drf(四)频率与节流
drf(四)访问频率与节流
问题引出:网站一般都存在爬虫机制,频率控制就是一种,如果一个IP或者用户在短时间内发起了多次请求显然不是正常的应用请求,此时应该加以访问频率的控制;
1.访问频率源码流程
与前几节的介绍相同源码入口依旧为dispatch()和inital();
def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Runs anything that needs to occur prior to calling the method handler.
"""
self.format_kwarg = self.get_format_suffix(**kwargs)
# Perform content negotiation and store the accepted info on the request
neg = self.perform_content_negotiation(request)
request.accepted_renderer, request.accepted_media_type = neg
# Determine the API version, if versioning is in use.
version, scheme = self.determine_version(request, *args, **kwargs)
request.version, request.versioning_scheme = version, scheme
# Ensure that the incoming request is permitted
self.perform_authentication(request)
self.check_permissions(request)
self.check_throttles(request) #选择节流的功能
check_throttles函数()
def check_throttles(self, request):
"""
Check if request should be throttled.
Raises an appropriate exception if the request is throttled.
"""
throttle_durations = [] #定义空列表
for throttle in self.get_throttles(): # 循环改方法
if not throttle.allow_request(request, self):
#表示节流类中需要有get_throttles()方法。
throttle_durations.append(throttle.wait())
# throttle.wait()表明对象中需要有wait()方法。并将方法的结果填入列表
# 表示列表不为空
if throttle_durations:
# Filter out `None` values which may happen in case of config / rate
# changes, see #1438
durations = [
duration for duration in throttle_durations
if duration is not None
] # 生成返回值不为空的值
duration = max(durations, default=None)# 返回列表中最大的元素
self.throttled(request, duration)
get_throttles() 方法
def get_throttles(self):
"""
Instantiates and returns the list of throttles that this view uses.
"""
# 依旧是列表生成式,用来循环生成对象
return [throttle() for throttle in self.throttle_classes]
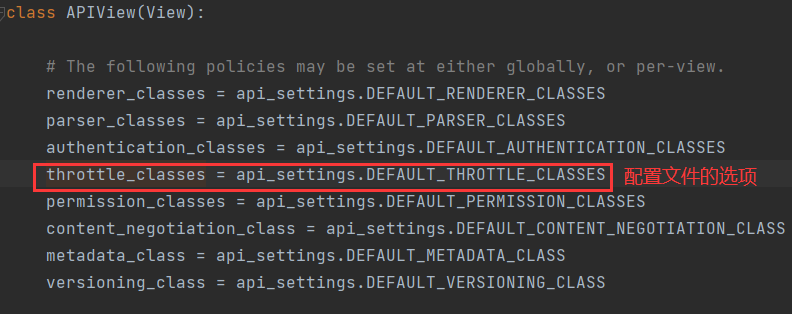
throttled() 方法。
def throttled(self, request, wait):
"""
If request is throttled, determine what kind of exception to raise.
"""
raise exceptions.Throttled(wait) # 抛出异常。
2.自定义及局部使用
