论文解读(PERL)《PERL: Pivot-based Domain Adaptation for Pre-trained Deep Contextualized Embedding Models》
Note:[ wechat:Y466551 | 可加勿骚扰,付费咨询 ]
论文信息
论文标题:PERL: Pivot-based Domain Adaptation for Pre-trained Deep Contextualized Embedding Models
论文作者:Eyal Ben-David、Carmel Rabinovitz、Roi Reichart
论文来源:2020 TACL
论文地址:download
论文代码:download
视屏讲解:click
1 介绍
动机:之前 Pivot-based 的方法只利用了来自源域的标记数据和来自源域和目标域的未标记数据,而忽略了合并不一定来自这些域的大量未标记语料库;
2 相关
Pivot features are:
-
- Frequent in the unlabeled data from the source and target domains;
- Among those frequent features, pivot features are the ones whose mutual information with the task label according to source domain labeled data crosses a pre-defined threshold. Features that do not meet the above two criteria form the non-pivot feature subset;
3 方法
模型框架
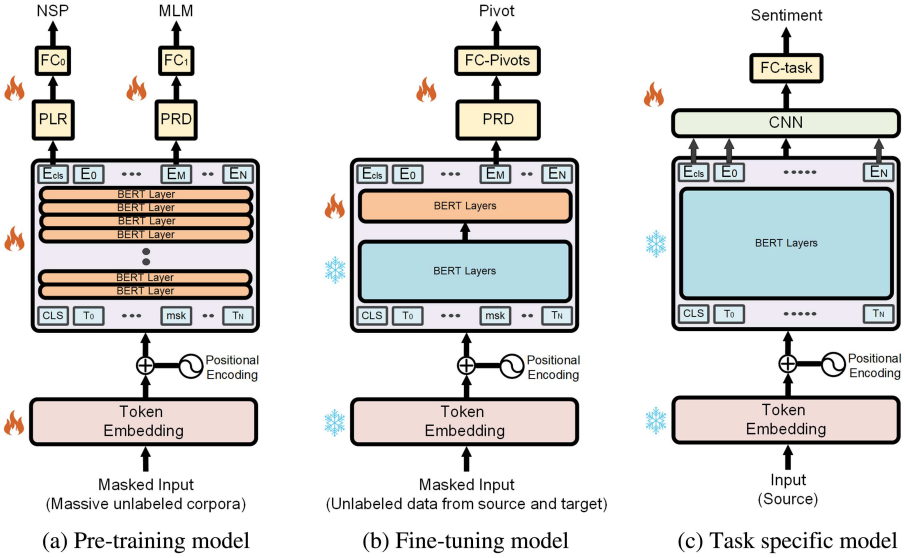
Step 1
Figure 1a:使用一个强大的预训练的 CWE 模型初始化 PERL 编码器,这里的 CWE 模型要能实现 MLM、NSP 任务;
Step 2
使用 不同的掩码概率对 $\text{pivot}$ 和 $\text{non-pivot}$ 进行 $\text{mask}$ ,并预测 $\text{mask}$ 的词是否是 $\text{pivot}$ ;
$p\left(y_{i}=j\right)=\frac{e^{f\left(h_{i}\right) \cdot W_{j}}}{\sum_{k=1}^{|P|} e^{f\left(h_{i}\right) \cdot W_{k}}+e^{f\left(h_{i}\right) \cdot W_{\text {none }}}}$
其中,$P$ 是 $\text{pivot feature}$ 的集合;
Step 3
在对来自源域的标记数据进行训练和对目标域进行测试时,每个输入文本首先由编码器表示,然后被输入给分类网络。因为我们的工作重点是表示学习,所以分类网络保持简单,由一个卷积层,然后是一个平均池化层和一个线性层组成。当训练下游任务时,编码器的权重会被冻结。4 实验
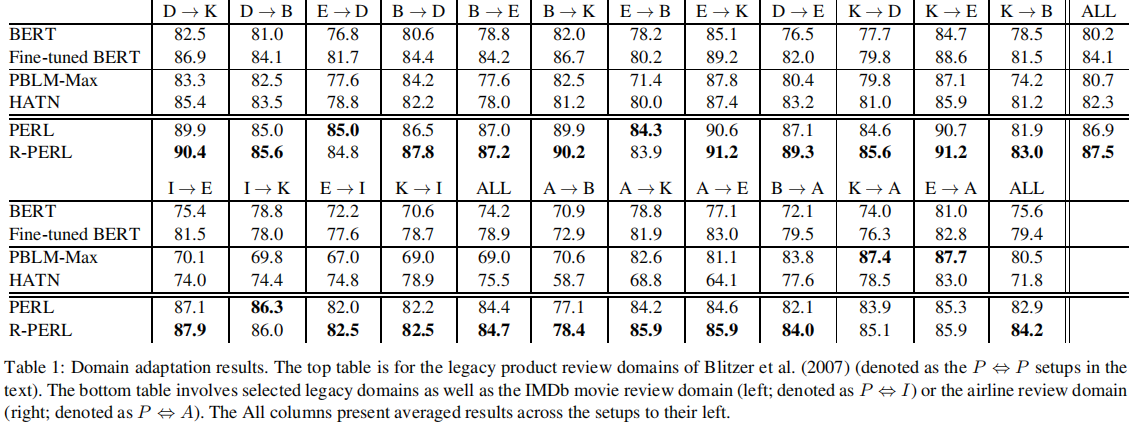
Domain adaptation results
因上求缘,果上努力~~~~ 作者:图神经网络,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/BlairGrowing/p/17659385.html


