第五次实验
part1:使用二分法查找数据所在数组的位置
形参是数组,实参是数组名
// 练习:使用二分查找,在一组有序元素中查找数据项
// 形参是数组,实参是数组名
#include <stdio.h>
const int N=5;
int binarySearch(int x[], int n, int item);
int main() {
int a[N]={1,3,9,16,21};
int i,index, key;
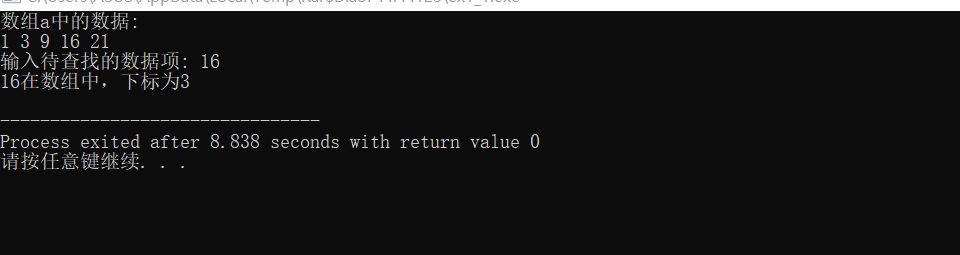
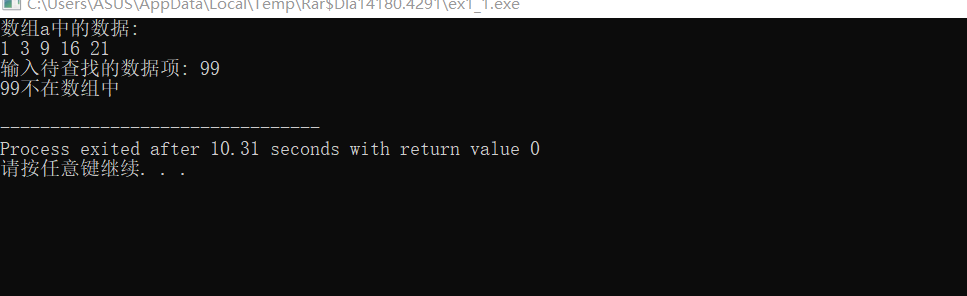
printf("数组a中的数据:\n");
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
printf("%d ",a[i]);
printf("\n");
printf("输入待查找的数据项: ");
scanf("%d", &key);
// 调用函数binarySearch()在数组a中查找指定数据项item,并返回查找结果给index
index=binarySearch(a , N , key); // 补足代码①
if(index>=0)
printf("%d在数组中,下标为%d\n", key, index);
else
printf("%d不在数组中\n", key);
return 0;
}
//函数功能描述:
//使用二分查找算法在数组x中查找特定值item,数组x大小为n
// 如果找到,返回其下标
// 如果没找到,返回-1
int binarySearch(int x[], int n, int item) {
int low, high, mid;
low = 0;
high = n-1;
while(low <= high) {
mid = (low+high)/2;
if (item == x[mid])
return mid;
else if(item < x[mid])
high = mid - 1;
else
low = mid + 1;
}
return -1;
}
运行结果
1.1形参是指针变量,实参是数组名
// 练习:使用二分查找,在一组有序元素中查找数据项
// 形参是指针变量,实参是数组名
#include <stdio.h>
const int N=5;
int binarySearch(int *x, int n, int item);
int main() {
int a[N]={1,3,9,16,21};
int i,index, key;
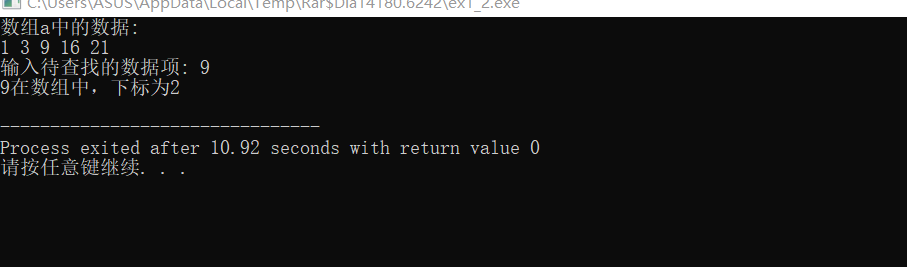
printf("数组a中的数据:\n");
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
printf("%d ",a[i]);
printf("\n");
printf("输入待查找的数据项: ");
scanf("%d", &key);
// 调用函数binarySearch()在数组a中查找指定数据项item,并返回查找结果
index=binarySearch(a ,N ,key); // 补足代码①
if(index>=0)
printf("%d在数组中,下标为%d\n", key, index);
else
printf("%d不在数组中\n", key);
return 0;
}
