数据类型扩展
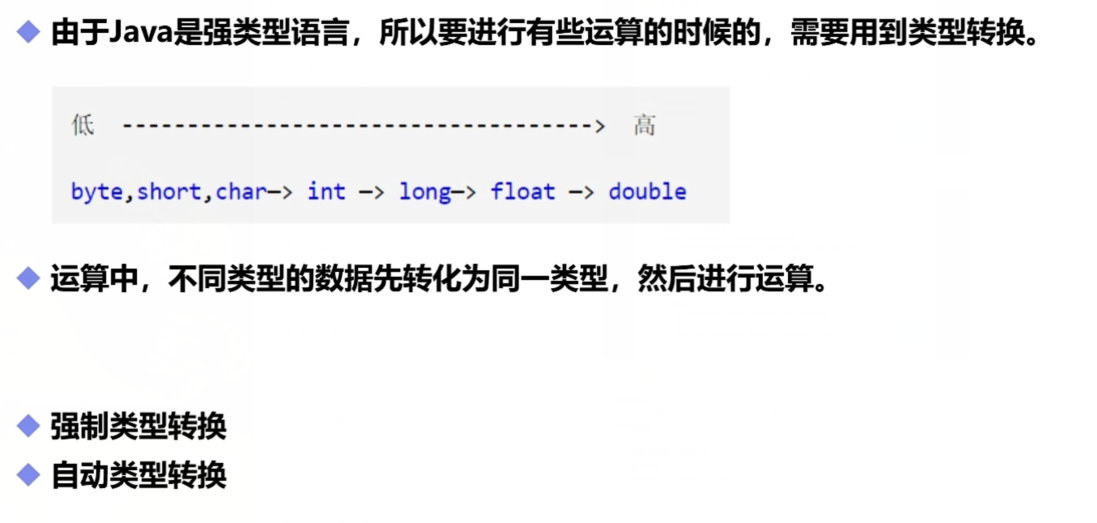
类型转换
import com.sun.management.VMOption; public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { // ①整数扩展: // 进制 二进制0b 十进制 八进制0 十六进制0x int i = 10; int i2 = 010;//八进制 int i3 = 0x10;//十六进制 0-9 A-F 16 System.out.println(i); System.out.println(i2); System.out.println(i3); System.out.println("==========================================================="); //②浮点数扩展:float+double //银行业务,钱的计算 //BigDecimal 数学工具类 float f = 0.1f;//0.1 double d = 1.0/10;//0.1 System.out.println(f == d); //false System.out.println(f); System.out.println(d); float d1 = 2333154545123454f; float d2 = d1 + 1; System.out.println(d1 == d2);//true //原因: //float 有限、离散、舍入误差、大约、接近但不等于 //double //解决:最好完全使用浮点数进行计算!!!!!!! System.out.println("==========================================================="); //③字符扩展: char c1 = 'a'; char c2 = '中'; System.out.println(c1);//a System.out.println((int)c1);//97 强制转换 System.out.println(c2);//中 System.out.println((int)c2);//20013 强制转换 //所有字符的本质还是数字 //编码 Unicode表:a = 97/A = 65 2字节 65536=2^16 //U0000 - UFFFF char c3 = '\u0061'; System.out.println(c3);//a //转义字符: // \t:制表符 System.out.println("hello\tyy"); // \ n:换行 System.out.println("hello\nyy"); System.out.println("==========================================================="); String sa = new String("hello world"); String sb = new String("hello world"); System.out.println(sa == sb);//false String sc = "hello world"; String sd = "hello world"; System.out.println(sc == sd);//true //对象:从内存分析 System.out.println("==========================================================="); //④布尔值扩展 : boolean flag = true; if (flag == true){ }//新手 if (flag){ //老手 //Less is More !代码要简洁易懂! } } }
public class Demo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 128; byte b = (byte) i;//内存溢出 double b1 = i; //强制转换: (类型)变量名 高--低 //自动转换:低--高 System.out.println(i);//128 System.out.println(b);//-128 System.out.println(b1);//128.0 /* 注意点: ①不能对布尔值进行转换 ②不能把对象类型转换为不相干的类型 ③高容量转换为低容量,强制转换 ④转换的时候可能出现内存溢出或者精度问题! */ System.out.println((int)23.7);//23 System.out.println((int)-45.89f);//-45 System.out.println("==========================================================="); char c = 'a'; int d = c + 1; System.out.println(d);//98 System.out.println((char) d);//b } }
public class Demo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { //操作比较大的数的时候,注意溢出问题 //JDK7新特性:数字之间可以用下滑线分割 int money = 10_0000_0000; System.out.println(money);//1000000000 int years = 20; int total = money * years;//计算的时候溢出了 System.out.println(total);//-1474836480 long total2 = money * years; System.out.println(total2);//-1474836480,还是溢出。 //原因:默认是int,转换之前可以就已经存在问题了 long total3 =money * (long)years;//先把一个数转换成long,整体格式会都转成long System.out.println(total3);//20000000000 long total4 = (long)money * years; System.out.println(total4);//20000000000 } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号