DeepLearning.ai-Week4-Deep Learning & Art: Neural Style Transfer
1 - Task
- Implement the neural style transfer algorithm
- Generate novel artistic images using your algorithm
2 - Import Packages
import os import sys import scipy.io import scipy.misc import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow from PIL import Image from nst_utils import * import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf %matplotlib inline
3 - Problem Statement

4 - Transfer Learning
加载已经在ImageNet数据集上训练好的VGG网络。
model = load_vgg_model("pretrained-model/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat") print(model)
Result: {'conv5_3': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_14:0' shape=(1, 19, 25, 512) dtype=float32>, 'avgpool1': <tf.Tensor 'AvgPool:0' shape=(1, 150, 200, 64) dtype=float32>, 'conv5_2': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_13:0' shape=(1, 19, 25, 512) dtype=float32>, 'conv3_3': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_6:0' shape=(1, 75, 100, 256) dtype=float32>, 'conv3_2': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_5:0' shape=(1, 75, 100, 256) dtype=float32>, 'conv4_2': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_9:0' shape=(1, 38, 50, 512) dtype=float32>, 'avgpool3': <tf.Tensor 'AvgPool_2:0' shape=(1, 38, 50, 256) dtype=float32>, 'conv4_3': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_10:0' shape=(1, 38, 50, 512) dtype=float32>, 'avgpool5': <tf.Tensor 'AvgPool_4:0' shape=(1, 10, 13, 512) dtype=float32>, 'conv3_1': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_4:0' shape=(1, 75, 100, 256) dtype=float32>, 'conv5_1': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_12:0' shape=(1, 19, 25, 512) dtype=float32>, 'conv2_2': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_3:0' shape=(1, 150, 200, 128) dtype=float32>, 'conv5_4': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_15:0' shape=(1, 19, 25, 512) dtype=float32>, 'input': <tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(1, 300, 400, 3) dtype=float32_ref>, 'conv3_4': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_7:0' shape=(1, 75, 100, 256) dtype=float32>, 'conv4_1': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_8:0' shape=(1, 38, 50, 512) dtype=float32>, 'conv4_4': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_11:0' shape=(1, 38, 50, 512) dtype=float32>, 'avgpool2': <tf.Tensor 'AvgPool_1:0' shape=(1, 75, 100, 128) dtype=float32>, 'avgpool4': <tf.Tensor 'AvgPool_3:0' shape=(1, 19, 25, 512) dtype=float32>, 'conv1_1': <tf.Tensor 'Relu:0' shape=(1, 300, 400, 64) dtype=float32>, 'conv2_1': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_2:0' shape=(1, 150, 200, 128) dtype=float32>, 'conv1_2': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_1:0' shape=(1, 300, 400, 64) dtype=float32>}
5 - Neural Style Transfer
实现NST算法有如下几个步骤:
- Build the content cost function J_{content}(C,G)
- Build the style cost function J_{style}(S,G)$
- Put it together to get J(G)=α J_{content}(C,G)+β J_{style}(S,G)
5.1 - Computing the content cost
浏览浏览图片。
content_image = scipy.misc.imread("images/louvre.jpg") imshow(content_image)
Result:
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x21eca6026d8>

5.1.1 - How do you ensure the generated image G matches the content of the image C?
