【数据结构系列】——二叉搜索树的操作集合
二叉树
二叉树的遍历
void traverse(TreeNode root) {
// root 需要做什么? 在这做。
// 其他的不用 root 操作, 抛给框架
traverse(root.left);
traverse(root.right);
}
二叉搜索树
热个身
1. 如何把二叉树所有节点中的值加一
void plusOne(TreeNode root){
if(root == null)
return;
root.val += 1;
plusOne(root.left);
plusOne(root.right);
}
2. 如何判断两颗二叉树是否完全相同?
boolean isSameTree(TreeNode root1,TreeNode root2){
//都为空的话,显然相同
if(root1 == null && root2 == null)
return true;
//一个为空,一个非空,显然不同
if(root1 == null || root2 == null)
return false;
//两个都非空,但val不一样也不行
if(root1.val != root2.val)
return false;
//root1和root2该比的都比完了
return isSameTree(root1.left,root2.left)
&& isSameTree(root1.right,root2.right);
}
二叉搜索树的定义:
二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree, 简称 BST) 是一种很常见的的二叉树。 它的定义是:一个二叉树中, 任意节点的值要大于等于左子树所有节点的值,且要小于等于右边子树的所有节点的值。
3. 判断 BST 的合法性
boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
if (root.left != null && root.val <= root.left.val) return false;
if (root.right != null && root.val >= root.right.val) return false;
return isValidBST(root.left)
&& isValidBST(root.right);
}
如果直接用递归判断左右孩子是错误的,而应该判断每个结点都小于右子树的所有节点,正确的是:给子树上的所有节点添加一个min和max边界,约束root的左子树节点值不超过root的值,右子树节点值不小于root的值。
boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return isValidBST(root, null, null);
}
boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root, TreeNode min, TreeNode max) {
if (root == null) return true;
if (min != null && root.val <= min.val) return false;
if (max != null && root.val >= max.val) return false;
return isValidBST(root.left, min, root)
&& isValidBST(root.right, root, max);
}
4. 在 BST 中查找一个数是否存在
boolean isInBST(TreeNode root, int target) {
if (root == null) return false;
if (root.val == target) return true;
return isInBST(root.left, target)
|| isInBST(root.right, target);
}
优化代码,使用二分查找的思想,使用上BST”左小右大“的特性,根据target和root.val的大小比较
boolean isInBST(TreeNode root, int target) {
if (root == null) return false;
if (root.val == target)
return true;
if (root.val < target)
return isInBST(root.right, target);
if (root.val > target)
return isInBST(root.left, target);
// root 该做的事做完了, 顺带把框架也完成了, 妙
}
5. 在BST中插入一个数
对数据结构的操作无非遍历 + 访问, 遍历就是“找”, 访问就是“改”。
插入一个数, 就是先找到插入位置, 然后进行插入操作。
TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
// 找到空位置插入新节点
if (root == null) return new TreeNode(val);
// if (root.val == val)
// BST 中一般不会插入已存在元素
if (root.val < val)
root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, val);
if (root.val > val)
root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, val);
return root;
}
6. 在 BST 中删除一个数
TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root.val == key) {
// 找到啦, 进行删除
} else if (root.val > key) {
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
} else if (root.val < key) {
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
}
return root;
}
删除节点有三种情况,因为删除节点会破坏BST的性质。
-
情况 1: A 恰好是末端节点, 两个⼦节点都为空, 那么它可以当场去世了。

if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return null; -
情况 2: A 只有一个非空子节点,那么它要让这个孩子接替自己的位置。

// 排除了情况 1 之后 if (root.left == null) return root.right; if (root.right == null) return root.left; -
情况 3: A 有两个子节点, 为了不破坏 BST 的性质, A 必须找到左子树中最大的那个节点, 或者右子树中最小的那个节点来接替自己。
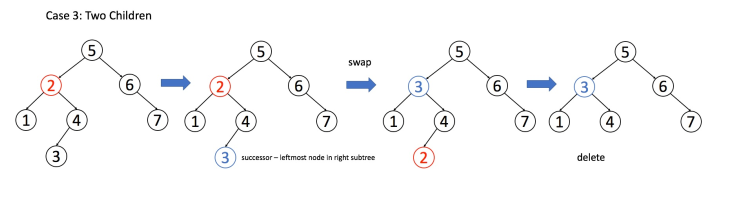
if (root.left != null && root.right != null) { // 找到右子树的最小节点 TreeNode minNode = getMin(root.right); // 把 root 改成 minNode root.val = minNode.val; // 转而去删除 minNode root.right = deleteNode(root.right, minNode.val); }汇总代码
TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) { if (root == null) return null; if (root.val == key) { // 这两个 if 把情况 1 和 2 都正确处理了 if (root.left == null) return root.right; if (root.right == null) return root.left; // 处理情况 3 TreeNode minNode = getMin(root.right); root.val = minNode.val; root.right = deleteNode(root.right, minNode.val); } else if (root.val > key) { root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key); } else if (root.val < key) { root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key); } return root; } TreeNode getMin(TreeNode node) { // BST 最左边的就是最小的 while (node.left != null) node = node.left; return node; }
二叉搜索树节点最小距离
//leetcode submit region begin(Prohibit modification and deletion)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution_783 {
/**
* 中序遍历,然后把遍历出来的结果放进数组中,查找两个相邻数组的最小差值
* @param root
* @return
*/
public int minDiffInBST_1(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> l1 = new ArrayList();
help(root,l1);
int[] a = new int[l1.size()];
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) {
a[i] = l1.get(i);
}
for(int i=0; i<a.length-1; i++) {
a[i] = a[i+1]-a[i];
}
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) {
if(a[i]<a[0]) {
a[0] = a[i];
}
}
return a[0];
}
public void help(TreeNode root, List<Integer> l1){
if(root == null)
return;
help(root.left,l1);
l1.add(root.val);
help(root.right,l1);
}
/**
* DFS
*/
private int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private TreeNode pre = null;
private void DFS(TreeNode node){
if (node == null)
return;
DFS(node.left);
if (pre != null)
res = Math.min(node.val - pre.val,res);
pre = node;
DFS(node.right);
}
public int minDiffInBST_2(TreeNode root){
DFS(root);
return res;
}
/**
* BFS
*/
public int minDiffInBST(TreeNode root){
int Min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
TreeNode preNode = null,curNode = root;
Stack<TreeNode> st = new Stack<>();
while (!st.isEmpty() || curNode!= null){
while (curNode!= null){
st.push(curNode);
curNode = curNode.left;
}
curNode = st.pop();
if (preNode != null)
Min = Math.min(Min,curNode.val - preNode.val);
preNode = curNode;
curNode = curNode.right;
}
return Min;
}
}
//leetcode submit region end(Prohibit modification and deletion)
二叉搜索树的范围和
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int res = 0;
public int rangeSumBST(TreeNode root,int L,int R){
if (root != null){
if (root.val < L){//当前小于L,则只需要遍历右子树即可
rangeSumBST(root.right,L,R);
}else if (root.val > R){//当前大于R,则只需要遍历左子树即可
rangeSumBST(root.left,L,R);
}else {//当前在L~R,则两个子树都要遍历
res += root.val;
rangeSumBST(root.left,L,R);
rangeSumBST(root.right,L,R);
}
}
return res;
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号