TMS320F28335利用ePWM改变ADC采样频率(双通道)示例代码
2020-05-31 17:41:09
TMS320F28335 想实现设定ADC采样频率,通过设置 ADC_CKPS 和 ADC_SHCLK 分频系数是可以在一定范围内改变ADC采样频率的,但是只调节分频系数时,ADC采样频率最低只能到十几KHz: 28335 ADC 对100Hz方波采样,于是问题变得复杂了一些。
参考了有相同需求的帖子:28335的ADC采样频率如何设置? 、DSP28335中如何设置ADC采样的频率?
得出结论:若想把ADC采样频率降低到一定水平(如1000Hz、2000Hz等),仅改变ADC分频系数是不够的,还需利用ePWM来生成ADC的启停信号,使其作为ADC的开关,释放启停信号来控制ADC,进而改变ADC的采样频率可调,而ePWM的频率就是ADC启停频率,
于是我们现在关心ePWM的频率/周期设置:
ePWM的寄存器主要有7个,我们这里重点关注:时基周期寄存器TBPRD和时基计数器模式:

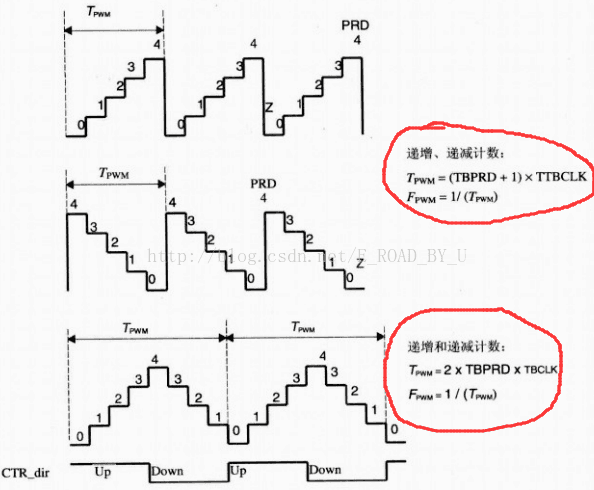
于是,决定Tpwm的变量有计算公式、TBPRD和TBCLK:
(1).计算公式:不同计数模式的计算公式不同,从图中看出:
在增减计数模式下,Tpwm = (TBPRD+1) x TBCLK ;
在递增和递减计数模式下,Tpwm = 2 x TBPRD x TBCLK ;
(2).TBCLK = SYSCLKOUT / ( (2*HSPCLKDIV) * (2^CLKDIV) );
TBCLK由 SYSCLKOUT、HSPCLKDIV和CLKDIV决定,这里28335的SYSCLKOUT默认150MHz,查表后得知:代码中 CLKDIV = n ,公式中变为:CLKDIV = 2^n ;在程序中 HSPCLKDIV = n,公式中 HSPCLKDIV = 2n ;
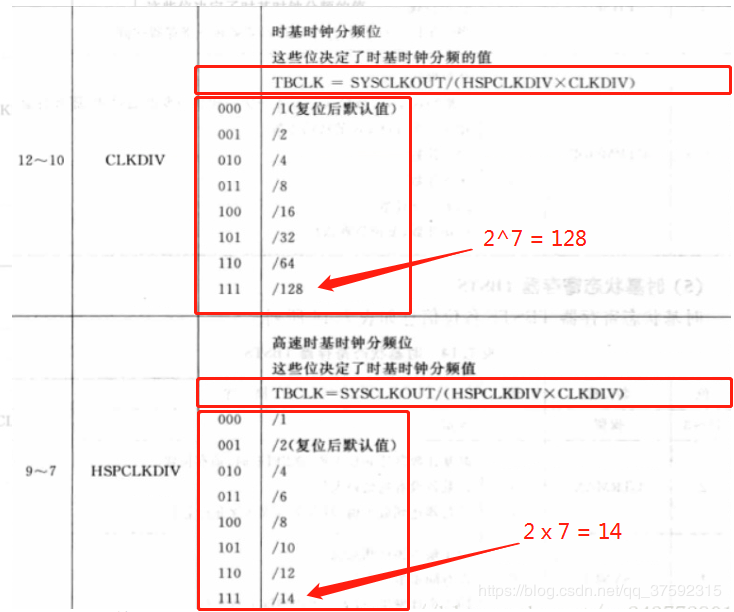
(3).TBPRD:按照公式(不同计数模式的Tpwm公式不同)计算得出数,手动填入,例如要把PWM的频率、(即ADC的采样频率)设置为2000Hz:
1 // Set Period for EPWM1 2 // up-and-down count mode: 3 // Tpwm = 2*(1/TBCLK)*TBPRD; 4 5 // up-count mode or down-count mode:( use this mode here ) 6 // Tpwm = (1/TBCLK)*(1+TBPRD); 7 EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = (12500-1); // max = 65536 8 // Setup T(PWM1)=(1/TBCLK)*(1+TBPRD)=(1/25000000)*(1+12500-1)=0.0005s ,F(PWM1) = 1/T(PWM1) = 1/0.0005s = 2000Hz
完整的可用ADC.c代码如下:
1 #include "DSP2833x_Device.h" // DSP2833x Headerfile Include File 2 #include "DSP2833x_Examples.h" // DSP2833x Examples Include File 3 #include "math.h" 4 #include "DSP2833x_Project.h" 5 #include "DSP2833x_EPwm.h" 6 #include "DSP2833x_EPwm_defines.h" 7 // lower sample rate to 2KHz using ePWM interrupt 8 // as well as turn on 2 channels 9 10 // Determine when the shift to right justify the data takes place 11 // Only one of these should be defined as 1. 12 // The other two should be defined as 0. 13 #define POST_SHIFT 0 // Shift results after the entire sample table is full 14 #define INLINE_SHIFT 1 // Shift results as the data is taken from the results regsiter 15 #define NO_SHIFT 0 // Do not shift the results 16 17 #define BUF_SIZE 512 // Sample buffer size 18 19 // Prototype statements for functions found within this file. 20 interrupt void adc_isr(void); 21 22 // Global variables used in this example: 23 Uint16 LoopCount_1; 24 Uint16 LoopCount_2; 25 Uint16 ConversionCount; 26 27 Uint16 SampleTable_1[BUF_SIZE]={0}; 28 Uint16 SampleTable_2[BUF_SIZE]={0}; 29 30 31 main() 32 { 33 34 // Initialize System Control: 35 // PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks 36 // This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file. 37 InitSysCtrl(); 38 39 EALLOW; 40 #if (CPU_FRQ_150MHZ) // Default - 150 MHz SYSCLKOUT 41 #define ADC_MODCLK 0x3 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 150/(2*3) = 25.0 MHz 42 #endif 43 #if (CPU_FRQ_100MHZ) 44 #define ADC_MODCLK 0x2 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 100/(2*2) = 25.0 MHz 45 #endif 46 EDIS; 47 // Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table: 48 // Disable CPU interrupts 49 DINT; 50 51 // Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state. 52 // The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags are cleared. 53 // This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file. 54 InitPieCtrl(); 55 56 EALLOW; 57 SysCtrlRegs.HISPCP.all = ADC_MODCLK; // set ADC CLOCK ,HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/ADC_MODCLK 58 EDIS; 59 60 // Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags: 61 IER = 0x0000; 62 IFR = 0x0000; 63 64 // Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt 65 // Service Routines (ISR). 