ES6 中的类
11.类
Es5 中类的定义,需要使用函数。
function Person(name,age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.sayName = function() {
return this.sayName;// 定义方法
}
let p = new Person('mjj',18);
console.log(p);
11.1 定义类
语法:
// 伪代码
class 类名{
//构造方法
constructor(参数..){
}
方法(){
方法体..
}
}
示例:
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
sayName() {
return this.name;
}
satAge() {
return this.age;
}
}
访问器属性 get()和set。
将方法当做属性使用,类似于python中的装饰器@property和get相似.
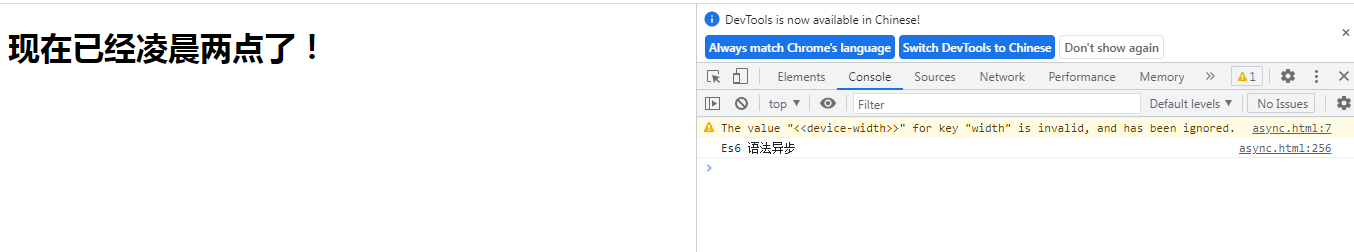
11.2 私有方法
使用Symbol值的唯一,来模拟私有方法,表示类的内部使用的私有方法。
const name = Symbol('name');
const age = Symbol('age');
class Obj {
// 类的实例属性
// 可以在constructor中定制,也可以在这里定制 目前已经支持
// myPro = 32;
// 类的静态属性
static yourPro = 45;
constructor() {
// console.log(this.myPro);
console.log(Obj.yourPro);
}
// 公有方法
say(a) {
return this[name](a);
}
// 私有方法
[name](a) {
return a;
}
// 静态方法 不能通过实例去调用,只能通过类本身去调用
static create() {
return new Obj();
}
}
let o = new Obj();
11.3 添加方法的额外补充
类似与反射的应用
Object.assign(Person.prototype, {
sayName() {
return this.name;
},
sayAge() {
return this.age;
}
})
const p1 = new Person('mjj', 19);
console.log(p1.sayName());
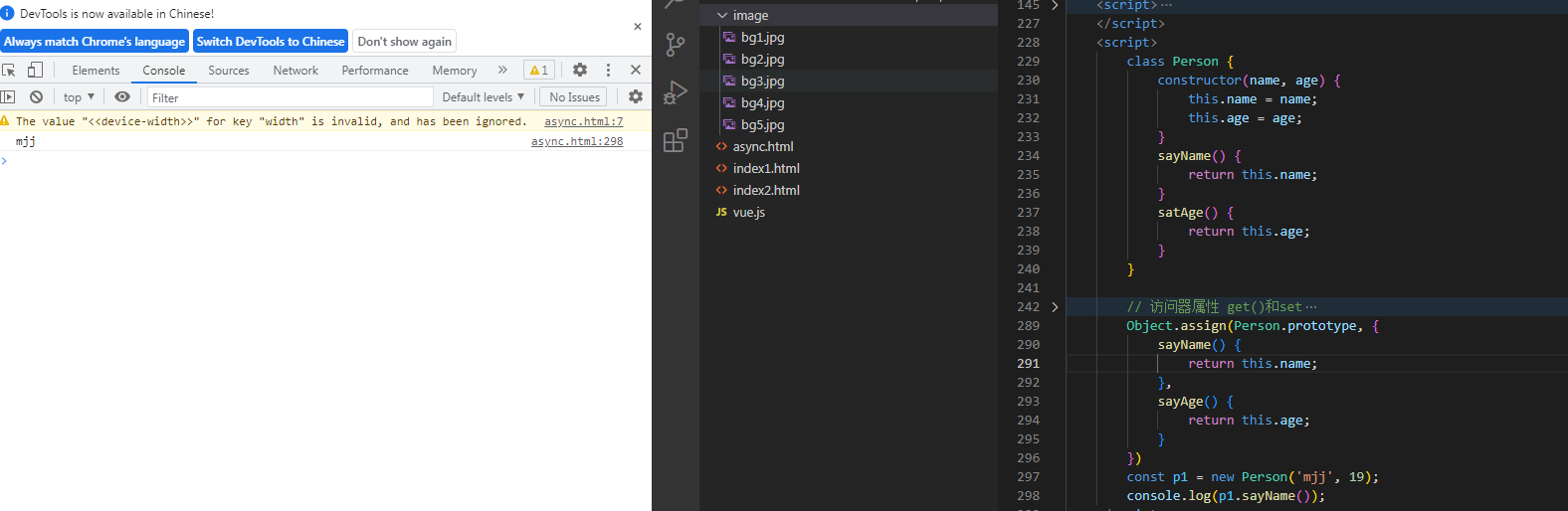
11.4 继承
类的继承关键字与java中继承的关键字是相同的都是extends.
