缓冲流的使用:BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream、BufferedReader、BufferedWriter
处理流之一 :缓冲流
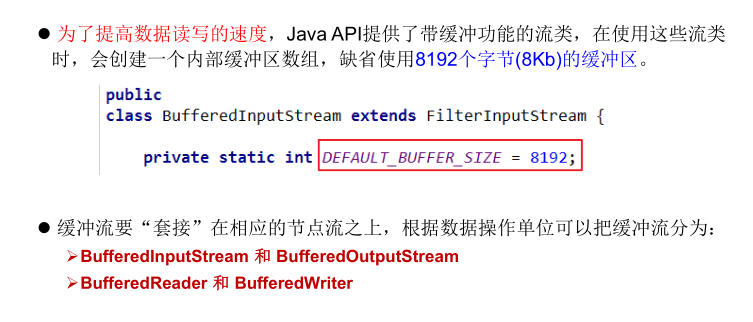
当读取数据时,数据按块读入缓冲区,其后的读操作则直接访问缓冲区
当使用BufferedInputStream读取字节文件时,BufferedInputStream会一次性从
文件中读取8192个(8Kb),存在缓冲区中,直到缓冲区装满了,才重新从文件中
读取下一个8192个字节数组。
向流中写入字节时,不会直接写到文件,先写到缓冲区中直到缓冲区写满,
BufferedOutputStream才会把缓冲区中的数据一次性写到文件里。使用方法
flush()可以强制将缓冲区的内容全部写入输出流
关闭流的顺序和打开流的顺序相反。只要关闭最外层流即可,关闭最外层流也
会相应关闭内层节点流
flush()方法的使用:手动将buffer中内容写入文件
如果是带缓冲区的流对象的close()方法,不但会关闭流,还会在关闭流之前刷
新缓冲区,关闭后不能再写出



/**
* 处理流之一:缓冲流的使用
*
* 1.缓冲流:
* BufferedInputStream
* BufferedOutputStream
* BufferedReader
* BufferedWriter
*
* 2.作用:提供流的读取、写入的速度
* 提高读写速度的原因:内部提供了一个缓冲区
*
* 3. 处理流,就是“套接”在已有的流的基础上。
*
* @author CH
* @create 2021 下午 2:44
*/
/* 实现非文本文件的复制 */ @Test public void BufferedStreamTest() throws FileNotFoundException { BufferedInputStream bis = null; BufferedOutputStream bos = null; try { //1.造文件 File srcFile = new File("爱情与友情.jpg"); File destFile = new File("爱情与友情3.jpg"); //2.造流 //2.1 造节点流 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream((srcFile)); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); //2.2 造缓冲流 bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); //3.复制的细节:读取、写入 byte[] buffer = new byte[10]; int len; while((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1){ bos.write(buffer,0,len); // bos.flush();//刷新缓冲区 } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //4.资源关闭 //要求:先关闭外层的流,再关闭内层的流 if(bos != null){ try { bos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(bis != null){ try { bis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //说明:关闭外层流的同时,内层流也会自动的进行关闭。关于内层流的关闭,我们可以省略. // fos.close(); // fis.close(); } }
//实现文件复制的方法 public void copyFileWithBuffered(String srcPath,String destPath){ BufferedInputStream bis = null; BufferedOutputStream bos = null; try { //1.造文件 File srcFile = new File(srcPath); File destFile = new File(destPath); //2.造流 //2.1 造节点流 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream((srcFile)); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); //2.2 造缓冲流 bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); //3.复制的细节:读取、写入 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; int len; while((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1){ bos.write(buffer,0,len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //4.资源关闭 //要求:先关闭外层的流,再关闭内层的流 if(bos != null){ try { bos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(bis != null){ try { bis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //说明:关闭外层流的同时,内层流也会自动的进行关闭。关于内层流的关闭,我们可以省略. // fos.close(); // fis.close(); } } @Test public void testCopyFileWithBuffered(){ long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); String srcPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\01-视频.avi"; String destPath = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\03-视频.avi"; copyFileWithBuffered(srcPath,destPath); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("复制操作花费的时间为:" + (end - start));//618 - 176 }
