冒泡排序
Code
package kb.algorithm;
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = new int[]{3, 6, 4, 9, 1, 7, 2, 5};
sort(a);
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(20);
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
sb.append(a[i]);
sb.append(",");
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
public static void sort(int[] a) {
int size = a.length;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < size - i - 1; j++) {
if (a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
int temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
执行结果
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,9,
分析改进
每次找出最大的一个元素移到最右边。
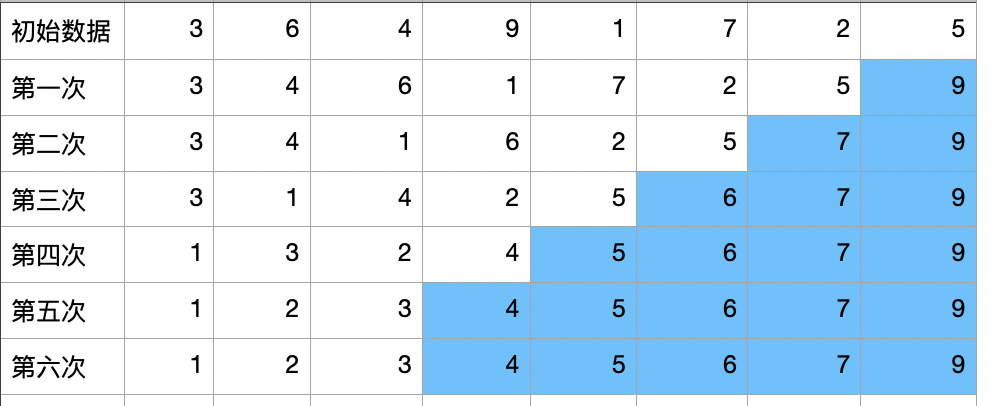
代码需要排序10次,当时上面的过程可以看到只需要5次即可完成这个排序,这是一个优化点,当内循环的执行完一次排序后如果没有发生数据交换(本例中的第五次),则说明整个列表已经全部排序排序完成了。
对上面的代码做一个改进。
package kb.algorithm;
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = new int[]{3, 6, 4, 9, 1, 7, 2, 5};
sort(a);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(20);
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
sb.append(a[i]);
sb.append(",");
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
public static void sort(int[] a) {
int size = a.length;
int executedCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
boolean switched = false;
for (int j = 0; j < size - i - 1; j++) {
if (a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
int temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
switched = true;
}
}
executedCount++;
if (!switched) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println("executedCount" + executedCount);
}
}
执行结果
executedCount6
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,9,
复杂度分析
时间复杂度O(n^2)。空间复杂度O(1)。
属于稳定性排序,当两个数字相同的时候,其位置是不会发生改变的。
作者:iBrake
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号