proto3学习
转自:https://colobu.com/2017/03/16/Protobuf3-language-guide/#指定字段类型
1.消息message类型
假设你想定义一个“搜索请求”的消息格式,每一个请求含有一个查询字符串、你感兴趣的查询结果所在的页数,以及每一页多少条查询结果。
syntax = "proto3";//指定使用proto3版本,必须在第一行 message SearchRequest { string query = 1;//类型、名字、唯一的标示符 int32 page_number = 2; int32 result_per_page = 3; }
在消息定义中,每个字段都有唯一的一个数字标识符。这些标识符是用来在消息的二进制格式中识别各个字段的,一旦开始使用就不能够再改变(?什么意思,不能随意更改吗?)。
对C++来说,当用protocol buffer编译器来运行.proto文件时,编译器会为每个.proto文件生成一个.h文件和一个.cc文件,.proto文件中的每一个消息有一个对应的类。
2.类型
2.1 枚举enum
可能想为一个字段指定某“预定义值序列”中的一个值,这时候可以通过枚举实现。假设要定义一个Corpus的枚举类型,需要:
- 在消息格式中添加了一个叫做Corpus的枚举类型——它含有所有可能的值 ——
- 以及一个类型为Corpus的字段:
message SearchRequest { string query = 1; int32 page_number = 2; int32 result_per_page = 3; enum Corpus {//可以定义在message外部 UNIVERSAL = 0; WEB = 1; IMAGES = 2; LOCAL = 3; NEWS = 4; PRODUCTS = 5; VIDEO = 6; } Corpus corpus = 4; }
Corpus枚举的第一个常量映射为0:每个枚举类型必须将其第一个类型映射为0,这是因为:
- 必须有有一个0值,我们可以用这个0值作为默认值。
- 这个零值必须为第一个元素,为了兼容proto2语义,枚举类的第一个值总是默认值。
2.2 map
关联映射:
map<key_type, value_type> map_field = N;
//添加成员:
auto p=a->mutable_map_field();
p->insert({key,value});
//如果只加一个,可以直接加
a->mutable_map_field()->insert({key,value});
//直接赋值:
*a->mutable_map_filed()={cpp_map.beign(),cpp_map.end()};//这种赋值方式相当简洁
//case
- key_type可以是任意Integer或者string类型;value_type可以是任意类型。
pb3的map源码,有一些可用的方法:
template<typename Key, typename T> { class Map { // Member types typedef Key key_type; typedef T mapped_type; typedef MapPair< Key, T > value_type; // Iterators iterator begin(); const_iterator begin() const; const_iterator cbegin() const; iterator end(); const_iterator end() const; const_iterator cend() const; // Capacity int size() const; bool empty() const; // Element access T& operator[](const Key& key); const T& at(const Key& key) const; T& at(const Key& key); // Lookup,查找 int count(const Key& key) const; const_iterator find(const Key& key) const; iterator find(const Key& key); // Modifiers pair<iterator, bool> insert(const value_type& value); template<class InputIt> void insert(InputIt first, InputIt last); size_type erase(const Key& Key); iterator erase(const_iterator pos); iterator erase(const_iterator first, const_iterator last); void clear(); // Copy Map(const Map& other); Map& operator=(const Map& other); }
2.3 package