内容损失函数如下:
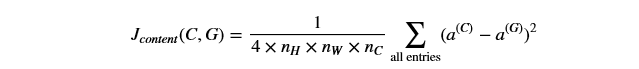
实现compute_content_cost()方法有如下步骤:
- Retrieve dimensions from a_G:
- To retrieve dimensions from a tensor X, use:
X.get_shape().as_list()
- To retrieve dimensions from a tensor X, use:
- Unroll a_C and a_G as explained in the picture above
- Compute the content cost:
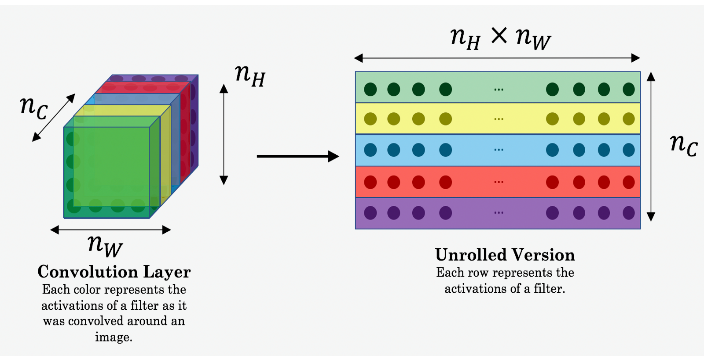
# GRADED FUNCTION: compute_content_cost def compute_content_cost(a_C, a_G): """ Computes the content cost Arguments: a_C -- tensor of dimension (1, n_H, n_W, n_C), hidden layer activations representing content of the image C a_G -- tensor of dimension (1, n_H, n_W, n_C), hidden layer activations representing content of the image G Returns: J_content -- scalar that you compute using equation 1 above. """ ### START CODE HERE ### # Retrieve dimensions from a_G (≈1 line) m, n_H, n_W, n_C = a_G.get_shape().as_list() # Reshape a_C and a_G (≈2 lines)
a_C_unrolled = tf.reshape(a_C, (n_H*n_W, n_C))
a_G_unrolled = tf.reshape(a_G, (n_H*n_W, n_C))# compute the cost with tensorflow (≈1 line) J_content = 1 / (4*n_H*n_W*n_C) * tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(tf.subtract(a_C_unrolled, a_G_unrolled))) ### END CODE HERE ### return J_content
tf.reset_default_graph() with tf.Session() as test: tf.set_random_seed(1) a_C = tf.random_normal([1, 4, 4, 3], mean=1, stddev=4) a_G = tf.random_normal([1, 4, 4, 3], mean=1, stddev=4) J_content = compute_content_cost(a_C, a_G) print("J_content = " + str(J_content.eval()))
Result:
J_content = 6.76559
5.2 - Computing the style cost
预览图片。
style_image = scipy.misc.imread("images/monet_800600.jpg") imshow(style_image)
Result:
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x21eccaeff28>

5.2.1 - Style matrix
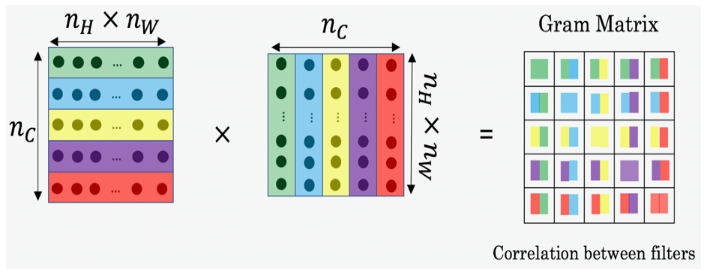
# GRADED FUNCTION: gram_matrix
# G_A = AA^T
def gram_matrix(A): """ Argument: A -- matrix of shape (n_C, n_H*n_W) Returns: GA -- Gram matrix of A, of shape (n_C, n_C) """ ### START CODE HERE ### (≈1 line) GA = tf.matmul(A, tf.transpose(A)) ### END CODE HERE ### return GA
tf.reset_default_graph() with tf.Session() as test: tf.set_random_seed(1) A = tf.random_normal([3, 2*1], mean=1, stddev=4) GA = gram_matrix(A) print("GA = " + str(GA.eval()))
Result: GA = [[ 6.42230511 -4.42912197 -2.09668207] [ -4.42912197 19.46583748 19.56387138] [ -2.09668207 19.56387138 20.6864624 ]]
5.2.2 - Style cost
风格损失函数如下:
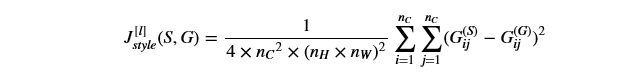
实现compute_layer_style_cost()方法有如下步骤:
- Retrieve dimensions from the hidden layer activations a_G:
- To retrieve dimensions from a tensor X, use:
X.get_shape().as_list()
- To retrieve dimensions from a tensor X, use:
- Unroll the hidden layer activations a_S and a_G into 2D matrices, as explained in the picture above.
- Compute the Style matrix of the images S and G. (Use the function you had previously written.)
