高级搜索题集
题集转自以下链接:
https://blog.csdn.net/shahdza/article/details/7986044
胜利大逃亡(续) HDU - 1429
题意:就是二维地图,有障碍;重点有门,和钥匙(用于开门)。
理解:因为找钥匙,这个解答路径可能会走回头路。
思路:第一遍,因为有时间限制,并且20*20;所以简单bfs,然后MLimit了。感觉就是重复存储点在队列。
那么难点就在于判重了。因为走回头路,简单二维判重肯定不行。
回想和之前炮台那题,因为子弹的原因也是走回头路,所以判重数组多加了一个时间维度。
这题关键因素是钥匙,所以加一个钥匙拥有状态的判重,就ac了。(用2进制状态压缩,这里因为a-j,所以数组开个1024就够了。)

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <queue> using namespace std; int n,m,t; char ditu[21][21]; bool vis[1025][21][21]; int Sx,Sy,Fx,Fy; int xx[] = {0,0,1,-1}; int yy[] = {1,-1,0,0}; struct node{ int x,y,step,k=0; node(int a,int b,int c,int d):x(a),y(b),step(c),k(d) {}; }; bool bfs(){ memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); queue<node> q;q.push(node(Sx,Sy,0,0));vis[0][Sx][Sy] = true; while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.front();q.pop(); for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x = p.x+xx[i],y = p.y+yy[i]; if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||ditu[x][y]=='*'||p.step+1>=t) continue; int step = p.step + 1,k = p.k; if(ditu[x][y]>='A'&&ditu[x][y]<='Z'&&!(p.k&(1<<ditu[x][y]-'A'))) continue; if(ditu[x][y] == '^') {cout<<step<<endl;return true;} if(ditu[x][y]>='a'&&ditu[x][y]<='z') k |= 1<<(ditu[x][y]-'a'); if(vis[k][x][y]) continue; q.push(node(x,y,step,k));vis[k][x][y] = true; } } return false; } int main() { while(cin>>n>>m>>t){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++)for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ char ch = getchar();while(ch==' '||ch=='\n') ch = getchar(); ditu[i][j] = ch; if(ch=='^') Fx = i,Fy = j; else if(ch=='@') Sx = i,Sy = j; } if(!bfs()) puts("-1"); } return 0; }
这题给我启发就是,判重作用在于剪枝,避免重复的入队操作。那么关键在于什么?关键在于点状态更新,并且取决于什么要素关键,炮台那题,因为子弹原因,时间是关键。这题因为门的原因,钥匙是关键。所以添加关键要素的判重数组是解题关键。
Key Task HDU - 1885
题意与上题一样。但是地图大小和钥匙,门出口数量不同。

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <queue> #include <map> using namespace std; int n,m; char ditu[101][101]; bool vis[17][101][101]; int Sx,Sy,Fx,Fy; int xx[] = {0,0,1,-1}; int yy[] = {1,-1,0,0}; struct node{ int x,y,step,k=0; node(int a,int b,int c,int d):x(a),y(b),step(c),k(d) {}; }; int mp[5]; bool bfs(){ memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); queue<node> q;q.push(node(Sx,Sy,0,0));vis[0][Sx][Sy] = true; while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.front();q.pop(); for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x = p.x+xx[i],y = p.y+yy[i]; if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||ditu[x][y]=='#') continue; int step = p.step + 1,k = p.k; if(ditu[x][y] == 'X') {cout<<"Escape possible in "<<step<<" steps."<<endl;return true;} if(ditu[x][y]>='A'&&ditu[x][y]<='Z'&&!(p.k&(1<<mp[ditu[x][y]-'A']))) continue; if(ditu[x][y]>='a'&&ditu[x][y]<='z') k |= 1<<mp[ditu[x][y]-'a']; if(vis[k][x][y]) continue; q.push(node(x,y,step,k));vis[k][x][y] = true; } } return false; } int main() { mp['B'-'A'] = 0,mp['Y'-'A'] = 1,mp['R'-'A'] = 2,mp['G'-'A'] = 3; while(cin>>n>>m&&n&&m){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++)for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ char ch = getchar();while(ch==' '||ch=='\n') ch = getchar(); ditu[i][j] = ch; if(ch=='X') Fx = i,Fy = j; else if(ch=='*') Sx = i,Sy = j; } if(!bfs()) puts("The poor student is trapped!"); } return 0; }
扩展思考:我这里想到如果钥匙并非永久产品而是一次性,那该怎么办?
我感觉难点可能在于不止走一次回头路。
我一开始能想到就是:像多重背包操作一样,将问题转化为0-1,多个相同门和钥匙,对应将他们分类成不同颜色。额,好像不行,因为你不清楚那个钥匙对应哪个门即为最优。。。。
那判重函数多加一维度,有什么颜色钥匙,并且多一个钥匙数量的维度。
超级密码HDU - 1226
算法:BFS
思路:BFS向下操作,*进制数+构成数 然后 对N求余 得到 的余数,因为是要正整数倍,所以当余数为0则为答案。
K1%N = K2%N;(K1*C+M)%N = (K2*C+M)%N ;所以余数可以作为判重点。相同余数不需要重复入队。
用数组记录答案长度,因为BFS是有层次性,所以超过500就可以判负了。

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <queue> #include <map> using namespace std; int N,C,M; int yS[17],ySlen; int vis[5005],pre[5005],ans[5005],cnt[5005]; void init(){ memset(vis,0,sizeof vis); memset(cnt,0,sizeof cnt); memset(pre,-1,sizeof pre); scanf("%d%d%d",&N,&C,&M); for(int i=0;i<M;i++){ char ch = getchar();while(ch == ' '|| ch == '\n') ch = getchar(); if(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') yS[i] = ch - '0'; else yS[i] = ch - 'A' + 10; } sort(yS,yS+M); ySlen = unique(yS,yS+M) - yS; } void showAns(int num){ if(num == -1) return ; showAns(pre[num]); if(ans[num]<10) printf("%d",ans[num]); else printf("%c",ans[num] - 10 + 'A'); } bool solve(){ queue<int> q; for(int i=0;i<ySlen;i++){ if(!yS[i]) continue; int tnt = yS[i] % N; if(vis[tnt]) continue; vis[tnt] = 1;cnt[tnt] = 1; ans[tnt] = yS[i]; if(!tnt) return true; q.push(tnt); } while(!q.empty()){ int now = q.front();q.pop(); if(cnt[now]>500) return false; for(int i=0;i<ySlen;i++){ int tnt = (now*C + yS[i]) % N; if(vis[tnt]) continue; vis[tnt] = 1;cnt[tnt] = cnt[now] + 1; ans[tnt] = yS[i];pre[tnt] = now; if(!tnt) return true; q.push(tnt); } } return false; } int main() { int _;scanf("%d",&_); while(_--){ init(); if(!N) {if(!yS[0]) puts("0");else puts("give me the bomb please");} else{ if(!solve()) puts("give me the bomb please"); else showAns(0),puts(""); } } return 0; }
Different DigitsHDU - 1664
算法:数论+BFS
思路:感觉这题集出得挺不错,每道题总与上一道题有关联。这一题和上一题一样,也是求N的正整数倍。所以也是余数下手。
但是这题巧妙在于,最优解是,答案需尽量少不同数字构成且最小。
这里牵扯的数论就是:

很好理解:求10进制的余数,(*10+1)MOD,因为只加一个数字的求余存在一个循环,存在0则为答案。余数相同,就互减得到答案,互减将余数减掉就是N的整数倍了。
所以一个整数一定存在一个正整数倍的数,且由0和1的数构成。
所以,两不同数字就构成本题答案;
那么这题剩下就是求一个最优最小解,即不同数字的数量相同求最小。
分两层,第一层只用一个数叠加求,得到答案就是最优。得不到去第二层,循环从不同两个数字组合求出答案。

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <queue> #include <map> using namespace std; const int inf = 2e9; int N,ansLen; bool vis[65536]; string ans,res; bool gO(int x){ memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); int tmp = 0;res = ""; while(1){ tmp = (tmp*10+x) % N; if(vis[tmp]) return false; vis[tmp] = true; res += '0' + x; if(!tmp){ if(ansLen == inf||ans.length()>res.length()){ ans = res;ansLen = res.length();return true; } return false; } } } int val[65536],pre[65536],cnt[65536]; void getAns(int x){ if(x==-1) return ; getAns(pre[x]); res += '0' + val[x]; } bool gT(int x,int y){ memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); memset(pre,-1,sizeof pre); memset(cnt,0,sizeof cnt); queue<int> q; int fk,num[2]={x,y}; if(x) { fk = x%N;vis[fk] = true,val[fk] = x,cnt[fk] = 1;q.push(fk); } fk = y%N; if(!vis[fk]) {vis[fk] = true,val[fk] = y,cnt[fk] = 1;q.push(fk);} while(!q.empty()){ int now = q.front();q.pop(); if(cnt[now]>ansLen) return false; for(int i=0;i<2;i++){ fk = (now*10 + num[i]) % N; if(vis[fk]) continue; vis[fk] = true,val[fk] = num[i],cnt[fk] = cnt[now] + 1,pre[fk] = now; if(!fk){ res = "";getAns(0); if(ansLen==inf||ans.length()>res.length()||(ans.length()==res.length()&&res<ans)){ ans = res;ansLen = res.length(); return true; } return false; } q.push(fk); } } return false; } int main() { while(cin>>N&&N){ int flag = 0; ansLen = inf;ans = ""; for(int i=1;i<10;i++) if(gO(i)) flag = 1; if(flag) {cout<<ans<<endl;continue;} for(int i=0;i<10;i++) for(int j=i+1;j<10;j++) gT(i,j); cout<<ans<<endl; } return 0; }
Pusher HDU - 2821
算法:枚举+dfs(简单模拟)
题意:类似手机游戏,一副25*25的地图,有多个障碍物,障碍物由字母表示,a为一方块,b为内嵌的2方块,以此类推。
球体,要选取一个地方起步(这里我用全地图枚举),进行弹射必须有一个空格当空隙。
起步后,方向不变,直到撞到方块才停下,且推方块向后一步,方块数减一,剩余方块积累到后一步。后一步如果是地图外,则起步方块消失。
如果球飞出地图,则失败。

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <queue> #include <map> using namespace std; int n,m; int ditu[26][26],sum; int xx[4] = {0,0,1,-1}; int yy[4] = {1,-1,0,0}; char dire[5] = "RLDU"; int len; char ans[2500]; void init(){ sum = 0,len=0; memset(ditu,0,sizeof ditu); for(int i=0;i<n;i++)for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ char ch = getchar(); while(ch==' '||ch=='\n') ch = getchar(); if(ch>='a'&&ch<='z') ditu[i][j] += ch - 'a' + 1, sum+= ditu[i][j]; } } bool check(int a,int b,int c){ int x = a + xx[c] , y = b + yy[c]; if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||ditu[x][y]!=0) return false; return true; } int check3(int x,int y){ if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m) return 0; if(ditu[x][y]!=0) return 1; return 2; } bool check2(int &a,int &b,int c){ while(1){ a += xx[c],b += yy[c]; int tnt = check3(a,b); if(tnt==0) return false; if(tnt==1) return true; } } bool dfs(int x,int y,int z){ if(z==0) return true; for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ if(!check(x,y,i)) continue; int a = x,b = y; if(!check2(a,b,i)) continue; //cout<<x<<" "<<y<<" "<<a<<" "<<b<<" "<<z<<endl; bool flag = false; if(check3(a+xx[i],b+yy[i])!=0) flag = true; int fk = ditu[a][b],fkk,c; if(flag){ fkk = ditu[a+xx[i]][b+yy[i]]; ditu[a+xx[i]][b+yy[i]] += fk - 1; c = z - 1; }else c = z - fk; ditu[a][b] = 0; ans[len++] = dire[i]; if(dfs(a,b,c)) return true; len--; ditu[a][b] = fk; if(flag) ditu[a+xx[i]][b+yy[i]] = fkk; } return false; } int main() { while(cin>>m>>n){ init(); //cout<<sum<<endl; //for(int i=0;i<n;i++){for(int j=0;j<m;j++) cout<<ditu[i][j]<<" ";cout<<endl;} int cp = 1; for(int i=0;i<n&&cp;i++)for(int j=0;j<m&&cp;j++) if(ditu[i][j]==0&&dfs(i,j,sum)) { printf("%d\n%d\n",i,j); ans[len] = '\0';cout<<ans<<endl; cp = 0; } } return 0; }
Tempter of the Bone IIHDU - 2128
算法:BFS/DFS
题意:就是给一个有障碍的地图,图上有炸弹推,经过就可以捡上,不过只能捡一次。炸弹可以炸墙,不过算一步。
判重就简单的3维,坐标加炸弹。
BFS
这里我BFS,直接模拟,找到答案直接输出,然后wrong了。
后面看别人代码,得知原因,因为,我直接将炸开炸弹,与进入墙体两步,结合在一层进行模拟;
容易导致BFS跨步错误,就像之前做过的一道题,情侣被鬼追,G - Nightmare Ⅱ HDU - 3085 。这题我在kuangbin题集做了解析。
这里类似2步走,第二步vis标记会导致其他第一步入队而出现答案错误,wrong。
这里我是看别人代码学的操作,将vis移到出队再加,然后答案,通过ans记录,并进行求最短剪枝。这里就相当于将vis标记放到下一层去判断,虽然会增加入队冗余,但是ans优化也减了一部分。
一开始码的时候不知道这样对不对?不管先试了再说。然后就AC了。

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <queue> #include <map> using namespace std; const int inf = 2e9; int n,m,ans; int Sx,Sy; char ditu[9][9]; bool vis[9][9][600]; int xx[] = {1,-1,0,0}; int yy[] = {0,0,1,-1}; void init(){ memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); ans = inf; for(int i=0;i<n;i++)for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ char ch = getchar();while(ch==' '||ch=='\n') ch = getchar(); ditu[i][j] = ch; if(ch=='S') Sx = i,Sy = j; } } struct node{ int x,y,step,exp; bool state[9][9]; node(int a,int b,int c,int d):x(a),y(b),step(c),exp(d) { memset(state,false,sizeof state); }; }; bool bfs(){ queue<node> q;q.push(node(Sx,Sy,0,0)); while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.front();q.pop(); vis[p.x][p.y][p.exp] = true; if(p.x>=ans) continue; for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ node now = p; now.x = p.x + xx[i] , now.y = p.y + yy[i],now.step++; if(now.x<0||now.x>=n||now.y<0||now.y>=m) continue; if(ditu[now.x][now.y]=='D') {ans = min(ans,now.step);continue;} if(ditu[now.x][now.y]=='X'&&!now.state[now.x][now.y]){ if(now.exp==0) continue; else now.state[now.x][now.y] = true,now.exp--,now.step++; } if(ditu[now.x][now.y]>='0'&&ditu[now.x][now.y]<='9'&&!now.state[now.x][now.y]){ now.state[now.x][now.y] = true; now.exp += ditu[now.x][now.y] - '0'; } if(vis[now.x][now.y][now.exp]) continue; q.push(now); } } if(ans==inf) return false; else {cout<<ans<<endl;return true;} } int main() { while(cin>>n>>m&&n&&m){ init(); if(!bfs()) puts("-1"); } return 0; }
后面想验证一下,到底是不是炸弹并步走,才导致的wrong,我就尝试将炸弹和入墙分为两步,再不同层进行。结果也AC。所以之前wrong就是BFS跨步走问题。

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <queue> #include <map> using namespace std; const int inf = 2e9; int n,m; int Sx,Sy; char ditu[9][9]; bool vis[9][9][600]; int xx[] = {1,-1,0,0}; int yy[] = {0,0,1,-1}; void init(){ memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); for(int i=0;i<n;i++)for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ char ch = getchar();while(ch==' '||ch=='\n') ch = getchar(); ditu[i][j] = ch; if(ch=='S') Sx = i,Sy = j; } } struct node{ int x,y,step,exp; int state[9][9]; node(int a,int b,int c,int d):x(a),y(b),step(c),exp(d) { memset(state,0,sizeof state); }; }; bool bfs(){ queue<node> q;q.push(node(Sx,Sy,0,0));vis[Sx][Sy][0] = true; while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.front();q.pop(); if(ditu[p.x][p.y]=='X'&&p.state[p.x][p.y]==2){ p.state[p.x][p.y]=1; p.step++; q.push(p); continue; } for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ node now = p; now.x = p.x + xx[i] , now.y = p.y + yy[i],now.step++; if(now.x<0||now.x>=n||now.y<0||now.y>=m) continue; if(ditu[now.x][now.y]=='D') {cout<<now.step<<endl;return true;} if(ditu[now.x][now.y]=='X'&&now.state[now.x][now.y]==0){ if(now.exp==0) continue; else { now.state[now.x][now.y] = 2,now.exp--; if(vis[now.x][now.y][now.exp]) continue; vis[now.x][now.y][now.exp] = true; q.push(now);continue; } } if(ditu[now.x][now.y]>='0'&&ditu[now.x][now.y]<='9'&&!now.state[now.x][now.y]){ now.state[now.x][now.y] = 1; now.exp += ditu[now.x][now.y] - '0'; } if(vis[now.x][now.y][now.exp]) continue; vis[now.x][now.y][now.exp] = true; q.push(now); } } return false; } int main() { while(cin>>n>>m&&n&&m){ init(); if(!bfs()) puts("-1"); } return 0; }
IDEA*
这里我DFS模拟,我决策函数用哈夫曼函数。然后模拟与上面BFS无疑,重点这里DFS也需要一步步来,因为想求得即最优。
可能存在没有答案,所以limit需要上限,8*8 = 64,64-2 = 62;然后取7个空作9炸弹,剩下55个空都是墙,然而63>55,所以55个墙为最坏情况,63+55 = 108步。上限为108;
(这里最坏情况假设,每次拿最近的炸弹必须用完之前的,每细想其他细节,所以大概就估算)

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <queue> #include <map> #include <cmath> using namespace std; const int inf = 2e9; int n,m; int Sx,Sy,Fx,Fy; int limit,nextd; char ditu[9][9]; bool vis[9][9][600]; int state[9][9]; int xx[] = {1,-1,0,0}; int yy[] = {0,0,1,-1}; void init(){ memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); memset(state,0,sizeof state); for(int i=0;i<n;i++)for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ char ch = getchar();while(ch==' '||ch=='\n') ch = getchar(); ditu[i][j] = ch; if(ch=='S') Sx = i,Sy = j;if(ch=='D') Fx = i,Fy = j; } } int check(int x,int y){ return abs(x-Fx) + abs(y-Fy); } bool dfs(int x,int y,int step,int exp,int limit){ int h = check(x,y); if(h+step>limit){ nextd = min(h+step,nextd); return false; } if(h==0) {cout<<step<<endl;return true;} if(ditu[x][y]=='X'&&state[x][y]==2){ state[x][y] = 1; if(dfs(x,y,step+1,exp,limit)) return true; return false; } for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int a = x + xx[i],b = y + yy[i],c = step+1,d = exp; if(a<0||a>=n||b<0||b>=m) continue; int flag = 0; if(ditu[a][b]=='X'&&!state[a][b]){ if(d==0) continue; else{ d--,state[a][b] = 2,flag = 1; if(vis[a][b][d]) continue; vis[a][b][d] = true; if(dfs(a,b,c,d,limit)) return true; vis[a][b][d] = false; if(flag) state[a][b] = 0; continue; } } if(ditu[a][b]>='0'&&ditu[a][b]<='9'&&!state[a][b]) state[a][b] = 1,flag = 1,d += ditu[a][b] - '0'; if(vis[a][b][d]) continue; vis[a][b][d] = true; if(dfs(a,b,c,d,limit)) return true; vis[a][b][d] = false; if(flag) state[a][b] = 0; } return false; } int main() { while(cin>>n>>m&&n&&m){ init(); int flag = 0;vis[Sx][Sy][0] = true; for(limit = check(Sx,Sy);limit<=102;){ nextd = inf; if(dfs(Sx,Sy,0,0,limit)) {flag = 1;break;} limit = nextd; }if(flag) continue; puts("-1"); } return 0; }
Ali and BabaHDU - 4101
算法:BFS + 博弈判奇偶
难点:题目在于理解。因为博弈,两人都是以自己最优的思路操作。所以胜负关键点很重要。
胜负关键点在于,谁最后打开宝藏包围圈谁输。
题意:一副地图,只有一个宝藏,然后存在石头推(以数字表示,<100),然后每人每步可以打碎一个石头。然后走路不算操作数。
思路:第一步:先标记从宝藏出发能达到的0点(包括宝藏自身也要标记),因为到达这里就表示已经赢了;这里如果标记点,存在于边界,就表示Ali不用破碎石头就能拿宝藏,所以Ali Win;
第二步:获取走到胜负关键点的总操作数。(胜负关键点就是谁可以走到那些上一步的标记点,因为谁都不想帮别人破最后的石头,所以就会选择破其他无关石头,所以要记录所有外围石头数即总操作数);这里简单联想一下,就是这一步宝藏外围一定有一个石头包围圈即屏障,谁先打破谁输。
第三步:第二步的重点在于记录石头数量,因为最后屏障是一个石头数量1的包围圈,这个包围圈石头数不用记录;然后所有外围石头数量总和判奇偶,奇数表示Baba要去破壁,所以Ali Win;反之同义。
失误:这里我wrong了;有两点:1)Baba Win 我写成了BaBa Win;2)第二步,我只用了(0,0)入队判断,其实不行,因为包围圈可能已经覆盖到边界了。所以要所有边界点入队判断;

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <queue> #include <map> #include <cmath> using namespace std; int n,m,Sx,Sy,ans; int ditu[303][303]; bool vis[303][303],vis2[303][303]; int xx[] = {1,-1,0,0}; int yy[] = {0,0,1,-1}; void init(){ memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); memset(vis2,false,sizeof vis2); ans = 0; } struct node{ int x,y; node(int a,int b):x(a),y(b) {}; }; bool bfs(){ queue<node> q; q.push(node(Sx,Sy));vis2[Sx][Sy] = true; while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.front();q.pop(); if(p.x==0||p.x==n-1||p.y==0||p.y==m-1) return true; for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x = p.x + xx[i],y = p.y + yy[i]; if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||ditu[x][y]!=0||vis2[x][y]) continue; q.push(node(x,y)); vis2[x][y] = true; } } return false; } bool check(int x,int y){ for(int i=0;i<4;i++) if(vis2[x+xx[i]][y+yy[i]]) return true; return false; } void bfs2(){ queue<node> q; for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ if(!vis[0][j]) q.push(node(0,j)),vis[0][j] = true,ans += ditu[0][j]; if(!vis[n-1][j]) q.push(node(n-1,j)),vis[n-1][j] = true,ans += ditu[n-1][j]; } for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ if(!vis[i][0]) q.push(node(i,0)),vis[i][0] = true,ans += ditu[i][0]; if(!vis[i][m-1]) q.push(node(i,m-1)),vis[i][m-1] = true,ans += ditu[i][m-1]; } while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.front();q.pop(); if(check(p.x,p.y)) {ans --;continue;} for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x = p.x + xx[i],y = p.y + yy[i]; if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||vis[x][y]) continue; q.push(node(x,y)); vis[x][y] = true,ans+=ditu[x][y]; } } //cout<<ans<<endl; if(ans%2) puts("Ali Win"); else puts("Baba Win"); } void show(){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ for(int j=0;j<m;j++) cout<<vis2[i][j]<<" ";cout<<endl; } } int main() { while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){ init(); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ scanf("%d",&ditu[i][j]); if(ditu[i][j]==-1) Sx = i,Sy = j; } if(bfs()){ puts("Ali Win"); }else bfs2(); //show(); } return 0; }
Ancient Messages HDU - 3839
算法:BFS
题意:就是给你一副图,图里面有很多埃及象形字,然后图像由像素0,1构成,1表示颜色黑,0则表示白。
难点:第一点在于怎么巧妙区别埃及象形字? 每个埃及象形字都是有闭合空间并且数量对于每个埃及象形字不同,所以可以从空白入手。
第二点在于如何区分埃及象形字内的空白与外空白? 这里题目给出了关键点,就是每两个埃及象形字必不连接且不嵌套。并且黑色部分永远相连不断。
思路:预处理:这里使用十六进制代表二进制像素,所以需要还原。
第一步:从边界开始读空白,进行白色BFS,把所有埃及象形字的外空白标记。
第二步:从上到下从左到右,找埃及象形字,遇到则开始黑色BFS,每遇到白色没标记则开始白色BFS标记;重点记录,遇到几次空白,即这个埃及象形字有多少闭合空白空间。从而区分这个是什么埃及象形字;
第三步:通过BFS得出的埃及象形字数量,然后字典输出即可AC。

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <queue> #include <map> #include <cmath> using namespace std; int n,m,ditu[202][202],ans[8],cas=1; int gg[] = {1,5,3,2,4,0}; char gk[] = {'A','D','J','K','S','W'}; int xx[] = {1,-1,0,0}; int yy[] = {0,0,1,-1}; bool vis[202][202]; struct node{ int x,y; node(int a,int b):x(a),y(b) {}; }; void bfs_white(int a,int b){ queue<node> q; q.push(node(a,b)),vis[a][b] = true; while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.front();q.pop(); for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x = p.x + xx[i],y = p.y + yy[i]; if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||ditu[x][y]||vis[x][y]) continue; q.push(node(x,y)),vis[x][y] = true; } } return ; } void bfs_black(int a,int b){ queue<node> q; int acer = 0; q.push(node(a,b)),vis[a][b] = true; while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.front();q.pop(); for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x = p.x + xx[i],y = p.y + yy[i]; if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||vis[x][y]) continue; if(ditu[x][y]) q.push(node(x,y)),vis[x][y] = true; else bfs_white(x,y),acer++; } } ans[acer]++; return ; } void show(){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ for(int j=0;j<m;j++) cout<<ditu[i][j]<<" ";cout<<endl; } } int main() { while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){ if(!n&&!m) break; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0,z=0;j<m;j++){ char ch = getchar(); while(ch==' '||ch=='\n') ch = getchar(); int num; if(ch>='a'&&ch<='z') num = ch-'a'+10; else num = ch-'0'; if(num>=8) ditu[i][z++] = 1,num-=8; else ditu[i][z++] = 0; if(num>=4) ditu[i][z++] = 1,num-=4; else ditu[i][z++] = 0; if(num>=2) ditu[i][z++] = 1,num-=2; else ditu[i][z++] = 0; if(num>=1) ditu[i][z++] = 1; else ditu[i][z++] = 0; }m*=4; //show(); memset(ans,0,sizeof ans); memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); //边界找0 for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ if(!vis[0][j]&&ditu[0][j]==0) bfs_white(0,j); if(!vis[n-1][j]&&ditu[n-1][j]==0) bfs_white(n-1,j); } for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ if(!vis[i][0]&&ditu[i][0]==0) bfs_white(i,0); if(!vis[i][m-1]&&ditu[i][m-1]==0) bfs_white(i,m-1); } //找图像 for(int i=0;i<n;i++)for(int j=0;j<m;j++) if(!vis[i][j]&&ditu[i][j]) bfs_black(i,j); printf("Case %d: ",cas++); for(int i=0;i<6;i++) for(int j=0;j<ans[gg[i]];j++) printf("%c",gk[i]); puts(""); } return 0; }
Booksort HDU - 1685
算法:IDA* /dfs
题意:给你一个打乱顺序的序列,每次操作可以选择一个长度的 子连续序列 插入任意位置,问最少需要多少次操作变成升序序列。
条件就是序列的数字一定连续的数字,即 1,2,3,4,5这样的数字。然后错过4次操作的答案,一律为5 or more
举例:5 4 3 2 1 ------> 3 2 5 4 1 -------> 3 4 1 2 5 ------------> 1 2 3 4 5 只要3步。
思路一:题意明确只要4步以内就行了。那就使用 IDA*的dfs进行limit+1慢慢推进,直到得出答案。
难点:启发函数的设定。
解决:序列分块,连续的为一块,即1 4 2 3 5 序列 分成 4块 1、 4 、 23、 5;
这里注意, 如果第一块为1,其本身不应该算进去,因为至始至终都不会移动这一块;最末端块同理;因为 1 和 5 本身就在其最终位置上永远不需要动,
所以 只要改变 4,23两块就行了,即需要操作的块数为2。
然后每次操作都会影响3块的后缀块变化,即分离块的前一块的、分离块本身与被插入点前面那块这3块的后缀;理想情况下,每次改变都使得其连接成一块,即每次操作减少3块。
所以1 4 2 3 5 序列 启发函数 h(x) = ceil(操作块数/3),向下取整,即是1。

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int INF = 2e9; int n,num[20]; void init(){ cin>>n; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>num[i]; num[0]=0;num[n+1]=n+1; } void show(){ for(int i=1;i<n+1;i++){ cout<<num[i]<<" "; }cout<<endl; } int forLimit(){ double ans = 0; for(int i=0;i<=n;i++) if(num[i]+1!=num[i+1]) ans++; return ceil(ans/3); } bool dfs(int step,int limit){ int h = forLimit(); if(h+step>limit) return false; if(h==0){ cout<<step<<endl; //show(); return true; } int temp[20]; memcpy(temp,num,sizeof(num)); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int len=1;len<=n-i+1;len++) for(int pos=1;pos<=n-len+1;pos++) if(pos!=i){ for(int j=0;j<len;j++) num[pos+j] = temp[i+j]; for(int p=1,j=1;j<=n;){ if(j<pos) num[j++] = temp[p++]; else if(j==pos) j+=len; else if(p==i) p+=len; else num[j++] = temp[p++]; } if(dfs(step+1,limit)) { //memcpy(num,temp,sizeof(temp));show(); return true; } } memcpy(num,temp,sizeof(temp)); return false; } int main() { int _;cin>>_; while(_--){ init(); for(int limit=forLimit();;limit++){ if(limit>4) {puts("5 or more");break;} if(dfs(0,limit)) break; } } }
思路二:观看大神博客https://blog.csdn.net/ilsswfr/article/details/52012467
类似于双向遍历bfs一样。
第一步:从初始序列开始dfs两步,得出答案为解。用set记录所有得出的序列。
第二部:从目标序列开始dfs两步,如果出现的序列在set里面则步数+2为解。