思路:用户分为匿名用户和已登录用户,匿名用户控制频率主要依据的是IP地址,已登录的用户会根据系统定义的用户唯一标识进行控制。
import time
VISIT_RECORD = {}
class VisitThrottle(object):
"""60s内只能访问3次"""
def __init__(self):
self.history = None
def allow_request(self, request, view):
# 1. 获取用户IP
remote_addr = request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR')
ctime = time.time() #记录当前时间
if remote_addr not in VISIT_RECORD: # 初次访问
VISIT_RECORD[remote_addr] = [ctime, ] # 初始化列表
return True
history = VISIT_RECORD.get(remote_addr)
self.history = history # 将记录封装值对象中
while history and history[-1] < ctime - 60:
# 如果列表有值,且最后一次时间已经超过了一分钟,则直接将最后的元素移除,节省内存。
history.pop()
if len(history) < 3:
history.insert(0, ctime)
return True #未达到3次,可以进行访问
# return True # 表示可以继续访问
# return False # 表示访问频率太高,被限制
def wait(self):
"""
还需要等多少秒才能访问
:return:
"""
ctime = time.time() # 获取时间戳
return 60 - (ctime - self.history[-1])
# 60减去(最新的时间-被限制的时间)得到剩余被限制的时间并返回
使用登录接口进行测试:
class AuthView(APIView):
"""
用于用户登录认证
"""
throttle_classes=[VisitThrottle]# 进行频率的控制。
permission_classes = [] # 在登录认证中放开权限的要求
authentication_classes = [] #登录函数不需要使用验证,因此可以直接赋值给空列表。
def post(self,request,*args,**kwargs): #登录功能一般使用post进行操作
ret = {'code':1000,'msg':None} #初始化返回值
try:
user = request._request.POST.get('username')
pwd = request._request.POST.get('password')
# 往数据库查询参数
obj = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=user,password=pwd).first()
if not obj:# 用户不存在
ret['code'] = 1001
ret['msg'] = "用户名或密码错误"
# 为登录用户创建token
token = md5(user)
# 存在就更新,不存在就创建
models.UserToken.objects.update_or_create(user=obj,defaults={'token':token})
ret['token'] = token
except Exception as e:
ret['code'] = 1002
ret['msg'] = '请求异常'
return JsonResponse(ret)
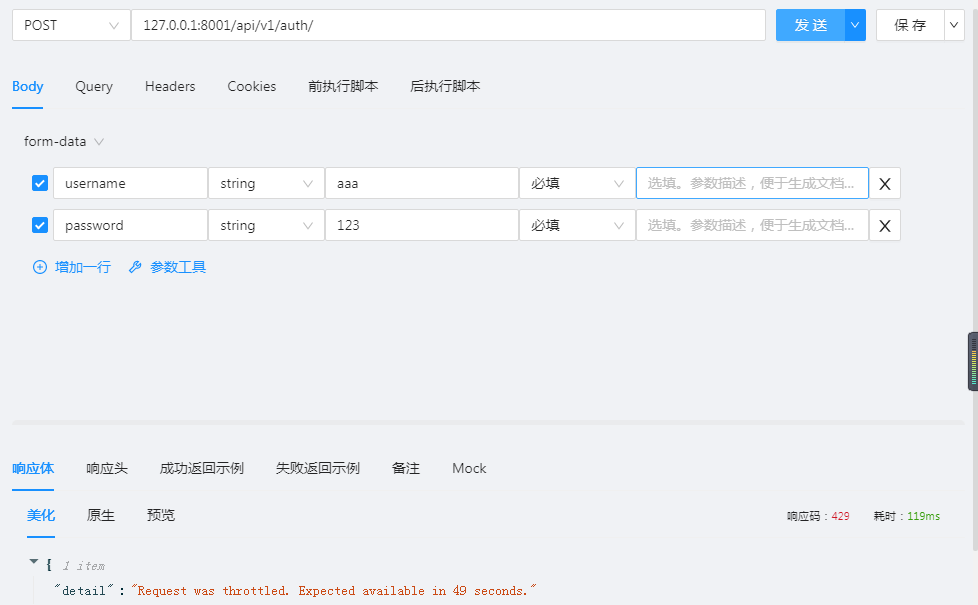
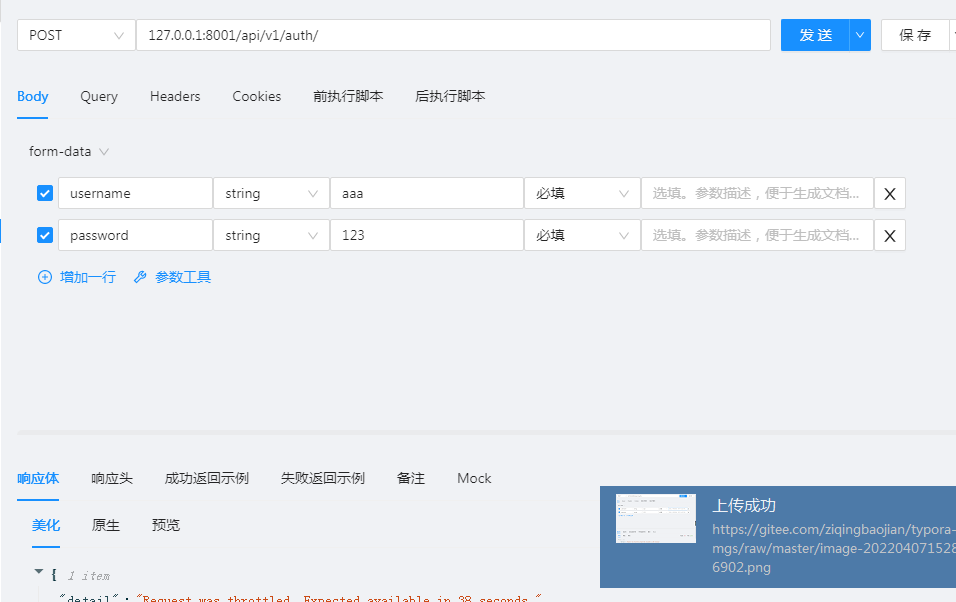
访问被限制且秒数在逐渐减少;
3.内置频率控制使用
3.1 内置类的源码剖析
- 基本节流类
from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle
# 导入查看节流控制类进行查看
class BaseThrottle:
"""
Rate throttling of requests.
"""
def allow_request(self, request, view):
"""
Return `True` if the request should be allowed, `False` otherwise.
