#YBT整理 高精度害死人
高精度加减乘除板子,整理一下成为函数。
思路
都是字符串读入,倒序存储。数组\(a_0\)表示\(a\)的位数。
加法
每一位相加,判断是否需要进位。循环结束后判断最高位是否需要进位,最终调整一下位数。
减法
每一位相减,不够减的向前一位借位 (感觉我在学习小学一年级知识??)最后需要调整位数,去掉前导0.
乘法
这里和普通的竖式乘法不同。高精乘高精思路为,答案的第i+j-1位,等于两乘数分别的第 i 位和第 j 位相乘。最后需要处理进位和位数的问题。
除法
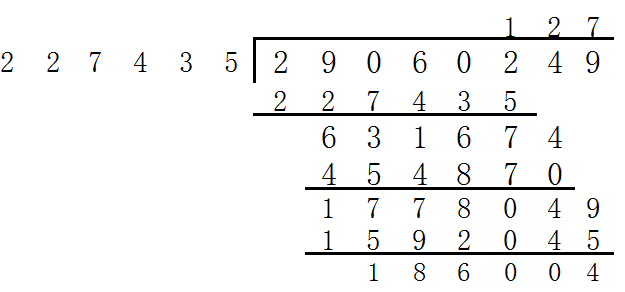
如上图,是地球人用纸和笔做的除法。但是很显然,计算机走试商的方法太麻烦,那就只能把除数移到被除数的最高位(空余的用0补上),再相减,直到剩下的数小于除数(同时记录商),然后进行下一位的计算。
代码
加法
#include<iostream>
#include"cmath"
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
string in;
int a[999],b[999],ans[999];
int strlen(string x){
int tot = 0;
while(x[tot++] != '\0');
return tot-1;
}
void _P(int x[],int y[]){
ans[0] = max(x[0],y[0]);
for(int i = 1;i <= ans[0]; i++){
ans[i] += x[i] + y[i];
ans[i+1] += ans[i]/10;
ans[i] %= 10;
}
if(ans[ans[0] + 1]) ans[0] ++;
}
int main(){
cin >> in;
a[0] = strlen(in);
for(int i = 1;i <= a[0]; i++){
a[i] = in[a[0] - i] - '0';
}
cin >> in;
b[0] = strlen(in);
for(int i = 1;i <= b[0]; i++){
b[i] = in[b[0] - i] - '0';
}
_P(a,b);
for(int i = ans[0];i >= 1; i--){
cout << ans[i];
}
cout <<endl;
}
减法
注意正负号的检验。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
string in;
int a[10100],b[10100];
int c[10100];
int strlen(string x){
int tot = 0;
while(x[tot++] != '\0');
tot--;
return tot;
}
void jian(int x[],int y[]){
c[0] = x[0];
for(int i = 1;i <= x[0]; i++){
c[i] += x[i]-y[i];
if(c[i] < 0){
c[i] += 10;
c[i+1]--;
}
}
while(c[0] > 1 && c[c[0]] == 0) c[0]--;
}
bool cmp(int x[],int y[]){
if(x[0] > y[0]) return 1;
if(x[0] < y[0]) return 0;
for(int i = y[0];i >= 1; i--){
if(x[i] > y[i]) return 1;
if(x[i] < y[i]) return 0;
}
return 1;
}
int main(){
cin >> in;
a[0] = strlen(in);
for(int i = 1;i <= a[0]; i++){
a[i] = in[a[0] - i] - '0';
}
cin >> in;
b[0] = strlen(in);
for(int i = 1;i <= b[0]; i++){
b[i] = in[b[0] - i] - '0';
}
if(!cmp(a,b)){
for(int i = 0;i <= max(a[0],b[0]); i++){
swap(a[i],b[i]);
}
cout << '-';
}
jian(a,b);
for(int i = c[0];i >= 1; i--)
cout << c[i] ;
cout << endl;
return 0;
}//lcez_cyc
乘法
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
string in;
int a[999],b[999],ans[999];
int strlen(string x){
int tot = 0;
while(x[tot++] != '\0');
return tot-1;
}
void _X(int x[],int y[]){
ans[0] = x[0] + y[0]-1;
for(int i = 1;i <= x[0]; i++){
for(int j = 1;j <= y[0]; j++){
ans[j+i-1] += x[i] * y[j];
ans[i+j] += ans[j+i-1] / 10;
ans[i+j-1] %= 10;
}
}
if(ans[ans[0]+1] != 0) ans[0]++;
while(ans[0] > 1 && ans[ans[0]] == 0) ans[0]--;
}
int main(){
cin >> in;
a[0] = strlen(in);
for(int i = 1;i <= a[0]; i++){
a[i] = in[a[0] - i] - '0';
}
cin >> in;
b[0] = strlen(in);
for(int i = 1;i <= b[0]; i++){
b[i] = in[b[0] - i] - '0';
}
_X(a,b);
for(int i = ans[0];i >= 1; i--){
cout << ans[i];
}
cout <<endl;
return 0;
}
除法
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
string in;
int a[10100],b[10100];
int c[10100];
int d[10100],r[10100];
int strlen(string x){
int tot = 0;
while(x[tot++] != '\0');
tot--;
return tot;
}
void jian(int x[],int y[]){
memset(c,0,sizeof c);
c[0] = x[0];
for(int i = 1;i <= x[0]; i++){
c[i] += x[i]-y[i];
if(c[i] < 0){
c[i] += 10;
c[i+1]--;
}
}
while(c[0] > 1 && c[c[0]] == 0) c[0]--;
}
int cmp(int x[],int y[]){
if(x[0] > y[0]) return 1;
if(x[0] < y[0]) return 0;
for(int i = y[0];i >= 1; i--){