//从初始情况搜索两层并记录每次状态,这两层中如果有解,直接输出 //若是无解,从有序状态往回搜一层和两层, //如果能达到与之前的相同的状态就是有解。 #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstdlib> #include<cctype> #include<cstdio> #include<string> #include<cstring> #include<vector> #include<set> #include<map> #include<queue> #include<cmath> #define pi acos(-1.0) #define inf 1<<29 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f #define zero 1e-8 using namespace std; int step, n; int arr[100]; int fin[100]; set<string> ff; int makenum(int num, char *s, int &k) { int i = 0, now[5] = {}; for (; num;) { now[++i] = num % 10; num /= 10; } for (int j = i; j; j--) { s[k++] = now[j] + '0'; } return k; } string makestr(int *s, int num) //样式 { string aa; char a[100]; int k = 0; for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) { makenum(s[i], a, k); a[k++] = ' '; } a[k] = '\0'; return a; } bool compare(int *s) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) if (fin[i] != s[i]) return false; return true; } void show(int *s) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) cout << s[i]; cout << endl; } void cop(int *en, int *be) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) en[i] = be[i]; } void dfs1(int *tem, int cnt, int now) { string str = makestr(tem, n); ff.insert(str); if (step != inf) return ; if (cnt == now) { if (compare(tem)) { step = cnt; } return ; } if (cnt < now) return ; int tt[100]; for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { int z; for (z = 0; z < j; ++z) tt[z] = tem[z]; for (int len = 1; len < n - j; ++len) { cop(tt, tem); int f = z + len; for (int sert = 0; sert < n - j - len; ++sert) { tt[z + sert] = tem[f + sert]; if (f + sert + 1 < n - j - len && tem[f + sert + 1] == tt[z + sert] + 1) continue; for (int kk = 1; kk <= len; ++kk) tt[z + sert + kk] = tem[j + kk - 1]; string str = makestr(tt, n); ff.insert(str); dfs1(tt, cnt, now + 1); } } } } void dfs2(int *tem, int cnt, int now) { if (step != inf) return ; string str = makestr(tem, n); if (cnt == now) { if (ff.find(str) != ff.end()) step = 0; return ; } int tt[100]; for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { int z; for (z = 0; z < j; ++z) tt[z] = tem[z]; for (int len = 1; len < n - j; ++len) { cop(tt, tem); int f = z + len; for (int sert = 0; sert < n - j - len; ++sert) { tt[z + sert] = tem[f + sert]; if (f + sert + 1 < n - j - len && tem[f + sert + 1] == tt[z + sert] + 1) continue; for (int kk = 1; kk <= len; ++kk) tt[z + sert + kk] = tem[j + kk - 1]; dfs2(tt, cnt, now + 1); } } } } void makefin() { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) fin[i] = i + 1; } int main() { int t; cin >> t; for (; t--;) { scanf("%d", &n); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { scanf("%d", &arr[i]); } makefin(); step = inf; for (int i = 0; i <= 2; ++i) { step = inf; ff.clear(); dfs1(arr, i, 0); if (step != inf) { printf("%d\n", step); break; } } if (step == inf) { for (int i = 1; i <= 2; ++i) { dfs2(fin, i, 0); if (step != inf) { printf("%d\n", i + 2); break; } } if (step == inf) printf("5 or more\n"); } } return 0; }
BeatHDU - 2614
算法:dfs
题意:给一个矩阵Tij,行为i,列为j,Tij数字为在做完第i题之后,会花费Tij时间去做第j题;这里题的难度与时间正相关。
条件:1.acm大佬只做难度递增的题,即时间需要递增;
2.永远从第一题开始做起,而且花费时间永远为0
思路:就是从第一行开始往下dfs,需要每次都做更难或者相同难度的题。

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; int T[20][20],n,ans; bool ck[20]; void init(){ memset(ck,false,sizeof ck); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) cin>>T[i][j]; ans=1; } //x:上一题 y:上一题花费时间 z:总做题数 void dfs(int x,int y,int z){ if(ans==n) return; if(z==n){ans = n;return ;} int flag = 1; for(int j=2;j<=n;j++) if(!ck[j]&&T[x][j]>=y){ flag = 0; ck[j]=true; dfs(j,T[x][j],z+1); ck[j]=false; } if(flag) ans = max(ans,z); return ; } int main() { while(cin>>n){ init(); ck[1] = true; dfs(1,0,1); cout<<ans<<endl; } }
Roll The CubeHDU - 3309
算法:bfs
题意:给一个外边界都是墙的地图,然后里边也有墙,即障碍物;给你两个球,可以上下左右滚动一格,然后每次操作都是同步,撞墙就不能动,两个球不能重叠。地图必有两个洞,目标就是算将两个球滚进洞里 的最短操作数。
思路/难点:简单的模拟题,用BFS。
第一:BFS需要记录每一操作状态;状态有:球1坐标、球2坐标、球1进洞状态、球2进洞状态、洞1状态、洞2状态、步数。
需要维护球进洞状态:因为如果球进洞了的话,不管这么滚,坐标都不动,并且,当一个球进洞了,那么两个球是可以重叠到一个坐标上。
需要维护洞状态:判断球是否能进此洞。
第二:排重:需要状态数组进行避免重复操作。这里因为两个球,所以就用四维数组,即球1坐标、球2坐标进行排重。不管球是否进洞都可以判断;

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> using namespace std; int n,m; bool mp[24][24]; bool ck[24][24][24][24]; int bx[3],by[3]; int hx[3],hy[3]; int xx[]={0,0,1,-1}; int yy[]={1,-1,0,0}; void init(){ memset(mp,true,sizeof mp); memset(ck,true,sizeof ck); cin>>n>>m; int bNum=0,hNum=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){ char ch = getchar(); while(ch=='\n'||ch==' ') ch=getchar(); if(ch=='*') mp[i][j]=false; else if(ch=='B') bx[bNum]=i,by[bNum++]=j; else if(ch=='H') hx[hNum]=i,hy[hNum++]=j; } } void show(){ cout<<n<<" "<<m<<endl; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) cout<<mp[i][j]<<" ";cout<<endl; }cout<<endl; cout<<bx[0]<<" "<<by[0]<<" "<<bx[1]<<" "<<by[1]<<endl; cout<<hx[0]<<" "<<hy[0]<<" "<<hx[1]<<" "<<hy[1]<<endl; cout<<endl; } struct node{ int x1,y1,x2,y2,bS1,bS2,hS1,hS2,step; node(int xx1,int yy1,int xx2,int yy2,int bbS1,int bbS2,int hhS1,int hhS2,int stepp) :x1(xx1),y1(yy1),x2(xx2),y2(yy2),bS1(bbS1),bS2(bbS2),hS1(hhS1),hS2(hhS2),step(stepp) {}; }; void change(int &x,int &y,int bS,int i){ if(bS==1) return ; if(mp[x+xx[i]][y+yy[i]]) x += xx[i] , y += yy[i]; return; } int check(int x,int y,int &hS1,int &hS2){ if(hS1==0&&x==hx[0]&&y==hy[0]) {hS1=1;return 1;} if(hS2==0&&x==hx[1]&&y==hy[1]) {hS2=1;return 1;} return 0; } int bfs(){ queue<node> q; q.push(node(bx[0],by[0],bx[1],by[1],0,0,0,0,0));ck[bx[0]][by[0]][bx[1]][by[1]] = false; while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.front();q.pop(); for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x1=p.x1,y1=p.y1,x2=p.x2,y2=p.y2,bS1=p.bS1,bS2=p.bS2,hS1=p.hS1,hS2=p.hS2; change(x1,y1,bS1,i);change(x2,y2,bS2,i); if(bS1==0&&bS2==0&&x1==x2&&y1==y2) continue; if(ck[x1][y1][x2][y2]==false) continue; ck[x1][y1][x2][y2]=false; if(bS1==0) bS1 = check(x1,y1,hS1,hS2); if(bS2==0) bS2 = check(x2,y2,hS1,hS2); if(hS1&&hS2) return p.step+1; q.push(node(x1,y1,x2,y2,bS1,bS2,hS1,hS2,p.step+1)); } } return -1; } int main() { int _;cin>>_; while(_--){ init();//show(); int ans = bfs(); if(ans==-1) puts("Sorry , sir , my poor program fails to get an answer."); else cout<<ans<<endl; } }
JerboasHDU - 2437
算法:优先队列+BFS
题意:就是一个老鼠,他有很多个洞,TP,临时和永久两种;给你一个洞与洞的单向路径图,而且没有自身到自身的路径;给出数字K,问从S洞开始,到任意一个永久洞的最短路,并且路径长度必须为K的倍数。
思路:这里求最短路径,立马就想到BFS。
1.因为洞S题目已经给出了,初始洞一定为临时洞。
2.这里没有明确表示两个洞之间只有唯一路径,所以需要考虑两个洞存在不同长度的路径,使用二维vector存储。
3.判重关键点,路径长度和K倍数,所以只要求路径长度对K求余的余数就能判断,K最大为1000 所以判重数组,二维只要开到1000左右,即vis[点数量][1001]。
4.这里因为并不是简单判断最短路径,并且需要K倍数,对路径排序并没有用,所以需要优先队列,对入队的最短路进行优先出队。
我的出错点:这里我受到之前做题的影响,因为我上一道题的bfs是步骤,每次只加一,所以把判断放在了入队前也没问题。然而对于现在这题来说不行。所以需要入队完,从队列取出来再判断,再加上是优先队列,每次取出来都是最短路,只要达到要求就是答案。

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <set> using namespace std; int n,m,s,k; char dong[1002]; struct guan{ int e,f; guan(int ee,int ff):e(ee),f(ff) {}; }; vector<guan> v[1002]; bool vis[1002][1001]; void init(){ cin>>n>>m>>s>>k; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ char ch = getchar();while(ch=='\n' || ch==' ') ch = getchar(); dong[i] = ch; } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) v[i].clear(); memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); for(int i=0;i<m;i++){ int a,b,c;cin>>a>>b>>c; v[a].push_back(guan(b,c)); } } struct node{ int x,y; node(int xx,int yy):x(xx),y(yy) {}; bool operator < (const node &a) const{ if(y==a.y ) return x>a.x; return y>a.y; } }; bool bfs(){ priority_queue<node> q; vis[s][0] = true;q.push(node(s,0)); while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.top();q.pop(); int x = p.x , y = p.y; if(dong[x]=='P'&&y%k==0){ cout<<y<<" "<<x<<endl; return true; } for(int i=0;i<v[x].size();i++){ int e = v[x][i].e , f = v[x][i].f + y; if(vis[e][f%k]) continue; vis[e][f%k] = true; q.push(node(e,f)); } } return false; } int main() { int _;cin>>_; for(int i=1;i<=_;i++){ init(); cout<<"Case "<<i<<": "; if(!bfs()) cout<<"-1 -1"<<endl; } }
Open the LockHDU - 1195
算法:BFS
题意:给一个4位数,然后对位数上面的数进行操作,可以加一减一,9+1 = 1,1-1=9;可以与相邻的位数互换。
思路:简单的模拟题。因为这里只给了四位数,判重方法直接用vis[10][10][10][10]记录4个位数变化就好了

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <set> using namespace std; int n[5],e[5]; bool vis[10][10][10][10]; void init(){ memset(vis,true,sizeof vis); int num;cin>>num; for(int i=3;i>=0;i--){ n[i] = num%10; num/=10; } cin>>num; for(int i=3;i>=0;i--){ e[i] = num%10; num/=10; } } struct node{ int t[5],step; node(int *a,int sstep){ for(int i=0;i<4;i++) t[i] = a[i]; step = sstep; } bool check(){ if(vis[t[0]][t[1]][t[2]][t[3]]) { vis[t[0]][t[1]][t[2]][t[3]] = false; return true; } return false; } void left(int i){ int a = t[i]; t[i] = t[i-1]; t[i-1] = a; } void right(int i){ int a = t[i]; t[i] = t[i+1]; t[i+1] = a; } bool ansCheck(){ for(int i=0;i<4;i++) if(t[i]!=e[i]) return false; return true; } }; int bfs(){ queue<node> q; q.push(node(n,0)); vis[n[0]][n[1]][n[2]][n[3]] = false; while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.front();q.pop(); if(p.ansCheck()) return p.step; for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ //============================== node temp = p;temp.step++; if(temp.t[i]==9) temp.t[i] = 1; else temp.t[i]++; if(temp.check()) q.push(temp); //============================== temp = p;temp.step++; if(temp.t[i]==1) temp.t[i] = 9; else temp.t[i]--; if(temp.check()) q.push(temp); //============================== temp = p;temp.step++; if(i!=0){ temp.left(i); if(temp.check()) q.push(temp); } //============================== temp = p;temp.step++; if(i!=3){ temp.right(i); if(temp.check()) q.push(temp); } } } return -1; } void show(){ for(int i=0;i<4;i++) cout<<n[i]<<" ";cout<<endl; for(int i=0;i<4;i++) cout<<e[i]<<" ";cout<<endl; } int main() { int _;cin>>_; while(_--){ init();//show(); cout<<bfs()<<endl; } }
Pushing Boxes POJ - 1475
算法:BFS
题意:推箱子游戏,游戏规则:人只能有两个操作,一个就是走,另一个就是推箱子。目标就是把箱子推到目标位置。然后求 推操作数量最小 为前提 的 最短路径。
思路1:这个是我想的,直接用优先队列,每个点记录,人位置、箱子位置、推的数量、步数;然后优先 推数量 最小 在前面,然后相同则步数最小。
排重这里我用 [ 人X坐标 ] [ 人Y坐标 ] [ 箱子X坐标 ] [ 箱子Y坐标 ] [ 推数量 ] 五维数组维护,然后TL了。后面把推数量去掉,就ac了。
(这里想了一下,优先队列已经维护了推数量最少,排重数组不需要维护,因为之前出现过推数量,在人与箱子相对位置的情况下,必为最优;即先存在为最优)
然后唯一注意的点是,这里输出答案 两个之间有一个空行。没留意,wrong了很多次。看了人家代码才发现。

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> using namespace std; const int INF = 2e9; int n,m; int Sx,Sy,Bx,By,Tx,Ty; bool mp[21][21]; bool vis[21][21][21][21]; int xx[] = {0,0,-1,1}; int yy[] = {1,-1,0,0}; char fch[] = {'e','w','n','s'}; char bch[] = {'E','W','N','S'}; bool checkXY(int a,int b){ if(a<=0||b<=0||a>n||b>m) return false; return mp[a][b]; } struct node{ int a,b,c,d,step,p; string ans; node(int aa,int bb,int cc,int dd,string ss,int sstep,int pp):a(aa),b(bb),c(cc),d(dd),ans(ss),step(sstep),p(pp) {}; bool check(){ if(c==Tx&&d==Ty) return true; return false; } bool operator < (const node &x) const{ if(p==x.p) return step>x.step; return p>x.p; } }; void init(){ memset(mp,true,sizeof mp); memset(vis,true,sizeof vis); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){ char ch=getchar();while(ch=='\n') ch=getchar(); if(ch=='#') mp[i][j] = false; else if(ch=='S') Sx=i,Sy=j; else if(ch=='B') Bx=i,By=j; else if(ch=='T') Tx=i,Ty=j; } } void show(){ for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) cout<<mp[i][j]<<" ";cout<<endl; } } bool bfs(){ priority_queue<node> q; q.push(node(Sx,Sy,Bx,By,"",0, 0)); vis[Sx][Sy][Bx][By] = false; while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.top();q.pop(); if(p.check()){ cout<<p.ans<<endl; return true; } for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ node u = p;u.a += xx[i],u.b += yy[i]; if(!checkXY(u.a,u.b)) continue; bool flag = false; if(u.a==u.c&&u.b==u.d) flag = true; if(flag){ u.c += xx[i],u.d += yy[i]; if(!checkXY(u.c,u.d)) continue; if(!vis[u.a][u.b][u.c][u.d]) continue; vis[u.a][u.b][u.c][u.d] = false; u.ans+=bch[i]; u.step++; u.p++; q.push(u); }else{ if(!vis[u.a][u.b][u.c][u.d]) continue; vis[u.a][u.b][u.c][u.d] = false; u.ans+=fch[i]; u.step++; q.push(u); } } } return false; } int main() { int cas = 1; while(cin>>n>>m&&n&&m){ cout<<"Maze #"<<cas++<<endl; init(); if(!bfs()) puts("Impossible."); cout<<endl; } }
思路2:这个是看别人博客学的。http://t.zoukankan.com/xiaoguapi-p-10389623.html
大意就是进行一次箱子到目标位置的BFS求最短路径,然后在箱子BFS内部嵌套一个人推箱子的BFS求人到箱子位置的最短路径。
重点:1.箱子每一步,都要去BFS判断人能不能走到箱子上一步位置,不行则箱子走不了。2.判重,外围bfs只需要维护箱子位置就行,内部每一次BFS判重也只维护人的位置即可。
代码详情看大神博客。
2022年的第一道题,虎年好!
Full Tank?POJ - 3635
算法:优先队列bfs
题意:给一张地图,上面有N个城市,M条双向非负权值道路,每条路的权值是油耗,即过这条路需要多少油量。然后每个城市油价不同。
然后给你一辆油箱容量为C的车,问你从城市S到城市E的一条花费最少油费的路。
思路:第一次:这里我一开始,通过测试数据发现,最短路径不是最优路径,因为你要考虑每个城市油价进行加油的最优策略,即需要每次都需要找路径进行总油价比较,就使用了dfs,然后TLE。
第二次:吸取教训,想着试一下BFS,需要判重数组,思考影响答案的因素是,路径中城市的选择还有每个城市的加油量,然后就用二维数组vis[x][y],x表示城市,y表示油量,vis数组表示在城市x时拥有 y升油的money花费,通过几时加油来控制计算money,总money小过vis数组的进队列,否则不进队列。队列的点需要维护点前城市now和油量fuel和总花费钱数money。因为这里求最小花费,我就用优先队列,进行money的排序,到达目标城市即最优。然后还是TLE了。
第三次:这个时候我看了别人大牛博客参考,https://www.cnblogs.com/SiriusRen/p/6532446.html。他和我思路不同的地方在于,我是直接两个循环嵌套,第一个循环找城市,第二个循环找加油量,通过已有状态向下推。他则是把加油和找城市去分开,而且他的加油是,一次只加一升。我一下子就意识到自己的错误了。
重点:以往的判重都是bool,而这次是维护一个money最小,而且你是用优先队列维护了,城市转移会影响油价,潜在地影响money,所以每次城市转移都需要进行入队维护,同理,加油直接影响了money,每加一升都会影响,所以加油之后也要进入队列进行维护。保证每次取出的点状态都是最优,不然就会产生冗余。

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; int n,m,c,s,e; int price[1001],vis[1001][101]; struct Edge{ int v,cost; Edge(int _v,int _cost):v(_v),cost(_cost) {} };vector<Edge> E[1001]; void addedge(int u,int v,int w){ E[u].push_back(Edge(v,w)); E[v].push_back(Edge(u,w)); } void init(){ cin>>n>>m; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>price[i]; for(int i=0;i<m;i++){ int a,b,c;cin>>a>>b>>c; addedge(a,b,c); } } struct node{ int now,fuel,money; node(int nn,int ff,int mm):now(nn),fuel(ff),money(mm) {} bool check(){ if(now==e) return true; return false; } bool operator < (const node &x) const{ if(money==x.money) return fuel<x.fuel; return money > x.money; } }; bool bfs(){ memset(vis,INF,sizeof vis); priority_queue<node> q; q.push(node(s,0,0));vis[s][0]=0; while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.top();q.pop(); if(p.check()){cout<<p.money<<endl;return true;} //-----加一升油--------------------------------- if(p.fuel<c){ int now = p.now , fuel = p.fuel, money = p.money; fuel++;money+=price[now]; if(money<vis[now][fuel]){ vis[now][fuel] = money; q.push(node(now,fuel,money)); } } //-----去下个城市----------------------------- for(int i=0;i<E[p.now].size();i++){ int now = p.now , fuel = p.fuel, money = p.money; if(E[now][i].cost>fuel) continue; int v = E[now][i].v,cost = E[now][i].cost; fuel -= cost; if(money<vis[v][fuel]){ vis[v][fuel] = money; q.push(node(v,fuel,money)); } } } return false; } int main() { init();int _;cin>>_; while(_--){ cin>>c>>s>>e; if(!bfs()) puts("impossible"); } }
大牛博客谈到:图上dp函数,F[i][j] = Min(F[i][j-L]+price[i]*L,F[k][j+dist(i,k)]) 。我们初学dp都是从左上开始往右下推,dp是从已经确定的状态往后推,而这个图上的dp给我感觉就是前面点状态不是最优,需要通过后面重新读图进行反复推敲。这里说到spfa,其实就是有同样感觉,我忘了差不多,等到后面刷最短路径的题再回来思考,这里spfa+dp为什么会TLE。
Weather ForecastPOJ - 2044
算法:BFS+判重减枝
题意:一个4*4的正方形地图上有16个城市,你是上帝,能控制一朵2*2正方形的云,云下面的城市一定是阴天下雨,其余一定是晴天。你可以控制云朵运动:1.留在原地,2.东南西北方向走一步 3.东南西北方向走两步;然后城市节假日不能有雨;一个城市最多只能6天不下雨。
思路:一开始,暴力bfs,TLE。然后加入判重数组减枝,重要因素就是,天数、云位置、城市干旱时间天数;由于干旱极限是7天,状态压缩7的16次方,开个三维数组,这个肯定MLE。然后思考,一朵云覆盖4个城市,刚好可以把地图分成9个重叠块,而四个角落城市,分别只有一个形式的云覆盖,因此这四个角落是最容易干旱的,如果出现错过7天的情况,最早出现的城市一定有这四个角落城市其中一个,所以干旱程度只要记录四个角落就行了,然后开个6维数组,vis【天数】【云朵位置】【西北角落】【东北角落】【西南角落】【东南角落】。
我的错误点:就是你要注意看题,我一开始理解为走两步,虽然已经说了不能走斜线,但是我想你走两步,第一步走北,第二步走东,合在一起不就是走了东北吗?其实不是的,只能同一方向走两步。

#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; int N,W[367][18]; int C[10][5]={{1,2,5,6},{2,3,6,7},{3,4,7,8},{5,6,9,10},{6,7,10,11},{7,8,11,12},{9,10,13,14},{10,11,14,15},{11,12,15,16}}; int G[10][4]={{4,5,7,8},{3,5,6,8},{3,4,6,7},{1,2,7,8},{0,2,6,8},{0,1,6,7},{1,2,4,5},{0,2,3,5},{0,1,3,4}}; bool VIS[367][10][7][7][7][7]; bool check(int a,int b){ for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ if(W[b][C[a][i]]==1) return false; } return true; } bool dfs(int a,int b,int zero,int two,int six,int eight){ if(b>N) return true; for(int i=0,j=0;i<9;i++){ if(i==G[a][j]) {j++;continue;} if(!check(i,b)) continue; int zz=zero,tt=two,ss=six,ee=eight; zz++,tt++,ss++,ee++; if(i==0) zz=0;else if(i==2) tt=0;else if(i==6) ss=0;else if(i==8) ee=0; if(zz>6||tt>6||ss>6||ee>6) continue; if(VIS[b][i][zz][tt][ss][ee]) continue; VIS[b][i][zz][tt][ss][ee]=true; if(dfs(i,b+1,zz,tt,ss,ee)) return true; } return false; } void show(){ for(int i=0;i<9;i++){ for(int j=0;j<4;j++) cout<<C[i][j]<<" ";cout<<endl; } for(int i=0;i<9;i++){ for(int j=0;j<4;j++) cout<<G[i][j]<<" ";cout<<endl; } for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=16;j++) cout<<W[i][j]<<" ";cout<<endl; } } int main() { while(cin>>N&&N){ memset(VIS,false,sizeof VIS); for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)for(int j=1;j<=16;j++) cin>>W[i][j]; if(!check(4,1)) {cout<<0<<endl;continue;} VIS[1][4][1][1][1][1] = true; if(!dfs(4,2,1,1,1,1)) cout<<0<<endl; else cout<<1<<endl; } return 0; }
Remmarguts' DatePOJ - 2449
题意:一个公主来外交,王子需要从他的车站走到公主的车站去接她,公主要求王子必须走第K短路线找她。地图是一个单向路径的有环图。其实就是经典K短路。
算法:SPFA+A* 这里简单解释一下啊 SPFA 可以求有环图的,并且能判断图是否有负环,最终可以求出从起点出发到地图所有点的最短路径
思路:第一步:先用SPFA反向从终点即公主,开始算出到所有其他车站的最短距离,用dist数组记录
第二步:从王子开始A* BFS遍历,用优先队列维护与公主终点的距离。f(x) = h(x) + g(x). 这里构造启发函数 就是 与起点的距离 + dist数组 来预估与公主的距离。然后开始出队找终点,找到第K个就是答案了。
第三步:剪枝,这题有没有都可以过。1) dist数组里是INF的点 都可以直接跳过;2)用cnt数组记录每个点的入队数,第K短里面的点 最多只可能入队K次 超过可以跳过
难点/易错点:第一:优先队列特性 是 取点就进行判断答案 以保证最优准确性。然后我是用cnt数组来判断,但是我犯了个错误,就是cnt数组剪枝的时候,放在了入队前。其实应该是出队后,因为要确保同一层的可能的答案点都进入队列,所以要放到下一层。
第二:就是特殊情况,当起点和终点 都是同一个点的时候,K要+1。因为你起点,一开始入队并且出队的时候,记录数值会加一,但是王子根本没有走任何一条路,所以K要加一,让循环推到下一层。

#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int MAXN = 1010; int n,m,s,t,k; struct Edge{ int v; int cost; Edge(int _v=0,int _cost=0):v(_v),cost(_cost) {} }; vector<Edge> E1[MAXN]; vector<Edge> E2[MAXN]; void addedge(int u,int v,int w){ E1[u].push_back(Edge(v,w)); E2[v].push_back(Edge(u,w)); } bool vis[MAXN]; int cnt[MAXN],dist[MAXN]; bool SPFA(int start,int n){ memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) dist[i]=INF; vis[start]=true;dist[start]=0; queue<int> que; que.push(start); memset(cnt,0,sizeof cnt);cnt[start]++; while(!que.empty()){ int u=que.front();que.pop(); vis[u]=false; for(int i=0;i<E2[u].size();i++){ int v = E2[u][i].v; if(dist[v]>dist[u]+E2[u][i].cost){ dist[v]=dist[u]+E2[u][i].cost; if(vis[v]) continue; vis[v]=true; que.push(v); if(++cnt[v]>n) return false; } } } return true; } void init(){ scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for(int i=0;i<m;i++){ int a,b,c; scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c); addedge(a,b,c); } scanf("%d%d%d",&s,&t,&k); if(s==t) k++; } struct node{ int cz,time,f; node(int _cz,int _time):cz(_cz),time(_time) { f = time + dist[cz]; } bool operator < (const node &a) const{ return f>a.f; } }; int AStar(){ priority_queue<node> q; memset(cnt,0,sizeof cnt); if(dist[s]==INF) return -1; q.push(node(s,0)); while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.top();q.pop(); int u = p.cz; cnt[u]++; if(cnt[u]>k) continue; if(u==t&&cnt[u]==k) return p.time; for(int i=0;i<E1[u].size();i++){ int v = E1[u][i].v; int cost = E1[u][i].cost; if(dist[v]==INF) continue; q.push(node(v,p.time+cost)); } } return -1; } int main() { init();SPFA(t,n); printf("%d\n",AStar()); return 0; }
Holedox MovingPOJ - 1324
题意:一个n,m的巢穴地图,里面有石头不能走,洞口永远为(1,1)。然后给你一条长度L[2,8]的蛇。然后蛇每一次移动,身体也会跟着走,然后你不能穿过石头和身体。问你到洞口的最短步数是多少?
算法:A*+状态压缩
思路:这里启发函数就直接蛇头与洞口曼哈顿距离就行了;
判重函数:这里每个点维护的信息:蛇头坐标,步数,蛇身体状态;其实区分每一个点入队的判重,这里就重要是蛇头和身体状态(因为身体也会阻碍蛇头前进);蛇头直接二维x,y就行了;然后就是蛇身体如何区分记录呢?一开始我的想法是,最大长度为8,那再记录身体其他坐标就好了,但是21的16次方直接爆了,MLE。然后想了很久,还是看了别人博客,学到了。只要记录蛇头,然后第二节只要记录方向就行,第三节只要记录相对于第二节的方向就行了,等等。因为方向只有4个方向,所以 最大只要 4的7次方 就是 2 的14次方;所以开三维,vis[21][21][1<<14]
难点/易错点:我直接1A了,没有什么地方出错;求方向四进制状态、还原身体坐标、维护新的四进制状态这几个可能会比较容易搞得混乱,我自己也码的不好看,但也懒得改了,希望能帮到你

