最小生成树MST
最小生成树(Minimum Spanning Trees)
Kruskal算法和Prim算法都是典型的贪心算法。
Kruskal
Kruskal算法的时间为:O(ElgE)。
➢ 如果再注意到|E|<|V|2,则有lg|E|=O(lgV ),所以Kruskal算法的时间可表示为O(ElgV)。
适合边数较少的情况。
//kruskal-->MST
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct Edge {
int src, dest, weight;
}Edge;
typedef struct Graph {
int V, E; //V: 总节点数 E: 总边数
Edge* edge;
}Graph;
Graph* createGraph(int V, int E) {
Graph* graph = new Graph;
graph->V = V;
graph->E = E;
graph->edge = new Edge[E];
return graph;
}
//union-find 并查集
typedef struct subset {
int parent;
int rank; //子树深度,合并时用
}subset;
int find(subset subsets[], int i) {
if (subsets[i].parent != i)
subsets[i].parent = find(subsets, subsets[i].parent);
return subsets[i].parent;
}
//合并 集合
void Union(subset subsets[], int x, int y) {
int xroot = find(subsets, x);
int yroot = find(subsets, y);
if (subsets[xroot].rank < subsets[yroot].rank)
subsets[xroot].parent = yroot;
else if (subsets[xroot].rank > subsets[yroot].rank)
subsets[yroot].parent = xroot;
else {
subsets[yroot].parent = xroot;
subsets[xroot].rank++;
}
}
int mycomp(const void* a, const void* b) {
// return ((Edge*)a)->weight > ((Edge*)b)->weight;
return (*(Edge*)a).weight > (*(Edge*)b).weight;
}
/*
*边排序-> 遍历-> 符合条件加入
*/
void KruskalMST(Graph* graph) {
int V = graph->V;
Edge* result = (Edge*)malloc(V * sizeof(Edge));
int e = 0;
int i = 0;
qsort(graph->edge, graph->E, sizeof(graph->edge[0]), mycomp);
subset* subsets = (subset*)malloc(V * sizeof(subset));
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { //初始化V个并查集
subsets[v].parent = v;
subsets[v].rank = 0;
}
/*-------核心代码--------*/
while (e < V - 1 && i < graph->E) { //V个点,V-1条边
Edge minEdge = graph->edge[i++];
int x = find(subsets, minEdge.src);
int y = find(subsets, minEdge.dest);
if (x != y) {
result[e++] = minEdge;
Union(subsets, x, y);
}
}
/*--------------------*/
printf("edges in MST:\n");
int minCost = 0;
for (i = 0; i < e; i++) {
printf("%d ------ %d == %d\n", result[i].src, result[i].dest, result[i].weight);
minCost += result[i].weight;
}
printf("minCost: %d\n", minCost);
return;
}
int main() {
//煮个栗子
int V = 4;
int E = 5;
Graph* graph = createGraph(V, E);
graph->edge[0].src = 0;
graph->edge[0].dest = 1;
graph->edge[0].weight = 10;
graph->edge[1].src = 0;
graph->edge[1].dest = 2;
graph->edge[1].weight = 6;
graph->edge[2].src = 0;
graph->edge[2].dest = 3;
graph->edge[2].weight = 5;
graph->edge[3].src = 1;
graph->edge[3].dest = 3;
graph->edge[3].weight = 15;
graph->edge[4].src = 2;
graph->edge[4].dest = 3;
graph->edge[4].weight = 4;
KruskalMST(graph);
return 0;
}
切割
无向图G=(V,E)的一个切割(S,V-S)是集合V的一个划分。
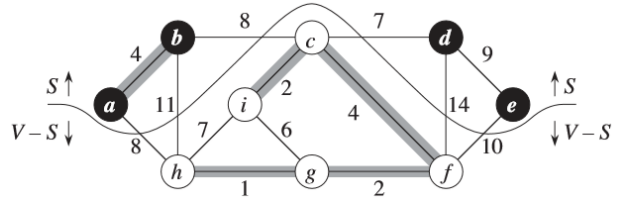
横跨切割
如果一条边(u,v)∈E的一个端点在集合S中,另一个端点在集合V-S中,则称该条边横跨切割(S,V-S)。
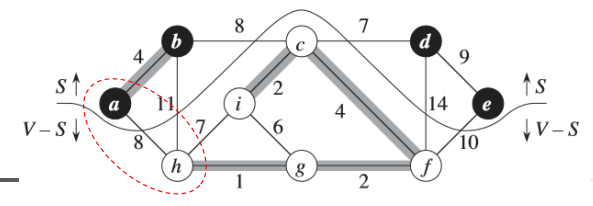
尊 重
如果边集A中不存在横跨该切割的边,则称该切割尊 重集合A。
轻量级边
在横跨一个切割的所有边中,权重最小的边称为轻量级边。
➢ 轻量级边可能不是唯一的。
➢ 一般,如果一条边是满足某个性质的所有边中权重最小的,则称该边是满足给定性质的一条轻量级边


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号