if(x[i] > y[i]) return 1;
if(x[i] < y[i]) return 0;
}
return 2;
}
//商d,余数r
void chu(int x[],int y[]){
memset(d,0,sizeof d);
memset(r,0,sizeof r);
int tmp[10100] = {};
for(int i = 0;i <= x[0]; i++){
r[i] = x[i];
}
d[0] = x[0];
for(int i = x[0] - y[0] + 1;i >= 1; i--){
memset(tmp,0,sizeof tmp);
int cnt = 1;
for(int j = i;j <= i + y[0] - 1; j++){
tmp[j] = y[cnt++];//移位操作
}
for(int j = i-1; j >= 1; j--) tmp[j] = 0;
tmp[0] = i-1 + y[0];
while(cmp(r,tmp)){//比较除数和剩下的被除数
d[i]++;
jian(r,tmp);
memset(r,0,sizeof r);
for(int i = 0;i <= max(r[0],c[0]); i++) r[i] = c[i];
}
}
while(d[0] > 1 && d[d[0]] == 0) d[0]--;
while(r[0] > 1 && c[c[0]] == 0) r[0]--;
}
int main(){
cin >> in;
a[0] = strlen(in);
for(int i = 1;i <= a[0]; i++){
a[i] = in[a[0] - i] - '0';
}
cin >> in;
b[0] = strlen(in);
for(int i = 1;i <= b[0]; i++)
b[i] = in[b[0]-i] - '0';
chu(a,b);
for(int i = d[0];i >= 1; i--) cout << d[i];
cout << endl;
for(int i = r[0];i >= 1; i--) cout << r[i];
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
例题
回文数
特殊的一点就是这里提到的是n进制,所以需要稍微进行一下优化(还好不是乘法除法)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[10086],b[10086];
int c[10086];
int n;string in;
int ans;
int strlen(string x){
int tot = 0;
while(x[tot++] != '\0');
return tot-1;
}
void pluss(int x[],int y[],int k){//k进制
memset(c,0,sizeof c);
c[0] = max(x[0],y[0]);
for(int i = 1;i <= max(x[0],y[0]); i++){
c[i] += x[i] + y[i];
if(c[i] >= k){
c[i+1] += 1;
c[i] %= k;//实际就是把10都改成了k
}
}
if(c[c[0] + 1])
c[0]++;
}
bool is_hw(int x[]){
for(int i = 1;i <= x[0]; i++){
if(x[i] != x[x[0] - i + 1]) return 0;
}
return 1;
}
int main(){
cin >> n;
cin >> in;
a[0] = strlen(in);
for(int i = 1;i <= a[0]; i++){
if(in[a[0] - i] >= '0' && in[a[0] - i] <= '9')
a[i] = in[a[0] - i] - '0';
else
a[i] = 10 + in[a[0]-i] -'A';
}
for(int i = 0;i <= a[0];i++) c[i] = a[i];
while(!is_hw(c)){
ans++;
b[0] = c[0];
a[0] = c[0];
for(int i = 1;i <= c[0]; i++){
b[i] = c[i];
a[i] = c[c[0] + 1 -i];//倒序
}
pluss(a,b,n);
if(ans >= 30){
cout << "Impossible" << endl;
return 0;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
阶乘之和
洛谷 一本通
这个真的是我也不知道为什么有点麻烦,之前是打表做的,今天重新写了一下。
整体如果出问题还是在高精的核心算法上。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int a[10000],b,anss[10000];
int n;
int ans[10000],now[10000];
void _x(int x,int y[]){
memset(ans,0,sizeof ans);
int x0 = 0,k = x;
while(k){k /= 10; x0++;}
ans[0] = x0 + y[0] -1;
for(int i = 1;i <= max(y[0],x0); i++){
ans[i] += x * y[i];
k = i;
while(ans[k] >= 10){
ans[k+1] += ans[k] / 10;
ans[k] %= 10;
k++;
}
ans[0] = max(k,ans[0]);
}
while(ans[0] > 1 && ans[ans[0]] == 0) ans[0]--;
}
void _p(int x[],int y[]){
memset(anss,0,sizeof anss);
anss[0] = max(a[0],y[0]);
for(int i = 1;i <= max(x[0],y[0]); i++){
anss[i] += x[i] + y[i];
if(anss[i] >= 10){
anss[i+1] += anss[i] / 10;
anss[i] %= 10;
}
}
if(anss[anss[0]+1]){anss[0]++;}
for(int i = 0;i <= anss[0]; i++)
now[i] = anss[i];
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++){
a[0] = a[1] = 1;
for(int j = 1;j <= i; j++){
_x(j,a);
for(int i = 0;i <= a[0]; i++) a[i] = ans[i];
}
_p(ans,now);
}
for(int i = now[0];i >= 1; i--){
cout << now[i];
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
结尾
其实高精是个上哪里都不会考到的东西,但是这个确实有助于提高代码能力啥的。所以以后还是多写写吧。