#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <cstdio> using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int MAXN = 1010; int four[7];//四进制基数 int n,m;//迷宫长宽 int stNum;bool ditu[21][21];//石头数+地图标记 int snakeNum;//蛇的长度 int snakeHeadX,snakeHeadY,snakeBody;//蛇头坐标 + 蛇形状的四进制表示(用四进制记录每一节对于前一节的方向) bool vis[21][21][1<<14];//蛇头坐标 + 蛇形状的四进制表示 de 三维标记判重函数 int xx[] = {0,1,0,-1}; int yy[] = {1,0,-1,0}; //用于求蛇身每一节对于前一节的方向,0,1,2,3,分别表示右下左上 int check(int a,int b,int c,int d){ if(c-a==0&&d-b==1) return 0; if(c-a==1&&d-b==0) return 1; if(c-a==0&&d-b==-1) return 2; if(c-a==-1&&d-b==0) return 3; } //初始输入+预处理 void init(){ cin>>snakeHeadX>>snakeHeadY; int a=snakeHeadX,b=snakeHeadY,c,d; snakeBody=0; for(int i=0;i<snakeNum-1;i++){ cin>>c>>d; snakeBody+=four[i]*check(a,b,c,d); a=c,b=d; } cin>>stNum; memset(ditu,true,sizeof ditu); for(int i=0;i<stNum;i++){ cin>>a>>b;ditu[a][b]=false; } } //测试函数 可删除 void show(){ cout<<n<<" "<<m<<" "<<snakeNum<<endl; cout<<snakeHeadX<<" "<<snakeHeadY<<" "<<snakeBody<<endl; for(int i=0;i<snakeNum-1;i++){ int tmp = snakeBody % 4; cout<<tmp<<" "; snakeBody/=4; }cout<<endl; cout<<stNum<<endl; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) cout<<ditu[i][j]<<" ";cout<<endl; } } //蛇头X,Y坐标 蛇的四进制表示 启发函数数值f(这里是蛇头与洞口(1,1)的曼哈顿距离) struct node{ int x,y,snake,step,f; node(int xx,int yy,int ssnake,int sstep):x(xx),y(yy),snake(ssnake),step(sstep){ f=step+abs(x-1)+abs(y-1); } bool operator < (const node &a) const{ return f > a.f; } }; //这个函数是通过 蛇头坐标 蛇身四进制 来求 蛇身坐标数组 和 蛇尾对于前一节的方向 void snakeXY(int SX,int SY,int (&snakeX)[8],int (&snakeY)[8],int &c,int d){ int x = SX,y = SY; for(int i=0;i<snakeNum-1;i++){ int tmp = d % 4; d/=4; x+=xx[tmp],y+=yy[tmp]; snakeX[i] = x ,snakeY[i] = y ; if(i==snakeNum-2) c = tmp; } } //判断蛇头是否能走(x,y) bool checkN(int x,int y,int a[],int b[]){ if(x<=0||x>n||y<=0||y>m||ditu[x][y]==false) return false; for(int i=0;i<snakeNum-1;i++){ if(x==a[i]&&y==b[i]) return false; } return true; } //A*算法 int Astar(){ memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); priority_queue<node> q; q.push(node(snakeHeadX,snakeHeadY,snakeBody,0)); vis[snakeHeadX][snakeHeadY][snakeBody] = true; while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.top();q.pop(); if(p.x==1&&p.y==1) return p.step; //这里记录蛇身坐标 和 蛇尾方向 int snakeX[8],snakeY[8],tail; snakeXY(p.x,p.y,snakeX,snakeY,tail,p.snake); //右、下、左、上 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x = p.x + xx[i],y = p.y + yy[i]; if(!checkN(x,y,snakeX,snakeY)) continue; //这里开始算新的方向四进制 去尾加头 int body = p.snake - four[snakeNum-2]*tail; body*=4; if(i==0) body+=2; else if(i==1) body+=3; else if(i==2) body+=0; else body += 1; if(vis[x][y][body]) continue; vis[x][y][body] = true; q.push(node(x,y,body,p.step+1)); } } return -1; } int main() { four[0]=1;for(int i=1;i<7;i++) four[i] = four[i-1]*4; int _=1; while(cin>>n>>m>>snakeNum&&n&&m&&snakeNum){ init(); cout<<"Case "<<_++<<": "; cout<<Astar()<<endl; } return 0; }
Bloxorz IPOJ - 3322
题意:游戏推一个由两个正方形组成的长方体,可以横着推也可以把长方体竖起来,然后地图由空白、紧固地、不坚固地(长方体不能立在上面,但可以横着站在上面)组成;问长方体从开始位置到目标位置的最短路径
算法:BFS 简单模拟题
思路:其实这题主要是判重,因为包括竖着与横着两个状态,横着由两个坐标表示,又因为地图最大为500,如果判重数组由两个坐标来维护,vis[X1][Y1][X2][Y2],则是500的4次方,绝对MLE。这里就想到上一题的思路,只要记住一个坐标就行,另一个方块只要记住方向就可以了;然后判重数组就变为 vis[X1][Y1][方向] 只要开三维,而且 500*500*5 绝对不MLE。这里我方向是:0——直立,1——右,2——下,3——左,4——上。
易错点:这里我又是1A,模拟题可能就细节比较容易出错,不过如果你清楚思路,数据也过了,基本就ac了

#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <cstdio> using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; int n,m; int ditu[505][505]; bool vis[505][505][5]; int xx[] = {0,1,0,-1}; int yy[] = {1,0,-1,0}; //dir 0:直立 1~4 左下右上 int sX,sY,dir; int tX,tY; int check(int x,int y,int a,int b){ if(a-x==0&&b-y==1) return 1; if(a-x==1&&b-y==0) return 2; if(a-x==0&&b-y==-1) return 3; if(a-x==-1&&b-y==0) return 4; } void init(){ memset(ditu,0,sizeof ditu); dir =-1; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){ char ch = getchar();if(ch=='\n') ch=getchar(); if(ch=='X'){ if(dir==-1) sX=i,sY=j,dir++; else dir=check(sX,sY,i,j); ditu[i][j]=1; } else if(ch=='O') tX=i,tY=j,ditu[i][j]=1; else if(ch=='.') ditu[i][j] = 1; else if(ch=='E') ditu[i][j] = 2; } } void show(){ cout<<sX<<" "<<sY<<" "<<dir<<" "<<tX<<" "<<tY<<endl; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) cout<<ditu[i][j]<<" ";cout<<endl; } } struct node{ int x,y,d,step; node(int xx,int yy,int dd,int sstep):x(xx),y(yy),d(dd),step(sstep) {} bool check(){ if(d==0&&x==tX&&y==tY) return true; return false; } }; bool checkXY(int a,int b,int z){ if(a<=0||a>n||b<=0||b>m) return false; if(ditu[a][b]==0) return false; if(z==0&&ditu[a][b]==2) return false; if(z==0) return true; int c,d; if(z==1) c=a,d=b+1; else if(z==2) c=a+1,d=b; else if(z==3) c=a,d=b-1; else if(z==4) c=a-1,d=b; if(c<=0||c>n||d<=0||d>m) return false; if(ditu[c][d]==0) return false; return true; } int BFS(){ queue<node> q; q.push(node(sX,sY,dir,0)); memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); vis[sX][sY][dir] = true; while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.front();q.pop(); if(p.check()) return p.step; //直立情况==================== if(p.d==0){ for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x = p.x + xx[i], y = p.y + yy[i]; int d = i + 1; if(!checkXY(x,y,d)) continue; if(vis[x][y][d]) continue; vis[x][y][d] = true; q.push(node(x,y,d,p.step+1)); } } //方向为1=============== if(p.d==1){ int x,y,d; //右================ x = p.x , y = p.y+2, d = 0; if(checkXY(x,y,d)&&!vis[x][y][d]){ vis[x][y][d] = true; q.push(node(x,y,d,p.step+1)); } //下================= x = p.x + 1, y = p.y ,d = 1; if(checkXY(x,y,d)&&!vis[x][y][d]){ vis[x][y][d] = true; q.push(node(x,y,d,p.step+1)); } //左================ x = p.x , y = p.y-1, d = 0; if(checkXY(x,y,d)&&!vis[x][y][d]){ vis[x][y][d] = true; q.push(node(x,y,d,p.step+1)); } //上================= x = p.x - 1, y = p.y ,d = 1; if(checkXY(x,y,d)&&!vis[x][y][d]){ vis[x][y][d] = true; q.push(node(x,y,d,p.step+1)); } } //方向为2=============== if(p.d==2){ int x,y,d; //右================ x = p.x , y = p.y+1, d = 2; if(checkXY(x,y,d)&&!vis[x][y][d]){ vis[x][y][d] = true; q.push(node(x,y,d,p.step+1)); } //下================= x = p.x + 2, y = p.y ,d = 0; if(checkXY(x,y,d)&&!vis[x][y][d]){ vis[x][y][d] = true; q.push(node(x,y,d,p.step+1)); } //左================ x = p.x , y = p.y-1, d = 2; if(checkXY(x,y,d)&&!vis[x][y][d]){ vis[x][y][d] = true; q.push(node(x,y,d,p.step+1)); } //上================= x = p.x - 1, y = p.y ,d = 0; if(checkXY(x,y,d)&&!vis[x][y][d]){ vis[x][y][d] = true; q.push(node(x,y,d,p.step+1)); } } //方向为3=============== if(p.d==3){ int x,y,d; //右================ x = p.x , y = p.y+1, d = 0; if(checkXY(x,y,d)&&!vis[x][y][d]){ vis[x][y][d] = true; q.push(node(x,y,d,p.step+1)); } //下================= x = p.x + 1, y = p.y ,d = 3; if(checkXY(x,y,d)&&!vis[x][y][d]){ vis[x][y][d] = true; q.push(node(x,y,d,p.step+1)); } //左================ x = p.x , y = p.y-2, d = 0; if(checkXY(x,y,d)&&!vis[x][y][d]){ vis[x][y][d] = true; q.push(node(x,y,d,p.step+1)); } //上================= x = p.x - 1, y = p.y ,d = 3; if(checkXY(x,y,d)&&!vis[x][y][d]){ vis[x][y][d] = true; q.push(node(x,y,d,p.step+1)); } } //方向为4=============== if(p.d==4){ int x,y,d; //右================ x = p.x , y = p.y+1, d = 4; if(checkXY(x,y,d)&&!vis[x][y][d]){ vis[x][y][d] = true; q.push(node(x,y,d,p.step+1)); } //下================= x = p.x + 1, y = p.y ,d = 0; if(checkXY(x,y,d)&&!vis[x][y][d]){ vis[x][y][d] = true; q.push(node(x,y,d,p.step+1)); } //左================ x = p.x , y = p.y-1, d = 4; if(checkXY(x,y,d)&&!vis[x][y][d]){ vis[x][y][d] = true; q.push(node(x,y,d,p.step+1)); } //上================= x = p.x - 2, y = p.y ,d = 0; if(checkXY(x,y,d)&&!vis[x][y][d]){ vis[x][y][d] = true; q.push(node(x,y,d,p.step+1)); } } } return -1; } int main() { while(cin>>n>>m&&n&&m){ init();//show(); int ans = BFS(); if(ans==-1) puts("Impossible"); else cout<<ans<<endl; } return 0; }
An interesting mobile gameHDU - 3295
题意:
1、一个最大6*6的方阵中有4种颜色的方块。
2、然后玩家可以进行点击颜色方块的操作,每次点击都会消除互相连接并且颜色相同的方块。
3、消除方块之后,向下向左靠的原则,如果一个列都空的话,右边的列就会向左补上。
4、求消除所有颜色方块的最少操作数
算法:BFS+最小生成树/DFS
思路:一道模拟题
求最少操作数,可以DFS搜索所有情况,或者BFS求最少。因为这里每个点只要记录步数+方阵状态,所以BFS的存储压力不大。我这里使用string来压缩状态,然后也是通过map来进行入队判重。
然后点击消除方块,则可以通过最小生成树的原理来区分出被消除的方块;对这些方块进行标记,来进行第二重的操作判重;
最后就是消除方块后的整合工作

#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <cstdio> #include <map> using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; int n,m; string str; int xx[]={0,0,-1,1}; int yy[]={1,-1,0,0}; void init(){ str=""; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ int a;cin>>a;str+=('0'+a); } } } struct node{ string s;int step; node(string ss,int sstep):s(ss),step(sstep) {} bool check(){ for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++) if(s[i]!='0') return false; return true; } }; int temp[6][6],ttem[6][6]; bool ck[6][6]; void make(string s){ int num = 0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++) temp[i][j] = s[num++] - '0'; } void dfs(int a,int b,int c){ for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x = a + xx[i] , y = b + yy[i]; if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||temp[x][y]!=c||ck[x][y]) continue; ck[x][y]=true; ttem[x][y]=0; dfs(x,y,c); } } string remake(){ int a[6][6]; memset(a,0,sizeof a); int aX,aY=0; for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ bool flag = false; aX = n-1; for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){ if(ttem[i][j]==0) continue; flag=true; a[aX--][aY] = ttem[i][j]; } if(flag) aY++; } string s = ""; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++) s+=('0'+a[i][j]); return s; } int bfs(){ queue<node> q;q.push(node(str,0)); map<string,bool> mp;mp[str]=true; while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.front();q.pop(); if(p.check()) return p.step; memset(ck,false,sizeof ck); make(p.s); for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){ if(temp[i][j]==0) break; if(ck[i][j]) continue; ck[i][j]=true; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++) ttem[i][j] = temp[i][j]; ttem[i][j]=0; dfs(i,j,temp[i][j]); string sss = remake(); if(mp[sss]) continue; mp[sss] = true; q.push(node(sss,p.step+1)); } } } } int main() { while(cin>>n>>m&&n&&m){ init(); cout<<bfs()<<endl; } return 0; }
Continuous Same Game (1)HDU - 2258
题意:和上一题一样是消除方块,下面空就下降,一列空就向左靠;题目规则是找最大块进行消除,同等大小则选最上面最左边的进行消除————贪心算法;
算法:模拟题
思路:从左上往右下搜索,找最大块进行消除

#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <cstdio> #include <map> using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; int n,m,ans; char ch[20][20]; int ditu[20][20]; bool flag[20][20]; int xx[]={0,0,-1,1}; int yy[]={1,-1,0,0}; void init(){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>ch[i]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++) ditu[i][j] = ch[i][j] - '0'; } int dfs(int a,int b,int c){ int ans = 0; for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x = a + xx[i] , y = b + yy[i]; if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||ditu[x][y]!=c) continue; if(flag[x][y]) continue;flag[x][y]=true; ans++;ans+=dfs(x,y,c); } return ans; } void dfs2(int a,int b,int c){ for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x = a + xx[i] , y = b + yy[i]; if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||ditu[x][y]!=c) continue; ditu[x][y]=0; dfs2(x,y,c); } } void remake(){ int ans[20][20]; memset(ans,0,sizeof ans); int ansX,ansY=0; for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ bool flag = false; ansX = n-1; for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){ if(ditu[i][j]==0) continue; flag=true; ans[ansX--][ansY] = ditu[i][j]; } if(flag) ansY++; } for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++) ditu[i][j] = ans[i][j]; } void show(){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ for(int j=0;j<m;j++) cout<<ditu[i][j];cout<<endl; } } int run(){ int ans = 0; bool fg=false; int maxNum = 1, aX,aY; memset(flag,false,sizeof flag); for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ if(ditu[i][j]==0) continue; if(flag[i][j]) continue; flag[i][j] = true; int cnt = dfs(i,j,ditu[i][j])+1; if(maxNum<cnt) {maxNum = cnt , aX = i, aY = j,fg = true;} } } if(fg) { ans += maxNum*(maxNum-1); int tnt = ditu[aX][aY]; ditu[aX][aY]=0; dfs2(aX,aY,tnt); remake(); ans+=run(); } return ans; } int main() { while(cin>>n>>m&&n&&m){ init(); cout<<run()<<endl; } return 0; }
Continuous Same Game (2)HDU - 2259
题意:上题的延续,需要一个比贪心算法还优秀的算法。
算法:优先队列+暴力评估
思路:1.首先这题我没有想出来,是看别人博客学的;
2.一个node状态存储地图,得分,评估价值,答案等;答案是从初始状态到现阶段的决策数组,即本体答案;得分是从初始状态到现阶段的所有清除方块后的n*(n-1)的总和;
3.优先队列通过评估价值来排序,价值最高则先出队;评估价值则是直接从现状态,在不移动方块前提下,计算所有可能被清除的方块堆的得分总和,再加上现阶段得分---------就是一种粗略计算最终得分数的方法
4.这里应该是博客大佬自己慢慢测试出来的,就是队列bfs循环至少要在24步内解决。少于24步不能得出答案,多于不超时也行。即测试数据中最大的答案是24个步骤的。

#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <cstdio> #include <map> using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; int n,m; int xx[]={0,0,-1,1}; int yy[]={1,-1,0,0}; char ch[20][20]; struct node{ int ditu[20][20];//地图 int ans,val;//得分(从最初到这个状态)、价值(用于优先队列排序) int step,X[26],Y[26];//答案 //以下都适用于价值评估函数eval所需要 int cnt,temp[20][20]; bool vis[20][20]; bool operator < (const node &a) const{ return val<a.val; } //坐标(a,b)向外扩展清零 void clean(int a,int b,int c){ for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x = a + xx[i] , y = b + yy[i]; if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||ditu[x][y]!=c) continue; ditu[x][y]=0; clean(x,y,c); } } //清零之后的向左向下靠齐 void remake(){ int tmp[20][20]; memset(tmp,0,sizeof tmp); int tmpX,tmpY=0; for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ bool flag = false; tmpX = n-1; for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){ if(ditu[i][j]==0) continue; flag=true; tmp[tmpX--][tmpY] = ditu[i][j]; } if(flag) tmpY++; } for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++) ditu[i][j] = tmp[i][j]; } //用于计算cnt,即扎堆数量 void clean2(int a,int b,int c){ for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x = a + xx[i] , y = b + yy[i]; if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||temp[x][y]!=c||!vis[x][y]) continue; temp[x][y]=0,cnt++; clean2(x,y,c); } } //价值评估函数 void eval(){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++) temp[i][j]=ditu[i][j]; memset(vis,true,sizeof vis); val = ans; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ if(temp[i][j]==0) continue; int tmp = temp[i][j]; temp[i][j]=0; cnt=1; clean2(i,j,tmp); if(cnt>1){ temp[i][j]=cnt;vis[i][j]=false; val += cnt*(cnt-1); } } } }t,ans; //测试用 void show(){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ for(int j=0;j<m;j++) cout<<t.temp[i][j]<<" "; cout<<endl; }cout<<t.val<<endl; } //输入 void init(){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>ch[i]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++) t.ditu[i][j] = ch[i][j] - '0'; t.ans=0, t.step=0;t.eval(); //show(); } void run(){ ans.ans=0; priority_queue<node> q; q.push(t); int stepNum=0; while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.top();q.pop(); if(ans.ans<p.ans) ans=p; if(++stepNum>24) break; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++) if(p.temp[i][j]){ node tp = p; p.clean(i,j,p.ditu[i][j]); p.ditu[i][j]=0; p.remake(); p.X[p.step]=i,p.Y[p.step]=j,p.step++; p.ans+=p.temp[i][j]*(p.temp[i][j]-1); p.eval(); q.push(p); p=tp; } } } int main() { while(cin>>n>>m&&n&&m){ init(); run(); cout<<ans.step<<endl; for(int i=0;i<ans.step;i++) cout<<ans.X[i]<<" "<<ans.Y[i]<<endl; } return 0; }
Prison Break HDU - 3681
题意:给你一个n,m地图,然后F是起点,G是充电点,Y是开关,要把所有开关关掉才能过关,D是不可穿越的障碍;初始状态下电池是满的,然后没走一部少一格电量,问主角至少要带多少电量的电池包才可以过关。
算法:BFS预处理距离+二分查找答案+暴力枚举测试是否过关
思路:首先,本题找最少可过关的电池量,我们可从0~15*15来二分查找,可过关的就向下找,否则向上,临界点则为答案。
然后,关键点是F\G\Y。F、Y是必经的点,G点是充电点,用于中途补给。G、Y总和小于15,加上F最多就是15,所以可以通过15位二进制数来表示状态。暴力从0~1<<15枚举所有可能情况,然后找到一个状态,覆盖所有Y点和F点,然后他的电量为非负数则该电量可通过。
易错点:需要先预处理,BFS出所有F\G\Y点之间的距离。

#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <cstdio> #include <map> using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; int n,m; char ch[15][16]; int dis[15][15][15][15]; int dp[1<<15][15]; int finalState,stateNum,startNum; int xx[] = {1,-1,0,0}; int yy[] = {0,0,-1,1}; struct node{ int x,y; node() {} node(int a,int b):x(a),y(b) {} }po[15]; void BFS(int nn){ queue<node> q; int sx = po[nn].x , sy = po[nn].y; dis[sx][sy][sx][sy]= 0; q.push(po[nn]); while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.front();q.pop(); for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x = p.x+xx[i], y = p.y+yy[i]; if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||ch[x][y]=='D') continue; if(dis[sx][sy][x][y]==-1){ dis[sx][sy][x][y] = dis[sx][sy][p.x][p.y]+1; q.push(node(x,y)); } } } } void init(){ finalState=0;stateNum=0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>ch[i]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ if(ch[i][j]=='S'||ch[i][j]=='D') continue; if(ch[i][j]=='F') startNum=stateNum; po[stateNum] = node(i,j); if(ch[i][j]=='F'||ch[i][j]=='Y') finalState+=1<<stateNum; stateNum++; } memset(dis,-1,sizeof dis); for(int i=0;i<stateNum;i++) BFS(i); } void show(){ int t = 1<<stateNum; cout<<stateNum<<" "<<startNum<<" "<<finalState<<" "<<t<<endl; for(int i=0;i<stateNum;i++){ int x = po[i].x , y = po[i].y; for(int j=0;j<stateNum;j++){ int a=po[j].x, b=po[j].y; cout<<dis[x][y][a][b]<<" "; }cout<<endl; } } bool check(int cup){ memset(dp,-1,sizeof dp); dp[1<<startNum][startNum] = cup; for(int st=0;st<1<<stateNum;st++){ for(int i=0;i<stateNum;i++){ if(st&1<<i==0 || dp[st][i]==-1) continue; if((st&finalState&finalState)==finalState) return true; for(int j=0;j<stateNum;j++){ int dist = dis[po[i].x][po[i].y][po[j].x][po[j].y]; if(i==j||st&1<<j||dist==-1||dp[st][i]-dist<0) continue; int newSt = st+(1<<j); dp[newSt][j] = max(dp[st][i] - dist,dp[newSt][j]); if(ch[po[j].x][po[j].y]=='G') dp[newSt][j] = cup; } } } return false; } int run(){ int left = 0, right = n*m; while(left<=right){ int mid = left + right >>1; if(check(mid)) right = mid-1; else left = mid +1; } if(left>n*m) return -1; return left; } int main() { while(cin>>n>>m&&n&&m){ init();//show(); cout<<run()<<endl; } return 0; }
Dearboy's PuzzlePOJ - 2308
题意:连连看,给你一幅地图然后,你只能用题目图中的连线消除。(这里看题目,有个疑惑就是连线可以走在图外面吗?我试着不走外面来消除,然后ac了。所以连线不能在外面的)
算法:DFS+BFS
思路:1.这里只需求是否可以把图案全部消除,所以DFS出一个答案就行了,顺便节省空间。
2.用char字符数组存地图,然后末尾加'\0',形成字符串,然后用map<string,bool> 来判重。
3.测试用例一知道,需要记录A、B、C、D的数量,存在单个字符奇数总和就可直接 no,这里要记录,就顺便将字符记录在vector中,方便后面使用,加快速度。
4.测试用例二知道,这种情况是无解的,所以也需要状态判断,当dfs走到这一步 可以直接 no
5.DFS从一个字母字符开始,用BFS找出所有可以消除的同字母字符,这里BFS通过从一个字符开始,只走三层,没走一层都在四个方向上,循环走到底,找出所有可能。
易错点:测试用例二的情况容易忽略掉。

