对比全分解和先验分解
单线的
def forward(self, x):
y = self.g_a(x)
y_hat, y_likelihoods = self.entropy_bottleneck(y)
x_hat = self.g_s(y_hat)
return {
"x_hat": x_hat,
"likelihoods": {
"y": y_likelihoods,
},
}
@classmethod
def from_state_dict(cls, state_dict):
"""Return a new model instance from `state_dict`."""
N = state_dict["g_a.0.weight"].size(0)
M = state_dict["g_a.6.weight"].size(0)
net = cls(N, M)
net.load_state_dict(state_dict)
return net
def compress(self, x):
y = self.g_a(x)
y_strings = self.entropy_bottleneck.compress(y)
return {"strings": [y_strings], "shape": y.size()[-2:]}
def decompress(self, strings, shape):
assert isinstance(strings, list) and len(strings) == 1
y_hat = self.entropy_bottleneck.decompress(strings[0], shape)
x_hat = self.g_s(y_hat).clamp_(0, 1)
return {"x_hat": x_hat}
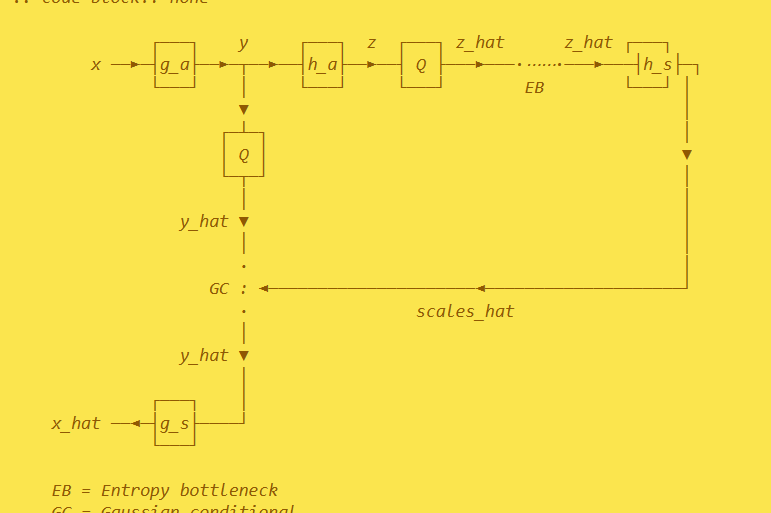
def forward(self, x):
y = self.g_a(x)
z = self.h_a(torch.abs(y))
z_hat, z_likelihoods = self.entropy_bottleneck(z)
scales_hat = self.h_s(z_hat)
y_hat, y_likelihoods = self.gaussian_conditional(y, scales_hat)
x_hat = self.g_s(y_hat)
return {
"x_hat": x_hat,
"likelihoods": {"y": y_likelihoods, "z": z_likelihoods},
}
@classmethod
def from_state_dict(cls, state_dict):
"""Return a new model instance from `state_dict`."""
N = state_dict["g_a.0.weight"].size(0)
M = state_dict["g_a.6.weight"].size(0)
net = cls(N, M)
net.load_state_dict(state_dict)
return net
def compress(self, x):
y = self.g_a(x)
z = self.h_a(torch.abs(y))
z_strings = self.entropy_bottleneck.compress(z)
z_hat = self.entropy_bottleneck.decompress(z_strings, z.size()[-2:])
scales_hat = self.h_s(z_hat)
indexes = self.gaussian_conditional.build_indexes(scales_hat)
y_strings = self.gaussian_conditional.compress(y, indexes)
return {"strings": [y_strings, z_strings], "shape": z.size()[-2:]}
def decompress(self, strings, shape):
assert isinstance(strings, list) and len(strings) == 2
z_hat = self.entropy_bottleneck.decompress(strings[1], shape)
scales_hat = self.h_s(z_hat)
indexes = self.gaussian_conditional.build_indexes(scales_hat)
y_hat = self.gaussian_conditional.decompress(strings[0], indexes, z_hat.dtype)
x_hat = self.g_s(y_hat).clamp_(0, 1)
return {"x_hat": x_hat}
其区别为:



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 如何调用 DeepSeek 的自然语言处理 API 接口并集成到在线客服系统
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 2025年我用 Compose 写了一个 Todo App