[ Wechat:Y466551 | 付费咨询,非诚勿扰 ]
论文信息
论文标题:Dynamic Weighted Learning for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
论文作者:Jihong Ouyang、Zhengjie Zhang、Qingyi Meng
论文来源:2023 aRxiv
论文地址:download
论文代码:download
视屏讲解:click
1 介绍
2 方法
2.1 出发点
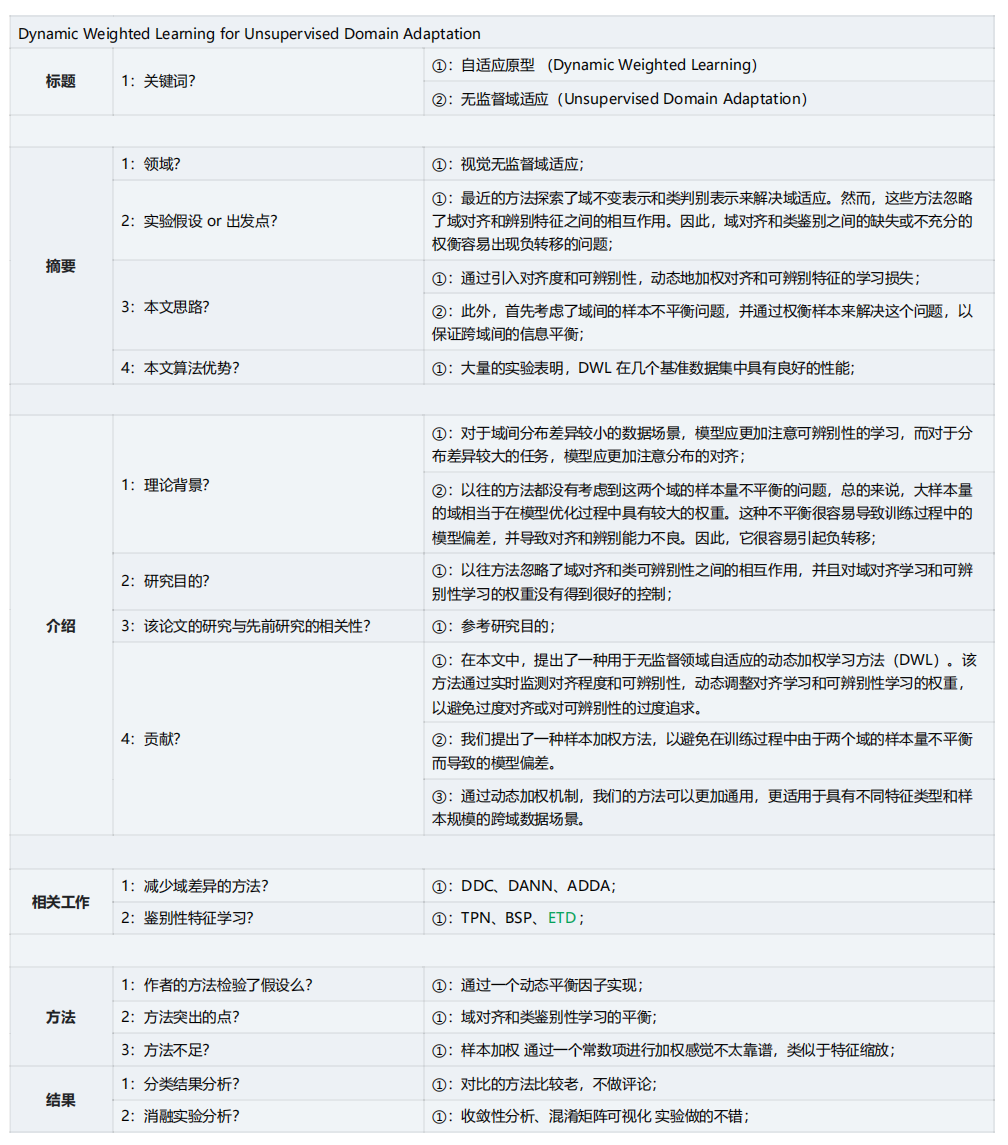
反应的问题:随着域对齐的实现,判别性在下降;
2.2 模型框架
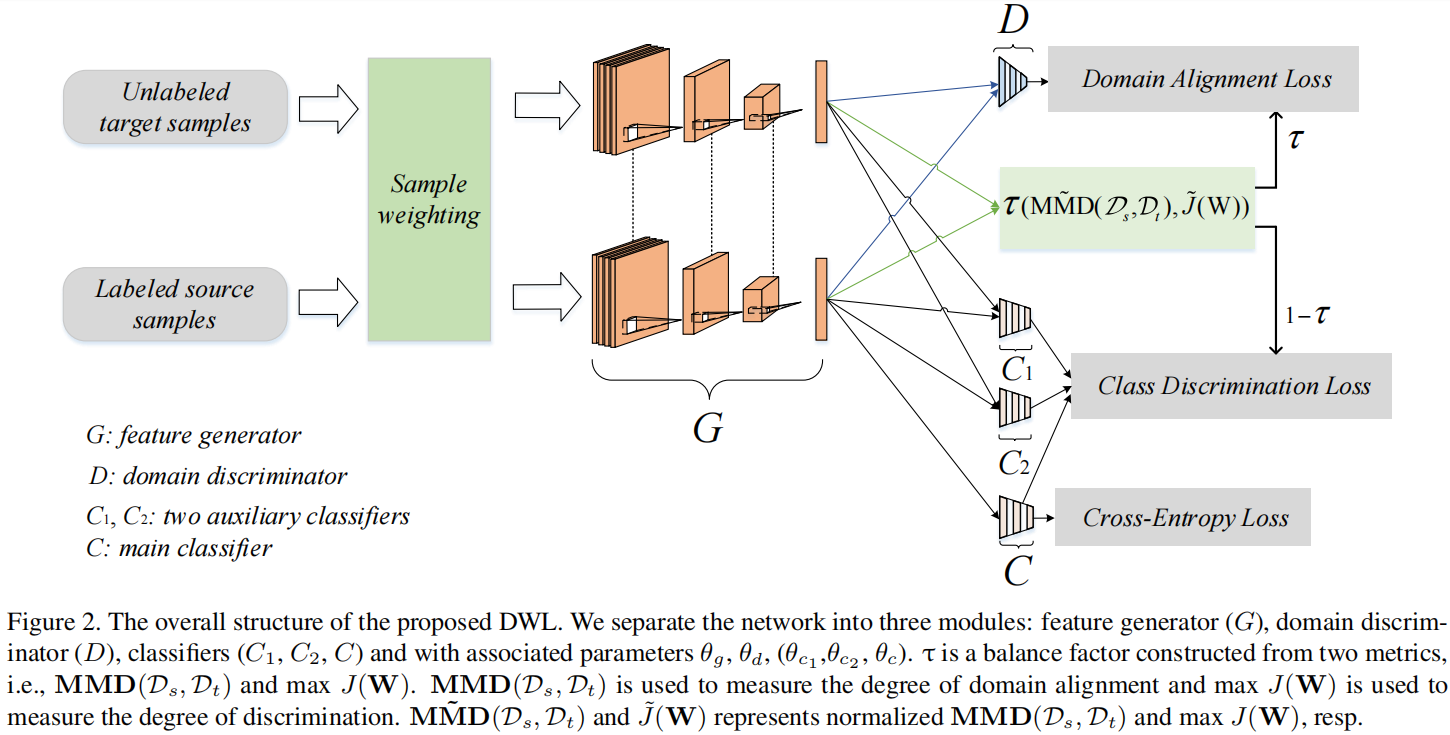
2.3 Sample Weighting
为避免源、目标域样本数量的不均衡造成的模型倾向性,对样本进行加权:
^xsi=a(1+ntns)xsi,i=1,2,…,ns^xtj=a(1+nsnt)xtj,j=1,2,…,nt
其中,a∈(0,1] 是一个控制样本加权程度的超参数。
2.4 Domain Alignment Learning and Class Discrimination Learning
域对齐(对抗性学习):
minθgmaxθdLda(θg,θd)=Exsi∼Dslog[D(G(^xsi))]+Extj∼Dtlog[1−D(G(^xtj))]
