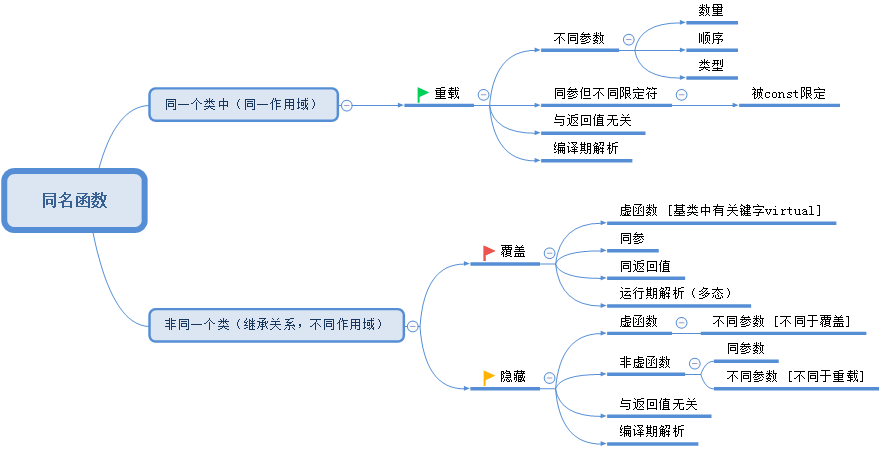
重载 覆盖 隐藏
【1】重载
(1)重载是指在同一个类内被声明的几个具有不同参数列的同名函数。
函数名必须相同,不考虑函数的返回值类型。
(2)示例代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class Sample 5 { 6 public: 7 void Func(int a, char ch) // 原函数 8 { 9 cout << "a " << a << " " << "ch " << ch << endl; 10 } 11 void Func(char ch, int a) // 重载1:参数顺序不同 12 { 13 cout << "ch " << ch << " " << "a " << a << endl; 14 } 15 void Func(int a) // 重载2:参数个数不同 16 { 17 cout << "a " << a << endl; 18 } 19 void Func(int a, double db) // 重载3:参数类型不同 20 { 21 cout << "a " << a << " " << "db " << db << endl; 22 } 23 void Func(int a, char ch) const // 重载4:常函数(被const修饰的函数) 24 { 25 cout << "a " << a << " " << "ch " << ch << endl; 26 } 27 /* 28 int Func(int a, char ch) // error! 非重载,编译无法通过。因为编译器认为是重定义。 29 { 30 cout << "a" << a << " " << "ch" << endl; 31 return a; 32 } 33 */ 34 }; 35 36 void main() 37 { 38 Sample ss; 39 ss.Func(10, 'a'); 40 ss.Func('a', 20); 41 ss.Func(30); 42 ss.Func(40, 12.34); 43 system("pause"); 44 } 45 46 // 运行结果: 47 /* 48 a 10 ch a 49 ch a a 20 50 a 30 51 a 40 db 12.34 52 请按任意键继续. . . 53 */
分析总结:
<1> 在同一个类中(同一作用域中)。
<2> 方法名相同。
<3> 参数个数、参数类型或者参数顺序不同。
<4> 与函数的返回值类型无关。
如果仅仅返回值类型不同,那么对编译器来说会在调用时产生二义性。
所以,抛开返回值类型再分析即相当于重定义,重定义是被禁止的(一个函数只允许有一份函数体)。
<5> const修饰。类中成员函数,const 用在函数后一般修饰的是this指针。所以,也算重载的范畴。
【2】覆盖
(1)覆盖也叫重写,是指在派生类中重写基类某虚函数的实现体的一种形式。
函数名、参数列表、返回值类型都必须同基类被重写的虚函数的严格一致。
仅仅只是函数实现体不同。即达到严格的覆盖目的。
(2)示例代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class Sample 5 { 6 public: 7 virtual void Func() 8 { 9 cout << "Sample::Func" << endl; 10 } 11 }; 12 13 class Test : public Sample 14 { 15 public: 16 void Func() 17 { 18 cout << "Test::Func" << endl; 19 } 20 }; 21 22 void main() 23 { 24 Sample* pa = new Test(); 25 pa->Func(); 26 delete pa; 27 pa = NULL; 28 system("pause"); 29 } 30 /* run out: 31 Test::Func 32 请按任意键继续. . . 33 */
分析总结:
<1> 不同的范围(分别位于基类和派生类,不同作用域中)。
<2> 方法名相同。
<3> 参数严格一致。
<4> 返回类型相同。
<5> 基类函数前必须要加关键字virtual,即必须是虚函数。
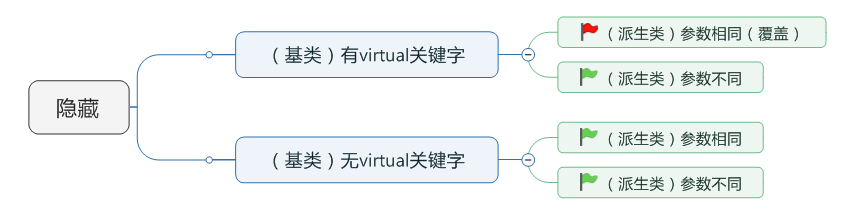
【3】隐藏
(1)隐藏是指在派生类中隐藏基类的同名函数。
与重载范围不同,隐藏函数和被隐藏函数不在同一个类中。
与覆盖条件不同,隐藏函数和被隐藏函数的参数可以相同,也可以不同,但是函数名必须要相同。
重要备注:
<1> 当参数相同时,如果基类中的函数被virtual修饰,基类的函数就是所谓被覆盖。
<2> 当参数相同时,如果基类中的函数没有被virtual修饰,基类的函数就是所谓被隐藏。
<3> 当参数不相同时,无论基类中的函数是否被virtua修饰,基类的函数都是所谓的被隐藏。