#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <cstdio> #include <map> using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; int n,m; char ditu[111];int dituNum; char ditu2[13][13]; int Anum,Bnum,Cnum,Dnum; map<string,bool> mp; struct node{ int x,y,z; node(int a,int b,int c):x(a),y(b),z(c) {} }; vector<node> v; void init(){ mp.clear();v.clear(); dituNum=0,Anum=0,Bnum=0,Cnum=0,Dnum=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){ char ch = getchar(); while(ch==' '||ch=='\n') ch = getchar(); ditu[dituNum++]=ch; ditu2[i][j]=ch; if(ch!='*') v.push_back(node(i,j,0)); if(ch=='A') Anum++; else if(ch=='B') Bnum++; else if(ch=='C') Cnum++; else if(ch=='D') Dnum++; } ditu[dituNum]='\0'; mp[ditu] = true; } bool check(){ if(Anum==0&&Bnum==0&&Cnum==0) return true; if(Anum==0&&Bnum==0&&Dnum==0) return true; if(Anum==0&&Dnum==0&&Cnum==0) return true; if(Bnum==0&&Dnum==0&&Cnum==0) return true; return false; } bool check3(char a,char b){ for(int i=0;i<v.size();i++){ int x = v[i].x , y = v[i].y; if(ditu2[x][y]==a){ if(ditu2[x+1][y+1]==a&&ditu2[x+1][y]==b&&ditu2[x][y+1]==b) return true; return false; }else if(ditu2[x][y]==b){ if(ditu2[x+1][y+1]==b&&ditu2[x+1][y]==a&&ditu2[x][y+1]==a) return true; return false; } } } bool check2(){ if(Anum==2&&Bnum==2&&check3('A','B')) return true; if(Anum==2&&Cnum==2&&check3('A','C')) return true; if(Anum==2&&Dnum==2&&check3('A','D')) return true; if(Cnum==2&&Bnum==2&&check3('C','B')) return true; if(Dnum==2&&Bnum==2&&check3('D','B')) return true; if(Cnum==2&&Dnum==2&&check3('C','D')) return true; return false; } int xx[] = {1,0,0,-1}; int yy[] = {0,1,-1,0}; vector<node> BFS(int u,int o){ vector<node> vv; bool vis[13][13]; memset(vis,true,sizeof vis); queue<node> q; q.push(node(u,o,0)); vis[u][o] = false; while(!q.empty()){ node p = q.front();q.pop(); if(p.z==3) break; for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x = p.x , y = p.y; while(1){ x+= xx[i], y+= yy[i]; if(x<1||x>n||y<1||y>m) break; if(!vis[x][y]) break; vis[x][y]=false; if(ditu2[x][y]=='*') q.push(node(x,y,p.z+1)); else if(ditu2[x][y]==ditu2[u][o]) {vv.push_back(node(x,y,0));break;} else break; } } } return vv; } bool dfs(){ vector<node> vv; if(check()) return true; if(check2()) return false; for(int i=0;i<v.size();i++){ int x = v[i].x , y = v[i].y; if(ditu2[x][y]=='*') continue; char c = ditu2[x][y]; vv = BFS(x,y); for(int j=0;j<vv.size();j++){ int u = vv[j].x , o =vv[j].y; int a = (x-1)*m + y-1 ,b = (u-1)*m + o-1; ditu[a]='*' , ditu[b]='*'; if(mp[ditu]) {ditu[a]=c , ditu[b]=c;continue;} mp[ditu] = true; ditu2[x][y]='*' , ditu2[u][o]='*'; if(c=='A') Anum-=2;else if(c=='B') Bnum-=2;else if(c=='C') Cnum-=2;else Dnum-=2; if(dfs()) return true; if(c=='A') Anum+=2;else if(c=='B') Bnum+=2;else if(c=='C') Cnum+=2;else Dnum+=2; ditu2[x][y]=c , ditu2[u][o]=c; ditu[a]=c , ditu[b]=c; } } return false; } int main() { while(cin>>n>>m&&n&&m){ init(); if(Anum%2||Bnum%2||Cnum%2||Dnum%2) {puts("no");continue;} if(dfs()) puts("yes"); else puts("no"); } return 0; }
Cleaning Robot POJ - 2688
题意:清洁机器人之求在有障碍的多个脏地板的地图上,清理完需要最短的步数。答案不存在输出-1
算法:BFS预处理+DFS
思路:1.因为都要清理完,所以起点和脏地板都是必经,这题和上面的Prison Break HDU - 3681 很像,所以这里就直接BFS先预处理这些必经点的距离
2.DFS枚举所有顺序,然后用答案大小剪枝
易错点:这里数组空间要开大一点,我wrong了几次。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 12 13 int n,m; 14 char ditu[21][21]; 15 struct node{ 16 int x,y; 17 node() {} 18 node(int a,int b):x(a),y(b) {} 19 }po[12]; 20 int stNum,allNum; 21 int dist[21][21][21][21]; 22 int xx[]={1,-1,0,0}; 23 int yy[]={0,0,-1,1}; 24 25 void BFS(int a){ 26 queue<node> q; 27 int u = po[a].x, v = po[a].y; 28 q.push(node(u,v)); 29 dist[u][v][u][v] =0 ; 30 while(!q.empty()){ 31 node p = q.front();q.pop(); 32 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 33 int x = p.x + xx[i] , y = p.y + yy[i]; 34 if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||ditu[x][y]=='x') continue; 35 if(dist[u][v][x][y]>dist[u][v][p.x][p.y]+1){ 36 dist[u][v][x][y]=dist[u][v][p.x][p.y]+1; 37 q.push(node(x,y)); 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 43 void init(){ 44 allNum=0; 45 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 46 for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ 47 char ch = getchar();while(ch==' '||ch=='\n') ch=getchar(); 48 ditu[i][j]=ch; 49 if(ditu[i][j]=='*') po[allNum].x = i, po[allNum++].y = j; 50 else if(ditu[i][j]=='o') stNum = allNum, po[allNum].x = i, po[allNum++].y = j; 51 } 52 memset(dist,INF,sizeof dist); 53 for(int i=0;i<allNum;i++) BFS(i); 54 } 55 56 bool vis[12]; 57 int ans; 58 59 bool check(){ 60 for(int i=0;i<allNum;i++) if(!vis[i]) return false; 61 return true; 62 } 63 64 void DFS(int p,int a){ 65 if(a>=ans) return; 66 if(check()) {ans = min(ans,a);return ;} 67 int u = po[p].x, v =po[p].y; 68 for(int i=0;i<allNum;i++){ 69 if(i==p||vis[i]) continue; 70 vis[i] = true; 71 int x = po[i].x, y =po[i].y; 72 DFS(i,a+dist[u][v][x][y]); 73 vis[i]=false; 74 } 75 return ; 76 } 77 78 void show(){ 79 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 80 for(int j=0;j<m;j++) cout<<ditu[i][j]<<" ";cout<<endl;} 81 for(int i=0;i<allNum;i++){ 82 int u = po[i].x, v = po[i].y; 83 cout<<i<<" "<<u<<" "<<v<<endl; 84 for(int j=0;j<allNum;j++){ 85 int x = po[j].x, y = po[j].y; 86 cout<<dist[u][v][x][y]<<" "; 87 }cout<<endl; 88 } 89 } 90 91 int main() 92 { 93 while(cin>>m>>n&&n&&m){ 94 init();//show(); 95 memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); 96 vis[stNum] = true; 97 ans = INF; 98 DFS(stNum,0); 99 cout<<(ans==INF?-1:ans)<<endl; 100 } 101 return 0; 102 }
RobotPOJ - 1376
题意:有一个机器人,一个人就占着四个格子,然后有障碍物,本身有个方向。每个命令执行需要一秒,命令分为90度转向,或者在本来方向上前进1\2\3步。
算法:BFS
易错点:这题没什么思路,按着题目进行模拟BFS就过,该注意的就是,机器人每次操作,都只能90度转向,然后只能前进一步或者两步或者三步,只要遇到障碍物就不能前进了。判重直接三维,坐标+方向。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 12 13 int n,m; 14 int ditu[51][51]; 15 int sx,sy,tx,ty,fx; 16 int xx[]={-1,0,1,0}; 17 int yy[]={0,1,0,-1}; 18 int ffx[4][2] = {{1,3},{0,2},{1,3},{0,2}}; 19 bool vis[51][51][5]; 20 21 int check(string ch){ 22 if(ch.compare("north")==0) return 0; 23 else if(ch.compare("east")==0) return 1; 24 else if(ch.compare("south")==0) return 2; 25 return 3; 26 } 27 28 void init(){ 29 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 30 for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) cin>>ditu[i][j]; 31 string s; 32 cin>>sx>>sy>>tx>>ty>>s; 33 fx = check(s); 34 } 35 36 struct node{ 37 int x,y,z,step; 38 node(int a,int b,int c,int d):x(a),y(b),z(c),step(d) {} 39 bool checkIn(){ 40 return x==tx&&y==ty; 41 } 42 }; 43 44 bool check2(int x,int y){ 45 int x2 = x+1 , y2 = y, x3 = x, y3 = y+1, x4 = x+1, y4 = y+1; 46 if(x<=0||x>n||y<=0||y>m||ditu[x][y]==1) return true; 47 if(x2<=0||x2>n||y2<=0||y2>m||ditu[x2][y2]==1) return true; 48 if(x3<=0||x3>n||y3<=0||y3>m||ditu[x3][y3]==1) return true; 49 if(x4<=0||x4>n||y4<=0||y4>m||ditu[x4][y4]==1) return true; 50 return false; 51 } 52 53 int bfs(){ 54 memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); 55 queue<node> q; 56 vis[sx][sy][fx] = true; 57 q.push(node(sx,sy,fx,0)); 58 while(!q.empty()){ 59 node p = q.front();q.pop(); 60 if(p.checkIn()) return p.step; 61 //90度转向-------------------------------- 62 for(int i=0;i<2;i++) { 63 int fffx = ffx[p.z][i]; 64 if(vis[p.x][p.y][fffx]) continue; 65 vis[p.x][p.y][fffx]=true; 66 q.push(node(p.x,p.y,fffx,p.step+1)); 67 } 68 //移动-------------------------------- 69 for(int i=1;i<=3;i++){ 70 int x = p.x+i*xx[p.z], y= p.y+i*yy[p.z]; 71 if(check2(x,y)) break; 72 if(vis[x][y][p.z]) continue; 73 vis[x][y][p.z] = true; 74 q.push(node(x,y,p.z,p.step+1)); 75 } 76 } 77 return -1; 78 } 79 80 int main() 81 { 82 while(cin>>n>>m&&n&&m){ 83 init(); 84 cout<<bfs()<<endl; 85 } 86 return 0; 87 }
这题有意思的地方是,我一开始用Astar算法,用曼哈顿距离做评估函数,然后wrong了。测试数据一看,就是判重问题,因为存在障碍物,导致不完美答案先一步入队了。后面乱改一通还是ac了。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 12 13 int n,m; 14 int ditu[51][51]; 15 int sx,sy,tx,ty,fx; 16 int xx[]={-1,0,1,0}; 17 int yy[]={0,1,0,-1}; 18 int ffx[4][2] = {{1,3},{0,2},{1,3},{0,2}}; 19 int vis[51][51][5]; 20 21 int check(string ch){ 22 if(ch.compare("north")==0) return 0; 23 else if(ch.compare("east")==0) return 1; 24 else if(ch.compare("south")==0) return 2; 25 return 3; 26 } 27 28 void init(){ 29 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 30 for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) cin>>ditu[i][j]; 31 string s; 32 cin>>sx>>sy>>tx>>ty>>s; 33 fx = check(s); 34 } 35 36 struct node{ 37 int x,y,z,step,f; 38 node(int a,int b,int c,int d):x(a),y(b),z(c),step(d) { 39 f = d + abs(a-tx) + abs(b-ty); 40 } 41 bool operator < (const node &a) const{ 42 //if(f==a.f) return step>a.step; 43 return f>a.f; 44 } 45 bool checkIn(){ 46 return x==tx&&y==ty; 47 } 48 }; 49 50 bool check2(int x,int y){ 51 int x2 = x+1 , y2 = y, x3 = x, y3 = y+1, x4 = x+1, y4 = y+1; 52 if(x<=0||x>n||y<=0||y>m||ditu[x][y]==1) return true; 53 if(x2<=0||x2>n||y2<=0||y2>m||ditu[x2][y2]==1) return true; 54 if(x3<=0||x3>n||y3<=0||y3>m||ditu[x3][y3]==1) return true; 55 if(x4<=0||x4>n||y4<=0||y4>m||ditu[x4][y4]==1) return true; 56 return false; 57 } 58 59 int bfs(){ 60 memset(vis,INF,sizeof vis); 61 priority_queue<node> q; 62 vis[sx][sy][fx] = 0; 63 q.push(node(sx,sy,fx,0)); 64 int ans = INF; 65 while(!q.empty()){ 66 node p = q.top();q.pop(); 67 if(ans<=p.step) continue; 68 if(p.checkIn()) {ans = min(ans,p.step);continue;} 69 //90度转向-------------------------------- 70 for(int i=0;i<2;i++) { 71 int fffx = ffx[p.z][i]; 72 if(vis[p.x][p.y][fffx]!=INF&&vis[p.x][p.y][fffx]<=p.step+1) continue; 73 vis[p.x][p.y][fffx]=p.step+1; 74 q.push(node(p.x,p.y,fffx,p.step+1)); 75 } 76 //移动-------------------------------- 77 for(int i=1;i<=3;i++){ 78 int x = p.x+i*xx[p.z], y= p.y+i*yy[p.z]; 79 if(check2(x,y)) break; 80 if(vis[x][y][p.z]!=INF&&vis[x][y][p.z]<=p.step+1) continue; 81 vis[x][y][p.z] = p.step+1; 82 q.push(node(x,y,p.z,p.step+1)); 83 } 84 } 85 return ans==INF?-1:ans; 86 } 87 88 int main() 89 { 90 while(cin>>n>>m&&n&&m){ 91 init(); 92 cout<<bfs()<<endl; 93 } 94 return 0; 95 }
题意:给你一个固定的体积N,和层数M,并且蛋糕都是由圆柱体构成,下面一层R、H都要大于上面一层的;求蛋糕最大表面积Q(不算底部且除了Q外,其他数字都是正整数)
算法:数论+DFS
思路:说实话,不太懂怎么下手,算公式算很久把自己绕进去了。后面看了大神博客https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46295292/article/details/105853440,原来需要在最大值、最小值入手。
1.首先需要枚举最底层R1,这里因为R1>R2>...>RM,又因为这些R都是正整数,所以R1>=M;因为1^3+2^3+...+n^3=[n(n+1)/2]^2,所以通过已知N,当Rm=1,Hm=1,Rm-1=2,Hm-1=2类推的情况下,并且H1=M的时候 R1最大为sqrt( [4N-M^2*(M-1)^2]/(4*M));
2.已知R1,相同情况下同理,保持底部体积最大求H1,且H1>=M;
3.通过范围枚举R1,H1开启dfs(int r,int h , int floor, int v,int s)
4.dfs出队条件:1)f到了M层,判断v是否刚好为N,然后比较s,记录答案;2) 层数大于M或者dfs中s小于答案可以直接跳出 3)最小剩余体积 大于 N-v 4)最大剩余体积 小于 N-v

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 12 13 int N,M; 14 int ans=INF; 15 16 int minV(int f){ 17 f = M - f; 18 return f*f*(f+1)*(f+1)/4; 19 } 20 21 int maxV(int r,int h,int f){ 22 int v = 0; 23 for(int R = r-1 , H = h-1;f<M;f++,R--,H--){ 24 v+=R*R*H; 25 } 26 return v; 27 } 28 29 void dfs(int r,int h,int f,int v,int s){ 30 if(f==M&&v==N&&s<ans){ 31 ans = s;return ; 32 } 33 if(f>M||s>=ans) return ; 34 if(minV(f)+v>N) return; 35 if(maxV(r,h,f)+v<N) return; 36 for(int R = r - 1;R>=M-f;R--) 37 for(int H=h-1;H>=M-f;H--) dfs(R,H,f+1,v+R*R*H,s+2*R*H); 38 } 39 40 void run(){ 41 int ttem = (4*N-(M-1)*(M-1)*M*M); 42 for(int r=M;r*r<=ttem/(4*M);r++){ 43 for(int h =ttem/(4*r*r);h>=M;h--){ 44 dfs(r,h,1,r*r*h,r*r+2*r*h); 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 49 int main() 50 { 51 cin>>N>>M; 52 run(); 53 cout<<(ans==INF?0:ans)<<endl; 54 return 0; 55 }
聪明的打字员POJ - 1184
题意:给你一个6位数打乱顺序的密码,然后你可以有6种操作:光标下的数字和位置1或者6交换、光标下的数字加一,光标的左右移动
算法:BFS
思路:正常BFS会TLE,所以开始构思,一开始思考是Astar,然后发现情况很复杂,影响结果的因素太多了,大概就是两种情况,一种就是单纯位数上加减,第二种就是考虑加减之后通过交换操作来进行交换,但是光标移动会消耗操作数。实在想不到,看了别人的博客。http://www.manongjc.com/detail/23-somyumfbupbiuxd.html
因为移动光标只对交换有影响,而且交换操作局限在于交换两个数的距离,存在很多无效操作,所以博主思路在于尽可能减少光标移动操作,加减优先于交换,而交换也是因为更接近于答案才进行对位置1和6的交换,优先服务于对2~5位置的需求,从左到右,2满足了,在移动到3,3满足了再移动4,...最后到位置6,可以都在位置6实现位置1和6的满足。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 12 13 int s[7],t[7],ss,tt; 14 bool vis[1000001][6]; 15 16 int getNum(int a[7]){ 17 int ans = 0; 18 for(int i=0;i<6;i++) ans*=10,ans+=a[i]; 19 return ans; 20 } 21 22 struct node{ 23 int a[7],step,gb; 24 node(int b[],int c,int d){ 25 for(int i=0;i<6;i++) a[i]=b[i]; 26 step = c; 27 gb = d; 28 } 29 }; 30 31 void init(){ 32 cin>>ss; 33 int tem = ss; 34 for(int i=5;i>=0;i--){ 35 s[i]=tem%10;tem/=10; 36 } 37 cin>>tt; 38 tem = tt; 39 for(int i=5;i>=0;i--){ 40 t[i]=tem%10;tem/=10; 41 } 42 memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); 43 } 44 45 int bfs(){ 46 queue<node> q; 47 vis[ss][0]=true; 48 q.push(node(s,0,0)); 49 while(!q.empty()){ 50 node p = q.front();q.pop(); 51 int nn = getNum(p.a); 52 if(nn==tt) return p.step; 53 //swag0-------------------- 54 if(p.gb!=0){ 55 node u = p; 56 int sw = u.a[0] ;u.a[0] = u.a[p.gb] , u.a[p.gb] = sw; 57 sw = getNum(u.a); 58 if(!vis[sw][p.gb]){ 59 vis[sw][p.gb] = true; 60 u.step++; 61 q.push(u); 62 } 63 } 64 //swag1-------------------- 65 if(p.gb!=5){ 66 node u = p; 67 int sw = u.a[5] ;u.a[5] = u.a[p.gb] , u.a[p.gb] = sw; 68 sw = getNum(u.a); 69 if(!vis[sw][p.gb]){ 70 vis[sw][p.gb] = true; 71 u.step++; 72 q.push(u); 73 } 74 } 75 //up------------------------------ 76 if(p.a[p.gb]!=9&&p.a[p.gb]!=t[p.gb]){ 77 node u = p; 78 u.a[p.gb]++; 79 int sw = getNum(u.a); 80 if(!vis[sw][p.gb]){ 81 vis[sw][p.gb] = true; 82 u.step++; 83 q.push(u); 84 } 85 } 86 //down------------------------------ 87 if(p.a[p.gb]!=0&&p.a[p.gb]!=t[p.gb]){ 88 node u = p; 89 u.a[p.gb]--; 90 int sw = getNum(u.a); 91 if(!vis[sw][p.gb]){ 92 vis[sw][p.gb] = true; 93 u.step++; 94 q.push(u); 95 } 96 } 97 //left----------------------- 98 if(p.gb!=0&&(p.a[p.gb]==t[p.gb]||p.gb==5)&&!vis[nn][p.gb-1]){ 99 vis[nn][p.gb-1] = true; 100 q.push(node(p.a,p.step+1,p.gb-1)); 101 } 102 //right----------------------- 103 if(p.gb!=5&&(p.a[p.gb]==t[p.gb]||p.gb==0)&&!vis[nn][p.gb+1]){ 104 vis[nn][p.gb+1] = true; 105 q.push(node(p.a,p.step+1,p.gb+1)); 106 } 107 } 108 return -1; 109 } 110 111 int main() 112 { 113 init(); 114 cout<<bfs()<<endl; 115 return 0; 116 }
Paint on a WallHDU - 4012
题意:给你一个最大2*8的画图板,一次只能上色一个长方形(正方形也是长方形的一种),新的颜色会覆盖旧的颜色,问要最少上色多少次可以变成目标颜色。
算法:BFS+位压缩
思路:总要的是说三遍:和颜色无关!和颜色无关!和颜色无关!
因为你每一次上色都必须留下一个最终颜色块,不然你的上色就是无效操作,即每次操作至少会产生一个目标颜色块。
用1<<16的数来记录方格是否达到目标色块,然后BFS每一次都在没有达到目标色块的方格上,进行长方形扩展,寻找达到目标色块的方格 记录入队就行了。
参考大神博客:https://blog.csdn.net/hexianhao/article/details/50791187
想了很久,终于想明白了,单行可以不向左扩展,因为都是从左到右把颜色判断过了。双行必须向左扩展,因为我们都是以上面的颜色判断,但是下面的目标颜色可能会出现在前面,所以需要向前扩展寻找。
扩展知识:for(int j=tmp;j>0;j=tmp&(j-1) 这里循环列举 tmp 所有子集合。位运算小知识

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 12 13 int n; 14 bool vis[1<<16]; 15 char ditu[17]; 16 17 struct node{ 18 int s,step; 19 node(int ss,int stepp):s(ss),step(stepp) {}; 20 bool check(){ 21 return s==((1<<2*n)-1) ; 22 } 23 }; 24 25 int bfs(){ 26 memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); 27 queue<node> q; 28 vis[0]=true; 29 q.push(node(0,0)); 30 while(!q.empty()){ 31 node p = q.front();q.pop(); 32 if(p.check()) return p.step; 33 for(int i=0;i<2*n;i++){ 34 if(p.s&(1<<i)) continue; 35 int tmp=0; 36 for(int j=i;j<(i/n+1)*n;j++){ 37 if(p.s&(1<<j)) break; 38 if(ditu[i]==ditu[j]) tmp|=(1<<j); 39 } 40 for(int j=tmp;j>0;j=tmp&(j-1)){ 41 if(vis[j|p.s]) continue; 42 vis[j|p.s]=true; 43 q.push(node(j|p.s,p.step+1)); 44 } 45 if(i>=n||p.s&(1<<i+n)) continue; 46 tmp=0; 47 for(int j=i;j<n;j++){ 48 if(p.s&(1<<j)||p.s&(1<<j+n)) break; 49 if(ditu[i]==ditu[j]) tmp|=(1<<j); 50 if(ditu[i]==ditu[j+n]) tmp|=(1<<j+n); 51 } 52 for(int j=i-1;j>=0;j--){ 53 if(p.s&(1<<j)||p.s&(1<<j+n)) break; 54 if(ditu[i]==ditu[j+n]) tmp|=(1<<j+n); 55 } 56 for(int j=tmp;j>0;j=tmp&(j-1)){ 57 if(vis[j|p.s]) continue; 58 vis[j|p.s]=true; 59 q.push(node(j|p.s,p.step+1)); 60 } 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 65 void init(){ 66 cin>>n; 67 for(int i=0;i<2*n;i++){ 68 char ch=getchar();while(ch==' '||ch=='\n') ch=getchar(); 69 ditu[i]=ch; 70 } 71 //cout<<((1<<2*n)-1) <<endl; 72 //for(int i=0;i<2*n;i++) cout<<ditu[i]<<" ";cout<<endl; 73 } 74 75 int main() 76 { 77 int cas;cin>>cas; 78 for(int i=1;i<=cas;i++){ 79 init(); 80 cout<<"Case #"<<i<<": "<<bfs()<<endl; 81 } 82 return 0; 83 }
Knight's TripHDU - 3766
题意:马走日,一开始坐标(0,0),给你一个目标(x,y),问你走到这个目标最少要多少步?棋盘坐标最大上下正负百万
算法:规律题
思路:这题其实只要找一个一个界限内的答案就行了,正负改为绝对值就行了。正常预处理BFS,需要二维数组开到百万的平方,绝对会MLE。
所以这题乖乖找规律就行了。
最近没什么耐心....v-v....所以画图想了一下。
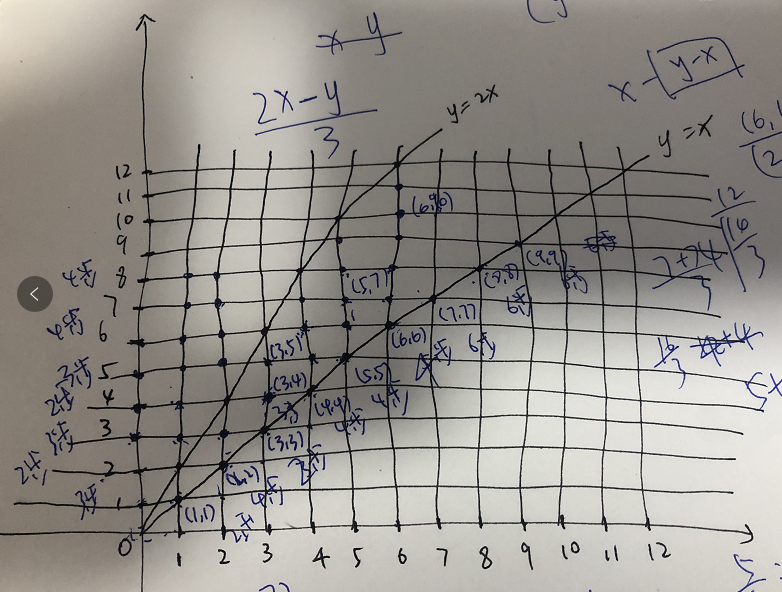
分析:1.这里通过x,y负数变正只考虑第一象限,然后将x,y大小比较置换,使得只考虑x=y线的上半部分;
2.然后我们分三种情况:
1)先考虑y=2x,因为这条线是从(0,0)只进行(1,2)操作形成的线,所以在这条线上的答案都是x
2)考虑y>2x,这部分是在线y=2x上面的,这部分的点可以先进行(-1,-2)操作进行下降接近(0,0),然后落在y轴上————这里操作数等于x,自己验证一下;然后都到达y轴,变成了(0,y-2x),剩下的就进行(1,-2)(-1,2)交替接近(0,0);就相当于(y-2x)/4,存在五种情况,1——落在了(0,0),答案就是(y-2x)/4; 2——然后特殊情况(0,1),这个点到(0,0)需要3步; 3——(0,5)到(0,0)也只需要3步,所以本来要落到(0,1)上面的点只要落到(0,5)就行了;4——落在了(0,2)这种2步;5——落在(0,3)3步
3)考虑y<2x,这部分也是通过(-1,-2)操作向下向左靠近(0,0),并且无一例外都掉在y=x线上,通过规律总结,下降操作数等于(y-x),会落在(2x-y,2x-y)的点上,然后y=x线上的点,到(0,0)是有规律的,除了(2,2)是特例,他是需要4步的,其他都是阶段性的递增,如图所示
易错点:这里输入我试了很多种办法都wrong了,然后学了其他博主的输入之后就ac了你们可以尝试一下

1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<string.h> 3 4 int run(int x,int y){ 5 if(x==2&&y==2) return 4; 6 if(x==0&&y==1) return 3; 7 if(y==2*x) return x; 8 if(y<2*x) return y-x + (2*x-y)/3*2 + ((2*x-y)%3?2:0); 9 return (y-2*x)/4*2+(y-2*x)%4+x; 10 } 11 12 int main() 13 { 14 char c[20]; 15 while(scanf("%s", c), strcmp(c, "END")) 16 { 17 int x, y; 18 int k; 19 sscanf(c, "%d", &x); 20 scanf("%d", &y); 21 if(x<0) x = -x; 22 if(y<0) y = -y; 23 if(y<x) {k=x, x=y, y=k;} 24 printf("%d\n", run(x,y)); 25 } 26 return 0; 27 }
SnakeHDU - 2605
题意:一条蛇在吃豆子,吃完豆子就会消失,且蛇身体不会变长,并且豆子之间存在关系,豆子必须在它的唯一关键豆子被吃掉的情况下才能被吃。蛇不能穿过自己的身体。
算法:状态压缩+BFS+剪枝
思路:和上面的题 Holedox MovingPOJ - 1324 思路一样。
判重,一开始我的想法是,vis[x][y][吃豆子状态][蛇身体状态],然后不出意外MLE了。后面我改用DFS,就TLE。然后尝试用DFS枚举所有吃豆子情况,然后每次吃豆子用Astar求最短路径,WrongAnser,所以这里中间吃豆子,最快并不是最优,因为存在蛇身状态的影响。
实在没办法,求助我的大学同学(大牛),然后他在我软磨硬泡之下,尝试了几次,后面被他AC了。他的思路就是,维护一个三维vis[x][y][吃豆子状态]最优,蛇身体状态则用其他思路弥补。
他的代码:

import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.*; public class Main { private static final FastReader cin = new FastReader(System.in); private static final int N = 21; private static final int ST = 1 << 7; private static final int WALL = 1; private static final int BEAN = 2; private static final int UNKNOWN = 4; private static final int HAS_BEAN_CAN_NOT_EAT = 5; private static final int HAS_BEAN_AND_EAT = 6; private static int H, W, L, K, R, n; private static final int[] key = new int[N * N]; private static final int[] next = new int[N * N]; private static final int[] beanX = new int[N]; private static final int[] beanY = new int[N]; private static final int[][] beanId = new int[N][N]; private static final int[][][] beanToAnywhere = new int[8][N][N]; private static final int[] dirX = new int[]{1, 0, 0, -1}; private static final int[] dirY = new int[]{0, 1, -1, 0}; private static final int[][][][] dp = new int[N][N][ST][8]; private static void init() { for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) { for (int st = 0; st < ST; ++st) { for (int k = 0; k <= K; ++k) { dp[i][j][st][k] = Integer.MAX_VALUE; } } } } for (int b = 0; b < K; ++b) { for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) { beanToAnywhere[b][i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE; } } } } private static void initBeanToAnywhere(int x, int y, int[][] dis, int step, int[][] map) { if (dis[x][y] <= step) return; dis[x][y] = step; for (int d = 0; d < 4; ++d) { int nx = x + dirX[d]; int ny = y + dirY[d]; if (nx <= 0 || ny <= 0 || nx > H || ny > W) continue; if (map[nx][ny] == WALL) continue; initBeanToAnywhere(nx, ny, dis, step + 1, map); } } private static int encodeBody(List<Integer> bodyX, List<Integer> bodyY) { int[] target = new int[L]; for (int i = 0; i < L - 1; ++i) { int x = bodyX.get(i); int y = bodyY.get(i); int nxtX = bodyX.get(i + 1); int nxtY = bodyY.get(i + 1); for (int d = 0; d < 4; ++d) { if (x + dirX[d] == nxtX && y + dirY[d] == nxtY) { target[i] = d; break; } } } int res = 0; for (int i = L - 2; i >= 0; --i) { res *= 4; res += target[i]; } return res; } private static List<Integer> decode(int begin, int code, int[] dir) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); res.add(begin); int pre = begin; for (int i = 1; i < L; ++i) { int d = code % 4; code /= 4; int now = pre + dir[d]; res.add(now); pre = now; } return res; } private static int move(int body, int d) { int nBody = body * 4 + (3 - d); int stSize = 1 << ((L - 1) * 2); return nBody & (stSize - 1); } private static boolean isBody(int headX, int headY, int x, int y, int code) { if (x == headX && y == headY) return true; int nowX = headX; int nowY = headY; for (int i = 1; i < L; ++i) { int d = code % 4; code /= 4; nowX += dirX[d]; nowY += dirY[d]; if (x == nowX && y == nowY) return true; } return false; } private static void checkEncode(List<Integer> bodyX, List<Integer> bodyY) { int code = encodeBody(bodyX, bodyY); List<Integer> decodeX = decode(bodyX.get(0), code, dirX); List<Integer> decodeY = decode(bodyY.get(0), code, dirY); for (int i = 0; i < L; ++i) { System.out.println(bodyX.get(i) + " " + bodyY.get(i) + " " + decodeX.get(i) + " " + decodeY.get(i)); // if(!Objects.equals(decodeX.get(i), bodyX.get(i))) {System.out.println("FUCK");break;} // if(!Objects.equals(decodeY.get(i), bodyY.get(i))) {System.out.println("FUCK");break;} } } public static final class Node { int x; int y; int st; int step; int body; int lastBeanId; Node(int x, int y, int st, int step, int body, int lastBeanId) { this.x = x; this.y = y; this.st = st; this.step = step; this.body = body; this.lastBeanId = lastBeanId; } public void show() { System.out.print(x + " " + y + " " + showSt(st) + " " + step + " " + showSt(body) + " ("); List<Integer> nxs = decodeBody(x, body, dirX); List<Integer> nys = decodeBody(y, body, dirY); for (int i = 0; i < L; ++i) System.out.print(nxs.get(i) + " " + nys.get(i) + ","); System.out.println(")"); } public long hash() { long res = 0; res |= body; // step 2800以内 res <<= 12; res |= step; // 吃豆状态 res <<= 7; res |= st; // 位置 400 以内 res <<= 9; res |= ((long) (x - 1) * W + y - 1); res <<= 3; res |= lastBeanId; return res; } public static Node decode(long code) { int lastBeanId = (int) (code & ((1L << 3) - 1)); code >>= 3; int posCode = (int) (code & ((1L << 9) - 1)); int x = (posCode / W) + 1; int y = (posCode % W) + 1; code >>= 9; int st = (int) (code & ((1L << 7) - 1)); code >>= 7; int step = (int) (code & ((1L << 12) - 1)); code >>= 12; int body = (int) code; return new Node(x, y, st, step, body, lastBeanId); } public int countSt() { int res = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 7; ++i) { if ((st & (1 << i)) > 0) res++; } return res; } } private static List<Integer> decodeBody(int begin, int code, int[] dir) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); res.add(begin); int pre = begin; for (int i = 1; i < L; ++i) { int d = code % 4; code /= 4; int now = pre + dir[d]; res.add(now); pre = now; } return res; } private static int bfs(int x, int y, int body, int[][] map) { Queue<Long> queue = new LinkedList<>(); Node start = new Node(x, y, 0, 0, body, 0); queue.add(start.hash()); dp[x][y][0][0] = 0; int maxSize = 0; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { maxSize = Math.max(maxSize, queue.size()); Node top = Node.decode(queue.poll()); if (top.st == (1 << K) - 1) { // System.out.println(maxSize); return top.step; } if (top.step > H * W * (top.countSt() + 1)) continue; // if (top.step - 2 > dp[top.x][top.y][top.st]) continue; // if (top.x == 3 && top.y == 7) // top.show(); for (int d = 0; d < 4; ++d) { int nx = top.x + dirX[d]; int ny = top.y + dirY[d]; int nSt = top.st; int nLastBeanId = top.lastBeanId; if (nx <= 0 || ny <= 0 || nx > H || ny > W) continue; int now = map[nx][ny]; if (now == WALL) continue; if (isBody(top.x, top.y, nx, ny, top.body)) continue; int eat = UNKNOWN; if (now == BEAN) { int id = beanId[nx][ny]; for (int i = 0; i < R; ++i) { if (next[i] == id && (((1 << key[i]) & top.st) == 0)) { eat = HAS_BEAN_CAN_NOT_EAT; break; } } if (eat == UNKNOWN) { eat = HAS_BEAN_AND_EAT; nSt = top.st | (1 << id); nLastBeanId = id; } } if (eat == HAS_BEAN_CAN_NOT_EAT) continue; int nStep = top.step + 1; boolean go = false; if (nStep < dp[nx][ny][nSt][nLastBeanId]) { dp[nx][ny][nSt][nLastBeanId] = nStep; go = true; } // 吃过豆, 并且上一个豆到当前点距离 int nowMinDis = dp[nx][ny][nSt][nLastBeanId]; int preToNowDis = beanToAnywhere[top.lastBeanId][nx][ny]; if (top.st != 0 && nStep < nowMinDis + L && preToNowDis < L) { go = true; } if (go) { int nBody = move(top.body, d); queue.add(new Node(nx, ny, nSt, nStep, nBody, nLastBeanId).hash()); } } } return Integer.MAX_VALUE; } /** * 入度判断环 */ private static boolean checkCircle() { int[] in = new int[K]; for (int i = 0; i < R; ++i) { in[next[i]]++; } Queue<Integer> root = new LinkedList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < K; ++i) { if (in[i] == 0) root.add(i); } while (!root.isEmpty()) { int nowRoot = root.poll(); for (int i = 0; i < R; ++i) { if (key[i] == nowRoot) { in[next[i]]--; if (in[next[i]] == 0) root.add(next[i]); } } } for (int i = 0; i < K; ++i) if (in[i] > 0) { return true; } return false; } /** * 判断可达 */ private static void checkReach(int x, int y, int[][] map, boolean[][] vis) { if (vis[x][y]) return; vis[x][y] = true; for (int d = 0; d < 4; ++d) { int nx = x + dirX[d]; int ny = y + dirY[d]; if (nx <= 0 || ny <= 0 || nx > H || ny > W) continue; if (map[nx][ny] == WALL) continue; checkReach(nx, ny, map, vis); } } private static void solve() { H = cin.nextInt(); W = cin.nextInt(); L = cin.nextInt(); K = cin.nextInt(); R = cin.nextInt(); n = cin.nextInt(); int[][] map = new int[21][21]; List<Integer> bodyX = new ArrayList<>(); List<Integer> bodyY = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < L; ++i) { int x = cin.nextInt(); int y = cin.nextInt(); bodyX.add(x); bodyY.add(y); } for (int i = 0; i < K; ++i) { int x = cin.nextInt(); int y = cin.nextInt(); beanX[i] = x; beanY[i] = y; map[x][y] = BEAN; beanId[x][y] = i; } for (int i = 0; i < R; ++i) { key[i] = cin.nextInt() - 1; next[i] = cin.nextInt() - 1; } for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int x = cin.nextInt(); int y = cin.nextInt(); map[x][y] = WALL; } init(); if (checkCircle()) { System.out.println(-1); return; } // 判断可达 boolean[][] vis = new boolean[21][21]; checkReach(bodyX.get(0), bodyY.get(0), map, vis); // 预处理豆到地图任一点距离 for (int i = 0; i < K; ++i) { initBeanToAnywhere(beanX[i], beanY[i], beanToAnywhere[i], 0, map); } for (int i = 0; i < K; ++i) { if (!vis[beanX[i]][beanY[i]]) { System.out.println(-1); return; } } int code = encodeBody(bodyX, bodyY); int ans = bfs(bodyX.get(0), bodyY.get(0), code, map); System.out.println(ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : ans); } public static void main(String[] args) { int t = cin.nextInt(); for (int tt = 0; tt < t; ++tt) solve(); } /** * 打印状态压缩 */ private static String showSt(int st) { StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0; i < 2 * L; ++i) { if ((st & (1 << i)) == 0) res.append("0"); else res.append("1"); } return res.toString(); } private static class FastReader { private InputStream stream; private byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; private int curChar; private int numChars; FastReader(InputStream stream) { this.stream = stream; } int read() { if (numChars == -1) { throw new InputMismatchException(); } if (curChar >= numChars) { curChar = 0; try { numChars = stream.read(buf); } catch (IOException e) { throw new InputMismatchException(); } if (numChars <= 0) { return -1; } } return buf[curChar++]; } int nextInt() { int c = read(); while (isSpaceChar(c)) { c = read(); } int sgn = 1; if (c == '-') { sgn = -1; c = read(); } int res = 0; do { if (c < '0' || c > '9') { throw new InputMismatchException(); } res *= 10; res += c - '0'; c = read(); } while (!isSpaceChar(c)); return res * sgn; } public long nextLong() { long ret = 0; int c = read(); while (c <= ' ') { c = read(); } boolean neg = (c == '-'); if (neg) { c = read(); } do { ret = ret * 10 + c - '0'; } while ((c = read()) >= '0' && c <= '9'); if (neg) { return -ret; } return ret; } public String next() { int c = read(); while (isSpaceChar(c)) { c = read(); } StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder(); do { res.appendCodePoint(c); c = read(); } while (!isSpaceChar(c)); return res.toString(); } boolean isSpaceChar(int c) { return c == ' ' || c == '\n' || c == '\r' || c == '\t' || c == -1; } } }
我看了他的代码,以下是我的理解:
存在一个情况,就是他不是吃到豆子最快,但是因为他的吃豆子蛇的状态,导致他到下一个豆子的后续步数优于最快吃到豆子的状况;所以只要步数不多于最快吃到豆子的最坏情况下,都可以入队进行角逐答案。
1.蛇身体之所以可以影响答案,在于蛇身会阻碍蛇某个方向前进,所以如果蛇可以掉头了,他所有方向都可以去了
2.理想情况下,蛇只需要走蛇身步数就可以掉头
3.为了减少存储,所以只让蛇在豆子蛇身范围内进行掉头,所有其他位置 蛇只要前进就行了。
4.这里理想情况下,蛇在最快吃到豆子之后,蛇身步数,离豆子蛇身范围内可以变换成任何形态(存在石头阻碍情况下,无法实现,但是测试数据没有)
5.如果你在最优情况外,在豆子附件蛇身范围内,小于蛇身步数,皆可入队,这里就是考虑到其他蛇身状态下,对最终答案的影响。
易错点:这里豆子会成环,导致成环豆子都无法被吃;然后这里为了节省空间,将node的所有东西 压缩到一个longlong里面。

#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <cstdio> #include <map> using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; int H,W,snakeNum,beanNum,R,stNum; int snakeHeadX,snakeHeadY,snakeBody; int ditu[21][21]; int dis[8][21][21];//预处理每个豆子到各点距离 int vis[21][21][1<<7];//三维 坐标+吃豆子状态 int xx[] = {0,1,0,-1}; int yy[] = {1,0,-1,0}; //豆子坐标 + 关键豆子ID struct bean{ int x,y,key; bean() {} bean(int a,int b,int c):x(a),y(b),key(c) {} }beans[8]; //预处理标记每个豆子蛇身长度范围内可达的点----------------- struct tmtp{ int x,y; tmtp(int a,int b):x(a),y(b) {}; }; void BFSFB(int b){ dis[b][beans[b-1].x][beans[b-1].y]=0; queue<tmtp> q; q.push(tmtp(beans[b-1].x,beans[b-1].y)); while(!q.empty()){ tmtp p = q.front();q.pop(); if(dis[b][p.x][p.y]>=snakeNum) continue; for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x = p.x + xx[i] , y = p.y +yy[i]; if(x<=0||x>H||y<=0||y>W||ditu[x][y]==-2) continue; if(dis[b][x][y]<=dis[b][p.x][p.y]+1) continue; dis[b][x][y]=dis[b][p.x][p.y]+1; q.push(tmtp(x,y)); } } } //各种输入和预处理----------------------------------------- void init(){ cin>>H>>W>>snakeNum>>beanNum>>R>>stNum; cin>>snakeHeadX>>snakeHeadY; int a=snakeHeadX,b=snakeHeadY,c,d; snakeBody=0; for(int i=0;i<snakeNum-1;i++){ cin>>c>>d; snakeBody<<=2; if(c-a==0&&d-b==1) snakeBody+=0; else if(c-a==1&&d-b==0) snakeBody+=1; else if(c-a==0&&d-b==-1) snakeBody+=2; else if(c-a==-1&&d-b==0) snakeBody+=3; a=c,b=d; } memset(ditu,-1,sizeof ditu); for(int i=0;i<beanNum;i++){ cin>>a>>b; ditu[a][b]=i; beans[i].x=a,beans[i].y=b;beans[i].key=-1; } for(int i=0;i<R;i++){ cin>>a>>b; beans[b-1].key=a-1; } for(int i=0;i<stNum;i++){ cin>>a>>b; ditu[a][b]=-2; } memset(dis,INF,sizeof dis); for(int i=0;i<beanNum;i++){ BFSFB(i+1); } } //有一个状态压缩函数和一个状态解压函数----------------------- struct node{ int x,y,snake,state,lastBeanId,step; node(int a,int b,int c,int d,int e,int f):x(a),y(b),snake(c),state(d),lastBeanId(e),step(f) {} node(long long tmt){ lastBeanId = (int) (tmt % (1L<<4)); tmt = tmt >>4; step = (int) (tmt % (1L<<12)); tmt = tmt >>12; state =(int) ( tmt % (1L<<7)); tmt = tmt>>7; snake = (int) (tmt % (1L<<14)); tmt = tmt>>14; y = (int) (tmt % 21),x = (int) (tmt / 21); } long long makeHash(){ long long ans = x*21+y; ans <<= 14;ans += snake; ans <<= 7;ans += state; ans <<= 12;ans+=step; ans <<= 4;ans+=lastBeanId; return ans; } }; //判断是否碰到蛇身------------------------------------ bool checkXY(int Sx,int Sy,int snake,int tx,int ty){ int w = (1<<((snakeNum-2)*2)); int t = snakeNum-1; while(t--){ int tmp = (snake / w)%4; Sx+=xx[tmp],Sy+=yy[tmp]; if(Sx==tx&&Sy==ty) return true; w>>=2; } return false; } //答案搜索---------------------------------- int BFS(){ queue<long long> q; memset(vis,INF,sizeof vis); vis[snakeHeadX][snakeHeadY][0]=0; node start = node(snakeHeadX,snakeHeadY,snakeBody,0,0,0); long long tnt = start.makeHash(); q.push(tnt); while(!q.empty()){ long long pNum = q.front();q.pop(); node p = node(pNum); if((1<<beanNum)-1 == p.state) return p.step; if(p.step>H*W*beanNum) continue; for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ int x = p.x + xx[i] , y = p.y +yy[i]; if(x<=0||x>H||y<=0||y>W||ditu[x][y]==-2) continue; if( ditu[x][y] != -1 && beans[ditu[x][y]].key != -1&&((1<<beans[ditu[x][y]].key)&p.state)==0) continue; if(checkXY(p.x,p.y,p.snake,x,y)) continue; int state = p.state, lastBeanId = p.lastBeanId; if(ditu[x][y] != -1&&((1<<ditu[x][y])&p.state)==0) {state |= (1<<ditu[x][y]);lastBeanId = ditu[x][y] +1;} bool flag = true; //维护步数最优------------------------------ //这里如果开思维,加上蛇的身体,1<<14-----就会MLE---------------- if(vis[x][y][state]>p.step+1) { vis[x][y][state]=p.step+1; flag = false; } //蛇身体之所以可以影响答案,在于蛇身会阻碍蛇某个方向前进,所以如果蛇可以掉头了,他所有方向都可以去了 //理想情况下,蛇只需要走蛇身步数就可以掉头 //为了减少存储,所以只让蛇在豆子蛇身范围内进行掉头 //这里理想情况下,蛇在最快吃到豆子之后,蛇身步数,离豆子蛇身范围内可以变换成任何形态(存在石头阻碍情况下,无法实现,但是测试数据没有) if(state!=0&&(p.step+1<vis[x][y][state]+snakeNum)&&dis[lastBeanId][x][y]<snakeNum) flag = false; if(flag) continue; int body = p.snake >>2 ; if(i==0) body+=(2<<((snakeNum-2)*2)); else if(i==1) body+=(3<<((snakeNum-2)*2)); else if(i==2) body+=(0<<((snakeNum-2)*2)); else body += (1<<((snakeNum-2)*2)); node tmp = node(x,y,body,state,lastBeanId,p.step+1); long long tnt = tmp.makeHash(); q.push(tnt); } } return -1; } //判断豆子是否成环 bool vis2[8]; bool ok(int x){ vis2[x]=true; int key = beans[x].key; if(key==-1) return false; if(vis2[key]) return true; return ok(key); } int main() { int _;cin>>_; while(_--){ init(); bool flag = false; for(int i=0;i<beanNum;i++){ memset(vis2,false,sizeof vis2); if(ok(i)) {flag=true;break;} } if(flag) puts("-1"); else cout<<BFS()<<endl; } return 0; }
FreeOpenHDU - 3121
题意:给你男生 女生 宠物进行配对,条件:男生和女生必须相互喜欢并且他们也要同时喜欢同一个宠物;(男生、女生、宠物只能配对一次)求最大能配对多少对?
算法:二分最大匹配+IDAstar
思路:一开始看到这题,就想到二分最大匹配;然后这里是三分图,所以就想到最大流;但是经典三分图匹配,是中间点拆分,然后左右两个点集合是没有关系要求的,这题不同,他们三方都互相牵制;女生和男生要互相喜欢,男生和女生要喜欢同一只宠物。
然后我就开始找三分图最大匹配看,有没有其他解决办法。然后百度到一个人问到类似的问题https://ask.csdn.net/questions/7763032

如上图所示,如果员工只要吃到喜欢的盒饭和饮料就行,只要将员工在中间拆点,然后最大流就可以解决。但是存在员工只喜欢特定的盒饭搭配,比如吃盒饭2只配饮料5、吃盒饭3只配饮料4。
这个回答,让我找到了方向,立马按他的想法,进行dfs深搜,然后不出意外,TLE了。
实在想不到办法的我,看了别人的博客,https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_30610755/article/details/94995863
他的思路就是,使用IDAstar算法,limit由三个集合最小量开始,逐1递减。启发判断函数,通过三次二分图最大匹配(女男、女宠、男宠)预估接下来的最大匹配数,如果其中一个求出的最大匹配加上 步数小于limit则跳出,让limit-=1;答案最大匹配数一定小于三个二分最大匹配的最小值,所以如果其中一个小于limit,表示当前limit不成立,不需要往下深搜了。
易错点:就算用上博主的IDAstar算法,还是容易TLE,然后我照着博主代码慢慢改自己的,然后在一个判断上,我把他分成两份了,但是其实合在一起一次判断会更快一点。

#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <cstdio> #include <map> using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; int g,b,p,G,B,P; int gb[21],gp[21],bp[21]; int gg[21],gr[21]; int ans; bool cmp(const int &a,const int &b){ return gr[a] < gr[b]; } void init(){ cin>>g>>b>>p; ans = min(g,b);ans = min(ans,p); G=0,B=0,P=0; memset(gb,0,sizeof gb); for(int i=0;i<g;i++){ for(int j=0;j<b;j++){ int t;cin>>t; if(t) gb[i] |= (1<<j); } } memset(gp,0,sizeof gp); for(int i=0;i<g;i++){ for(int j=0;j<p;j++){ int t;cin>>t; if(t) gp[i] |= (1<<j); } } memset(bp,0,sizeof bp); for(int i=0;i<b;i++){ for(int j=0;j<p;j++){ int t;cin>>t; if(t) bp[i] |= (1<<j); } } memset(gr,0,sizeof gr); for(int i=0;i<g;i++){ gg[i]=i; for(int j=0;j<b;j++)if(gb[i]&(1<<j)){ if(!(gp[i]&bp[j])) gb[i]^=(1<<j); else gr[i]++; } } sort(gg,gg+g,cmp); } int linker[21]; int vis; bool dfsFGB(int u){ for(int v=0;v<b;v++){ if(B&(1<<v)) continue; if(vis&(1<<v)) continue; if(!(gb[u]&(1<<v))) continue; vis |= (1<<v); if(linker[v] ==-1 || dfsFGB(linker[v])){ linker[v]=u;return true; } } return false; } bool dfsFGP(int u){ for(int v=0;v<p;v++){ if(P&(1<<v)) continue; if(vis&(1<<v)) continue; if(!(gp[u]&(1<<v))) continue; vis |= (1<<v); if(linker[v] ==-1 || dfsFGP(linker[v])){ linker[v]=u;return true; } } return false; } bool dfsFBP(int u){ for(int v=0;v<p;v++){ if(P&(1<<v)) continue; if(vis&(1<<v)) continue; if(!(bp[u]&(1<<v))) continue; vis |= (1<<v); if(linker[v] ==-1 || dfsFBP(linker[v])){ linker[v]=u;return true; } } return false; } bool forLimit(int step,int gN){ int res = 0; memset(linker,-1,sizeof linker); for(int u=gN;u<g;u++){ vis=0; if(dfsFGB(gg[u])) res++; if(res+step>=ans) break; } if(res+step<ans) return true; res = 0; memset(linker,-1,sizeof linker); for(int u=gN;u<g;u++){ vis=0; if(dfsFGP(gg[u])) res++; if(res+step>=ans) break; } if(res+step<ans) return true; res = 0; memset(linker,-1,sizeof linker); for(int u=0;u<b;u++){ if(B&(1<<u)) continue; vis=0; if(dfsFBP(u)) res++; if(res+step>=ans) break; } if(res+step<ans) return true; return false; } bool IDAstar(int step,int gN){ if(g-gN+step<ans) return false; if(step==ans) return true; if(forLimit(step,gN)) return false; for(int ii=gN;ii<g;ii++){ int i = gg[ii]; G |= (1<<i); for(int j=0;j<b;j++){ if(B&(1<<j)) continue; if(!(gb[i]&(1<<j))) continue; B |= (1<<j); for(int z=0;z<p;z++){ if(P&(1<<z)) continue; if(gp[i]&bp[j]&(1<<z)){ P |= (1<<z); if(IDAstar(step+1,ii+1)) return true; P ^= (1<<z); } } B ^= (1<<j); } G ^= (1<<i); } return false; } int main() { int _;cin>>_; while(_--){ init(); while(1){ if(IDAstar(0,0)) break; if(--ans==0) break; } cout<<ans<<endl; } return 0; }
Unblock MeHDU - 3900
题意:关羽走华容道小游戏,地图固定6*6,然后只有竖的和横的矩形,面积只有2或者3,竖的只能竖着走,横着只能横着走,不能重叠。
算法:状压+bfs
思路:一个矩形,只需要记录一个横竖状态、一个固定行走的行或者列、一个长度、和一个偏移量(只有这个变量是改变的,偏移量在0~4或者0~3之间,我这里是左上角坐标)。然后判重,就是直接记录地图信息,其实这里只要将偏移量压缩到一个longlong里面就行了,因为偏移量在0~4或者0~3之间,所以只要开3位记录当个矩形,这里6*6/2=18(个),最多18个矩形,18*3=54位,所以开个longlong够了。
易错点:判断是否可行,这里,分两部分,竖的就是上下、横的就是左右,判断同类型矩形是否挡道,然后不同类型是否交叉;然后就是判断是否得出答案,这里记得加一,因为要划出去。

#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <cstdio> #include <map> #include <set> using namespace std; #define LL long long const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; int n,red; LL s; struct node{ bool type;//true:竖的 int pos,len; node() {}; node(bool a,int b,int c):type(a),pos(b),len(c) {}; }blocks[19]; void init(){ s = 0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ int a,b,c,d,e;cin>>a>>b>>c>>d>>e; if(b==d){ blocks[a] = node(true,b,e-c); s |= (LL)c<<a*3; }else{ blocks[a] = node(false,c,d-b); s |= (LL)b<<a*3; } } cin>>red; } int cal(LL s,int id){ return (int)((s&(7LL<<id*3))>>id*3); } bool getAns(LL s){ int rl = cal(s,red),rr = rl + blocks[red].len; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ if(i==red) continue; int il = cal(s,i) , ir = il + blocks[i].len; if(!blocks[i].type&&blocks[i].pos==2&&il>rr) return false; if(!blocks[i].type) continue; if(blocks[i].pos<=rr) continue; if(il>2||ir<2) continue; return false; } return true; } bool check(LL s,int id,int ll,int rr){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ if(i==id) continue; int il = cal(s,i) , ir = il + blocks[i].len; if(blocks[i].type==blocks[id].type){ if(blocks[i].pos!=blocks[id].pos) continue; if(il>rr||ir<ll) continue; return true; }else if(ll<=blocks[i].pos&&rr>=blocks[i].pos&&il<=blocks[id].pos&&ir>=blocks[id].pos) return true; } return false; } LL change(LL s,int id,int l){ return s&(~(7LL<<3*id))|((LL)l<<3*id); } int BFS(){ queue<pair<LL,int>> q; set<LL> st; st.insert(s); q.push(make_pair(s,0)); while(!q.empty()){ LL p = q.front().first; int step = q.front().second; q.pop(); if(getAns(p)) return step+1; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ int il = cal(p,i) , ir = il + blocks[i].len; //向左或者向上 for(int j=il-1;j>=0;j--){ if(check(p,i,j,j+blocks[i].len)) break; LL u = change(p,i,j); if(st.find(u)!=st.end()) continue; st.insert(u); q.push(make_pair(u,step+1)); } //向右或者向下 for(int j=il+1;j+blocks[i].len<=5;j++){ if(check(p,i,j,j+blocks[i].len)) break; LL u = change(p,i,j); if(st.find(u)!=st.end()) continue; st.insert(u); q.push(make_pair(u,step+1)); } } } } int main() { while(cin>>n){ init(); cout<<BFS()<<endl; } return 0; }
Push BoxHDU - 1732
题意:推箱子,有三个箱子和三个洞,求将箱子推到洞口的最小步数
算法:BFS
思路:判重记录人+3个箱子的坐标;
易错点:就是这里洞口人是可以走过去的,然后箱子过了洞口还能推,自己想复杂了,因为题目说人只能走空地,我就以为洞口不可以走,所以人也不可能把箱子推出洞口,看了别人代码才发现错误的。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 #include <set> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 #define LL long long 13 14 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 15 16 int n,m; 17 char ditu[8][8]; 18 bool vis[8][8][8][8][8][8][8][8]; 19 int xx[]={1,0,0,-1}; 20 int yy[]={0,1,-1,0}; 21 22 struct node{ 23 int x[4],y[4],step; 24 bool check(){ 25 for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ 26 if(ditu[x[i]][y[i]]!='@') return false; 27 } 28 return true; 29 } 30 void show(){ 31 for(int i=0;i<4;i++) cout<<x[i]<<" "<<y[i]<<endl; 32 cout<<step<<endl; 33 } 34 }Start; 35 36 void init(){ 37 int num = 0; 38 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 39 for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ 40 char ch=getchar();while(ch==' '||ch=='\n') ch=getchar(); 41 if(ch=='X') Start.x[3] = i , Start.y[3] = j , ditu[i][j] = '.'; 42 else if(ch=='*') Start.x[num] = i , Start.y[num++] = j , ditu[i][j] = '.'; 43 else ditu[i][j] = ch; 44 }Start.step=0; 45 } 46 47 int bfs(){ 48 queue<node> q; 49 memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); 50 vis[Start.x[0]][Start.y[0]][Start.x[1]][Start.y[1]][Start.x[2]][Start.y[2]][Start.x[3]][Start.y[3]]=true; 51 q.push(Start); 52 while(q.size()){ 53 node p = q.front();q.pop(); 54 if(p.check()) return p.step; 55 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 56 node u = p;u.step++; 57 u.x[3] += xx[i] , u.y[3] += yy[i]; 58 if(u.x[3]<0||u.x[3]>=n||u.y[3]<0||u.y[3]>=m||ditu[u.x[3]][u.y[3]]=='#') continue; 59 int flag = 0; 60 for(int j=0,out = 1;j<3&&out;j++){ 61 if(u.x[j]==u.x[3]&&u.y[j]==u.y[3]){ 62 out = 0; 63 u.x[j] += xx[i] , u.y[j] += yy[i]; 64 if(u.x[j]<0||u.x[j]>=n||u.y[j]<0||u.y[j]>=m||ditu[u.x[j]][u.y[j]]=='#') {flag=1;break;} 65 for(int z=0;z<3;z++)if(z!=j){ 66 if(u.x[z]==u.x[j]&&u.y[z]==u.y[j]) {flag=1;break;} 67 } 68 } 69 } 70 if(flag) continue; 71 if(vis[u.x[0]][u.y[0]][u.x[1]][u.y[1]][u.x[2]][u.y[2]][u.x[3]][u.y[3]]) continue; 72 vis[u.x[0]][u.y[0]][u.x[1]][u.y[1]][u.x[2]][u.y[2]][u.x[3]][u.y[3]]=true; 73 q.push(u); 74 } 75 } 76 return -1; 77 } 78 79 int main() 80 { 81 while(cin>>n>>m){ 82 init(); 83 cout<<bfs()<<endl; 84 } 85 return 0; 86 }
Traveling CubeHDU - 2913
题意:另一种推箱子,这种推箱子是,箱子每次都会转动。箱子每一个面都有一个颜色,六种彩色,地图上有唯一的这六种彩色地板各六个,和多个白色或者黑色的地板,箱子可以随意进出白色地板,不能进入黑色地板,进入彩色地板的条件是,进入到的时候,箱子顶上的颜色要与地板颜色一样,并且彩色地板只能进一次。而且题目会给出一个顺序,问按顺序依次进入这些彩色地板的最小步数
算法:BFS + 状压
思路:这里就是模拟题,思考上下左右转,颜色会怎么变化就好了。最主要是判重的状态压缩。我一开始直接开4维[x][y][543210][7] 直接编译不了,数组开不了那么大,后面少记录一个颜色[x][y][54321][7],直接MLE。后面看了别人代码,写成map<LL,bool> vis[x][y][7] 就过了。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 #include <set> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 #define LL long long 13 14 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 15 16 //543210 r-0 c-1 g-2 m-3 b-4 y-5 17 int n,m,Sx,Sy; 18 int tS[6]; 19 int ditu[31][31];//w- -1 k- -2 20 int xx[]={0,0,-1,1}; 21 int yy[]={1,-1,0,0}; 22 23 struct node{ 24 int x,y,state,nowID,step; 25 node(int a,int b,int c,int d,int e):x(a),y(b),state(c),nowID(d),step(e) {}; 26 void show(){ 27 cout<<x<<' '<<y<<' '<<state<<' '<<nowID<<' '<<step<<endl; 28 } 29 }; 30 31 int num[6]; 32 void getNum(int x){ 33 int sum = 0; 34 for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ 35 num[i] = x %10;x/=10; 36 sum+=num[i]; 37 }num[5] = 15 - sum; 38 } 39 int change(int x,int i){ 40 if(i==0) return num[0]*10000 + num[3]*1000 + num[2]*100 + num[4]*10 + num[5]; 41 if(i==1) return num[1]*10000 + num[3]*1000 + num[2]*100 + num[5]*10 + num[4]; 42 if(i==2) return num[4]*10000 + num[1]*1000 + num[0]*100 + num[2]*10 + num[3]; 43 return num[4]*10000 + num[0]*1000 + num[1]*100 + num[3]*10 + num[2]; 44 } 45 46 void init(){ 47 memset(ditu,-1,sizeof ditu); 48 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 49 for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ 50 char ch=getchar();while(ch=='\n'||ch==' ') ch=getchar(); 51 if(ch=='#') Sx = i,Sy = j; 52 else if(ch=='k') ditu[i][j] = -2;else if(ch=='r') ditu[i][j] = 0;else if(ch=='c') ditu[i][j] = 1; 53 else if(ch=='g') ditu[i][j] = 2;else if(ch=='m') ditu[i][j] = 3;else if(ch=='b') ditu[i][j] = 4;else if(ch=='y') ditu[i][j] = 5; 54 } 55 for(int i=0;i<6;i++){ 56 char ch=getchar();while(ch=='\n'||ch==' ') ch=getchar(); 57 if(ch=='r') tS[i] = 0; 58 else if(ch=='c') tS[i] = 1; 59 else if(ch=='g') tS[i] = 2; 60 else if(ch=='m') tS[i] = 3; 61 else if(ch=='b') tS[i] = 4; 62 else tS[i] = 5; 63 } 64 } 65 66 int bfs(){ 67 map<LL, bool> vis[31][31][7]; 68 queue<node> q; 69 vis[Sx][Sy][0][43210] = true; 70 q.push(node(Sx,Sy,43210,0,0)); 71 72 while(q.size()){ 73 node p = q.front();q.pop(); 74 if(p.nowID==6) return p.step; 75 getNum(p.state); 76 int mubic = tS[p.nowID]; 77 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 78 int x = p.x + xx[i] , y = p.y + yy[i]; 79 if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||ditu[x][y]==-2) continue; 80 int state = change(p.state,i); 81 int top = state % 10; 82 int nowID = p.nowID; 83 if(ditu[x][y]!=-1){ 84 if(ditu[x][y]!=mubic||top != mubic) continue; 85 else nowID = p.nowID + 1; 86 } 87 if(vis[x][y][nowID][state]) continue; 88 vis[x][y][nowID][state] = true; 89 q.push(node(x,y,state,nowID,p.step+1)); 90 } 91 } 92 93 return -1; 94 } 95 96 int main() 97 { 98 while(cin>>m>>n&&n&&m){ 99 init(); 100 int ans = bfs(); 101 if(ans==-1) puts("unreachable"); 102 else cout<<ans<<endl; 103 } 104 return 0; 105 }
优化:这里看了其他人代码,其实还可以优化,颜色就只有6种,6个不同位置,所以6进制就行。并且因为箱子颜色是固定的,所以只要记录3个面就行了。颜色划分0~5,所以,状态最大只需要5*36+4*6+3=207 所以vis只需要开到 vis[31][31][208][7]