鉴别性特征学习:
minθg,θcmaxθc1,θc2Lcd(θg,θc,θc1,θc1)=Extj∼Dt∥∥C1(G(^xtj))−C2(G(^xtj))∥∥1+∥∥C(G(^xtj))−C1(G(^xtj))∥∥1+∥∥C(G(^xtj))−C2(G(^xtj))∥∥1
Note:C、C1、C2 是使用源域数据预训练得到的分类器;
对抗性训练步骤:
- 固定 G 和 C 最大化 C1 和 C2 的差异;
- 固定 C1 和 C2 训练 G 和 C;
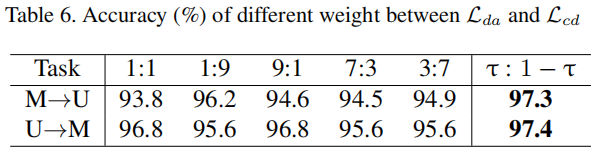
2.5 Dynamic Weighted Learning
域对齐度量 [ MMD ]:
MMD(Ds,Dt)=∥∥Exsi∼DsG(^xsi)−Extj∼DtG(^xtj)∥∥2
鉴别性度量 [ LDA ]:
maxWJ(W)=tr(W⊤SbW)tr(W⊤SwW)
其中,Sb 为类间散射矩阵,Sw 为类内散射矩阵。
注意:J(W) 越大,具有更好的辨别性。
由于上述两个评价标准不在一个数量级上,本文对其进行了归一化处理:
M~MD(Ds,Dt)=MMD(Ds,Dt)−MMD(Ds,Dt)minMMD(Ds,Dt)max−MMD(Ds,Dt)min
~J(W)=J(W)−J(W)minJ(W)max−J(W)min
构造一个动态平衡因子:
τ=M~M(Ds,Dt)M~M(Ds,Dt)+(1−~J(W))
因此:
-