(2)示例代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class Sample 5 { 6 public: 7 virtual void Func0() 8 { 9 cout << "Sample::Func0" << endl; 10 } 11 12 virtual void Func1() 13 { 14 cout << "Sample::Func1" << endl; 15 } 16 17 void Func2(int a) 18 { 19 cout << "Sample::Func2" << endl; 20 } 21 22 void Func3(const char *db) 23 { 24 cout << "Sample::Func3" << endl; 25 } 26 27 void Func4(int n, int m) 28 { 29 cout << "Sample::Func4" << endl; 30 } 31 }; 32 33 class Test : public Sample 34 { 35 public: 36 // 覆盖 37 void Func0() // 带virtual关键字,参数相同 38 { 39 cout << "Test::Func0" << endl; 40 } 41 // 隐藏1 42 void Func1(int a) // 带virtual关键字,参数不同 43 { 44 cout << "Test::Func1" << endl; 45 } 46 47 #if 0 48 int Func1() // 带virtual关键字,参数相同,但返回值不同 49 { 50 cout << "Test::Func1_R" << endl; 51 return 0; 52 } 53 // -- E0317 返回类型与重写虚拟函数 "Sample::Func1" 的返回类型 "void" 既不相同,也不协变 54 #endif 55 56 // 隐藏2 57 void Func2(int a) // 不带virtual,参数相同,返回值相同 58 { 59 cout << "Test::Func2" << endl; 60 } 61 62 #if 0 63 int Func2(int a) // 不带virtual,参数相同,但返回值不同 64 { 65 cout << "Test::Func2_R" << endl; 66 return 0; 67 } 68 // -- E0311 无法重载仅按返回类型区分的函数 69 #endif 70 71 // 隐藏3 72 void Func3(int a) // 不带virtual,参数不同,返回值相同 73 { 74 cout << "Test::Func3" << endl; 75 } 76 // 隐藏4 77 int Func4(double dn, double dm) // 不带virtual,参数不同, 返回值不同 78 { 79 cout << "Test::Func4" << endl; 80 return 0; 81 } 82 }; 83 84 int main() 85 { 86 Test t1; 87 t1.Func0(); // Test::Func0 88 // t1.Func1(); // error! 被隐藏,无法调用 89 t1.Func1(10); // Test::Func1 90 t1.Func2(20); // Test::Func2 91 92 const char *str = "kaizen"; 93 // t1.Func3(str); // error! 被隐藏,无法调用 94 t1.Func3(30); // Test::Func3 95 t1.Func4(10, 20); // Test::Func4 96 cout << endl; 97 98 Sample* pSamp = new Test(); 99 pSamp->Func0(); // Test::Func0 100 pSamp->Func1(); // Sample::Func1 101 pSamp->Func2(200); // Sample::Func2 102 pSamp->Func3(str); // Sample::Func3 103 pSamp->Func4(100, 200); // Sample::Func4 104 delete pSamp; 105 pSamp = NULL; 106 cout << endl; 107 108 Test* pTest = new Test(); 109 pTest->Func0(); // Test::Func0 110 // pTest->Func1(); // error! 参数不匹配 111 pTest->Func2(200); // Test::Func2 112 // pTest->Func3(str); // error! 参数不匹配 113 pTest->Func4(100, 200); // Test::Func4 114 delete pTest; 115 pTest = NULL; 116 117 system("pause"); 118 119 return 0; 120 } 121 // run out: 122 /* 123 Test::Func0 124 Test::Func1 125 Test::Func2 126 Test::Func3 127 Test::Func4 128 129 Test::Func0 130 Sample::Func1 131 Sample::Func2 132 Sample::Func3 133 Sample::Func4 134 135 Test::Func0 136 Test::Func2 137 Test::Func4 138 请按任意键继续. . . 139 */
分析总结:
<1> 不同的范围(分别位于基类和派生类,不同作用域)。
<2> 方法名相同。
<3> 有关键字virtual,必须要参数不同。
<4> 无关键字virtual,参数任意。
<5> 图解
【4】总结
三者的关系,总结为一张图:
Good Good Study, Day Day Up.
顺序 选择 循环 总结