- Compute the Style cost:
# GRADED FUNCTION: compute_layer_style_cost def compute_layer_style_cost(a_S, a_G): """ Arguments: a_S -- tensor of dimension (1, n_H, n_W, n_C), hidden layer activations representing style of the image S a_G -- tensor of dimension (1, n_H, n_W, n_C), hidden layer activations representing style of the image G Returns: J_style_layer -- tensor representing a scalar value, style cost defined above by equation (2) """ ### START CODE HERE ### # Retrieve dimensions from a_G (≈1 line) m, n_H, n_W, n_C = a_G.get_shape().as_list() # Reshape the images to have them of shape (n_C, n_H*n_W) (≈2 lines) a_S = tf.reshape(a_S, [n_H*n_W, n_C]) a_G = tf.reshape(a_G, [n_H*n_W, n_C]) # Computing gram_matrices for both images S and G (≈2 lines) GS = gram_matrix(tf.transpose(a_S)) GG = gram_matrix(tf.transpose(a_G)) # Computing the loss (≈1 line) J_style_layer = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(tf.subtract(GS, GG))) / (4*tf.square(tf.to_float(n_H*n_W*n_C))) ### END CODE HERE ### return J_style_layer
tf.reset_default_graph() with tf.Session() as test: tf.set_random_seed(1) a_S = tf.random_normal([1, 4, 4, 3], mean=1, stddev=4) a_G = tf.random_normal([1, 4, 4, 3], mean=1, stddev=4) J_style_layer = compute_layer_style_cost(a_S, a_G) print("J_style_layer = " + str(J_style_layer.eval()))
Result:
J_style_layer = 9.19028
5.2.3 - Style Weights
STYLE_LAYERS = [ ('conv1_1', 0.2), ('conv2_1', 0.2), ('conv3_1', 0.2), ('conv4_1', 0.2), ('conv5_1', 0.2)]
通过如下公式综合不同层的style costs:
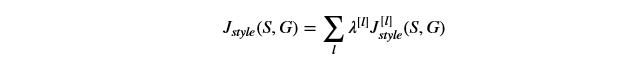
def compute_style_cost(model, STYLE_LAYERS): """ Computes the overall style cost from several chosen layers Arguments: model -- our tensorflow model STYLE_LAYERS -- A python list containing: - the names of the layers we would like to extract style from - a coefficient for each of them Returns: J_style -- tensor representing a scalar value, style cost defined above by equation (2) """ # initialize the overall style cost J_style = 0 for layer_name, coeff in STYLE_LAYERS: # Select the output tensor of the currently selected layer out = model[layer_name] # Set a_S to be the hidden layer activation from the layer we have selected, by running the session on out a_S = sess.run(out) # Set a_G to be the hidden layer activation from same layer. Here, a_G references model[layer_name] # and isn't evaluated yet. Later in the code, we'll assign the image G as the model input, so that # when we run the session, this will be the activations drawn from the appropriate layer, with G as input. a_G = out # Compute style_cost for the current layer J_style_layer = compute_layer_style_cost(a_S, a_G) # Add coeff * J_style_layer of this layer to overall style cost J_style += coeff * J_style_layer return J_style
5.3 - Defining the total cost to optimize
总的损失函数表示如下:
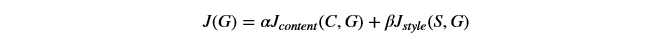
# GRADED FUNCTION: total_cost def total_cost(J_content, J_style, alpha = 10, beta = 40): """ Computes the total cost function Arguments: J_content -- content cost coded above J_style -- style cost coded above alpha -- hyperparameter weighting the importance of the content cost beta -- hyperparameter weighting the importance of the style cost Returns: J -- total cost as defined by the formula above. """ ### START CODE HERE ### (≈1 line) J = alpha * J_content + beta * J_style ### END CODE HERE ### return J
tf.reset_default_graph() with tf.Session() as test: np.random.seed(3) J_content = np.random.randn() J_style = np.random.randn() J = total_cost(J_content, J_style) print("J = " + str(J))
Result:
J = 35.34667875478276
6 - Solving the optimization problem
实现神经风格迁移需要实现以下内容:
- Create an Interactive Session
- Load the content image
- Load the style image
- Randomly initialize the image to be generated
- Load the VGG16 model
- Build the TensorFlow graph:
- Run the content image through the VGG16 model and compute the content cost
- Run the style image through the VGG16 model and compute the style cost
- Compute the total cost
- Define the optimizer and the learning rate
- Initialize the TensorFlow graph and run it for a large number of iterations, updating the generated image at every step.