可以为.proto文件新增一个可选的package声明符,用来防止不同的消息类型有命名冲突。
package foo.bar;
message Open { ... }
对于C++,产生的类会被包装在C++的命名空间中,如上例中的Open会被封装在 foo::bar空间中,namespace foo::bar.
在其他的消息格式定义中可以使用包名+消息名的方式来定义域的类型(访问该message类型),如:
message Foo { ... required foo.bar.Open open = 1;//使用其他pb文件中定义的类型 ... }
2.4 repeated修饰符
https://blog.csdn.net/tennysonsky/article/details/73921025
repeated 代表可重复,我们可以理解为数组:
syntax = "proto3";//指定版本信息,不指定会报错 message Person //message为关键字,作用为定义一种消息类型 { string name = 1; //姓名 int32 id = 2; //id string email = 3; //邮件 } message AddressBook { repeated Person people = 1; }
protoc3为其生成如下代码:
int people_size() const; void clear_people(); const ::Person& people(int index) const; ::Person* mutable_people(int index);//可以根据下标获取数组元素指针,并且可以更改其值 ::Person* add_people();//add 增加对象 ::google::protobuf::RepeatedPtrField< ::Person >* mutable_people(); const ::google::protobuf::RepeatedPtrField< ::Person >& people() const;
通过上述add_people添加,
void set_addressbook() { AddressBook obj; Person *p1 = obj.add_people(); //新增加一个Person p1->set_name("mike"); p1->set_id(1); p1->set_email("mike@qq.com"); }
注意到是先通过add_people返回一个指针类型的对象,然后再通过调用函数设置字段值的。
如果repeat是一个普通的数据类型,如uint32或string,那么直接add_uid(uid);即可
//普通的数据类型生成的函数 int gids_size() const;/ void clear_gids(); ::google::protobuf::uint64 gids(int index) const; void set_gids(int index, ::google::protobuf::uint64 value); void add_gids(::google::protobuf::uint64 value);
2.5 成员是message类型
message GetUserList { Error error = 1; repeated User list = 2;// repeated表示列表 } //比如上面的error,那么在添加时直接mutable一个然后修改即可 GetUserList p; Error* err = p.mutable_error(); err->set_errorcode(1); err->set_errormsg("xxx"); //repeated的要用add_list User* user = p.add_list(); user->set_age(10); user->set_name("zhangsan"); user->set_sex(User::MAN);
3.解析默认值
当一个消息被解析的时候,如果被编码的信息不包含一个特定的singular元素,被解析的对象对应的域被设置位一个默认值,对于不同类型指定如下:
- 对于string,默认是一个空string
- 对于bytes,默认是一个空的bytes
- 对于bool,默认是false
- 对于数值类型,默认是0
- 对于枚举,默认是第一个定义的枚举值,必须为0;
- 对于消息类型(message),域没有被设置,确切的消息是根据语言确定的;
- 对于可重复域的默认值是空。
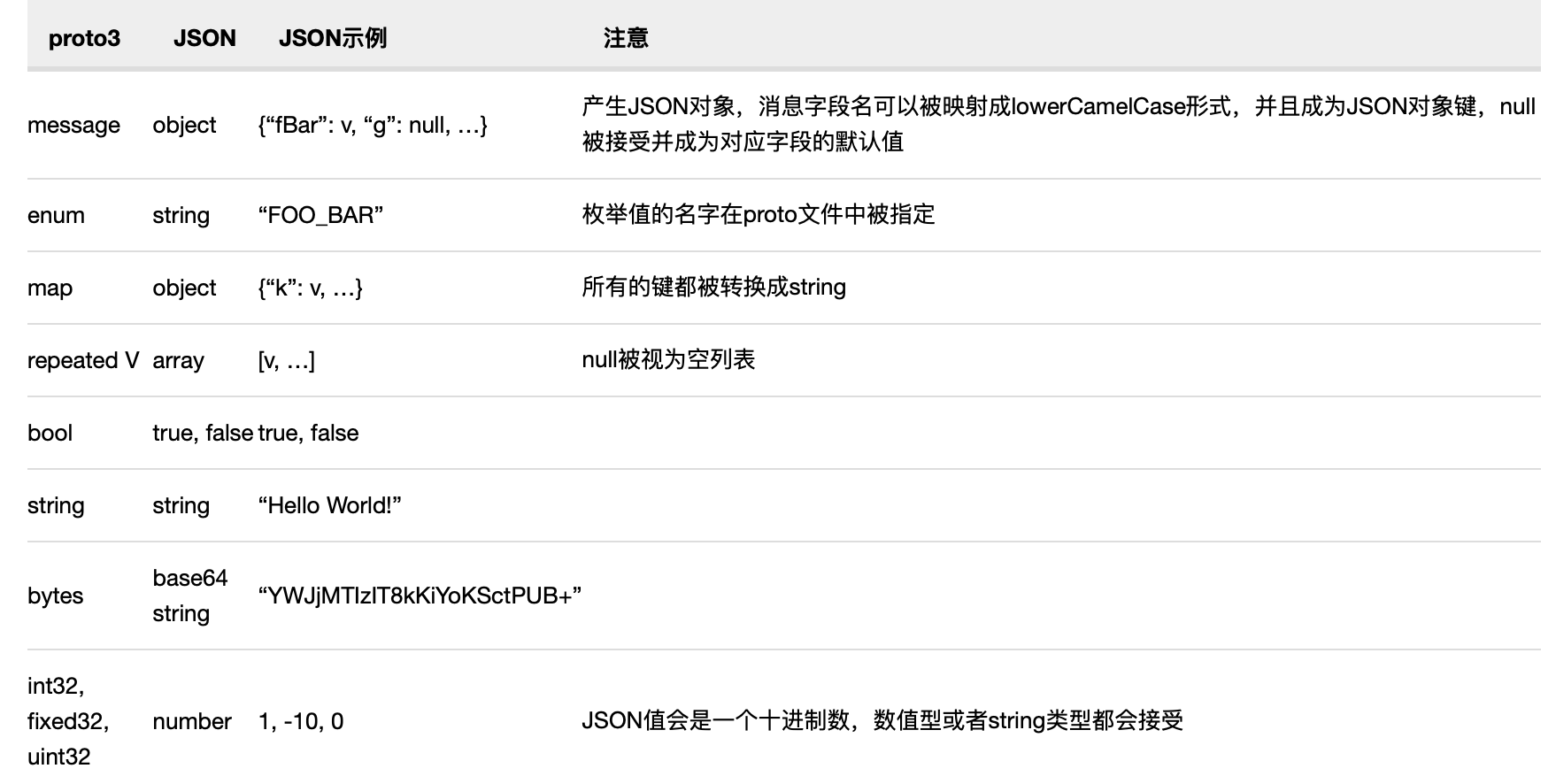
4.与json的映射关系
空值转换关系:
- 如果JSON编码的数据丢失或者其本身就是null,这个数据会在解析成protocol buffer的时候被表示成默认值。
- 如果一个字段在protocol buffer中表示为默认值,在转化成JSON的时候忽略掉以节省空间。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号