- 当域对齐的程度远优于类的可辨别性时,M~MD(Ds,Dt) 接近 0,1−~J(W) 接近 1 ,τ 接近 0;
- 当域对齐程度远低于类别识别程度时,M~MD(Ds,Dt) 接近 1,1−~J(W) 接近 0 ,τ 接近 1 ;
基于 τ 的良好特性,采用 τ 作为域对齐损失的权重,1−τ 作为类鉴别损失的权重。
因此,最终的动态加权模型如下:
minθg,θcmaxθθd,θc1,θc2τ⋅Lda(θg,θd)+(1−τ)⋅Lcd(θg,θc,θc1,θc2)
- 当域对齐学习的有效性远低于类辨别学习时,模型增加域对齐学习的权重;
- 当鉴别学习的学习效果远低于域对齐学习时,模型增加鉴别学习的权重;
在这种动态加权学习机制下,可保持域对齐与类辨别学习之间的一致性,避免过度的域对齐或类可辨别性。
2.6 Overall Training Objective
总体训练目标整合了样本加权、领域对齐学习、类判别学习和动态加权学习。此外,还需要最小化标记源样本的期望源误差。最终的极大极小目标:
minθg,θcmaxθd,θc1,θc2∑tsi=1Lce(C(G(xsi;θg);θc),ysi)+τ⋅Lda(θg,θd)+(1−τ)⋅Lcd(θg,θc,θc1,θc2)
3 实验
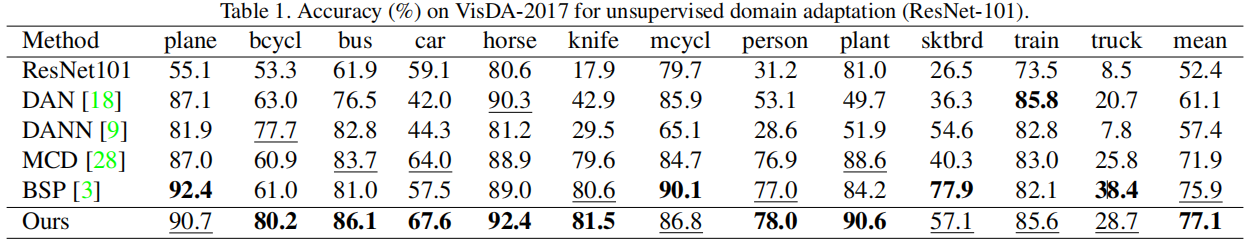
分类结果
收敛性分析
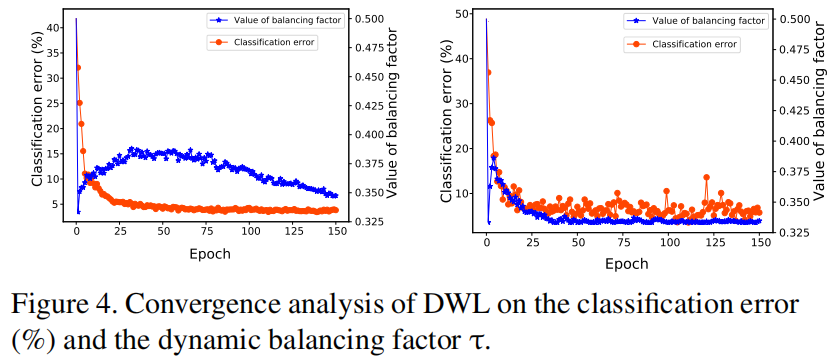