// 类的继承
// 类和类之间可以通过extends关键字实现继承
class Animal {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
sayName() {
return this.name;
}
sayAge() {
return this.age;
}
}
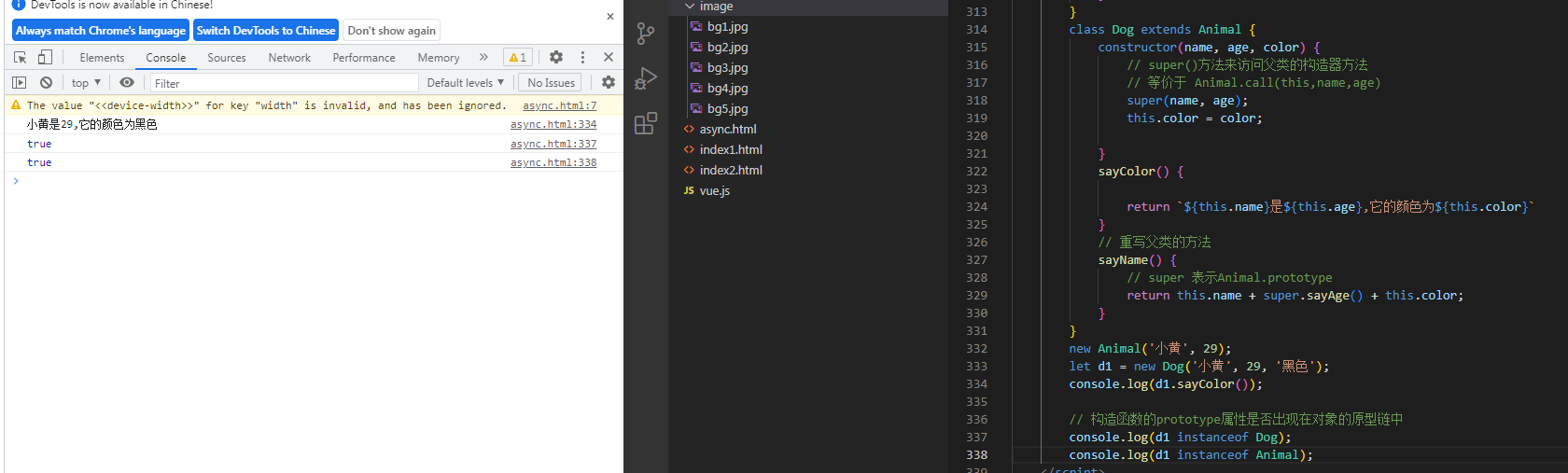
class Dog extends Animal {
constructor(name, age, color) {
// super()方法来访问父类的构造器方法
// 等价于 Animal.call(this,name,age)
super(name, age);
this.color = color;
}
sayColor() {
return `${this.name}是${this.age},它的颜色为${this.color}`
}
// 重写父类的方法
sayName() {
// super 表示Animal.prototype
return this.name + super.sayAge() + this.color;
}
}
new Animal('小黄', 29);
let d1 = new Dog('小黄', 29, '黑色');
console.log(d1.sayColor());
// 构造函数的prototype属性是否出现在对象的原型链中
console.log(d1 instanceof Dog);
console.log(d1 instanceof Animal);
// 混入 Mixin模式的实现
// 将多个类的接口混入到另一个类中
let A = {
getA() {
return 'A'
}
}
let B = {
getB() {
return 'B'
}
}
function mixin(...mixins) {
class Base {};
Object.assign(Base.prototype, ...mixins);
return Base
}
class C extends mixin(A, B) {
constructor(){
super();
}
}
let cobj = new C();
console.log(cobj.getA());
console.log(cobj.getB());



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号