Mysql知识总结
MySql
1.多列作为主键,自增;
mysql的自增属于会话级别,不能修改下次自增的设置,可以修改相关的配置表
create table t1(
'nid' int(11) not null AUTO_INCREMENT,
'PID' int(11) not null,
primary key('nid',pid)
)ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4,DEFAULT CHARSET=UTF8
2.唯一索引
create table t2(
id int ...,
xx int,
unique uq1(num,xx),#设置唯一索引
constraint fk_t1_t2 foreign key(id) REFERENCES UserInfo(id)#设置外键
)
2.外键的变种
a.外键加唯一约束一对一的关系
b.外键多个对应多对多
c.外键原生一对多
3、常用的SQL语句
3.1增
-- 增加一条数据
insert into t1(name,age)values('wusie','19')
-- 增加多条数据
insert into t1(name,age)values('wusie','19'),('傻狗','18')
-- 将某张表的数据插入到本表中,查询语句按照需求编写
insert into t2(name,age) select name,age from tb11
3.2删
-- 删除整张表的数据
DELETE FROM T1
-- 按照条件删除
delete from t1 where id !=2
delete from t1 where id >2
delete from t1 where id <2
delete from t1 where id >=2
-- where后的逻辑关系
delete from t1 where id !=2 or name='傻狗'
delete from t1 where id =2 and name='傻狗'
3.3改
-- 指定修改字段以及where条件
update tb2 set name='啊哈' where id>=1
3.4查(普通查询)
-- 查询所有
select * from T1
-- 查询指定列
select name from t1
-- 使用where
select name from t1 where id>2
-- 使用AS修改表头
select id as cid from t1
-- 增加常量(‘1’的作用,多出一列常量列,列名和值均为一)
select name,age,1 from t1
-- mysql中的不等于 <> 和 !=
-
其他常用查询
-
in 用法
-- 例:查询id为1,5,12的数据 select * from t1 where id in(1,5,12) -- 例:查询id除了1,5,12的数据 select * from t1 where id not in(1,5,12) -- 动态使用id的范围(括号中的查询语句只能写一个查询结果) select * from t1 where id in(select id from T2) -
between用法
-- 半开半闭区间,取左不取右 select * from t1 where id between 5 and 12 -
通配符
-- 查询以a开头的数据 a% a开头任意字符 a_ a开头在加一个字符 例如 ab -- 包含a select * from t1 where id like "%a%" -- A开头 select * from t1 where id like "a%" -- a开头一个字符 select * from t1 where id like "a_" -
Limit 查看数据(分页)
-- 查看前十条,limit写一个参数的时候,就是前几条 select * from t1 limit 10 -- 两个参数(起始值,步长),例:从第十条开始取,十条 select * from t1 limit 10,10 -- 指定区间(从第十条取到第20条) select * from t1 limit 10 offset 20 -
排序
-- DESC 大到小 -- asc小到大 -- 记忆技巧abcd select * from t1 order by id desc;大到小 select * from t1 order by id asc;小到大 -- 排序后查询,通常用来查看后几条数据; select * from t1 order by id desc limit 10; -- 多列排序,如果第一列出现重复,则按照第二列的值进行排序 select * from t1 order age desc,id desc;
-
4、分组
-
创建示例表
-
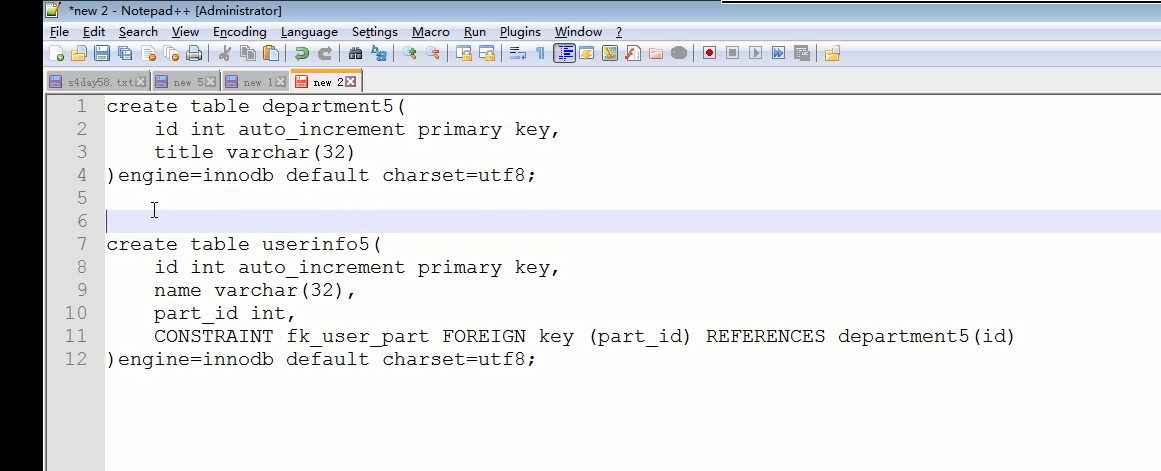
-
-- 分组关键字:group by select count(id),part_id from userinfo5 group by part_id; -- 聚合函数 /* 常见聚合函数 count()统计个数 max()取最大值 min()取最小值 sum()求和 avg()求平均 */ -- 不使用分组条件,默认所有数据为一组,直接使用聚合函数 select count(id)from userinfo5 -
如果对聚合结果进行二次筛选是必须使用having关键字
-- 例如,取出部门人数中大于1的,使用having才能将count聚合函数的结果进行返回
select count(id),part_id from userinfo5 group by part_id having count(id) >1
注:where中不能出现聚合函数的结果
5、连表操作
重要!!!