//函数功能描述:
//使用二分查找算法在x指向的数据项开始的n个数据中,查找item
// 如果找到,返回其位置
// 如果没找到,返回-1
int binarySearch(int *x, int n, int item) {
int low, high, mid;
low = 0;
high = n-1;
while(low <= high) {
mid = (low+high)/2;
if (item == *(x+mid))
return mid;
else if(item < *(x+mid))
high = mid - 1;
else
low = mid + 1;
}
return -1;
}

part2:选择排序法
按字典排序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
void selectSort(char str[][20], int n ); // 函数声明,形参str是二维数组名
int main() {
char name[][20] = {"John", "Alex", "Joseph", "Candy", "Geoge"};
int i;
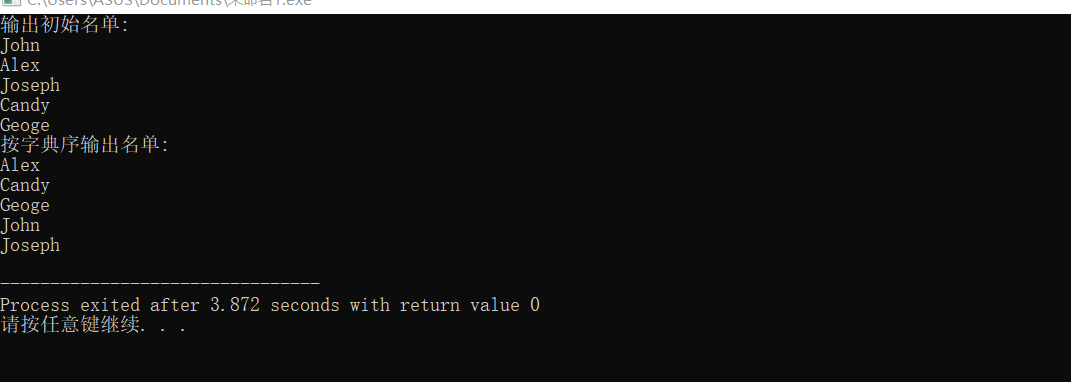
printf("输出初始名单:\n");
for(i=0; i<5; i++)
printf("%s\n", name[i]);
selectSort(name, 5); // 调用选择法对name数组中的字符串排序
printf("按字典序输出名单:\n");
for(i=0; i<5; i++)
printf("%s\n", name[i]);
return 0;
}
// 函数定义
// 函数功能描述:使用选择法对二维数组str中的n个字符串按字典序排序
void selectSort(char str[][20], int n) {
int i,j,k; char temp[20];
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++){
k=i;
for(j=i+1;j<n;j++)
if(strcmp(str[j],str[k])<0)
k=j;
if(k!=i){
strcpy(temp,str[i]);
strcpy(str[i],str[k]);
strcpy(str[k],temp);}
}
// 补足代码
// ×××
}
part3:总结与体会
1.数组名作为参数 VS 指针变量作为参数
形参 实参
数组的写法 int fun(int a[ ], int n ) fun(a,n)
指针的写法 int swap(int*p ,int*q) swap(p ,q)
2.使用选择法对字符串的排序应注意字符串之间的关系比较需要借助字符串处理函数,
对于某些边界值的考虑也要清楚。
3.选择排序法还有点不明白。
互评:
https://www.cnblogs.com/xu9729/p/10918429.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/weiyuyang/p/10896239.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/silentisland/p/10913271.html

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号