"""
raise NotImplementedError('.allow_request() must be overridden')
def get_ident(self, request):
xff = request.META.get('HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR')
remote_addr = request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR') #获取IP
num_proxies = api_settings.NUM_PROXIES # 读取配置
if num_proxies is not None:
if num_proxies == 0 or xff is None:
return remote_addr
addrs = xff.split(',')
client_addr = addrs[-min(num_proxies, len(addrs))]
return client_addr.strip()
return ''.join(xff.split()) if xff else remote_addr
def wait(self):
"""
Optionally, return a recommended number of seconds to wait before
the next request.
"""
return None
- 源码中的其他节流类
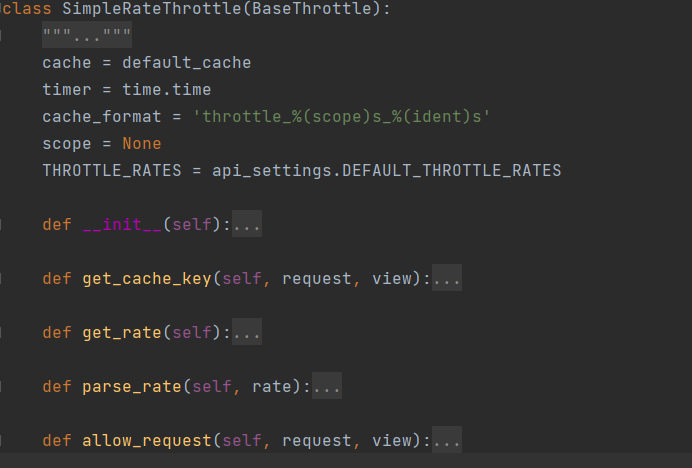
该类继承了BaseThrottle类,但是多出来许多方法与变量,下面进行源码剖析。
class SimpleRateThrottle(BaseThrottle):
cache = default_cache # django默认缓存
timer = time.time #时间戳对象,未加括号
cache_format = 'throttle_%(scope)s_%(ident)s'# 缓存存储格式
scope = None # 标志,一般在配置文件中配置
THROTTLE_RATES = api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES # 配置文件中的选项
def __init__(self):
if not getattr(self, 'rate', None):
self.rate = self.get_rate()
self.num_requests, self.duration = self.parse_rate(self.rate)
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
"""
Should return a unique cache-key which can be used for throttling.
Must be overridden.
May return `None` if the request should not be throttled.
"""
# 继承该类时候,此函数必须被重写
raise NotImplementedError('.get_cache_key() must be overridden')
def get_rate(self):
"""
Determine the string representation of the allowed request rate.
"""
if not getattr(self, 'scope', None): # 使用反射查看socpe的值
msg = ("You must set either `.scope` or `.rate` for '%s' throttle" %
self.__class__.__name__)
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg) #未传入则抛出异常
try:
return self.THROTTLE_RATES[self.scope]
#将scope作为配置文件中字典的键,DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES配置参数为字典。
except KeyError:
msg = "No default throttle rate set for '%s' scope" % self.scope
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg)
def parse_rate(self, rate):
"""
Given the request rate string, return a two tuple of:
<allowed number of requests>, <period of time in seconds>
"""
if rate is None:
return (None, None)
num, period = rate.split('/')
num_requests = int(num)
# 解析传入的速率
# 表名传入的速率按照1/m的形式进行编写。
duration = {'s': 1, 'm': 60, 'h': 3600, 'd': 86400}[period[0]]
return (num_requests, duration)
def allow_request(self, request, view):
"""
Implement the check to see if the request should be throttled.
On success calls `throttle_success`.
On failure calls `throttle_failure`.
"""
if self.rate is None:
return True
self.key = self.get_cache_key(request, view)
if self.key is None:
return True
self.history = self.cache.get(self.key, [])
# 我们是将值写在字典中,此处是将值保存在了缓存里
self.now = self.timer() # 加括号执行当前的时间戳函数。
# Drop any requests from the history which have now passed the
# throttle duration
while self.history and self.history[-1] <= self.now - self.duration: # 查看是否超出60秒
self.history.pop()
if len(self.history) >= self.num_requests:
return self.throttle_failure()
return self.throttle_success()
def throttle_success(self):
"""
Inserts the current request's timestamp along with the key
into the cache.
"""
self.history.insert(0, self.now)
self.cache.set(self.key, self.history, self.duration)
return True
def throttle_failure(self):
"""
Called when a request to the API has failed due to throttling.
"""
return False
def wait(self):
"""
Returns the recommended next request time in seconds.