对于每个子图,红色曲线的左轴表示分类误差,蓝色曲线的右轴表示平衡因子 τ 的值。可以发现,随着迭代,它们两者都逐渐收敛到一个平坦的值。这意味着随着 τ 的减少,使得类的可鉴别性被强调,使得分类误差也减小。
在迭代过程中,当 τ 的变化相对明显时,识别精度的提高也相对明显。我们将 τ 的初始值设为 0.5,可以发现 τ 在第一个时期急剧下降到 0.5 以下,说明该模型的对齐性相对较好,但可辨别性相对较差。
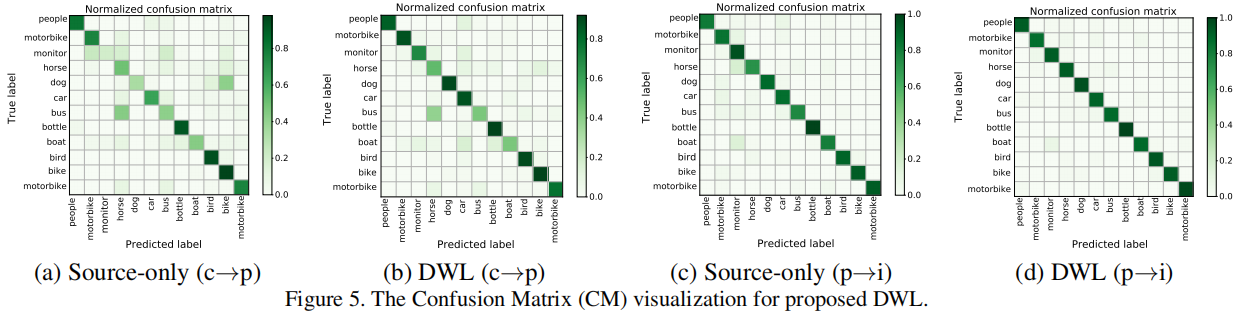
混淆矩阵可视化
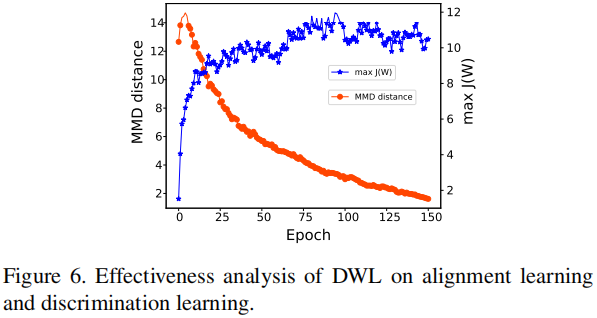
对齐度和可鉴别性度的分析
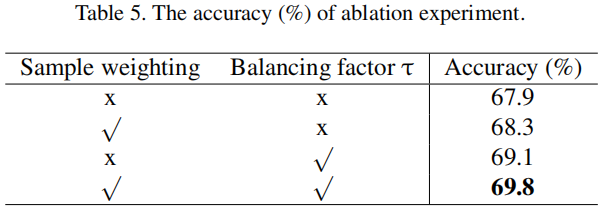
消融实验












【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
2022-08-04 论文解读( AF-GCL)《Augmentation-Free Graph Contrastive Learning with Performance Guarantee》
2022-08-04 论文解读(PPNP)《Predict then Propagate: Graph Neural Networks meet Personalized PageRank》
2020-08-04 STL----vector
2020-08-04 1528. 重新排列字符串