1、制作一个如图所示的界面(使用FlowLayout布局),不要求实现功能。
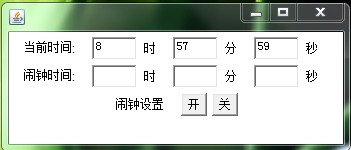
package experiment; import java.awt.FlowLayout; import javax.swing.*; public class MyFrame { JFrame f; JButton b1,b2; JLabel l1,l2,l3,l5,l4,l6,l7,l8,l9; JPanel p; JTextField t1,t2,t3,t4,t5,t6; public MyFrame(){ f=new JFrame("闹钟"); l1 = new JLabel("当前时间:"); l2 = new JLabel("时"); l3 = new JLabel("分"); l4 = new JLabel("秒"); l5 = new JLabel("闹钟时间:"); l6 = new JLabel("时"); l7 = new JLabel("分"); l8 = new JLabel("秒"); l9 = new JLabel("闹钟设置"); p = new JPanel(); t1 = new JTextField(7); t2 = new JTextField(7); t3 = new JTextField(7); t4 = new JTextField(7); t5 = new JTextField(7); t6 = new JTextField(7); b1= new JButton("开"); b2= new JButton("关"); setLayout(new FlowLayout(2,8,8)); p.add(l1); p.add(t1); p.add(l2); p.add(t2); p.add(l3); p.add(t3); p.add(l4); p.add(l5); p.add(t4); p.add(l6); p.add(t5); p.add(l7); p.add(t6); p.add(l8); p.add(l9); p.add(b1); p.add(b2); f.add(p); f.setSize(430,200); f.setVisible(true); } private void setLayout(FlowLayout flowLayout) { } public static void main(String[] args) { new MyFrame(); } }
2、设计一个用标签、文本行与按钮来登录的界面(用GridLayout布局方式)。如图所示。
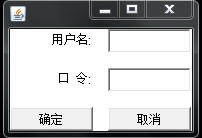
//流布局 package experiment; import java.awt.Color; import javax.swing.*; public class MyFrame1 { JFrame f; JButton b1,b2; JLabel l1,l2; JPanel p; JTextField t1,t2; public MyFrame1(){ f=new JFrame("登录"); l1 = new JLabel("用户名:"); l2 = new JLabel("口令:"); p = new JPanel(); t1 = new JTextField(); t2 = new JTextField(); b1= new JButton("确定"); b2= new JButton("取消"); p.setLayout( null ); b1.setBounds(10,200,155,50); b2.setBounds(200,200,155,50); l1.setBounds(75, 80, 80, 30); l2.setBounds(80, 140, 80, 30); t1.setBounds(160,82,200,28); t2.setBounds(160,140,200,28); p.add(t1); p.add(t2); f.add(p); p.add(b1); p.add(b2); p.add(l1); p.add(l2); p.setBackground(new Color(210,180,140)); f.setSize(380,300); f.setLocation(700,400); f.setVisible(true); } public static void main(String[] args) { new MyFrame1(); } }
1、设计一个如图所示的界面,不需要提供组件的功能。
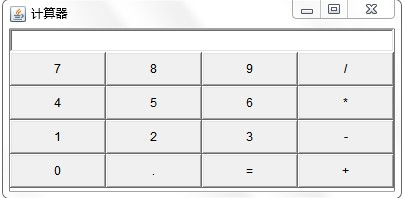
package experiment; import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.GridLayout; public class counter { JFrame f; JButton[] b; JTextField t; JPanel p; GridLayout g; String title[]= {"7","8","9","/","4","5","6","*","1","2","3","-","0",".","=","+"}; public counter() { f=new JFrame("计算器"); p = new JPanel(); t = new JTextField(); b= new JButton[title.length]; g = new GridLayout(4,4); p.setLayout(g); for(int i=0;i < title.length;i++) { b[i]= new JButton(title[i]); p.add(b[i]); } f.add(t,BorderLayout.NORTH); f.add(p,BorderLayout.CENTER); f.setVisible(true); f.setSize(400,300); } public static void main(String[] args) { new counter(); } }
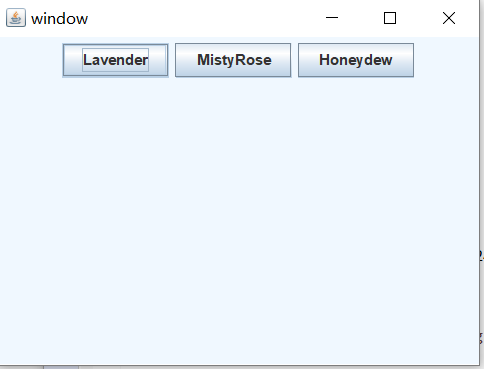
2、编写可改变背景颜色的窗口。
import java.awt.Color; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JPanel; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { JFrame frame = new JFrame(); final JPanel panel = new JPanel(); frame.setSize(300, 200); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); final JButton redButton = new JButton("Red"); final JButton greenButton = new JButton("Green"); final JButton blueButton = new JButton("Blue"); class Listener extends JPanel implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { Color color; if (event.getSource() == redButton) { color = Color.red; redButton.setBackground(color); panel.setBackground(color); } else if (event.getSource() == greenButton) { color = Color.green; greenButton.setBackground(color); panel.setBackground(color); } else { color = Color.blue; blueButton.setBackground(color); panel.setBackground(color); } setBackground(color); repaint(); } } redButton.addActionListener(new Listener()); greenButton.addActionListener(new Listener()); blueButton.addActionListener(new Listener()); panel.add(redButton); panel.add(greenButton); panel.add(blueButton); frame.add(panel); frame.setVisible(true); } }
package experiment; import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.Color; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; public class color implements ActionListener { JFrame f; JPanel p; JButton b1,b2,b3; public color() { f=new JFrame("window"); p = new JPanel(); b1= new JButton("Lavender"); b2= new JButton("MistyRose"); b3= new JButton("Honeydew"); b1.addActionListener(this); b2.addActionListener(this); b3.addActionListener(this); f.add(p); p.add(b1); p.add(b2); p.add(b3); p.setBackground(new Color(240,248,255)); f.setSize(400,300); f.setVisible(true); } public static void main(String[] args) { new color(); } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { if(e.getSource()==b1) p.setBackground(new Color(230,230,250)); else if(e.getSource()==b2) p.setBackground(new Color(255,228,225)); else if(e.getSource()==b3) p.setBackground(new Color(240,255,240)); } }