66 // This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt 67 // is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes. 68 // The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c. 69 // This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c. 70 InitPieVectTable(); 71 72 // Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to 73 // ISR functions found within this file. 74 EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected register 75 PieVectTable.ADCINT = &adc_isr; 76 EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers 77 78 InitAdc(); // For this example, init the ADC 79 80 // Enable ADCINT in PIE 81 PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER1.bit.INTx6 = 1; 82 IER |= M_INT1; // Enable CPU Interrupt 1 83 EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM 84 ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM 85 86 LoopCount_1 = 0; 87 LoopCount_2 = 0; 88 ConversionCount = 0; 89 90 // Configure ADC 91 ///////////////////////设置最大通道数:2///////////////////////////// 92 AdcRegs.ADCMAXCONV.all = 0x0001; // Setup 2 conv's on SEQ1 93 AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV00 = 0x0; // Setup ADCINA3 as 1st SEQ1 conv. 94 AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV01 = 0x1; // Setup ADCINA2 as 2nd SEQ1 conv. 95 ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 96 AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.EPWM_SOCA_SEQ1 = 1; // Enable SOCA from ePWM to start SEQ1 97 AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.INT_ENA_SEQ1 = 1; // Enable SEQ1 interrupt (every EOS) 98 99 // Assumes ePWM1 clock is already enabled in InitSysCtrl(); 100 EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCAEN = 1; // Enable SOC on A group 101 EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCASEL = 4; // Select SOC from from CPMA on upcount 102 EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.SOCAPRD = 1; // Generate pulse on 1st event 103 EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value 104 EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = 0; // 0 -- count up and start 105 106 ///////////////配置ePWM中断频率,即设置ADC采样频率//////////////// 107 // High Speed Time-base Clock Prescale Bits,These bits determine part of the time-base clock prescale 108 // SYSCLKOUT = 150MHz 109 // TBCLK = SYSCLKOUT / ( (2*HSPCLKDIV) * (2^CLKDIV) )=150MHz/(2*3*1)=25MHz 110 EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.HSPCLKDIV =0x03; 111 EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CLKDIV = 0x00; 112 113 // Set Period for EPWM1 114 // up-and-down count mode: 115 // Tpwm = 2*(1/TBCLK)*TBPRD; 116 117 // up-count mode or down-count mode:( use this mode here ) 118 // Tpwm = (1/TBCLK)*(1+TBPRD); 119 EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = (12500-1); // max = 65536 120 // Setup T(PWM1)=(1/TBCLK)*(1+TBPRD)=(1/25000000)*(1+12500-1)=0.0005s ,F(PWM1) = 1/T(PWM1) = 1/0.0005s = 2000Hz 121 ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 122 123 // Wait for ADC interrupt 124 while(1) 125 { 126 LoopCount_1++; 127 } 128 129 } 130 131 132 interrupt void adc_isr(void) 133 { 134 LoopCount_2++; 135 if(LoopCount_2 == 10000) 136 { 137 LoopCount_2 = 0; 138 } 139 SampleTable_1[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 >>4; 140 SampleTable_2[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT1 >>4; 141 142 // If BUF_SIZE(512) conversions have been logged, start over 143 if(ConversionCount == BUF_SIZE) 144 { 145 ConversionCount = 0; 146 } 147 else ConversionCount++; 148 149 // Reinitialize for next ADC sequence 150 AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.RST_SEQ1 = 1; // Reset SEQ1 151 AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1_CLR = 1; // Clear INT SEQ1 bit 152 PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP1; // Acknowledge interrupt to PIE 153 154 return; 155 }
参考:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号