PQL学习[已迁移]
转自:https://yunlzheng.gitbook.io/prometheus-book/parti-prometheus-ji-chu/promql/prometheus-query-language
//非常全面易懂的教程
1.语法
当我们直接使用监控指标名称查询时,可以查询该指标下的所有时间序列,只会返回瞬时向量表达式,返回值中只会包含该时间序列中的最新的一个样本值:
http_requests_total{code="200",handler="alerts",instance="localhost:9090",job="prometheus",method="get"}=(20889@1518096812.326)
http_requests_total{code="200",handler="graph",instance="localhost:9090",job="prometheus",method="get"}=(21287@1518096812.326)
http_requests_total //直接使用监控指标名称查询时,可以查询该指标下的所有时间序列。如上。
http_requests_total{}
1.1 筛选
PromQL支持使用
=和!=两种完全匹配模式:- 通过使用
label=value可以选择那些标签满足表达式定义的时间序列; - 反之使用
label!=value则可以根据标签匹配排除时间序列;
需要查询所有http_requests_total时间序列中满足或不满足标签instance为localhost:9090的时间序列:
http_requests_total{instance="localhost:9090"}
http_requests_total{instance!="localhost:9090"}
除了使用完全匹配的方式对时间序列进行过滤以外,PromQL还可以支持使用正则表达式作为匹配条件,多个表达式之间使用
|进行分离: - 使用
label=~regx表示选择那些标签符合正则表达式定义的时间序列; - 反之使用
label!~regx进行排除; (这里~号是什么意思?可以理解为表示正则的符号?)
