JavaScript ES5 与 ES6 中的类(Class)详解
在 JavaScript 中,ES5 通过 **构造函数(Constructor)** 和 **原型链(Prototype Chain)** 实现面向对象编程(OOP),而 ES6 引入了 `class` 关键字,提供更清晰、更接近传统面向对象语言的语法。以下是两者的对比与详细说明:
一、ES5 中的类实现
ES5 没有正式的类语法,通过以下方式模拟类:
1. 构造函数与实例方法
// 定义构造函数(类)
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 添加实例方法到原型
Person.prototype.sayHello = function() {
console.log(`Hello, I'm ${this.name}, ${this.age} years old.`);
};
// 创建实例
const alice = new Person("Alice", 25);
alice.sayHello(); // 输出: Hello, I'm Alice, 25 years old.
2. 静态方法
// 静态方法(直接挂载到构造函数)
Person.compareAge = function(person1, person2) {
return person1.age - person2.age;
};
// 调用静态方法
const bob = new Person("Bob", 30);
console.log(Person.compareAge(alice, bob)); // 输出: -5
3. 继承(原型链继承)
// 子类构造函数
function Student(name, age, grade) {
Person.call(this, name, age); // 调用父类构造函数
this.grade = grade;
}
// 继承父类原型
Student.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);
Student.prototype.constructor = Student; // 修正构造函数指向
// 子类方法
Student.prototype.study = function() {
console.log(`${this.name} is studying in grade ${this.grade}.`);
};
// 创建子类实例
const student = new Student("Charlie", 18, 12);
student.sayHello(); // 继承父类方法
student.study(); // 输出: Charlie is studying in grade 12.
4. ES5 类的缺点
语法冗长:需要手动操作原型链。
继承复杂:需要处理构造函数和原型的绑定。
缺乏直观性:与传统面向对象语言的类语法差异较大。
二、ES6 中的类语法
ES6 的 `class` 语法是 **语法糖**,底层仍基于原型链,但更简洁直观。
1. 基本类定义
class Person {
// 构造函数
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 实例方法
sayHello() {
console.log(`Hello, I'm ${this.name}, ${this.age} years old.`);
}
// 静态方法
static compareAge(person1, person2) {
return person1.age - person2.age;
}
}
// 创建实例
const alice = new Person("Alice", 25);
alice.sayHello(); // 输出: Hello, I'm Alice, 25 years old.
// 调用静态方法
const bob = new Person("Bob", 30);
console.log(Person.compareAge(alice, bob)); // 输出: -5
2. 继承(extends 和 super)
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name, age, grade) {
super(name, age); // 调用父类构造函数
this.grade = grade;
}
study() {
console.log(`${this.name} is studying in grade ${this.grade}.`);
}
}
// 创建子类实例
const student = new Student("Charlie", 18, 12);
student.sayHello(); // 继承父类方法
student.study(); // 输出: Charlie is studying in grade 12.
3. 特性增强
Getter/Setter方法:
class Person {
constructor(firstName, lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
get fullName() {
return `${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}`;
}
set fullName(name) {
[this.firstName, this.lastName] = name.split(" ");
}
}
const person = new Person("John", "Doe");
console.log(person.fullName); // 输出: John Doe
person.fullName = "Jane Smith";
console.log(person.firstName); // 输出: Jane
私有字段(ES2022+):
使用 `#` 前缀定义私有属性(需现代浏览器或 Node.js 支持):
class Person {
#secret = "This is private!";
getSecret() {
return this.#secret;
}
}
const person = new Person();
console.log(person.getSecret()); // 输出: This is private!
console.log(person.#secret); // 报错: SyntaxError
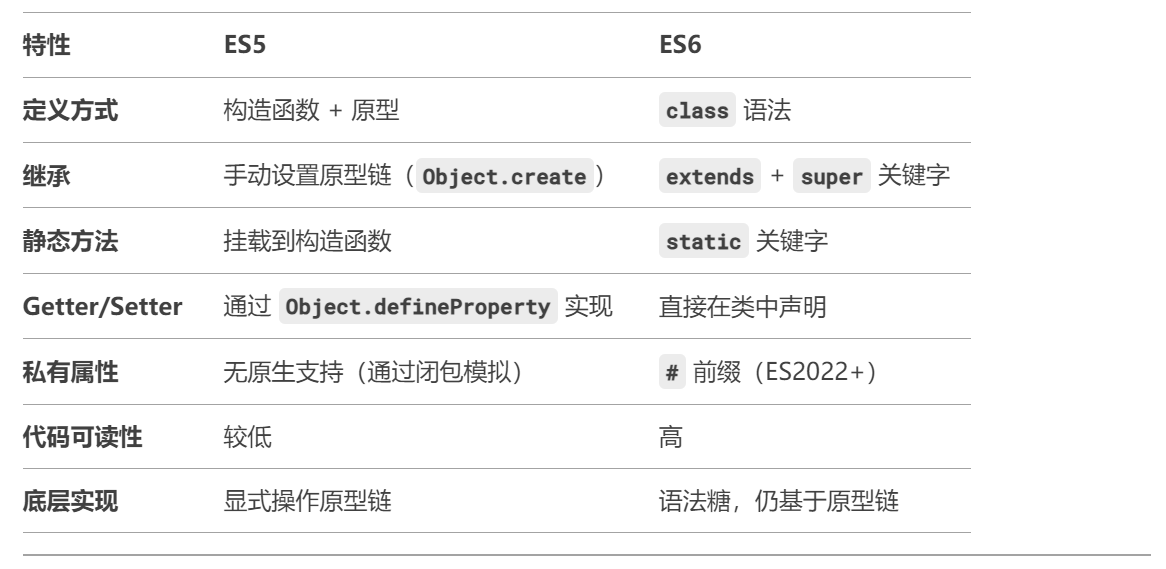
三、ES5 与 ES6 类的对比
四、ES6 类的注意事项
1. 没有变量提升:
类声明不会提升到作用域顶部,必须先定义后使用。
const obj = new MyClass(); // 报错: ReferenceError
class MyClass {}
2. 方法不可枚举:
类中定义的方法默认不可枚举(`Object.keys` 不会列出)。
class Person { sayHello() {} } console.log(Object.keys(Person.prototype)); // 输出: []
3.严格模式:
类声明和类表达式默认在严格模式下执行。
五、总结
ES5 类:通过构造函数和原型链实现,灵活但代码冗长。
ES6 类:语法简洁,支持 `extends`、`super`、`static` 等关键字,更接近传统面向对象语言。
适用场景:
ES6 类:新项目或现代环境,需提高代码可读性和维护性。
ES5 类:兼容旧环境或需要更细粒度控制原型的场景。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号