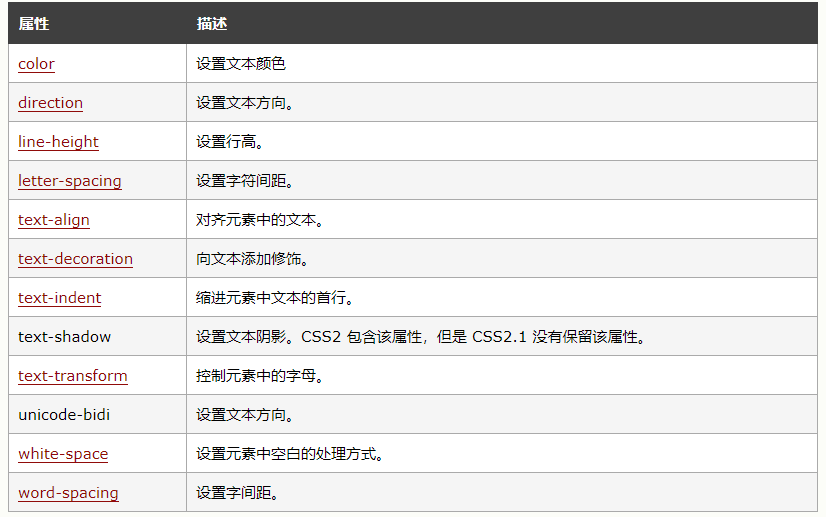
CSS 文本--样式
1.缩进文本【text-indent】
p {text-indent: 5em;}
注意:一般来说,可以为所有块级元素应用 text-indent,但无法将该属性应用于行内元素,图像之类的替换元素上也无法应用 text-indent 属性。不过,如果一个块级元素(比如段落)的首行中有一个图像,它会随该行的其余文本移动。
提示:如果想把一个行内元素的第一行“缩进”,可以用左内边距或外边距创造这种效果。
使用负值
p {text-indent: -5em;}
不过在为 text-indent 设置负值时要当心,如果对一个段落设置了负值,那么首行的某些文本可能会超出浏览器窗口的左边界。为了避免出现这种显示问题,建议针对负缩进再设置一个外边距或一些内边距。
p {text-indent: -5em; padding-left: 5em;}
使用百分比值
div {width: 500px;}
p {text-indent: 20%;}
<div>
<p>this is a paragragh</p>
</div>
继承
div#outer {width: 500px;}
div#inner {text-indent: 10%;}
p {width: 200px;}
<div id="outer">
<div id="inner">some text. some text. some text.
<p>this is a paragragh.</p>
</div>
</div
2.水平对齐【text-align】
影响一个元素中的文本行互相之间的对齐方式。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>水平对齐</title> <style type="text/css"> div{ height: 200px; width: 300px; border: solid 1px #000000; text-align: center; } </style> </head> <body> <div>我在哪?</div> </body> </html>
3.字间隔【word-spacing】
默认值 normal 与设置值为 0 是一样的。
word-spacing 属性接受一个正长度值或负长度值。如果提供一个正长度值,那么字之间的间隔就会增加。为 word-spacing 设置一个负值,会把它拉近。【负值对中文无效】
所有浏览器都支持 word-spacing 属性。
注释:任何的版本的 Internet Explorer (包括 IE8)都不支持属性值 "inherit"。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>字间距</title> <style type="text/css"> p{word-spacing: -1em;} </style> </head> <body> <p>This is some text. This is some text.</p> </body> </html>
inherit 规定应该从父元素继承 word-spacing 属性的值。【未能理解】
4.字母间隔【letter-spacing】

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>字母间距</title> <style type="text/css"> h1 {letter-spacing: -0.5em} h4 {letter-spacing: 20px} </style> </head> <body> <h1>我是谁</h1> <h4>This is header 4</h4> </body> </html>
所有浏览器都支持 word-spacing 属性。
注释:任何的版本的 Internet Explorer (包括 IE8)都不支持属性值 "inherit"。
inherit 规定应该从父元素继承 word-spacing 属性的值。【未能理解】
5.字符转换【text-transform】

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>字符转换</title> <style type="text/css"> h1 {text-transform: none} p.uppercase {text-transform: uppercase} p.lowercase {text-transform: lowercase} p.capitalize {text-transform: capitalize} </style> </head> <body> <h1>This Is An H1 Element</h1> <p class="uppercase">This is some text in a paragraph.</p> <p class="lowercase">This is some text in a paragraph.</p> <p class="capitalize">This is some text in a paragraph.</p> </body> </html>
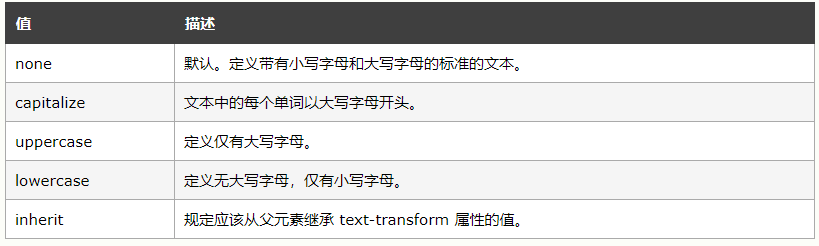
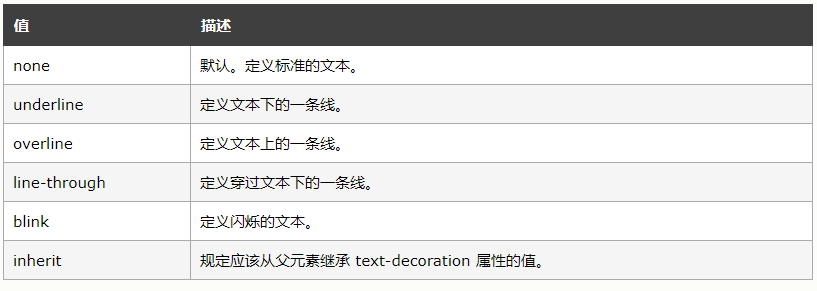
6.文本装饰【text-decoration】
注释:任何的版本的 Internet Explorer (包括 IE8)都不支持属性值 "inherit"。
注释:IE、Chrome 或 Safari 不支持 "blink" 属性值。【不太理解blink】