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 #include <set> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 #define LL long long 13 14 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 15 16 // r-0 c-5 g-2 m-3 b-1 y-4 17 int n,m,Sx,Sy; 18 int tS[6]; 19 int ditu[31][31];//w- -1 k- -2 20 bool vis[31][31][208][7]; 21 int xx[]={0,0,-1,1}; 22 int yy[]={1,-1,0,0}; 23 24 struct node{ 25 int x,y,state,nowID,step; 26 node(int a,int b,int c,int d,int e):x(a),y(b),state(c),nowID(d),step(e) {}; 27 void show(){ 28 cout<<x<<' '<<y<<' '<<state<<' '<<nowID<<' '<<step<<endl; 29 } 30 }; 31 32 int num[6]; 33 void getNum(int x){ 34 num[0] = x%6; x/=6; 35 num[1] = x%6; x/=6; 36 num[2] = x; 37 num[3] = 5 - num[2]; 38 num[4] = 5 - num[1]; 39 num[5] = 5 - num[0]; 40 } 41 int change(int i){ 42 if(i==0) return num[2]*36 + num[0]*6 + num[4]; 43 if(i==1) return num[2]*36 + num[5]*6 + num[1]; 44 if(i==2) return num[0]*36 + num[1]*6+ num[3]; 45 return num[5]*36 + num[1]*6 + num[2]; 46 } 47 48 void init(){ 49 memset(ditu,-1,sizeof ditu); 50 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 51 for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ 52 char ch=getchar();while(ch=='\n'||ch==' ') ch=getchar(); 53 if(ch=='#') Sx = i,Sy = j; 54 else if(ch=='k') ditu[i][j] = -2;else if(ch=='r') ditu[i][j] = 0;else if(ch=='c') ditu[i][j] = 5; 55 else if(ch=='g') ditu[i][j] = 2;else if(ch=='m') ditu[i][j] = 3;else if(ch=='b') ditu[i][j] = 1;else if(ch=='y') ditu[i][j] = 4; 56 } 57 for(int i=0;i<6;i++){ 58 char ch=getchar();while(ch=='\n'||ch==' ') ch=getchar(); 59 if(ch=='r') tS[i] = 0; 60 else if(ch=='c') tS[i] = 5; 61 else if(ch=='g') tS[i] = 2; 62 else if(ch=='m') tS[i] = 3; 63 else if(ch=='b') tS[i] = 1; 64 else tS[i] = 4; 65 } 66 } 67 68 int bfs(){ 69 queue<node> q; 70 memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); 71 vis[Sx][Sy][78][0] = true; 72 q.push(node(Sx,Sy,78,0,0)); 73 74 while(q.size()){ 75 node p = q.front();q.pop(); 76 if(p.nowID==6) return p.step; 77 getNum(p.state); 78 int mubic = tS[p.nowID]; 79 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 80 int x = p.x + xx[i] , y = p.y + yy[i]; 81 if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||ditu[x][y]==-2) continue; 82 int state = change(i); 83 int top = state % 6; 84 int nowID = p.nowID; 85 if(ditu[x][y]!=-1){ 86 if(ditu[x][y]!=mubic||top != mubic) continue; 87 else nowID = p.nowID + 1; 88 } 89 if(vis[x][y][state][nowID]) continue; 90 vis[x][y][state][nowID] = true; 91 q.push(node(x,y,state,nowID,p.step+1)); 92 } 93 } 94 95 return -1; 96 } 97 98 int main() 99 { 100 while(cin>>m>>n&&n&&m){ 101 init(); 102 int ans = bfs(); 103 if(ans==-1) puts("unreachable"); 104 else cout<<ans<<endl; 105 } 106 return 0; 107 }
GemAnd PrinceHDU - 4090
题意:消消乐,消除后宝石自动向左向下靠,3个以上才能消,8各方向算。(前面有三道题一样是消消乐,代码直接拿来用就行了)
算法:dfs+剪枝
思路:简单dfs,然后预估函数潜在最大价值就是,直接找出每种宝石的数量总和的平方和。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 12 13 int n,m,k,ans; 14 int xx[]={0,0,-1,1,-1,-1,1,1}; 15 int yy[]={1,-1,0,0,1,-1,1,-1}; 16 int ditu[8][8]; 17 int cnt; 18 19 void init(){ 20 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 21 for(int j=0;j<m;j++) cin>>ditu[i][j]; 22 ans = 0; 23 } 24 25 int eval(){ 26 int res[7] = {0}; 27 int tmp = 0; 28 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 29 for(int j=0;j<m;j++) 30 if(ditu[i][j]) res[ditu[i][j]]++; 31 for(int i=1;i<=k;i++) tmp += res[i]*res[i]; 32 return tmp; 33 } 34 35 //清零之后的向左向下靠齐 36 void remake(){ 37 int tmp[8][8]; 38 memset(tmp,0,sizeof tmp); 39 int tmpX,tmpY=0; 40 for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ 41 bool flag = false; 42 tmpX = n-1; 43 for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){ 44 if(ditu[i][j]==0) continue; 45 flag=true; 46 tmp[tmpX--][tmpY] = ditu[i][j]; 47 } 48 if(flag) tmpY++; 49 } 50 memcpy(ditu,tmp,sizeof ditu); 51 } 52 53 //坐标(a,b)向外扩展清零 54 void clean(int a,int b,int c,bool vis[8][8]){ 55 for(int i=0;i<8;i++){ 56 int x = a + xx[i] , y = b + yy[i]; 57 if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||ditu[x][y]!=c||vis[x][y]) continue; 58 vis[x][y] = true,ditu[x][y]=0,cnt++; 59 clean(x,y,c,vis); 60 } 61 } 62 63 void show(){ 64 puts("------------------------------"); 65 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){for(int j=0;j<m;j++) cout<<ditu[i][j]<<" ";cout<<endl;} 66 puts("------------------------------"); 67 } 68 69 void dfs(int now){ 70 if(ans<now) ans = now; 71 if(now+eval()<=ans) return ; 72 int res[8][8]; 73 memcpy(res,ditu,sizeof res); 74 bool vis[8][8]; 75 memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); 76 //show();cout<<now<<" "<<ans<<endl; 77 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 78 for(int j=0;j<m;j++) if(ditu[i][j]&&!vis[i][j]){ 79 vis[i][j]=true;cnt = 1; 80 clean(i,j,ditu[i][j],vis);ditu[i][j]=0; 81 if(cnt>=3){ 82 remake(); 83 dfs(now+cnt*cnt); 84 } 85 memcpy(ditu,res,sizeof ditu); 86 } 87 } 88 89 int main() 90 { 91 while(cin>>n>>m>>k){ 92 init(); 93 dfs(0); 94 cout<<ans<<endl; 95 } 96 return 0; 97 }
SolitaireHDU - 1401
题意:一个8*8的地图,4个相同的棋子,然后给出两个布局,问从布局1到布局2,8步内是否能完成?棋子只能上下左右走一格,或者可以隔着一个棋子跳一格。
算法:状压+双向bfs
思路:状压:因为8*8地图,坐标可以变成(0~7),所以可以3位二进制表示,4个棋子就只需要24位,用一个int。然后因为相同棋子,所以状压之前需要排序。
一开始用了dfs,TLE了,后面用双向bfs,一层层进行,只进行4层。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 12 13 int xx[]={1,0,-1,0}; 14 int yy[]={0,1,0,-1}; 15 16 struct po{ 17 int x,y; 18 bool operator < (const po &a){ 19 if(x==a.x) return y<a.y; 20 return x<a.x; 21 } 22 }; 23 24 struct node{ 25 po pp[4]; 26 int step; 27 int makeHash(){ 28 sort(pp,pp+4); 29 int tmp = 0; 30 tmp += pp[0].x;tmp<<=3;tmp += pp[0].y;tmp<<=3;tmp += pp[1].x;tmp<<=3;tmp += pp[1].y;tmp<<=3; 31 tmp += pp[2].x;tmp<<=3;tmp += pp[2].y;tmp<<=3;tmp += pp[3].x;tmp<<=3;tmp += pp[3].y; 32 return tmp; 33 } 34 }s,t; 35 36 int one; 37 void init(){ 38 s.pp[0].x = one-1; 39 cin>>one;s.pp[0].y = one-1; 40 for(int i=1;i<4;i++){ 41 int a,b;cin>>a>>b; 42 s.pp[i].x = a-1,s.pp[i].y = b-1; 43 } 44 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 45 int a,b;cin>>a>>b; 46 t.pp[i].x = a-1,t.pp[i].y = b-1; 47 } 48 } 49 50 bool check(int x,int y,node a){ 51 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 52 if(a.pp[i].x==x&&a.pp[i].y==y) return true; 53 } 54 return false; 55 } 56 57 bool bfs(){ 58 map<int,bool> mp1; 59 map<int,bool> mp2; 60 int a = s.makeHash() , b = t.makeHash(); 61 if(a==b) return true; 62 mp1[a] = true; 63 mp2[b] = true; 64 s.step = 0;t.step=0; 65 queue<node> q1;q1.push(s); 66 queue<node> q2;q2.push(t); 67 int step = 0; 68 while(q1.size()&&q2.size()&&step<4){ 69 70 while(q1.size()){ 71 node p1 = q1.front(); 72 if(mp2[p1.makeHash()]) return true; 73 if(p1.step>step) break; 74 else q1.pop(); 75 76 for(int cN=0;cN<4;cN++){ 77 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 78 int x = p1.pp[cN].x + xx[i] , y = p1.pp[cN].y + yy[i]; 79 if(x<0||x>=8||y<0||y>=8) continue; 80 if(check(x,y,p1)){ 81 x+=xx[i], y+=yy[i]; 82 if(x<0||x>=8||y<0||y>=8) continue; 83 if(check(x,y,p1)) continue; 84 node u = p1; 85 u.pp[cN].x = x , u.pp[cN].y = y; 86 int tmp = u.makeHash(); 87 if(mp2[tmp]) return true; 88 if(mp1[tmp]) continue; 89 mp1[tmp] = true; 90 u.step++;q1.push(u); 91 }else{ 92 node u = p1; 93 u.pp[cN].x = x , u.pp[cN].y = y; 94 int tmp = u.makeHash(); 95 if(mp2[tmp]) return true; 96 if(mp1[tmp]) continue; 97 mp1[tmp] = true; 98 u.step++;q1.push(u); 99 } 100 } 101 } 102 } 103 //---------------------------------------------------------------------- 104 while(q2.size()){ 105 node p2 = q2.front(); 106 if(mp1[p2.makeHash()]) return true; 107 if(p2.step>step) break; 108 else q2.pop(); 109 110 for(int cN=0;cN<4;cN++){ 111 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 112 int x = p2.pp[cN].x + xx[i] , y = p2.pp[cN].y + yy[i]; 113 if(x<0||x>=8||y<0||y>=8) continue; 114 if(check(x,y,p2)){ 115 x+=xx[i], y+=yy[i]; 116 if(x<0||x>=8||y<0||y>=8) continue; 117 if(check(x,y,p2)) continue; 118 node u = p2; 119 u.pp[cN].x = x , u.pp[cN].y = y; 120 int tmp = u.makeHash(); 121 if(mp1[tmp]) return true; 122 if(mp2[tmp]) continue; 123 mp2[tmp] = true; 124 u.step++;q2.push(u); 125 }else{ 126 node u = p2; 127 u.pp[cN].x = x , u.pp[cN].y = y; 128 int tmp = u.makeHash(); 129 if(mp1[tmp]) return true; 130 if(mp2[tmp]) continue; 131 mp2[tmp] = true; 132 u.step++;q2.push(u); 133 } 134 } 135 } 136 } 137 step++; 138 } 139 return false; 140 } 141 142 int main() 143 { 144 while(cin>>one){ 145 init(); 146 if(bfs()) puts("YES"); 147 else puts("NO"); 148 } 149 return 0; 150 }
Flood-it!HDU - 4127
题意:8*8的地图,然后有6中颜色,对左上角进行着色,每一次着色都会把相同颜色划分到一起,下次会跟着左上角一起变色,问将所有地图变成一种颜色的最小步数。
算法:IDAstar
思路:因为求最小,所以每次状态都预估一个到达目标的最小步数,这题的最小步数就是剩余多少颜色与左上角不同。
易错点:每次操作都需要找相邻的点的颜色进行对左上角着色,这里使用vis数组,1表示已经着色过,与左上角颜色一致;2表示相邻的点;然后每次操作,只需要列举颜色就行了。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 12 13 int ditu[8][8]; 14 int vis[8][8]; 15 int n,nextd; 16 int xx[]={1,-1,0,0}; 17 int yy[]={0,0,1,-1}; 18 19 int dis_h(){ 20 int res = 0; 21 int visC[6]={0}; 22 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 23 for(int j=0;j<n;j++) if(vis[i][j]!=1&&!visC[ditu[i][j]]){ 24 visC[ditu[i][j]] = 1; 25 res++; 26 } 27 return res; 28 } 29 30 void dfs(int a,int b,int c){ 31 vis[a][b] = 1; 32 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 33 int x = a + xx[i] , y = b + yy[i]; 34 if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=n||vis[x][y]) continue; 35 if(ditu[x][y]==c) dfs(x,y,c); 36 else vis[x][y]=2; 37 } 38 } 39 40 bool color(int c){ 41 bool res = false; 42 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 43 for(int j=0;j<n;j++) if(ditu[i][j]==c&&vis[i][j]==2){ 44 res=true; 45 dfs(i,j,c); 46 } 47 return res; 48 } 49 50 bool IDAstar(int depth,int limit){ 51 int h = dis_h(); 52 if(depth+h>limit){ 53 nextd = min(nextd, depth+h); 54 return false; 55 } 56 if(h==0){ 57 cout<<depth<<endl; 58 return true; 59 } 60 int visT[8][8]; 61 memcpy(visT,vis,sizeof visT); 62 for(int i=0;i<6;i++){ 63 if(!color(i)) continue; 64 if(IDAstar(depth+1,limit)) return true; 65 memcpy(vis,visT,sizeof vis); 66 } 67 return false; 68 } 69 70 void init(){ 71 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 72 for(int j=0;j<n;j++) cin>>ditu[i][j]; 73 memset(vis,0,sizeof vis); 74 dfs(0,0,ditu[0][0]); 75 } 76 77 int main() 78 { 79 while(cin>>n&&n){ 80 init(); 81 for(int limit=dis_h();;limit=nextd){ 82 nextd = INF; 83 if(IDAstar(0,limit)) break; 84 } 85 } 86 return 0; 87 }
IslandsHDU - 2808
题意:就是100*100的地图,上面有海和岛,岛是8各方向判断是否连接的,然后如果一座岛里面没有其他岛的话,他的岛等级就是0,如果存在其他岛的话,他的等级就是他的子岛最大等级+1.
算法:dfs
思路:这题和前面那道埃及文字题目差不多,Ancient Messages HDU - 3839。就是从边缘开始判断,海的话就进行dfs判断,把所有外海标记了,然后与外海邻接的岛就记录;然后在从这些岛开始dfs判断,一座岛一座岛标记,然后每次都把与这些岛邻接的内海进行记录,再对这些内海进行标记,反正就是互相套娃。当一座岛里面没有海或者内海里面没有外岛,他的等级就是0了。
易错点:注意细节,耐心耐心耐心

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 12 13 char ditu[100][100]; 14 bool vis[100][100]; 15 bool visB[100][100]; 16 bool visW[100][100]; 17 int n,m; 18 int xx[]={1,-1,0,0,-1,-1,1,1}; 19 int yy[]={0,0,1,-1,-1,1,1,-1}; 20 int ans[100],ansN; 21 22 void show(){ 23 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 24 for(int j=0;j<m;j++) cout<<ditu[i][j];cout<<endl; 25 }cout<<endl; 26 } 27 28 void init(){ 29 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>ditu[i]; 30 memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); 31 memset(visB,false,sizeof visB); 32 memset(visW,false,sizeof visW); 33 memset(ans,0,sizeof ans); 34 ansN = -1; 35 } 36 37 struct node{ 38 int x,y; 39 node(int a,int b):x(a),y(b) {}; 40 }; 41 42 void show2(vector<node> a){ 43 cout<<"vector: "; 44 for(int i=0;i<a.size();i++){ 45 cout<<a[i].x<<" "<<a[i].y<<" | "; 46 }cout<<endl; 47 } 48 49 void show3(){ 50 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 51 for(int j=0;j<m;j++) cout<<vis[i][j]<<" ";cout<<endl; 52 }cout<<endl; 53 } 54 55 void cleanW(int a,int b,vector<node> &v){ 56 vis[a][b]=true; 57 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 58 int x = a + xx[i] , y = b+ yy[i]; 59 if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||vis[x][y]) continue; 60 if(ditu[x][y]=='.') cleanW(x,y,v); 61 else if(!visB[x][y]) visB[x][y] = true,v.push_back(node(x,y)); 62 } 63 } 64 65 void cleanB(int a,int b,vector<node> &v,int &c){ 66 vis[a][b]=true;c++; 67 for(int i=0;i<8;i++){ 68 int x = a + xx[i] , y = b+ yy[i]; 69 if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=m||vis[x][y]) continue; 70 if(ditu[x][y]=='x') cleanB(x,y,v,c); 71 else if(!visW[x][y]) visW[x][y] = true,v.push_back(node(x,y)); 72 } 73 } 74 75 int dfs(int x,int y) { 76 vector<node> v,v2; 77 int res = 0; 78 int level = 0; 79 cleanB(x,y,v,res); 80 if(v.size()==0) {ans[0]+=res;return 0;} 81 //show2(v);show3(); 82 for(int i=0;i<v.size();i++){ 83 int a = v[i].x , b = v[i].y; 84 if(vis[a][b]) continue; 85 cleanW(a,b,v2); 86 } 87 // show2(v2);show3(); 88 if(v2.size()==0) {ans[0]+=res;return 0;} 89 for(int i=0;i<v2.size();i++){ 90 int a = v2[i].x , b = v2[i].y; 91 if(vis[a][b]) continue; 92 level = max(level,dfs(a,b)+1); 93 } 94 ans[level]+=res; 95 return level; 96 }; 97 98 void solve(){ 99 vector<node> v; 100 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 101 if(!vis[i][0]){ 102 if(ditu[i][0]=='.') cleanW(i,0,v); 103 else if(!visB[i][0]) visB[i][0] = true,v.push_back(node(i,0)); 104 } 105 if(!vis[i][m-1]){ 106 if(ditu[i][m-1]=='.') cleanW(i,m-1,v); 107 else if(!visB[i][m-1]) visB[i][m-1] = true,v.push_back(node(i,m-1)); 108 } 109 } 110 for(int j=1;j<m-1;j++){ 111 if(!vis[0][j]){ 112 if(ditu[0][j]=='.') cleanW(0,j,v); 113 else if(!visB[0][j]) visB[0][j] = true,v.push_back(node(0,j)); 114 } 115 if(!vis[n-1][j]){ 116 if(ditu[n-1][j]=='.') cleanW(n-1,j,v); 117 else if(!visB[n-1][j]) visB[n-1][j] = true,v.push_back(node(n-1,j)); 118 } 119 } 120 //------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 121 //show2(v);show3(); 122 for(int i=0;i<v.size();i++){ 123 int a = v[i].x , b = v[i].y; 124 if(vis[a][b]) continue; 125 ansN = max(ansN,dfs(a,b)); 126 } 127 } 128 129 int main() 130 { 131 while(cin>>n>>m){ 132 init();//show(); 133 solve(); 134 //cout<<ansN<<endl; 135 if(ansN==-1) {cout<<endl;continue;} 136 for(int i=0;i<ansN;i++) cout<<ans[i]<<" ";cout<<ans[ansN]<<endl; 137 } 138 return 0; 139 }
题意:给两个字符串,有3种字符串操作方式,问从字符串1到字符串2最小步数
算法:bfs预处理
思路:和前面 A - Eight HDU - 1043 题目思路一样,不赘述了。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 12 13 char s[9],t[9]; 14 map<string,string> mp; 15 16 struct node{ 17 char s[9]; 18 node(char a[9]) { 19 for(int i=0;i<8;i++) s[i] = a[i]; 20 s[8]='\0'; 21 } 22 }; 23 24 void changeA(char (&b)[9],char a[9]){ 25 b[0] = a[7]; 26 b[1] = a[6]; 27 b[2] = a[5]; 28 b[3] = a[4]; 29 b[4] = a[3]; 30 b[5] = a[2]; 31 b[6] = a[1]; 32 b[7] = a[0]; 33 b[8] = '\0'; 34 } 35 //41236785 36 void changeB(char (&b)[9],char a[9]){ 37 b[0] = a[3]; 38 b[1] = a[0]; 39 b[2] = a[1]; 40 b[3] = a[2]; 41 b[4] = a[5]; 42 b[5] = a[6]; 43 b[6] = a[7]; 44 b[7] = a[4]; 45 b[8] = '\0'; 46 } 47 //17245368 48 void changeC(char (&b)[9],char a[9]){ 49 b[0] = a[0]; 50 b[1] = a[6]; 51 b[2] = a[1]; 52 b[3] = a[3]; 53 b[4] = a[4]; 54 b[5] = a[2]; 55 b[6] = a[5]; 56 b[7] = a[7]; 57 b[8] = '\0'; 58 } 59 60 void bfs(){ 61 char s[9];for(int i=0;i<8;i++) s[i] = '0' + i + 1;s[8] = '\0'; 62 mp[s] = ""; 63 queue<node> q; 64 q.push(node(s)); 65 66 while(q.size()){ 67 node p = q.front();q.pop(); 68 //A--------------------------------------------- 69 char ch[9]; 70 changeA(ch,p.s); 71 if(!(mp.find(ch)!=mp.end())){mp[ch]=mp[p.s]+"A";q.push(node(ch));} 72 //B---------------------------------- 73 changeB(ch,p.s); 74 if(!(mp.find(ch)!=mp.end())){mp[ch]=mp[p.s]+"B";q.push(node(ch));} 75 //C------------------------------------ 76 changeC(ch,p.s); 77 if(!(mp.find(ch)!=mp.end())){mp[ch]=mp[p.s]+"C";q.push(node(ch));} 78 } 79 } 80 81 int main() 82 { 83 bfs(); 84 while(cin>>s>>t){ 85 s[8]='\0';t[8]='\0'; 86 int c[9]; 87 for(int i=0;i<8;i++) c[s[i]-'0'] = '0'+i+1; 88 for(int i=0;i<8;i++) t[i] = c[t[i]-'0']; 89 //cout<<t<<endl; 90 cout<<mp[t]<<endl; 91 } 92 return 0; 93 }
The Rotation Gam HDU - 1667

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 12 13 int nextd,one; 14 int ans,tmpC; 15 string ansStr,tmpStr; 16 int num[24]; 17 int cg[8][7]={{ 0, 2, 6,11,15,20,22},{ 1, 3, 8,12,17,21,23},{10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4},{19,18,17,16,15,14,13}, 18 {23,21,17,12, 8, 3, 1},{22,20,15,11, 6, 2, 0},{13,14,15,16,17,18,19},{ 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,10}}; 19 int ck[8] ={6,7,8,11,12,15,16,17}; 20 21 int dis_h(){ 22 int res[4]= {0}; 23 for(int i=0;i<8;i++) res[num[ck[i]]]++; 24 int maxNum = res[1];tmpC = 1; 25 if(maxNum<res[2]) maxNum = res[2] , tmpC = 2; 26 if(maxNum<res[3]) maxNum = res[3] , tmpC = 3; 27 return maxNum; 28 } 29 30 void init(){ 31 num[0]=one; 32 for(int i=1;i<24;i++) cin>>num[i]; 33 ansStr=""; 34 } 35 36 bool IDAstar(int step,int limit,int id){ 37 int h = 8 - dis_h(); 38 if(h+step>limit){ 39 nextd = min(nextd,h+step); 40 return false; 41 } 42 if(h==0){ 43 if(ansStr.length()<step||(ansStr.length()==step&&ansStr>tmpStr)) ans = tmpC , ansStr = tmpStr; 44 return true; 45 } 46 for(int i=0;i<8;i++){ 47 if((id==0&&i==5)||(id==5&&i==0)||(id==1&&i==4)||(id==4&&i==1)||(id==2&&i==7)||(id==7&&i==2)||(id==3&&i==6)||(id==6&&i==3)) continue; 48 string tmpS = tmpStr; 49 int c = num[cg[i][0]]; 50 for(int j=0;j<6;j++) num[cg[i][j]] = num[cg[i][j+1]]; 51 num[cg[i][6]] = c; 52 tmpStr+='A'+i; 53 if(IDAstar(step+1,limit,i)) return true; 54 tmpStr = tmpS; 55 c = num[cg[i][6]]; 56 for(int j=6;j>0;j--) num[cg[i][j]] = num[cg[i][j-1]]; 57 num[cg[i][0]] = c; 58 } 59 return false; 60 } 61 62 void solve(){ 63 int limit = 8 - dis_h(); 64 if(limit==0) {puts("No moves needed");cout<<tmpC<<endl;return ;} 65 //------------------------------------------------------------- 66 for(bool flag=true;flag;limit = nextd){ 67 nextd = INF; 68 tmpStr = ""; 69 if(IDAstar(0,limit,-1)) break; 70 } 71 cout<<ansStr<<endl; 72 cout<<ans<<endl; 73 } 74 75 int main() 76 { 77 while(cin>>one&&one){ 78 init(); 79 solve(); 80 } 81 return 0; 82 }
思路2:这种思路用了状压,同时可以判重。因为只有3种颜色,只记录一种颜色的分布情况,用24位二进制记录,启发函数和思路1一样,中间不是该颜色的总和;然后进行三种颜色的IDAstar搜索;
易错点:这题判重不是重点,重点是字母顺序操作+启发函数的编写