# Reset the graph tf.reset_default_graph() # Start interactive session sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
# load, reshape, and normalize "content" image content_image = scipy.misc.imread("images/louvre_small.jpg") content_image = reshape_and_normalize_image(content_image)
# load, reshape, and normalize "style" image style_image = scipy.misc.imread("images/monet.jpg") style_image = reshape_and_normalize_image(style_image)
# initialize the "generated" Image as a noisy image created from the content_image generated_image = generate_noise_image(content_image) imshow(generated_image[0])
# load the VGG16 model model = load_vgg_model("pretrained-model/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat")
- Assign the content image to be the input to the VGG model.
- Set a_C to be the tensor giving the hidden layer activation for layer "conv4_2".
- Set a_G to be the tensor giving the hidden layer activation for the same layer.
- Compute the content cost using a_C and a_G.
# Assign the content image to be the input of the VGG model. sess.run(model['input'].assign(content_image)) # Select the output tensor of layer conv4_2 out = model['conv4_2'] # Set a_C to be the hidden layer activation from the layer we have selected a_C = sess.run(out) # Set a_G to be the hidden layer activation from same layer. Here, a_G references model['conv4_2'] # and isn't evaluated yet. Later in the code, we'll assign the image G as the model input, so that # when we run the session, this will be the activations drawn from the appropriate layer, with G as input. a_G = out # Compute the content cost J_content = compute_content_cost(a_C, a_G)
# Assign the input of the model to be the "style" image sess.run(model['input'].assign(style_image)) # Compute the style cost J_style = compute_style_cost(model, STYLE_LAYERS)
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line) J = total_cost(J_content, J_style, alpha=10, beta=40) ### END CODE HERE ###
# define optimizer (1 line) optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(2.0) # define train_step (1 line) train_step = optimizer.minimize(J)
def model_nn(sess, input_image, num_iterations = 200): # Initialize global variables (you need to run the session on the initializer) ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line) sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) ### END CODE HERE ### # Run the noisy input image (initial generated image) through the model. Use assign(). ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line) sess.run(model["input"].assign(input_image)) ### END CODE HERE ### for i in range(num_iterations): # Run the session on the train_step to minimize the total cost ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line) sess.run(train_step) ### END CODE HERE ### # Compute the generated image by running the session on the current model['input'] ### START CODE HERE ### (1 line) generated_image = sess.run(model["input"]) ### END CODE HERE ### # Print every 20 iteration. if i%20 == 0: Jt, Jc, Js = sess.run([J, J_content, J_style]) print("Iteration " + str(i) + " :") print("total cost = " + str(Jt)) print("content cost = " + str(Jc)) print("style cost = " + str(Js)) # save current generated image in the "/output" directory save_image("output/" + str(i) + ".png", generated_image) # save last generated image save_image('output/generated_image.jpg', generated_image) return generated_image
model_nn(sess, generated_image)
Result:
Iteration 0 :
total cost = 5.04752e+09
content cost = 7865.72
style cost = 1.26186e+08
Iteration 20 :
total cost = 9.44841e+08
content cost = 15236.9
style cost = 2.36172e+07
Iteration 40 :
total cost = 4.80354e+08
content cost = 16712.4
style cost = 1.20047e+07
Iteration 60 :
total cost = 3.10203e+08
content cost = 17443.6
style cost = 7.75072e+06
(略)
Result:




7 - Summary
- Neural Style Transfer is an algorithm that given a content image C and a style image S can generate an artistic image
- It uses representations (hidden layer activations) based on a pretrained ConvNet.
- The content cost function is computed using one hidden layer's activations.
- The style cost function for one layer is computed using the Gram matrix of that layer's activations. The overall style cost function is obtained using several hidden layers.
- Optimizing the total cost function results in synthesizing new images.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号