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>文本装饰</title> <style type="text/css"> h1 {text-decoration: overline} h2 {text-decoration: line-through} h3 {text-decoration: underline} h4 {text-decoration:blink} a {text-decoration: none} </style> </head> <body> <h1>这是标题 1</h1> <h2>这是标题 2</h2> <h3>这是标题 3</h3> <h4>这是标题 4</h4> <p>这是标题 4</p> <p><a href="http://www.w3school.com.cn/index.html">这是一个链接</a></p> </body> </html> <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>文本装饰</title> <style type="text/css"> h1 {text-decoration: overline} h2 {text-decoration: line-through} h3 {text-decoration: underline} h4 {text-decoration:blink} a {text-decoration: none} </style> </head> <body> <h1>这是标题 1</h1> <h2>这是标题 2</h2> <h3>这是标题 3</h3> <h4>这是标题 4</h4> <p>这是标题 4</p> <p><a href="http://www.w3school.com.cn/index.html">这是一个链接</a></p> </body> </html>
还可以在一个规则中结合多种装饰。如果希望所有超链接既有下划线,又有上划线,则规则如下:
a:link a:visited {text-decoration: underline overline;}
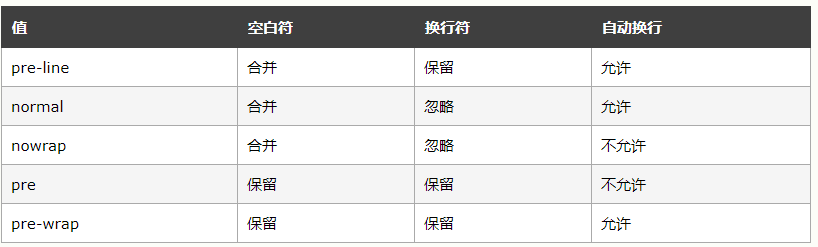
7.处理空白符【white-space】
通过使用该属性,可以影响浏览器处理字之间和文本行之间的空白符的方式。从某种程度上讲,默认的 XHTML 处理已经完成了空白符处理:它会把所有空白符合并为一个空格。所以给定以下标记,它在 Web 浏览器中显示时,各个字之间只会显示一个空格,同时忽略元素中的换行。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>处理空白符</title> <style type="text/css"> p {white-space: normal;} </style> </head> <body> <p>This paragraph has many spaces in it.</p> <p>注释:当 white-space 属性设置为 normal 时,会合并所有的空白符,并忽略换行符。</p> </body> </html>
不过,如果将 white-space 设置为 pre,受这个属性影响的元素中,空白符的处理就有所不同,其行为就像 XHTML 的 pre 元素一样;空白符不会被忽略。
如果 white-space 属性的值为 pre,浏览器将会注意额外的空格,甚至回车。在这个方面,而且仅在这个方面,任何元素都可以相当于一个 pre 元素。
值 nowrap和值 pre-wrap 和 pre-line【不懂】
8.文本方向【direction】
direction 属性规定文本的方向 / 书写方向。
该属性指定了块的基本书写方向,以及针对 Unicode 双向算法的嵌入和覆盖方向。不支持双向文本的用户代理可以忽略这个属性。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>文本方向</title> <style type="text/css"> div.one { direction: rtl } div.two { direction: ltr } </style> </head> <body> <div class="one">Some text. Right-to-left direction.</div> <div class="two">Some text. Left-to-right direction.</div> </body> </html>
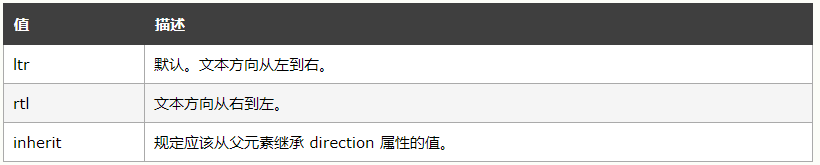
注释:对于行内元素,只有当 unicode-bidi 属性设置为 embed 或 bidi-override 时才会应用 direction 属性。
unicode-bidi 属性设置文本的方向。
normal 元素不会对双向算法打开附加的一层嵌套。对于行内元素,顺序的隐式重排会跨元素边界进行。
embed 如果是一个行内元素,这个值对于双向算法会打开附件的一层嵌套。这个嵌套层的方向由 direction 属性指定。
bidi-override 这会为行内元素创建一个覆盖。对于块级元素,将为不在另一块中的行内后代创建一个覆盖。这说明,顺序重排在元素内部严格按照 direction 属性进行;【不懂】