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 12 13 int nextd,one,two,three; 14 int ans,ansLen; 15 string ansStr,tmpStr; 16 int num[24]; 17 bool vis[3][1<<24]; 18 19 int cg[8][7]={{ 0, 2, 6,11,15,20,22},{ 1, 3, 8,12,17,21,23},{10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4},{19,18,17,16,15,14,13}, 20 {23,21,17,12, 8, 3, 1},{22,20,15,11, 6, 2, 0},{13,14,15,16,17,18,19},{ 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,10}}; 21 int ck[8] ={6,7,8,11,12,15,16,17}; 22 23 int dis_h(int x){ 24 int res = 0; 25 for(int i=0;i<8;i++) if((x&1<<ck[i])==0) res++; 26 return res; 27 } 28 29 void init(){ 30 num[0]=one; 31 for(int i=1;i<24;i++) cin>>num[i]; 32 one = 0 , two = 0 , three = 0; 33 ansLen = 0;ansStr=""; 34 memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); 35 for(int i=0;i<24;i++){ 36 if(num[i]==1) one |= 1<<i; 37 else if(num[i]==2) two |= 1<<i; 38 else three |= 1<<i; 39 } 40 } 41 42 bool IDAstar(int n,int c,int step,int limit){ 43 int h = dis_h(n); 44 if(h+step>limit){ 45 nextd = min(nextd,h+step); 46 return false; 47 } 48 if(h==0){ 49 if(ansLen<step||(ansLen==step&&ansStr>tmpStr)) { 50 ansLen = step; 51 ans = c , ansStr = tmpStr; 52 //cout<<ansLen<<" "<<ans<<" "<<ansStr<<endl; 53 } 54 return true; 55 } 56 for(int i=0;i<8;i++){ 57 int tmp = n; 58 bool flag = false; 59 string tmpS = tmpStr; 60 if(tmp&1<<cg[i][0]) flag = true; 61 for(int j=0;j<6;j++){ 62 if(tmp&1<<cg[i][j]) tmp^=1<<cg[i][j]; 63 if(tmp&1<<cg[i][j+1]) tmp|=1<<cg[i][j]; 64 } 65 if(tmp&1<<cg[i][6]) tmp^=1<<cg[i][6]; 66 if(flag) tmp|=1<<cg[i][6]; 67 if(vis[c-1][tmp]) continue; 68 tmpStr+='A'+i; 69 vis[c-1][tmp]=true; 70 if(IDAstar(tmp,c,step+1,limit)) return true; 71 vis[c-1][tmp]=false; 72 tmpStr = tmpS; 73 } 74 return false; 75 } 76 77 void solve(){ 78 int a = dis_h(one) , b = dis_h(two) , c=dis_h(three); 79 if(a==0) {puts("No moves needed");puts("1");return ;} 80 if(b==0) {puts("No moves needed");puts("2");return ;} 81 if(c==0) {puts("No moves needed");puts("3");return ;} 82 int limit = min(a,min(b,c)); 83 vis[0][one] = true , vis[1][two] = true , vis[2][three] = true; 84 //------------------------------------------------------------- 85 for(bool flag=true;flag;limit = nextd){ 86 nextd = INF; 87 tmpStr = ""; 88 if(IDAstar(one,1,0,limit)) flag=false; 89 tmpStr = ""; 90 if(IDAstar(two,2,0,limit)) flag=false; 91 tmpStr = ""; 92 if(IDAstar(three,3,0,limit)) flag=false; 93 } 94 cout<<ansStr<<endl; 95 cout<<ans<<endl; 96 } 97 98 int main() 99 { 100 while(cin>>one&&one){ 101 init(); 102 solve(); 103 } 104 return 0; 105 }
无题IHDU - 2234
题意:给出一个4*4地图,元素:1、2、3、4分别有4个,4种操作:行的左右转动、列的上下转动;问给出一个随机状态,问需要多少步(5步内)可以使这个地图,要不行全相同,或者列相同。
算法:IDAstar
思路:启发函数,首先是找行,因为每一行之间是相互影响的,合作关系找最大,所以一行的至少操作步数:找出一行里面最大相同元素总和x,然后4-x,然后再从这至少操作数里面找最大,得a;列同理可得b。因为行和列只要其中一个达到条件都行,竞争关系找最小,所以是min(a,b);我这里和上一题一样,加了个不走上一步相反操作的剪枝。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 12 13 int ditu[4][4],nextd; 14 void turn(int x){ 15 int t = ditu[x][0]; 16 for(int i=0;i<3;i++) ditu[x][i] = ditu[x][i+1]; 17 ditu[x][3] = t; 18 } 19 void turn2(int x){ 20 int t = ditu[x][3]; 21 for(int i=3;i>0;i--) ditu[x][i] = ditu[x][i-1]; 22 ditu[x][0] = t; 23 } 24 void turn3(int x){ 25 int t = ditu[0][x]; 26 for(int i=0;i<3;i++) ditu[i][x] = ditu[i+1][x]; 27 ditu[3][x] = t; 28 } 29 void turn4(int x){ 30 int t = ditu[3][x]; 31 for(int i=3;i>0;i--) ditu[i][x] = ditu[i-1][x]; 32 ditu[0][x] = t; 33 } 34 int dis_h(){ 35 int a = 0; 36 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 37 int ans=0,num[4]={0}; 38 for(int j=0;j<4;j++) num[ditu[i][j]-1]++; 39 for(int j=0;j<4;j++) ans = max(ans,num[j]); 40 a = max(a,4-ans); 41 } 42 int b=0; 43 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 44 int ans=0,num[4]={0}; 45 for(int j=0;j<4;j++) num[ditu[j][i]-1]++; 46 for(int j=0;j<4;j++) ans = max(ans,num[j]); 47 b = max(b,4-ans); 48 } 49 return min(a,b); 50 } 51 bool IDAstar(int step,int limit,int id,int cz,int cd){ 52 int h = dis_h(); 53 if(step+h>limit) {nextd=min(nextd,step+h);return false;} 54 if(h==0) {cout<<step<<endl;return true;} 55 for(int x=0;x<4;x++){ 56 if(!(id==x&&cz==0&&cd==0)){ 57 turn(x); 58 if(IDAstar(step+1,limit,x,1,0)) return true; 59 turn2(x); 60 } 61 if(!(id==x&&cz==1&&cd==0)){ 62 turn2(x); 63 if(IDAstar(step+1,limit,x,0,0)) return true; 64 turn(x); 65 } 66 if(!(id==x&&cz==0&&cd==1)){ 67 turn3(x); 68 if(IDAstar(step+1,limit,x,1,1)) return true; 69 turn4(x); 70 } 71 if(!(id==x&&cz==1&&cd==1)){ 72 turn4(x); 73 if(IDAstar(step+1,limit,x,0,1)) return true; 74 turn3(x); 75 } 76 } 77 return false; 78 } 79 80 int main() 81 { 82 int _;cin>>_; 83 while(_--){ 84 for(int i=0;i<4;i++) 85 for(int j=0;j<4;j++) cin>>ditu[i][j]; 86 int limit=dis_h(); 87 if(limit==0) {puts("0");continue;} 88 for(;limit<6;limit=nextd){ 89 nextd = INF; 90 if(IDAstar(0,limit,-1,-1,-1)) break; 91 } 92 if(limit>5) puts("-1"); 93 } 94 return 0; 95 }
Escape from Tetris HDU - 1813
题意:给你一副0、1地图,1表示墙壁,出口是边界,走到边界的0也算出去了,你可以走东南西北4个方向,问是否存在一个最小步数的操作,使你不管在地图上的任意一点都能靠这个操作走出去?如果你的这个操作撞墙的话,就原地等待下一个操作。
算法:IDAstar
思路:预处理,从边界0进行入队,求出所有点到边界0的最小距离。然后IDAstar 从所有非边界0开始,一步步向下搜索,如果走到边界就消除,撞墙就原地等待,每个步骤都维护一个当前还有多少个没有走出去,启发函数就是求这些还没走出去的距离出口最远的距离。
易错点:这里是每个测试数据答案之间有空行

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 12 13 int n,dis[9][9],nextd; 14 int ans[82]; 15 bool vis[9][9]; 16 char ditu[9][9]; 17 int xx[4]={0,-1,1,0}; 18 int yy[4]={1,0,0,-1}; 19 20 void show(){ 21 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 22 for(int j=0;j<n;j++) cout<<vis[i][j]<<" ";cout<<endl; 23 }cout<<endl; 24 } 25 void init(){ 26 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>ditu[i]; 27 memset(dis,INF,sizeof dis); 28 memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); 29 queue<pair<int,int>> q; 30 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 31 if(ditu[i][0]=='0') dis[i][0]=0,q.push(make_pair(i,0)); 32 if(ditu[i][n-1]=='0') dis[i][n-1]=0,q.push(make_pair(i,n-1)); 33 } 34 for(int j=1;j<n-1;j++){ 35 if(ditu[0][j]=='0') dis[0][j]=0,q.push(make_pair(0,j)); 36 if(ditu[n-1][j]=='0') dis[n-1][j]=0,q.push(make_pair(n-1,j)); 37 } 38 while(q.size()){ 39 int px = q.front().first,py = q.front().second;q.pop(); 40 for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ 41 int x = px + xx[i] , y = py + yy[i]; 42 if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=n||ditu[x][y]=='1') continue; 43 if(dis[x][y]>dis[px][py]+1){ 44 vis[x][y] = true; 45 dis[x][y]=dis[px][py]+1; 46 q.push(make_pair(x,y)); 47 } 48 } 49 } 50 //show(); 51 } 52 int dis_h(){ 53 int res = 0; 54 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 55 for(int j=0;j<n;j++) if(vis[i][j]){ 56 res = max(res,dis[i][j]); 57 } 58 return res; 59 } 60 bool IDAstar(int step,int limit){ 61 int h = dis_h(); 62 if(h+step>limit){nextd = min(nextd,h+step);return false;} 63 if(h==0){ 64 //cout<<step<<endl; 65 //show(); 66 for(int i=0;i<step;i++){ 67 if(ans[i]==0) puts("east"); 68 else if(ans[i]==1) puts("north"); 69 else if(ans[i]==2) puts("south"); 70 else puts("west"); 71 } 72 return true; 73 } 74 bool visTmp[9][9]; 75 memcpy(visTmp,vis,sizeof visTmp); 76 for(int cz=0;cz<4;cz++){ 77 memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); 78 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 79 for(int j=0;j<n;j++) if(visTmp[i][j]){ 80 int x = i + xx[cz] , y= j + yy[cz]; 81 if(x<0||x>=n||y<0||y>=n) continue; 82 if(ditu[x][y]=='1') vis[i][j] = true; 83 else if(x!=0&&x!=n-1&&y!=0&&y!=n-1) vis[x][y] = true; 84 } 85 //cout<<step<<" "<<cz<<endl; 86 //show(); 87 ans[step] = cz; 88 if(IDAstar(step+1,limit)) return true; 89 } 90 return false; 91 } 92 int main() 93 { 94 int ca=0; 95 while(cin>>n){ 96 if(ca++) puts(""); 97 init(); 98 for(int limit = dis_h();;limit=nextd){ 99 bool visTmp[9][9];memcpy(visTmp,vis,sizeof visTmp); 100 nextd = INF; 101 //cout<<"limit: "<<limit<<endl; 102 if(IDAstar(0,limit)) break; 103 memcpy(vis,visTmp,sizeof vis); 104 } 105 //cout<<endl; 106 } 107 return 0; 108 }
Tobo or not Tob HDU - 2918
题意:给你一个123456789的3*3玩具,然后你可以按照题目那样旋转,给你一个随机状态和最大步数,问能否在这最大步数以内,将玩具复原,能则回复最小步数,否则-1
算法:康托+bfs预处理 或者 IDAStar
思路1:这里可以从123456789bfs向外扩散9步,记录所有状态;这里使用康托展开进行状态压缩;

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 12 13 char num[10]; 14 int limit; 15 int vis[400000]; 16 17 const int fk[10] = {1,1,2,6,24,120,720,5040,40320,362880}; 18 int cantor(int *a){ 19 int ans = 0; 20 for(int i=0;i<8;i++){ 21 int small = 0; 22 for(int j=i+1;j<9;j++) if(a[j]<a[i]) small++; 23 ans += small*fk[8-i]; 24 } 25 return ans; 26 } 27 28 void getNum(int x,int (&a)[10]){ 29 for(int i=8;i>=0;i--) a[i] = x%10,x/=10; 30 } 31 32 struct node{ 33 int a[10],step; 34 }s; 35 36 void turnA(int (&a)[10]){ 37 int t = a[0]; 38 a[0] = a[3] , a[3] = a[4] , a[4] = a[1] , a[1] = t; 39 } 40 void turnA1(int (&a)[10]){ 41 int t = a[0]; 42 a[0] = a[1] , a[1] = a[4] , a[4] = a[3] , a[3] = t; 43 } 44 void turnB(int (&a)[10]){ 45 int t = a[1]; 46 a[1] = a[4] , a[4] = a[5] , a[5] = a[2] , a[2] = t; 47 } 48 void turnB1(int (&a)[10]){ 49 int t = a[1]; 50 a[1] = a[2] , a[2] = a[5] , a[5] = a[4] , a[4] = t; 51 } 52 void turnC(int (&a)[10]){ 53 int t = a[3]; 54 a[3] = a[6] , a[6] = a[7] , a[7] = a[4] , a[4] = t; 55 } 56 void turnC1(int (&a)[10]){ 57 int t = a[3]; 58 a[3] = a[4] , a[4] = a[7] , a[7] = a[6] , a[6] = t; 59 } 60 void turnD(int (&a)[10]){ 61 int t = a[4]; 62 a[4] = a[5] , a[5] = a[8] , a[8] = a[7] , a[7] = t; 63 } 64 void turnD1(int (&a)[10]){ 65 int t = a[4]; 66 a[4] = a[7] , a[7] = a[8] , a[8] = a[5] , a[5] = t; 67 } 68 69 void init(){ 70 memset(vis,-1,sizeof vis); 71 int num = 12345678; 72 getNum(num,s.a);vis[cantor(s.a)] = 0;s.step = 0; 73 queue<node> q;q.push(s); 74 while(q.size()){ 75 node p = q.front();q.pop(); 76 if(p.step==9) break; 77 node u = p;turnA(u.a);int tmp = cantor(u.a); 78 if(vis[tmp]==-1){vis[tmp] = u.step+1;u.step++;q.push(u);} 79 u = p;turnA1(u.a);tmp = cantor(u.a); 80 if(vis[tmp]==-1){vis[tmp] = u.step+1;u.step++;q.push(u);} 81 u = p;turnB(u.a);tmp = cantor(u.a); 82 if(vis[tmp]==-1){vis[tmp] = u.step+1;u.step++;q.push(u);} 83 u = p;turnB1(u.a);tmp = cantor(u.a); 84 if(vis[tmp]==-1){vis[tmp] = u.step+1;u.step++;q.push(u);} 85 u = p;turnC(u.a);tmp = cantor(u.a); 86 if(vis[tmp]==-1){vis[tmp] = u.step+1;u.step++;q.push(u);} 87 u = p;turnC1(u.a);tmp = cantor(u.a); 88 if(vis[tmp]==-1){vis[tmp] = u.step+1;u.step++;q.push(u);} 89 u = p;turnD(u.a);tmp = cantor(u.a); 90 if(vis[tmp]==-1){vis[tmp] = u.step+1;u.step++;q.push(u);} 91 u = p;turnD1(u.a);tmp = cantor(u.a); 92 if(vis[tmp]==-1){vis[tmp] = u.step+1;u.step++;q.push(u);} 93 } 94 } 95 96 int main() 97 { 98 init(); 99 int ca = 1; 100 while(cin>>num){ 101 limit = num[0] - '0'; 102 if(limit==0&&num[1]=='0') break; 103 cout<<ca++<<". "; 104 int a[10]; 105 for(int i=1;i<10;i++) a[i-1] = num[i] - '0' - 1; 106 int ans = vis[cantor(a)]; 107 if(ans>limit) cout<<-1<<endl; 108 else cout<<ans<<endl; 109 } 110 return 0; 111 }
思路2:这里也可以用IDAstar,启发函数是,与最终状态有多少不同,然后除以4向上取整。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 #include <math.h> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 13 14 char num[10]; 15 int a[10],nextd; 16 bool vis[400000]; 17 18 const int fk[10] = {1,1,2,6,24,120,720,5040,40320,362880}; 19 int cantor(){ 20 int ans = 0; 21 for(int i=0;i<8;i++){ 22 int small = 0; 23 for(int j=i+1;j<9;j++) if(a[j]<a[i]) small++; 24 ans += small*fk[8-i]; 25 } 26 return ans; 27 } 28 void getNum(int x){ 29 for(int i=8;i>=0;i--) a[i] = x%10,x/=10; 30 } 31 void turnA(){ 32 int t = a[0]; 33 a[0] = a[3] , a[3] = a[4] , a[4] = a[1] , a[1] = t; 34 } 35 void turnA1(){ 36 int t = a[0]; 37 a[0] = a[1] , a[1] = a[4] , a[4] = a[3] , a[3] = t; 38 } 39 void turnB(){ 40 int t = a[1]; 41 a[1] = a[4] , a[4] = a[5] , a[5] = a[2] , a[2] = t; 42 } 43 void turnB1(){ 44 int t = a[1]; 45 a[1] = a[2] , a[2] = a[5] , a[5] = a[4] , a[4] = t; 46 } 47 void turnC(){ 48 int t = a[3]; 49 a[3] = a[6] , a[6] = a[7] , a[7] = a[4] , a[4] = t; 50 } 51 void turnC1(){ 52 int t = a[3]; 53 a[3] = a[4] , a[4] = a[7] , a[7] = a[6] , a[6] = t; 54 } 55 void turnD(){ 56 int t = a[4]; 57 a[4] = a[5] , a[5] = a[8] , a[8] = a[7] , a[7] = t; 58 } 59 void turnD1(){ 60 int t = a[4]; 61 a[4] = a[7] , a[7] = a[8] , a[8] = a[5] , a[5] = t; 62 } 63 int dis_h(){ 64 double res = 0; 65 for(int i=0;i<9;i++) if(a[i]!=i) res++; 66 return ceil(res/4); 67 } 68 69 bool IDAstar(int step,int limit){ 70 int h = dis_h(); 71 if(h+step>limit){ 72 nextd = min(nextd,h+step); 73 return false; 74 } 75 if(h==0){ 76 cout<<step<<endl;return true; 77 } 78 int tmp; 79 turnA();tmp=cantor(); 80 if(!vis[tmp]){ 81 vis[tmp]=true; 82 if(IDAstar(step+1,limit)) return true; 83 vis[tmp]=false; 84 }turnA1(); 85 turnA1();tmp=cantor(); 86 if(!vis[tmp]){ 87 vis[tmp]=true; 88 if(IDAstar(step+1,limit)) return true; 89 vis[tmp]=false; 90 }turnA(); 91 turnB();tmp=cantor(); 92 if(!vis[tmp]){ 93 vis[tmp]=true; 94 if(IDAstar(step+1,limit)) return true; 95 vis[tmp]=false; 96 }turnB1(); 97 turnB1();tmp=cantor(); 98 if(!vis[tmp]){ 99 vis[tmp]=true; 100 if(IDAstar(step+1,limit)) return true; 101 vis[tmp]=false; 102 }turnB(); 103 turnC();tmp=cantor(); 104 if(!vis[tmp]){ 105 vis[tmp]=true; 106 if(IDAstar(step+1,limit)) return true; 107 vis[tmp]=false; 108 }turnC1(); 109 turnC1();tmp=cantor(); 110 if(!vis[tmp]){ 111 vis[tmp]=true; 112 if(IDAstar(step+1,limit)) return true; 113 vis[tmp]=false; 114 }turnC(); 115 turnD();tmp=cantor(); 116 if(!vis[tmp]){ 117 vis[tmp]=true; 118 if(IDAstar(step+1,limit)) return true; 119 vis[tmp]=false; 120 }turnD1(); 121 turnD1();tmp=cantor(); 122 if(!vis[tmp]){ 123 vis[tmp]=true; 124 if(IDAstar(step+1,limit)) return true; 125 vis[tmp]=false; 126 }turnD(); 127 return false; 128 } 129 130 int main() 131 { 132 int ca = 1; 133 while(cin>>num){ 134 int k = num[0] - '0'; 135 if(k==0&&num[1]=='0') break; 136 cout<<ca++<<". "; 137 for(int i=1;i<10;i++) a[i-1] = num[i] - '0' - 1; 138 memset(vis,false,sizeof vis); 139 vis[cantor()]=true; 140 int limit; 141 for(limit = dis_h();limit<=k;limit=nextd){ 142 nextd=INF; 143 if(IDAstar(0,limit)) break; 144 } 145 if(limit>k) puts("-1"); 146 } 147 return 0; 148 }
Rubik 2×2×2HDU - 3459
题意:给你一个2*2的2阶魔方,你只能按题目X、Y、Z旋转,给你一个打乱的魔方,你要给出复原的步骤,这里答案不是最小步数亦可。
算法:IDAstar
思路:这里关键就是求每一个面的颜色,左小角的那一块是永远不会动的,所以三个面的颜色,一开始就给出了。然后找其余的7个角,如果一个角存在两个已知颜色,第三个未知颜色一定是与这两个颜色接触的那一面的颜色。这里启发函数,就是先求每个面的不同颜色块总和,然后除以8向上取整。
易错点:就是这里不能判重,会超时,然后注意细节

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 #include <math.h> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 13 14 int nextd; 15 char a[49],color[7]; 16 string ansStr; 17 18 int dis_h(){ 19 int res = 0; 20 if(a[16]!=color[0]) res++;if(a[17]!=color[0]) res++;if(a[25]!=color[0]) res++; 21 if(a[34]!=color[1]) res++;if(a[35]!=color[1]) res++;if(a[43]!=color[1]) res++; 22 if(a[22]!=color[2]) res++;if(a[23]!=color[2]) res++;if(a[30]!=color[2]) res++; 23 if(a[18]!=color[3]) res++;if(a[19]!=color[3]) res++;if(a[26]!=color[3]) res++;if(a[27]!=color[3]) res++; 24 if(a[2]!=color[4]) res++;if(a[3]!=color[4]) res++;if(a[10]!=color[4]) res++;if(a[11]!=color[4]) res++; 25 if(a[20]!=color[5]) res++;if(a[21]!=color[5]) res++;if(a[28]!=color[5]) res++;if(a[29]!=color[5]) res++; 26 return (res+7)/8; 27 } 28 29 void turnX(){ 30 int t = a[20]; a[20] = a[21],a[21] = a[29],a[29] = a[28],a[28] = t; 31 int u = a[3] , v = a[11];a[3] = a[30] ,a[11] = a[22] , a[30] = a[35] ,a[22] = a[43] ,a[35] = a[19] ,a[43] = a[27] ,a[19] = u ,a[27] = v; 32 } 33 void Xturn(){ 34 int t = a[20]; a[20] = a[28],a[28] = a[29],a[29] = a[21],a[21] = t; 35 int u = a[30] , v = a[22]; 36 a[30] = a[3] ,a[22] = a[11] , a[3] = a[19] ,a[11] = a[27] ,a[19] = a[35] ,a[27] = a[43] ,a[35] = u ,a[43] = v; 37 } 38 void turnY(){ 39 int t = a[2]; a[2] = a[3],a[3] = a[11],a[11] = a[10],a[10] = t; 40 int u = a[18] , v = a[19]; 41 a[18] = a[16] ,a[19] = a[17] , a[16] = a[22] ,a[17] = a[23] ,a[22] = a[20] ,a[23] = a[21] ,a[20] = u ,a[21] = v; 42 } 43 void Yturn(){ 44 int t = a[2]; a[2] = a[10],a[10] = a[11],a[11] = a[3],a[3] = t; 45 int u = a[18] , v = a[19]; 46 a[18] = a[20] ,a[19] = a[21] , a[20] = a[22] ,a[21] = a[23] ,a[22] = a[16] ,a[23] = a[17] ,a[16] = u ,a[17] = v; 47 } 48 void turnZ(){ 49 int t = a[18]; a[18] = a[19],a[19] = a[27],a[27] = a[26],a[26] = t; 50 int u = a[20] , v = a[28]; 51 a[20] = a[35] ,a[28] = a[34] , a[35] = a[25] ,a[34] = a[17] ,a[25] = a[10] ,a[17] = a[11] ,a[10] = u ,a[11] = v; 52 } 53 void Zturn(){ 54 int t = a[18]; a[18] = a[26],a[26] = a[27],a[27] = a[19],a[19] = t; 55 int u = a[20] , v = a[28]; 56 a[20] = a[10] ,a[28] = a[11] , a[10] = a[25] ,a[11] = a[17] ,a[25] = a[35] ,a[17] = a[34] ,a[35] = u ,a[34] = v; 57 } 58 59 char getColor(char x,char y){ 60 if(a[17]==x&&a[18]==y) return a[10];if(a[17]==x&&a[10]==y) return a[18];if(a[10]==x&&a[18]==y) return a[17]; 61 if(a[17]==y&&a[18]==x) return a[10];if(a[17]==y&&a[10]==x) return a[18];if(a[10]==y&&a[18]==x) return a[17]; 62 63 if(a[25]==x&&a[26]==y) return a[34];if(a[25]==x&&a[34]==y) return a[26];if(a[26]==x&&a[34]==y) return a[25]; 64 if(a[25]==y&&a[26]==x) return a[34];if(a[25]==y&&a[34]==x) return a[26];if(a[26]==y&&a[34]==x) return a[25]; 65 66 if(a[11]==x&&a[19]==y) return a[20];if(a[11]==x&&a[20]==y) return a[19];if(a[19]==x&&a[20]==y) return a[11]; 67 if(a[11]==y&&a[19]==x) return a[20];if(a[11]==y&&a[20]==x) return a[19];if(a[19]==y&&a[20]==x) return a[11]; 68 69 if(a[27]==x&&a[28]==y) return a[35];if(a[27]==x&&a[35]==y) return a[28];if(a[28]==x&&a[35]==y) return a[27]; 70 if(a[27]==y&&a[28]==x) return a[35];if(a[27]==y&&a[35]==x) return a[28];if(a[28]==y&&a[35]==x) return a[27]; 71 72 if(a[16]==x&&a[2]==y) return a[23];if(a[16]==x&&a[23]==y) return a[2];if(a[23]==x&&a[2]==y) return a[16]; 73 if(a[16]==y&&a[2]==x) return a[23];if(a[16]==y&&a[23]==x) return a[2];if(a[23]==y&&a[2]==x) return a[16]; 74 75 if(a[43]==y&&a[29]==x) return a[30];if(a[43]==y&&a[30]==x) return a[29];if(a[29]==y&&a[30]==x) return a[43]; 76 if(a[43]==x&&a[29]==y) return a[30];if(a[43]==x&&a[30]==y) return a[29];if(a[29]==x&&a[30]==y) return a[43]; 77 78 if(a[3]==y&&a[21]==x) return a[22];if(a[3]==y&&a[22]==x) return a[21];if(a[21]==y&&a[22]==x) return a[3]; 79 if(a[3]==x&&a[21]==y) return a[22];if(a[3]==x&&a[22]==y) return a[21];if(a[21]==x&&a[22]==y) return a[3]; 80 } 81 82 bool IDAstar(int step,int limit){ 83 int h = dis_h(); 84 if(h+step>limit){nextd=min(nextd,h+step);return false;} 85 if(h==0){cout<<ansStr<<endl;return true;} 86 string tmpStr = ansStr; 87 88 turnX(); 89 ansStr+='X'; 90 if(IDAstar(step+1,limit)) return true; 91 ansStr = tmpStr; 92 Xturn(); 93 94 turnY(); 95 ansStr+='Y'; 96 if(IDAstar(step+1,limit)) return true; 97 ansStr = tmpStr; 98 Yturn(); 99 100 turnZ(); 101 ansStr+='Z'; 102 if(IDAstar(step+1,limit)) return true; 103 ansStr = tmpStr; 104 Zturn(); 105 106 return false; 107 } 108 109 int main() 110 { 111 while(1){ 112 for(int i=0;i<48;i++){ 113 char ch=getchar();while(ch==' '||ch=='\n') ch=getchar(); 114 a[i]=ch; 115 } a[48]='\0'; 116 if(a[2]=='.') break; 117 color[0] = a[24],color[1] = a[42], color[2] = a[31]; 118 color[3] = getColor(color[0],color[1]); 119 color[4] = getColor(color[0],color[2]); 120 color[5] = getColor(color[1],color[2]); 121 //----------------------------------------------------- 122 for(int limit = dis_h();;limit=nextd){ 123 ansStr="";nextd=INF; 124 if(IDAstar(0,limit)) break; 125 } 126 } 127 }
Rubiks Cube HDU - 2953
题意:给你一个2*2*2的2阶魔方,问复原所需要最小步数?
算法:bfs预处理+bfs(双向BFS)
思路:这题和上题Rubik 2×2×2HDU - 3459思路差不多,但是这题使用IDAstar会TLE,因为用例有100,且只有1s;
2阶魔方,有一个独特之处,在于,你只需要想上面那样操作3个面就行,你这个面的顺时针就相当于反面逆时针,所以操作只要像上一题一样,多加一个逆时针操作。
并且也和上一题那样,确定颜色。
然后预处理BFS,先存从终点OOOORRGGBBWWRRGGBBWWYYYY向外BFS七步的所有状态;再然后,再确定颜色之后,按照这个最终颜色来改变颜色,再正向BFS,求步数,如果中途,遇到所存状态,可以直接输出。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 #include <math.h> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 13 14 int nextd,ans; 15 char a[25],color[7]; 16 map<string,int> mp; 17 18 struct node{ 19 char a[25];int step; 20 node(char b[25],int c){ 21 memcpy(a,b,sizeof a); 22 step = c; 23 } 24 }; 25 26 void turnXX(char (&a)[25]){ 27 int t = a[6]; a[6] = a[7],a[7] = a[15],a[15] = a[14],a[14] = t; 28 int u = a[1] , v = a[3];a[1] = a[16] ,a[3] = a[8] , a[16] = a[21] ,a[8] = a[23] ,a[21] = a[5] ,a[23] = a[13] ,a[5] = u ,a[13] = v; 29 } 30 void XXturn(char (&a)[25]){ 31 int t = a[6]; a[6] = a[14],a[14] = a[15],a[15] = a[7],a[7] = t; 32 int u = a[16] , v = a[8]; 33 a[16] = a[1] ,a[8] = a[3] , a[1] = a[5] ,a[3] = a[13] ,a[5] = a[21] ,a[13] = a[23] ,a[21] = u ,a[23] = v; 34 } 35 void turnYY(char (&a)[25]){ 36 int t = a[0]; a[0] = a[1],a[1] = a[3],a[3] = a[2],a[2] = t; 37 int u = a[4] , v = a[5]; 38 a[4] = a[10] ,a[5] = a[11] , a[10] = a[8] ,a[11] = a[9] ,a[8] = a[6] ,a[9] = a[7] ,a[6] = u ,a[7] = v; 39 } 40 void YYturn(char (&a)[25]){ 41 int t = a[0]; a[0] = a[2],a[2] = a[3],a[3] = a[1],a[1] = t; 42 int u = a[4] , v = a[5]; 43 a[4] = a[6] ,a[5] = a[7] , a[6] = a[8] ,a[7] = a[9] ,a[8] = a[10] ,a[9] = a[11] ,a[10] = u ,a[11] = v; 44 } 45 void turnZZ(char (&a)[25]){ 46 int t = a[4]; a[4] = a[5],a[5] = a[13],a[13] = a[12],a[12] = t; 47 int u = a[6] , v = a[14]; 48 a[6] = a[21] ,a[14] = a[20] , a[21] = a[19] ,a[20] = a[11] ,a[19] = a[2] ,a[11] = a[3] ,a[2] = u ,a[3] = v; 49 } 50 void ZZturn(char (&a)[25]){ 51 int t = a[4]; a[4] = a[12],a[12] = a[13],a[13] = a[5],a[5] = t; 52 int u = a[6] , v = a[14]; 53 a[6] = a[2] ,a[14] = a[3] , a[2] = a[19] ,a[3] = a[11] ,a[19] = a[21] ,a[11] = a[20] ,a[21] = u ,a[20] = v; 54 } 55 56 void bfs(){ 57 queue<node> q; 58 char ch[25]={"OOOORRGGBBWWRRGGBBWWYYYY"};ch[24]='\0'; 59 mp[ch]=0; 60 q.push(node(ch,0)); 61 while(q.size()){ 62 node p = q.front();q.pop(); 63 int step = p.step+1; 64 65 node u = p;XXturn(u.a); 66 if(mp.find(u.a)==mp.end()){ 67 mp[u.a]=step; 68 if(step<7) u.step++,q.push(u); 69 } 70 u = p;turnXX(u.a); 71 if(mp.find(u.a)==mp.end()){ 72 mp[u.a]=step; 73 if(step<7) u.step++,q.push(u); 74 } 75 u = p;YYturn(u.a); 76 if(mp.find(u.a)==mp.end()){ 77 mp[u.a]=step; 78 if(step<7) u.step++,q.push(u); 79 } 80 u = p;turnYY(u.a); 81 if(mp.find(u.a)==mp.end()){ 82 mp[u.a]=step; 83 if(step<7) u.step++,q.push(u); 84 } 85 u = p;ZZturn(u.a); 86 if(mp.find(u.a)==mp.end()){ 87 mp[u.a]=step; 88 if(step<7) u.step++,q.push(u); 89 } 90 u = p;turnZZ(u.a); 91 if(mp.find(u.a)==mp.end()){ 92 mp[u.a]=step; 93 if(step<7) u.step++,q.push(u); 94 } 95 } 96 } 97 98 char getColor(char x,char y){ 99 if(a[11]==x&&a[4]==y) return a[2];if(a[11]==x&&a[2]==y) return a[4];if(a[2]==x&&a[4]==y) return a[11]; 100 if(a[11]==y&&a[4]==x) return a[2];if(a[11]==y&&a[2]==x) return a[4];if(a[2]==y&&a[4]==x) return a[11]; 101 102 if(a[19]==x&&a[12]==y) return a[20];if(a[19]==x&&a[20]==y) return a[12];if(a[12]==x&&a[20]==y) return a[19]; 103 if(a[19]==y&&a[12]==x) return a[20];if(a[19]==y&&a[20]==x) return a[12];if(a[12]==y&&a[20]==x) return a[19]; 104 105 if(a[13]==x&&a[14]==y) return a[21];if(a[13]==x&&a[21]==y) return a[14];if(a[14]==x&&a[21]==y) return a[13]; 106 if(a[13]==y&&a[14]==x) return a[21];if(a[13]==y&&a[21]==x) return a[14];if(a[14]==y&&a[21]==x) return a[13]; 107 108 if(a[3]==x&&a[5]==y) return a[6];if(a[3]==x&&a[6]==y) return a[5];if(a[5]==x&&a[6]==y) return a[3]; 109 if(a[3]==y&&a[5]==x) return a[6];if(a[3]==y&&a[6]==x) return a[5];if(a[5]==y&&a[6]==x) return a[3]; 110 111 if(a[10]==x&&a[0]==y) return a[9];if(a[9]==x&&a[10]==y) return a[0];if(a[0]==x&&a[9]==y) return a[10]; 112 if(a[10]==y&&a[0]==x) return a[9];if(a[9]==y&&a[10]==x) return a[0];if(a[0]==y&&a[9]==x) return a[10]; 113 114 if(a[23]==y&&a[15]==x) return a[16];if(a[23]==y&&a[16]==x) return a[15];if(a[15]==y&&a[16]==x) return a[23]; 115 if(a[23]==x&&a[15]==y) return a[16];if(a[23]==x&&a[16]==y) return a[15];if(a[15]==x&&a[16]==y) return a[23]; 116 117 if(a[1]==y&&a[7]==x) return a[8];if(a[1]==y&&a[8]==x) return a[7];if(a[7]==y&&a[8]==x) return a[1]; 118 if(a[1]==x&&a[7]==y) return a[8];if(a[1]==x&&a[8]==y) return a[7];if(a[7]==x&&a[8]==y) return a[1]; 119 } 120 //OOOORRGGBBWWRRGGBBWWYYYY 121 void changeColor(){ 122 for(int i=0;i<24;i++){ 123 if(a[i]==color[0]) a[i]='W'; 124 else if(a[i]==color[1]) a[i]='Y'; 125 else if(a[i]==color[2]) a[i]='B'; 126 else if(a[i]==color[3]) a[i]='R'; 127 else if(a[i]==color[4]) a[i]='O'; 128 else a[i]='G'; 129 } 130 } 131 132 void bfs2(){ 133 queue<node> q; 134 map<string,bool> vis; 135 vis[a] = true; 136 q.push(node(a,0)); 137 while(q.size()){ 138 node p = q.front();q.pop(); 139 140 if(mp.find(p.a)!=mp.end()){ 141 cout<<p.step+mp[p.a]<<endl; 142 break; 143 } 144 145 node u = p;XXturn(u.a); 146 if(!vis[u.a]) vis[u.a]=true,u.step++,q.push(u); 147 u = p;turnXX(u.a); 148 if(!vis[u.a]) vis[u.a]=true,u.step++,q.push(u); 149 u = p;YYturn(u.a); 150 if(!vis[u.a]) vis[u.a]=true,u.step++,q.push(u); 151 u = p;turnYY(u.a); 152 if(!vis[u.a]) vis[u.a]=true,u.step++,q.push(u); 153 u = p;ZZturn(u.a); 154 if(!vis[u.a]) vis[u.a]=true,u.step++,q.push(u); 155 u = p;turnZZ(u.a); 156 if(!vis[u.a]) vis[u.a]=true,u.step++,q.push(u); 157 158 } 159 } 160 161 int main() 162 { 163 bfs(); 164 int _;cin>>_; 165 while(_--){ 166 for(int i=0;i<24;i++){ 167 char ch=getchar();while(ch==' '||ch=='\n') ch=getchar(); 168 a[i]=ch; 169 } a[24]='\0'; 170 //----------------------------------------------------- 171 color[0] = a[18],color[1] = a[22], color[2] = a[17]; 172 color[3] = getColor(color[0],color[1]); 173 color[4] = getColor(color[0],color[2]); 174 color[5] = getColor(color[1],color[2]); 175 changeColor(); 176 bfs2(); 177 } 178 }
2-Dimensional Rubik's Cube HDU - 2691
题意:同样是2阶魔方,然后给出两个状态,问状态1到状态2最少需要多少步?(一定有解)
算法:双向BFS+状压
思路:这里IDAStar同样会TLE,然后队列节点不进行数组压缩成一个LongLong的话,会MLE,因为这里一定有解,所以双向BFS,不需要分层来寻找答案。
易错点:注意细节、然后要状态压缩

