=n; i++) { f = read(); e[f].push_back(i); } dfs(1); while(q[1].size()) { ans += q[1].top(); q[1].pop(); } printf("%lld\n", ans); return 0; }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 按钮权限的设计及实现