![]()
/* 使用BufferedReader和BufferedWriter实现文本文件的复制 */ @Test public void testBufferedReaderBufferedWriter(){ BufferedReader br = null; BufferedWriter bw = null; try { //创建文件和相应的流 br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File("dbcp.txt"))); bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(new File("dbcp1.txt"))); //读写操作 //方式一:使用char[]数组 // char[] cbuf = new char[1024]; // int len; // while((len = br.read(cbuf)) != -1){ // bw.write(cbuf,0,len); // // bw.flush(); // } //方式二:使用String String data; while((data = br.readLine()) != null){ //方法一: // bw.write(data + "\n");//data中不包含换行符 //方法二: bw.write(data);//data中不包含换行符 bw.newLine();//提供换行的操作 } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //关闭资源 if(bw != null){ try { bw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(br != null){ try { br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
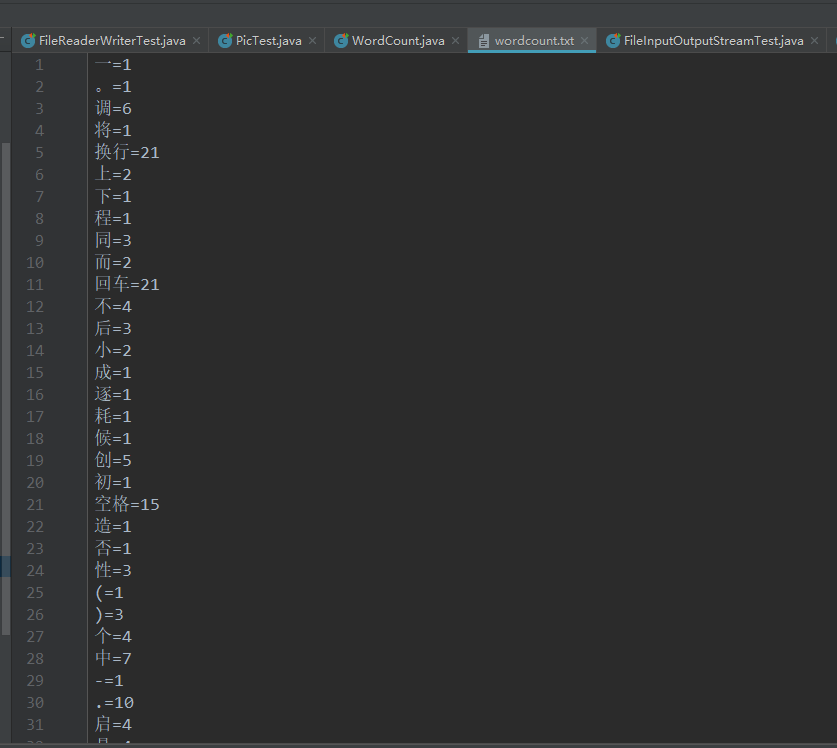
练习3:获取文本上字符出现的次数,把数据写入文件
package com.atguigu.exer; import org.junit.Test; import java.io.*; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; /** * 练习3:获取文本上字符出现的次数,把数据写入文件 * * 思路: * 1.遍历文本每一个字符 * 2.字符出现的次数存在Map中 * * Map<Character,Integer> map = new HashMap<Character,Integer>(); * map.put('a',18); * map.put('你',2); * * 3.把map中的数据写入文件 * * @author CH * @create 2021 下午 3:47 */ public class WordCount { /* 说明:如果使用单元测试,文件相对路径为当前module 如果使用main()测试,文件相对路径为当前工程 */ @Test public void testWordCount() { FileReader fr = null; BufferedWriter bw = null; try { //1.创建Map集合 Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<Character, Integer>(); //2.遍历每一个字符,每一个字符出现的次数放到map中 fr = new FileReader("dbcp.txt"); int c = 0; while ((c = fr.read()) != -1) { //int 还原 char char ch = (char) c; // 判断char是否在map中第一次出现 if (map.get(ch) == null) { map.put(ch, 1); } else { map.put(ch, map.get(ch) + 1); } } //3.把map中数据存在文件count.txt //3.1 创建Writer bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("wordcount.txt")); //3.2 遍历map,再写入数据 Set<Map.Entry<Character, Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry<Character, Integer> entry : entrySet) { switch (entry.getKey()) { case ' ': bw.write("空格=" + entry.getValue()); break; case '\t'://\t表示tab 键字符 bw.write("tab键=" + entry.getValue()); break; case '\r':// bw.write("回车=" + entry.getValue()); break; case '\n':// bw.write("换行=" + entry.getValue()); break; default: bw.write(entry.getKey() + "=" + entry.getValue()); break; } bw.newLine(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //4.关流 if (fr != null) { try { fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (bw != null) { try { bw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
不积跬步,无以至千里;不积小流,无以成江海。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号