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 #include <math.h> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 13 14 int nextd; 15 int a[25],b[25]; 16 int face[6][4]={{0,1,3,2},{4,5,13,12},{6,7,15,14},{8,9,17,16},{10,11,19,18},{20,21,23,22}}; 17 int faceX[6][4]={{10,8,6,4},{0,6,20,19},{2,8,21,13},{3,10,23,15},{1,4,22,17},{14,16,18,12}}; 18 int faceY[6][4]={{11,9,7,5},{2,14,22,11},{3,16,20,5},{1,18,21,7},{0,12,23,9},{15,17,19,13}}; 19 20 void turn(int x,int flag,int (&a)[25]){ 21 if(flag){ 22 int tmp = a[face[x][0]];for(int i=0;i<3;i++) a[face[x][i]] =a[face[x][i+1]];a[face[x][3]] = tmp; 23 tmp = a[faceX[x][0]];for(int i=0;i<3;i++) a[faceX[x][i]] =a[faceX[x][i+1]];a[faceX[x][3]] = tmp; 24 tmp = a[faceY[x][0]];for(int i=0;i<3;i++) a[faceY[x][i]] =a[faceY[x][i+1]];a[faceY[x][3]] = tmp; 25 }else{ 26 int tmp = a[face[x][3]];for(int i=3;i>0;i--) a[face[x][i]] =a[face[x][i-1]];a[face[x][0]] = tmp; 27 tmp = a[faceX[x][3]];for(int i=3;i>0;i--) a[faceX[x][i]] =a[faceX[x][i-1]];a[faceX[x][0]] = tmp; 28 tmp = a[faceY[x][3]];for(int i=3;i>0;i--) a[faceY[x][i]] =a[faceY[x][i-1]];a[faceY[x][0]] = tmp; 29 } 30 } 31 32 void init(){ 33 for(int i=0;i<24;i++){ 34 char ch=getchar();while(ch==' '||ch=='\n') ch=getchar(); 35 if(ch=='O') a[i] = 0; 36 else if(ch=='R') a[i] = 1; 37 else if(ch=='G') a[i] = 2; 38 else if(ch=='B') a[i] = 3; 39 else if(ch=='W') a[i] = 4; 40 else a[i] = 5; 41 } 42 for(int i=0;i<24;i++){ 43 char ch=getchar();while(ch==' '||ch=='\n') ch=getchar(); 44 if(ch=='O') b[i] = 0; 45 else if(ch=='R') b[i] = 1; 46 else if(ch=='G') b[i] = 2; 47 else if(ch=='B') b[i] = 3; 48 else if(ch=='W') b[i] = 4; 49 else b[i] = 5; 50 } 51 //for(int i=0;i<24;i++) cout<<a[i]<<" ";cout<<endl; 52 } 53 54 struct node{ 55 long long a;int step; 56 node(int b[25],int c){ 57 a = b[0]; 58 for(int i=1;i<24;i++) a*=6,a+=b[i]; 59 step = c; 60 } 61 void makeSZ(int (&b)[25]){ 62 long long x =a ; 63 for(int i=23;i>=0;i--){ 64 b[i] = (int)( x % 6); x = x / 6; 65 } 66 } 67 }; 68 69 int solve(){ 70 queue<node> q1,q2; 71 map<long long,int> vis1,vis2; 72 node s = node(a,0) , t = node(b,0); 73 vis1[s.a]=0;vis2[t.a]=0; 74 q1.push(s);q2.push(t); 75 int step=0; 76 while(q1.size()&&q2.size()){ 77 78 while(q1.size()){ 79 node p1 = q1.front(); 80 if(vis2.find(p1.a)!=vis2.end()) return p1.step+vis2[p1.a]; 81 if(p1.step>step) break; 82 else q1.pop(); 83 for(int i=0;i<6;i++){ 84 for(int j=0;j<2;j++){ 85 int tmp[25]; 86 p1.makeSZ(tmp); 87 turn(i,j,tmp); 88 node u = node(tmp,p1.step+1); 89 if(vis2.find(u.a)!=vis2.end()) return u.step+vis2[u.a]; 90 if(vis1.find(u.a)!=vis1.end()) continue; 91 vis1[u.a]=u.step; 92 q1.push(u); 93 } 94 } 95 } 96 //---------------------------------------------------------------------- 97 while(q2.size()){ 98 node p2 = q2.front(); 99 if(vis1.find(p2.a)!=vis1.end()) return p2.step+vis1[p2.a]; 100 if(p2.step>step) break; 101 else q2.pop(); 102 for(int i=0;i<6;i++){ 103 for(int j=0;j<2;j++){ 104 int tmp[25]; 105 p2.makeSZ(tmp); 106 turn(i,j,tmp); 107 node u = node(tmp,p2.step+1); 108 if(vis1.find(u.a)!=vis1.end()) return u.step+vis1[u.a]; 109 if(vis2.find(u.a)!=vis2.end()) continue; 110 vis2[u.a]=u.step; 111 q2.push(u); 112 } 113 } 114 } 115 step++; 116 } 117 return -1; 118 } 119 120 int main() 121 { 122 int _;cin>>_; 123 while(_--){ 124 init(); 125 cout<<solve()<<endl; 126 } 127 }
上面 :两个队列 分别一层层出 下面:两个队列一个个的出

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 #include <math.h> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 13 14 int nextd; 15 int a[25],b[25]; 16 int face[6][4]={{0,1,3,2},{4,5,13,12},{6,7,15,14},{8,9,17,16},{10,11,19,18},{20,21,23,22}}; 17 int faceX[6][4]={{10,8,6,4},{0,6,20,19},{2,8,21,13},{3,10,23,15},{1,4,22,17},{14,16,18,12}}; 18 int faceY[6][4]={{11,9,7,5},{2,14,22,11},{3,16,20,5},{1,18,21,7},{0,12,23,9},{15,17,19,13}}; 19 20 void turn(int x,int flag,int (&a)[25]){ 21 if(flag){ 22 int tmp = a[face[x][0]];for(int i=0;i<3;i++) a[face[x][i]] =a[face[x][i+1]];a[face[x][3]] = tmp; 23 tmp = a[faceX[x][0]];for(int i=0;i<3;i++) a[faceX[x][i]] =a[faceX[x][i+1]];a[faceX[x][3]] = tmp; 24 tmp = a[faceY[x][0]];for(int i=0;i<3;i++) a[faceY[x][i]] =a[faceY[x][i+1]];a[faceY[x][3]] = tmp; 25 }else{ 26 int tmp = a[face[x][3]];for(int i=3;i>0;i--) a[face[x][i]] =a[face[x][i-1]];a[face[x][0]] = tmp; 27 tmp = a[faceX[x][3]];for(int i=3;i>0;i--) a[faceX[x][i]] =a[faceX[x][i-1]];a[faceX[x][0]] = tmp; 28 tmp = a[faceY[x][3]];for(int i=3;i>0;i--) a[faceY[x][i]] =a[faceY[x][i-1]];a[faceY[x][0]] = tmp; 29 } 30 } 31 32 void init(){ 33 for(int i=0;i<24;i++){ 34 char ch=getchar();while(ch==' '||ch=='\n') ch=getchar(); 35 if(ch=='O') a[i] = 0; 36 else if(ch=='R') a[i] = 1; 37 else if(ch=='G') a[i] = 2; 38 else if(ch=='B') a[i] = 3; 39 else if(ch=='W') a[i] = 4; 40 else a[i] = 5; 41 } 42 for(int i=0;i<24;i++){ 43 char ch=getchar();while(ch==' '||ch=='\n') ch=getchar(); 44 if(ch=='O') b[i] = 0; 45 else if(ch=='R') b[i] = 1; 46 else if(ch=='G') b[i] = 2; 47 else if(ch=='B') b[i] = 3; 48 else if(ch=='W') b[i] = 4; 49 else b[i] = 5; 50 } 51 //for(int i=0;i<24;i++) cout<<a[i]<<" ";cout<<endl; 52 } 53 54 struct node{ 55 long long a;int step; 56 node(int b[25],int c){ 57 a = b[0]; 58 for(int i=1;i<24;i++) a*=6,a+=b[i]; 59 step = c; 60 } 61 void makeSZ(int (&b)[25]){ 62 long long x =a ; 63 for(int i=23;i>=0;i--){ 64 b[i] = (int)( x % 6); x = x / 6; 65 } 66 } 67 }; 68 69 int solve(){ 70 queue<node> q1,q2; 71 map<long long,int> vis1,vis2; 72 node s = node(a,0) , t = node(b,0); 73 vis1[s.a]=0;vis2[t.a]=0; 74 q1.push(s);q2.push(t); 75 while(q1.size()&&q2.size()){ 76 77 node p1 = q1.front();q1.pop(); 78 if(vis2.find(p1.a)!=vis2.end()) return p1.step+vis2[p1.a]; 79 80 for(int i=0;i<6;i++){ 81 for(int j=0;j<2;j++){ 82 int tmp[25]; 83 p1.makeSZ(tmp); 84 turn(i,j,tmp); 85 node u = node(tmp,p1.step+1); 86 if(vis2.find(u.a)!=vis2.end()) return u.step+vis2[u.a]; 87 if(vis1.find(u.a)!=vis1.end()) continue; 88 vis1[u.a]=u.step; 89 q1.push(u); 90 } 91 } 92 //---------------------------------------------------------------------- 93 node p2 = q2.front();q2.pop(); 94 if(vis1.find(p2.a)!=vis1.end()) return p2.step+vis1[p2.a]; 95 96 for(int i=0;i<6;i++){ 97 for(int j=0;j<2;j++){ 98 int tmp[25]; 99 p2.makeSZ(tmp); 100 turn(i,j,tmp); 101 node u = node(tmp,p2.step+1); 102 if(vis1.find(u.a)!=vis1.end()) return u.step+vis1[u.a]; 103 if(vis2.find(u.a)!=vis2.end()) continue; 104 vis2[u.a]=u.step; 105 q2.push(u); 106 } 107 } 108 109 } 110 return -1; 111 } 112 113 int main() 114 { 115 int _;cin>>_; 116 while(_--){ 117 init(); 118 cout<<solve()<<endl; 119 } 120 }
Déjà vuHDU - 2467
题意:N:表面数字都在(0~2^N-1)内,N最大20;M:0~2^N-1内不同的正整数,并且二进制都只有3个1,(这里因为不同,所以1的位置排列也不同);S一个初始状态,T一个最终状态;问是否存在多个M数实现公式 S^M1^M2^M3^...=T?
算法:IDAstar
思路:1.这里公式可以左右两边都异或S,就变成M1^M2^M3^……=T^S,然后继续异或:M2^M3^……=T^S^M1,最终会变成 0 = T^S^M1^M2^……;公式左边会变成0;所以每次选举一个M出来异或就行,再者这里是异或操作,所以一个数只能异或一次,那么它在公式里状态只能是 存在 或者 不存在;所以IDAstar向下枚举可以随着id,循环减少;
2.这里启发函数维护一个,当前状态,剩余多少个二进制状态1,没有消除,因为最后要变成0才算成功。一开始是觉得一次操作,一个数可以消除3个1,所以就除以3向上取整了,不出意味TLE了,这里异或,所以这样不行,就一个个手算出来,因为只有20位,所以cnt数组:int cnt[]={0,3,2,1,2,3,2,3,4,3,4,5,4,5,6,5,6,7,6,7,8}; 当剩余0个1,不需要操作;剩余1个1,则至少需要3次操作;以此类推。
3.这里有个优化,可以事先预处理,0~2^N-1里面的数,二进制有多少个1;
4.这里只有20位个1,理想情况下,不能存在无效消除1的情况,所以limit最大20

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <cstdio> 7 #include <map> 8 #include <math.h> 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 13 14 int n,m,S,T,ans,nextd; 15 int num[1<<20]; 16 int res[1<<20]; 17 int cnt[]={0,3,2,1,2,3,2,3,4,3,4,5,4,5,6,5,6,7,6,7,8}; 18 19 int dis_h(int x){ 20 return cnt[res[x]]; 21 } 22 23 bool IDAstar(int x,int step,int id,int limit){ 24 int h = dis_h(x); 25 if(h+step>limit){ 26 nextd = min(nextd , h+step);return false; 27 } 28 if(h==0) {ans = step;return true;} 29 for(int i=id;i<m;i++) if(IDAstar(x^num[i],step+1,i+1,limit)) return true; 30 return false; 31 } 32 33 int main() 34 { 35 res[0]=0; 36 for(int i=1;i<(1<<20);i++) res[i] = res[i>>1] + (i&1); 37 int cas = 1; 38 while(cin>>n>>m&&n&&m){ 39 cin>>S>>T; 40 for(int i=0;i<m;i++) cin>>num[i]; 41 int num = S^T,f = min(20,m);ans = INF; 42 for(int limit = dis_h(num);limit<=f;limit=nextd){ 43 nextd = INF; 44 if(IDAstar(num,0,0,limit)) break; 45 } 46 cout<<"Case #"<<cas++<<": "; 47 if(ans==INF) puts("Impossible"); 48 else cout<<ans<<endl; 49 } 50 }
Destroying the bus stationsHDU - 2485
题意:给你一个n个点巴士站,单向边,每条边只需1分钟车程,军队车会从巴士站1出发,最终到达n点,问你至少要炸毁多少个车站,才能让军队不在K分钟内到达n点??
算法:网络流:最大流/最小割、最小费用最大流问题
这题,我知道是网络流,但是我还没学到,也不想半懂半解的解决它,等我学完再回来补吧。
学完回来补了,网路流的最大流问题、最小割问题,最小费用最大流问题。算法学习:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/617967342
最大流问题就是图每个路径都有流通容量,即这条路流过这个量就不能再通过了,问从源点到底最多可以流多少水到汇点??;
最小割问题就是问割去一些边使得汇点源点不相通的情况下,这些边的总容量和最小??这里最小割问题其实就是最大流问题(这个我就不解释了。)
最小费用最大流,其实就是每个边增加一个代价,即过路费,问在保持最大流情况下,路径总费用最少?
思路:这题刚好涉及到这三个东西;首先最小割是割边,而这里是割点,我们其实可以把点拆分成两个,然后两个点构造一个边,边容量为1(即这个点只用删一次,最后最大流就表示要删多少次这种边,即删多少个点),其他边容量为INF(这里题目巴士可以无限次走这条路所以是INF),巧妙地把最小割点变成最小割问题。
解法1:最小割问题,是使得s、t点不连通,而这题是,使得到达t点的时间大于K,这里思维转换一下,如果我们只保留时间小于等于K的路径,再求最小割(最大流)不就是答案了吗?预处理一下,从s点跑一次spfa,得到dis1【i】——这个点到s的距离;用反向边从t点跑一次是spafa,得到dis2【i】——这个点到t的距离。然后对每个存在的边(u,v)进行判断——dis1[u]+dis2[v]+1>k——这个边就不要进图了。构建完图之后,跑一次最大流就是答案。
解法2:这里用最小费用最大流,拆点之后的内边费用为0——因为点自己内部走不需要费用,其他边费用为1;因为最小费用,已经维护了一个最短路径,然后我们只要在循环spfa到汇点的费用大于K的时候中止,这之前的最大流与解法1同理。
注意:这里s、t点不能炸,所以不能拆点。而且也不合理。
最大流
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <string.h>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <limits.h>
#include <float.h>
#define sc scanf
#define pf printf
#define REP(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<(b);i++)
#define CLR(x,m) memset(x,m,sizeof x);
#define LOCAL freopen("test.txt","r",stdin)
#define UCCU ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
#define XSD(i) cout << fixed << setprecision(i);
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define xx first
#define yy second
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef double DB;
typedef long double LDB;
const double eps = 1e-8;
//const int inf = 1<<30;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const long long llinf = (long long)300100*1000000000;
const DB PI = acos(-1.0);
const LL mod = 1e9+7;
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------
const int MAXN = 100 + 10;
const int MAXM = 8100 + 10;
struct Edge{
int to,next,cap,flow;
}edge[MAXM];
int tol,head[MAXN];
void init(){
tol = 2;
memset(head, -1, sizeof head);
}
void addedge(int u,int v,int w,int rw = 0){
edge[tol].to = v;edge[tol].cap = w;edge[tol].flow = 0;
edge[tol].next = head[u];head[u] = tol++;
edge[tol].to = u;edge[tol].cap = rw;edge[tol].flow = 0;
edge[tol].next = head[v];head[v] = tol++;
}
int Q[MAXN];
int dep[MAXN],cur[MAXN],sta[MAXN];
bool bfs(int s,int t,int n){
int front = 0,tail = 0;
memset(dep, -1, sizeof(dep[0])*(n+n+1));
dep[s] = 0;
Q[tail++] = s;
while(front < tail){
int u = Q[front++];
for(int i = head[u];i != -1;i = edge[i].next){
int v = edge[i].to;
if(edge[i].cap > edge[i].flow && dep[v] == -1){
dep[v] = dep[u] + 1;
if(v == t) return true;
Q[tail++] = v;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int dinic(int s,int t,int n){
int maxflow = 0;
while(bfs(s,t,n)){
for(int i=0;i<n+n;i++) cur[i] = head[i];
int u = s,tail = 0;
while(cur[s] != -1){
if(u == t){
int tp = INF;
for(int i=tail-1;i>=0;i--) tp = min(tp, edge[sta[i]].cap-edge[sta[i]].flow);
maxflow+=tp;
for(int i=tail-1;i>=0;i--){
edge[sta[i]].flow+=tp;
edge[sta[i]^1].flow-=tp;
if(edge[sta[i]].cap-edge[sta[i]].flow==0) tail = i;
}
u = edge[sta[tail]^1].to;
}else if(cur[u] != -1 && edge[cur[u]].cap > edge[cur[u]].flow && dep[u] +1 ==dep[edge[cur[u]].to]){
sta[tail++] = cur[u];
u = edge[cur[u]].to;
}else{
while(u != s && cur[u] == -1) u = edge[sta[--tail]^1].to;
cur[u] = edge[cur[u]].next;
}
}
}
return maxflow;
}
int n,m,k;
vector<int> E1[MAXN],E2[MAXN];
int dis1[MAXN],dis2[MAXN];
bool vis1[MAXN],vis2[MAXN];
void SPFA(int start,int n,int (&dis)[MAXN],bool vis[MAXN],vector<int> E[MAXN]){
vis[start]=true,dis[start]=0;
queue<int> q;q.push(start);
while(q.size()){
int u = q.front();q.pop();
vis[u]=false;
for(int i=0;i<E[u].size();i++){
int v = E[u][i];
if(dis[v]>dis[u]+1){
dis[v]=dis[u]+1;
if(!vis[v]){
vis[v] = true;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
}
void init_2(){
bool ee[MAXN][MAXN];
memset(ee,false,sizeof ee);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
E1[i].clear();E2[i].clear();
dis1[i] = INF;dis2[i] = INF;
vis1[i] = false;vis2[i] = false;
}
while(m--){
int a,b;cin>>a>>b;
E1[a-1].push_back(b-1);
E2[b-1].push_back(a-1);
ee[a-1][b-1] = true;
}
SPFA(0,n,dis1,vis1,E1);
SPFA(n-1,n,dis2,vis2,E2);
//puts("=============");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(i!=0&&i!=n-1) addedge(i,i+n,1);
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(i==j||!ee[i][j]) continue;
if(dis1[i]+dis2[j]+1>k) continue;
//cout<<i<<" "<<j<<endl;
if(i!=0&&i!=n-1) addedge(i+n,j,INF);
else addedge(i,j,INF);
}
}
}
int main(){
while(cin>>n>>m>>k&&n&&m&&k){
init();
init_2();
cout<<dinic(0,n-1,n)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}最小费用最大流
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <string.h>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <limits.h>
#include <float.h>
#define sc scanf
#define pf printf
#define REP(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<(b);i++)
#define CLR(x,m) memset(x,m,sizeof x);
#define LOCAL freopen("test.txt","r",stdin)
#define UCCU ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
#define XSD(i) cout << fixed << setprecision(i);
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define xx first
#define yy second
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef double DB;
typedef long double LDB;
const double eps = 1e-8;
//const int inf = 1<<30;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const long long llinf = (long long)300100*1000000000;
const DB PI = acos(-1.0);
const LL mod = 1e9+7;
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------
const int MAXN = 100 + 10;
const int MAXM = 8100 + 10;
struct Edge{
int to,next,cap,flow,cost;
}edge[MAXM];
int tol,head[MAXN];
int pre[MAXN],dis[MAXN];
bool vis[MAXN];
int N,M,K;
void init(){
tol = 0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof head);
}
void addedge(int u,int v,int cap,int cost){
edge[tol].to = v;
edge[tol].cap = cap;
edge[tol].cost = cost;
edge[tol].flow = 0;
edge[tol].next = head[u];
head[u] = tol++;
edge[tol].to = u;
edge[tol].cap = 0;
edge[tol].cost = -cost;
edge[tol].flow = 0;
edge[tol].next = head[v];
head[v] = tol++;
}
bool spfa(int s,int t){
queue<int> q;
for(int i=1;i<=N+N;i++){
dis[i] = INF;
vis[i] = false;
pre[i] = -1;
}
dis[s] = 0;
vis[s] = true;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
vis[u] = false;
for(int i=head[u];i!=-1;i=edge[i].next){
int v = edge[i].to;
if(edge[i].cap>edge[i].flow && dis[v] > dis[u] + edge[i].cost){
dis[v] = dis[u] + edge[i].cost;
pre[v] = i;
if(!vis[v]){
vis[v] = true;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
if(pre[t]==-1) return false;
if(dis[t]>K) return false;
return true;
}
int minCostMaxflow(int s,int t,int &cost){
int flow = 0;
cost = 0;
while(spfa(s,t)){
int Min = INF;
for(int i=pre[t];i != -1;i = pre[edge[i^1].to]){
if(Min > edge[i].cap - edge[i].flow) Min = edge[i].cap - edge[i].flow;
}
for(int i=pre[t];i!=-1;i=pre[edge[i^1].to]){
edge[i].flow+=Min;
edge[i^1].flow-=Min;
cost += edge[i].cost * Min;
}
flow += Min;
}
return flow;
}
int main(){
while(cin>>N>>M>>K&&N&&M&&K){
init();
for(int i=2;i<N;i++) addedge(i,i+N,1,0);
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
int a,b;cin>>a>>b;
if(a==1||a==N) addedge(a,b,INF,1);
else addedge(a+N,b,INF,1);
}
int cost;
cout<<minCostMaxflow(1,N,cost)<<endl;
}
}至此, 我所有的搜索专题,全部完成了,接下来就会做kuangbin专题三了,到时候有空再说。谢谢。



