会员
周边
新闻
博问
闪存
众包
赞助商
Chat2DB
所有博客
当前博客
我的博客
我的园子
账号设置
会员中心
简洁模式
...
退出登录
注册
登录
Catch Spark. Code Life
博客园
首页
新随笔
管理
上一页
1
2
3
4
5
6
···
21
下一页
2021年9月23日
堆操作(1)-堆中插入元素,删除元素
摘要: 一、堆定义 堆是一个优先队列,右二叉树来表示,其特性: 是一颗完全二叉树 任意节点的元素是其子树的最大值(最小值) 最大值,大顶堆 最小值,小顶堆 示例: 完全二叉树用数组继续存储。定义如下: public class HeapStruct { private Integer[] elements;
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-09-23 23:09 ibrake
阅读(2240)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
2021年9月11日
二叉树层次化遍历
摘要: 一、层次化遍历说明 层次化遍历:abcdefghij 二、层次化遍历代码 思想:采用队列先进先出的特性来实现 public static void levelTraversal(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } Queue<TreeNode
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-09-11 23:36 ibrake
阅读(64)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
二叉树后序遍历
摘要: 一、递归后序遍历 public static void postOrder(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } postOrder(root.getLeft()); postOrder(root.getRight()); System.out
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-09-11 23:19 ibrake
阅读(408)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
二叉树中序遍历
摘要: 中序遍历:左子树,根节点,右子树。 一、递归中序遍历 public static void inOrder(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } inOrder(root.getLeft()); System.out.println(root.
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-09-11 23:07 ibrake
阅读(439)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
二叉树先序遍历
摘要: 先序遍历:根节点,左节点,右节点。 一、递归先序遍历 递归方式比较直接明了。 public static void preOrder(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } System.out.println(root.getValue());
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-09-11 22:45 ibrake
阅读(401)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
将数组转化为二叉树
摘要: 一、数组和二叉树的关系 二叉树可以通过数组来进行存储。https://www.cnblogs.com/Brake/p/15058906.html 数组从0开始,如果父节点在数组中的下标是i,那么其左二子在数组中对应的下标则为2i+1。右儿子子对应的下标为2i+2。 同理,已知某节点在数组中对应的下标
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-09-11 22:34 ibrake
阅读(1771)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
2021年8月22日
【备忘】几个排序算法复杂度对比
摘要: 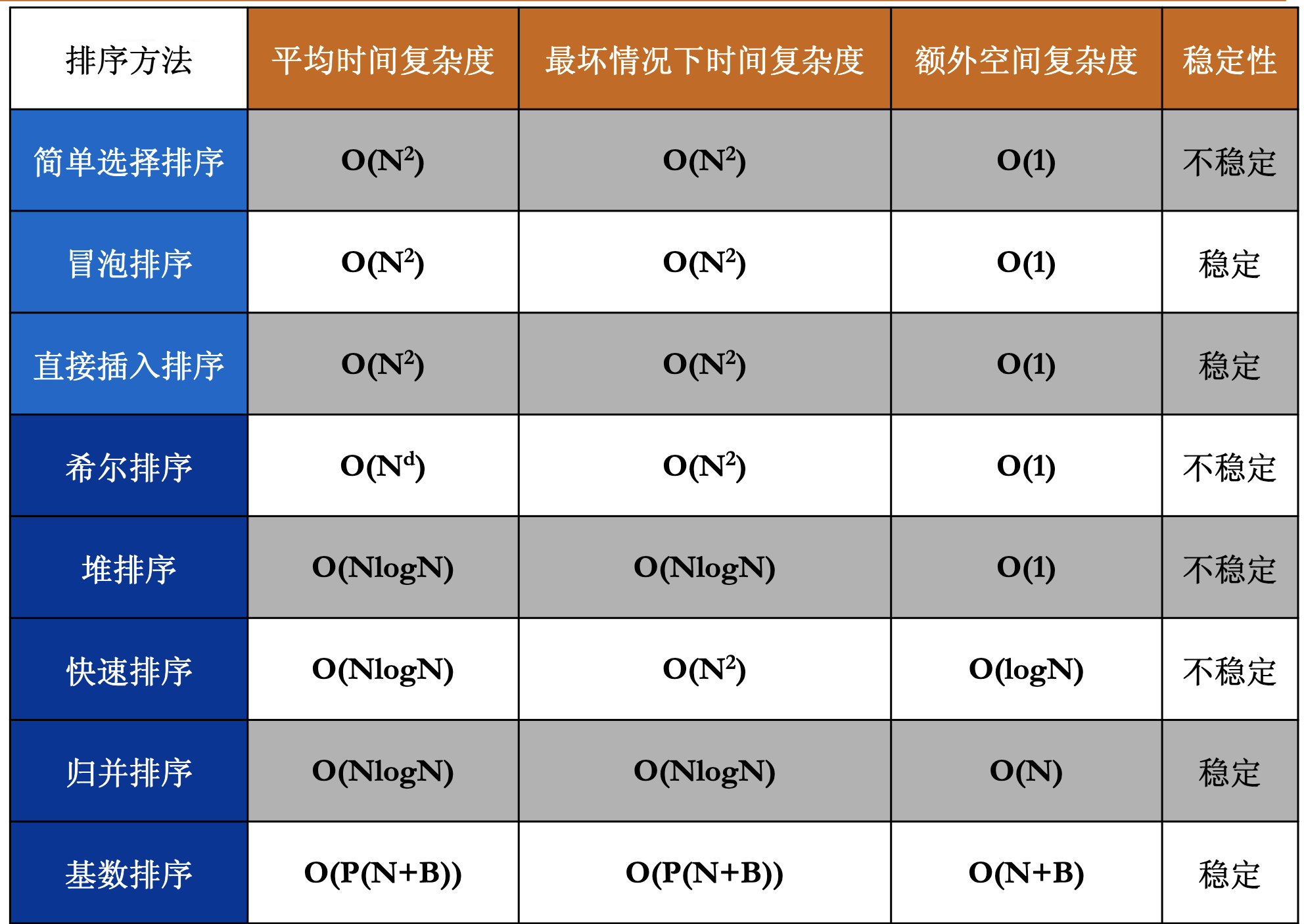
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-08-22 21:41 ibrake
阅读(36)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
2021年7月25日
二叉树存储
摘要: 顺序存储和链式存储
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-07-25 20:37 ibrake
阅读(301)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
2021年5月18日
选择排序
摘要: Code package kb.algorithm; public class SelectionSort { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a = new int[]{3, 6, 4, 7, 2}; sort(a); StringBu
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-05-18 23:22 ibrake
阅读(61)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
2021年5月16日
插入排序
摘要: 现实中打牌 接收到新牌后在已有的牌里面进行排序,然后找到属于自己的位置进行插入: 手中的牌永远是有序的 Code package kb.algorithm; public class InsertionSort { public static void main(String[] args) { i
阅读全文
posted @ 2021-05-16 14:42 ibrake
阅读(79)
评论(0)
推荐(0)
上一页
1
2
3
4
5
6
···
21
下一页
公告