- 查询两张或多张表的时候通常使用连表查询
5.1连接
-- 普通连接
select * from userinfo5,department5
-- 注:此方法返回的结果是两张表的笛卡尔集,要实现相关的连接需要使用where中的条件,如下
select * from userinfo5,department5 where userinfo5.part_id=department5.id
5.2左连接和右连接
-
5.1中的方法虽然可以达到连接的效果但是一般不使用,个人认为最常用的是 左连接
-
左连接
-
语法:left join 表 on 条件
多表连接素材
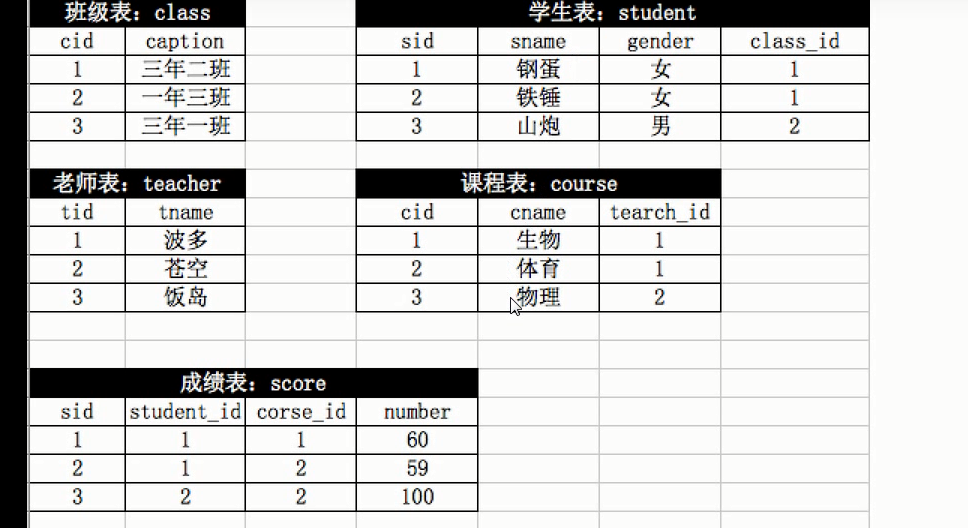
-- 两表连接 select * from userinfo5 left join department5 on userinfo5.part_id=department5.id -- 多表连接 select * from score left join student on score.sid = student.sid left join course on score.crouse_id=course.cid left join class on student.class_id=class.cid left join teacher on course.teacher_id=teacher.tid -- 注:如果上述写*容易出错,因此需要写出查询结果,即修改为 -- 多表连接 select *score.sid from score left join student on score.sid = student.sid left join course on score.crouse_id=course.cid left join class on student.class_id=class.cid left join teacher on course.teacher_id=teacher.tid -
右连接
-- 两表连接 select * from userinfo5 right join department5 on userinfo5.part_id=department5.id -
区别:如果是左连接,左边的表会全部显示;右连接,右边的表会全部显示; -
左连接将两表的位置互换,则查询结果与右连接的结果相同,因此通常使用左连接left join
-
inner连接
-- 左连接或者右连接有时会产生空值,因此使用inner可以将空值行隐藏; select * from userinfo5 inner join department5 on userinfo5.part_id=department5.id
天雨虽宽,不润无根之草。学习虽难,勤奋可达巅峰



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号