例如,如果想查询多个环节下的时间序列序列可以使用如下表达式:
http_requests_total{environment=~"staging|testing|development",method!="GET"}
1.3 范围查询
http_request_total{} # 瞬时向量表达式,选择当前最新的数据 http_requests_total{}[5m] //选择最近5分钟内的所有样本数据 //时间位移操作 http_request_total{} offset 5m //5分钟前的瞬时样本数据 http_request_total{}[1d] offset 1d //昨天一天的区间内的样本数据
2.内置函数
2.1 sum和sum_over_time
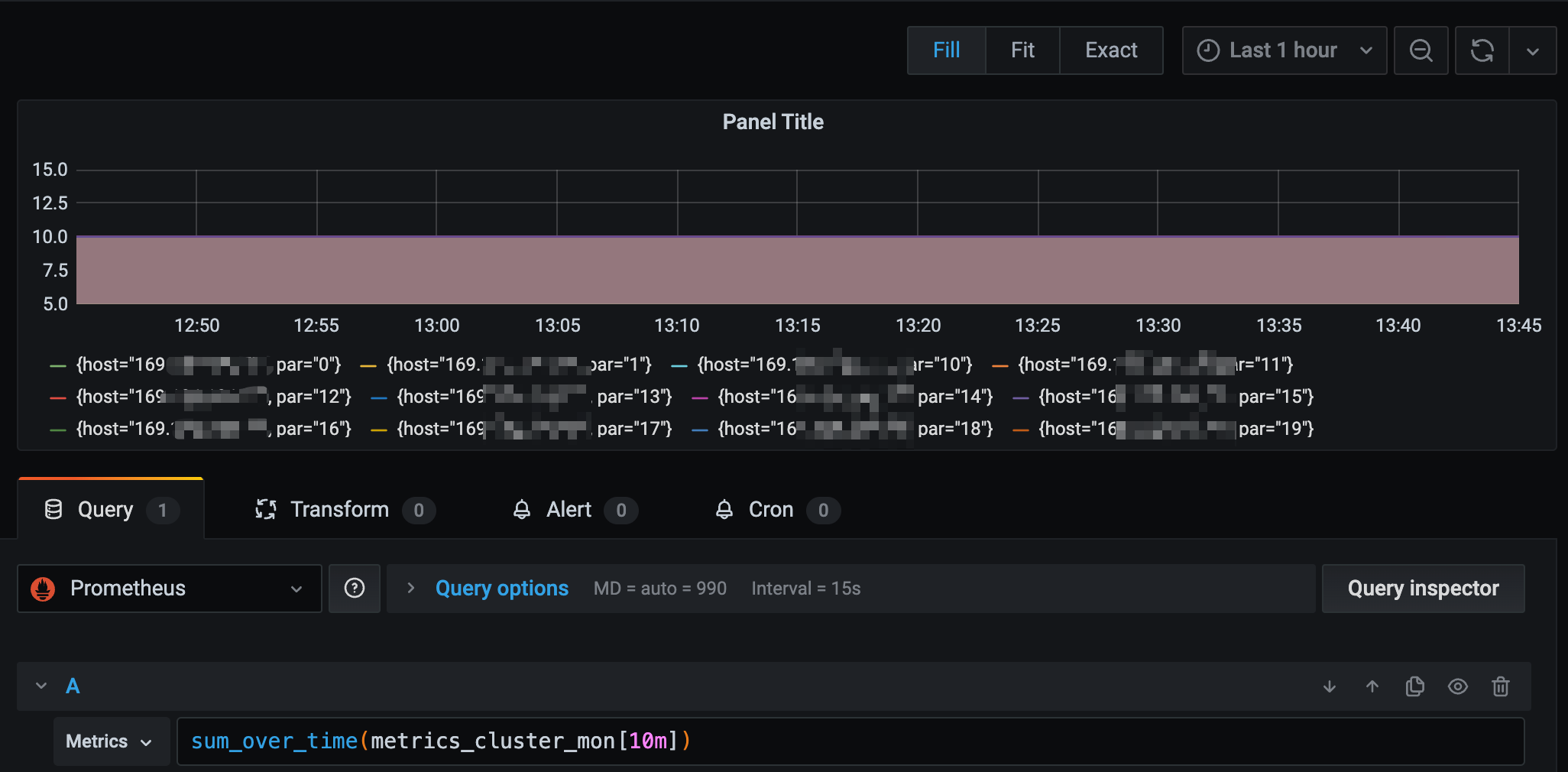
sum(求和)。所有序列最新一个数据(瞬时向量)求和,sum是对瞬时向量求和,不会对区间向量求和。返回的时间序列是没有标签的。sum_over_time(range-vector): 区间向量内每个度量指标的求和。各序列(tag组合维度)的2分钟数据(区间向量)求和。avg_over_time(range-vector): 区间向量内每个度量指标的平均值。【需要传入区间向量。】
sum/avg_over_time是给各序列求区间内的和/平均,sum/avg再结合by按照维度再求平均。
sum不区分tag维度,所有的瞬时向量一起求和。返回的时间序列是没有标签的。
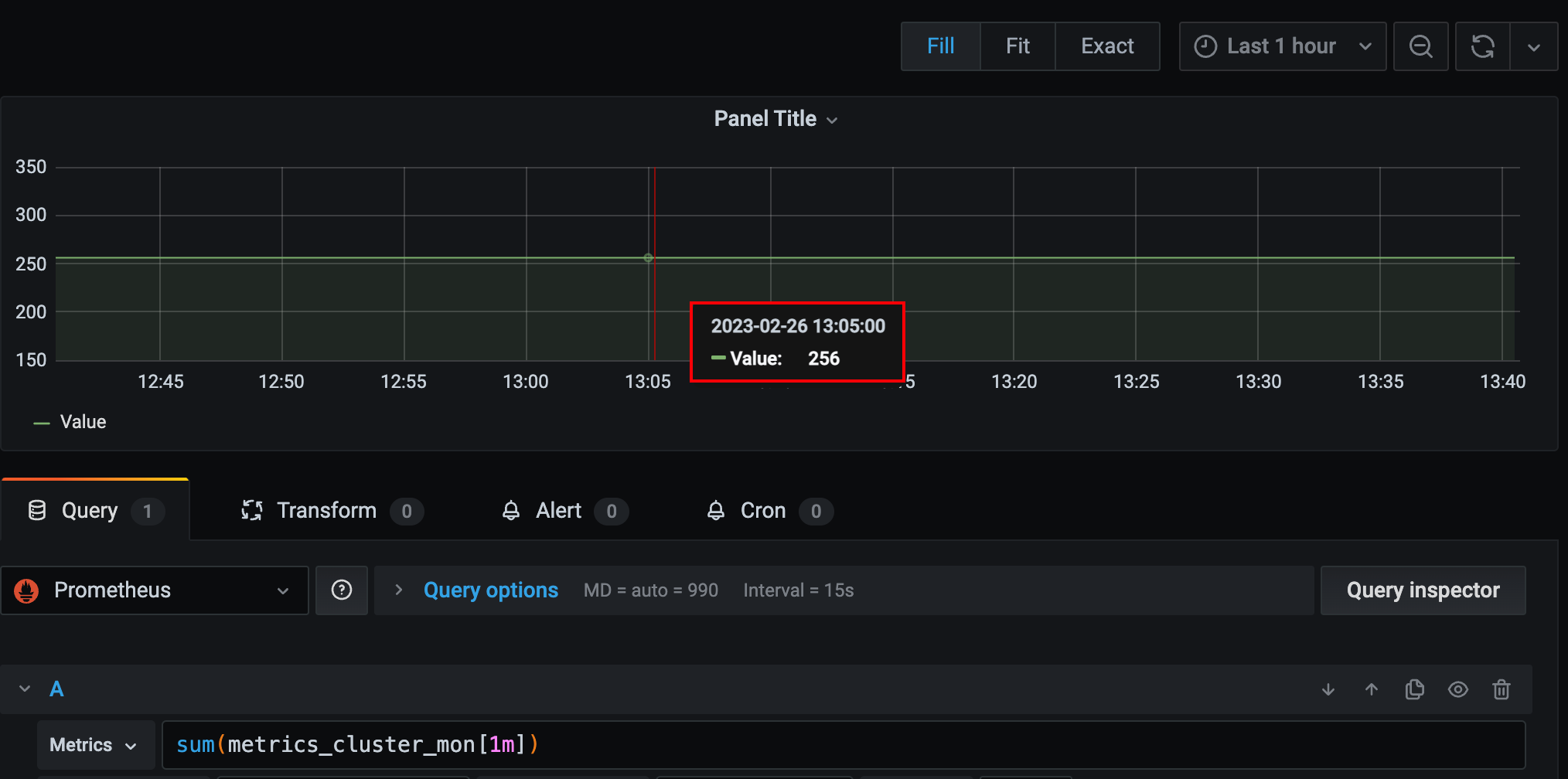
sum_over_time对各个序列单独求和,是对区间向量进行的。
2.2 absent
https://prometheus.fuckcloudnative.io/di-san-zhang-prometheus/di-4-jie-cha-xun/functions
2.3 增长情况
rate是求平均增长率,长尾效应无法避免,
increase是求区间第一个和最后一个之间的增长率。
还有irate。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号