"""
if self.history:
remaining_duration = self.duration - (self.now - self.history[-1])
else:
remaining_duration = self.duration
available_requests = self.num_requests - len(self.history) + 1
if available_requests <= 0:
return None
# 格式化抛出剩余时间。
return remaining_duration / float(available_requests)
3.2 使用
from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle,SimpleRateThrottle
# 使用内置类进行节流
class MyThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = "loginuser"
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
return request.user.username # 使用用户名作为限制的标识
class VisitThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = "visit"
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
return self.get_ident(request) # 使用 ip作为匿名用户的频率限制
REST_FRAMEWORK={
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES":['app01.utils.auth.MyAuthentication',],
"UNAUTHENTICATED_USER":None, # 匿名,request.user = None
"UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN":None,
"DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES":['app01.utils.permission.MyPermission',],
'''访问频率的控制 '''
"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES":['app01.utils.throttle.MyThrottle',],
# 匿名用户不能在全局配置需要为登录功能单独添加
"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES":{
"visit":'3/m',#一分钟三次,匿名用户
"loginuser":'10/m',# 登录成功,一分钟10次
}
}
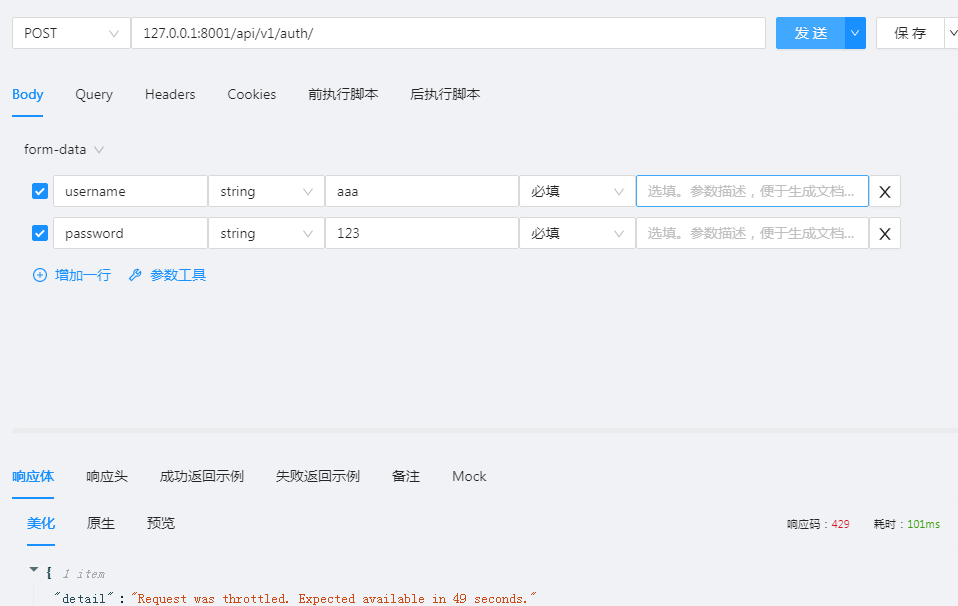
匿名用户,登录时使用,3次后限制60秒。
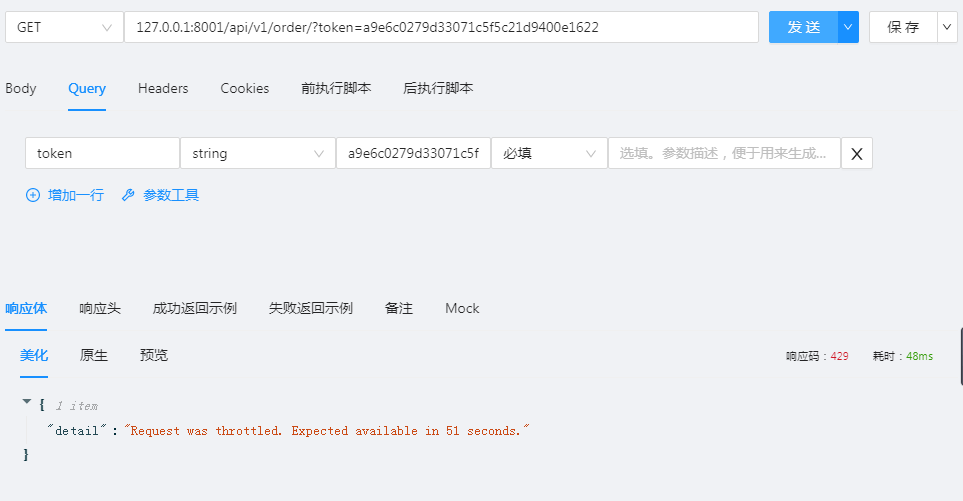
10次之后登录用户,10次之后限制查看。
继续努力,终成大器。
短暂的快乐只是短暂的,只有坚持才能带来巨大的成就感,当你坚持下来,你将进入下一个阶段!加油!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号