洛谷P6207 题解
题目传送门
这道题很显然是一道搜索题,这里讲讲宽搜的做法。
读题,这道题要求我们输出到终点的路径,所以我们不仅要考虑宽搜的过程,还要记录下经过的路径。
首先宽搜的模板可以先写出来,然后就是记录路径的问题了,怎么实现它呢?
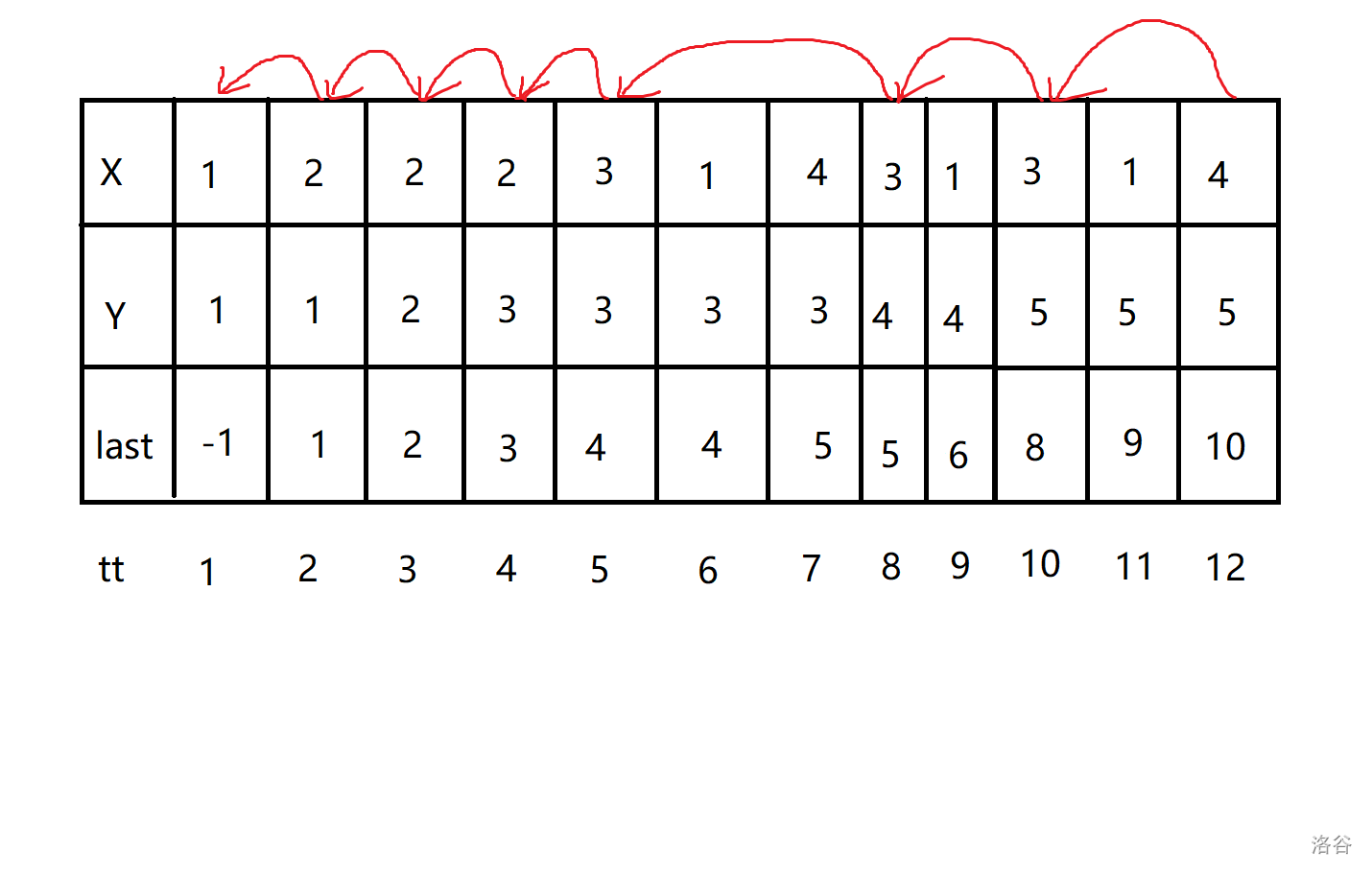
记录路径,其实就是记录每个点是由哪个点走来的,这里我构思了一种链式结构,在搜到终点后找到它的上一个点,再找到它的上上个点,再找到它的上上上个点……直到找到起点,然后利用递归来将它们反向输出。
如图所示:
4 5
.*...
...**
**...
**.*.
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 120, M = 100010;
struct node{
int now, x, y; //now存的是此点的坐标在point数组中的下标
}a, t;
struct path{
int las, px, py;
}point[M];
int n, m;
int dx[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1}; //下, 右, 上, 左
char mapp[N][N];
int tt; //point数组的下标
bool vis[N][N];
queue <node> q;
void print(int x) { //递归, 先输出前面的点, 再输出现在的点
if(x == -1) return ;
print(point[x].las);
printf("%d %d\n", point[x].px, point[x].py);
}
void bfs() {
a.x = 1, a.y = 1;
a.now = ++tt;
point[tt].px = a.x, point[tt].py = a.y;
point[tt].las = -1; //第一个点的前一个点的下标指向-1
vis[a.x][a.y] = true;
q.push(a);
while(!q.empty()) {
t = q.front();
q.pop();
if(t.x == n && t.y == m) {
print(t.now);
return ;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
a.x = t.x + dx[i], a.y = t.y + dy[i];
if(a.x < 1 || a.x > n || a.y < 1 || a.y > m ) continue;
if(vis[a.x][a.y]) continue;
a.now = ++tt;
point[tt].px = a.x, point[tt].py = a.y;
point[tt].las = t.now; //此点是由t走来的,因此它的las指针应该指向t在数组中的位置
vis[a.x][a.y] = true;
q.push(a);
}
}
}
int main() {
// x y
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
cin >> mapp[i][j];
if(mapp[i][j] == '*') vis[i][j] = true;
}
}
bfs();
for(int i = 1; i <= tt; i++) {
cout << point[i].px << " " << point[i].py << " " << point[i].las << endl;
}
return 0;
}


