论文信息
论文标题:Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for COVID-19 Information Service with Contrastive Adversarial Domain Mixup
论文作者:Huimin Zeng, Zhenrui Yue, Ziyi Kou, Lanyu Shang, Yang Zhang, Dong Wang
论文来源:aRxiv 2022
论文地址:download
论文代码:download
1 Abstract
在 COVID-19 错误信息检测的现实应用中,一个根本的挑战是使用缺乏标记的 COVID 数据,无法对模型进行端到端监督训练。为解决这一挑战,提出了一个无监督域自适应框架,使用对比学习和对抗域混合,将知识从现有的源数据域转移到目标数据 COVID-19 数据域。特别地,为弥合源域和目标域之间的差距,本文的方法减少了这两个域之间基于径向基函数(RBF)的差异。此外,本文利用域对抗性例子来建立一个中间域混合,其中来自两个领域的输入文本的潜在表示可以在训练过程中混合。在多个真实世界数据集上的大量实验表明,本文的方法可以有效地使错误信息检测系统适应未知的 COVID-19 目标域,与最先进的基线相比有了显著的改进。
2 Introduction
本文关注于 COVID-19 错误信息检测,由于监督学习需要大量的标签数据,这并不适合于早起检测,所以本文设计的无监督域自适应针对任何早期流行的设置。本文的无监督域适应框架对 COVID-19 错误信息检测至关重要,可以将现有数据领域的知识就能够适应并转移到看不见的新冠病毒数据领域,而不需要任何地面真实训练标签。
3 Problem Statement
Regarding misinformation detection, we aim at training a model f , which takes an input text x (a COVID-19 claim or a piece of news) to predict whether the information contained in x is valid or not (i.e., a binary classification task). Moreover, in our domain adaptation problem, we use P to denote source domain data distribution and Q for the target domain data distribution. Each data point (x, y) contains an input segment of COVID-19 claim or news (x) and a label y∈{0,1} ( y=1 for true information and y=0 for false information). To differentiate the notations of the data sampled from the source distribution P and the target distribution Q , we further introduce two definitions of the domain data:
-
- Source domain: The subscript s is used to denote the source domain data: Xs={(xs,ys)∣(xs,ys)∼P} .
- Target domain: Similarly, the subscript t is used to denote the target domain data: Xt={xt∣xt∼P} . Note that in our unsupervised setting, the ground truth labels of target domain data yt are not used during training.
Our goal is to adapt a classifier f trained on P to Q . For a given target domain input xt , a well-adapted model aims at making predictions as correctly as possible.
4 Method
4.1 Domain Discriminator
域鉴别器 fD :用于判断输入数据是属于源域还是属于目标域。
特征提取编码器 fe 采用 BERT Encoder,域鉴别器 fD 采用线性分类器(二分类)。
域鉴别器 fD 以 fe 输出中的 [CLS] 表示 z 作为输入,来预测输入数据的域:
ˆy=fD(z)(1)
域鉴别器的训练目标是正确区分源域 yD=0 和目标域 yD=1 :
minfDE(x,yD)∼X′[l(fD(fe(x)),yD)](2)
其中,X′ 表示带有域标签的源域和目标域训练数据的合并数据集。
4.2 Adversarial Domain Mixup
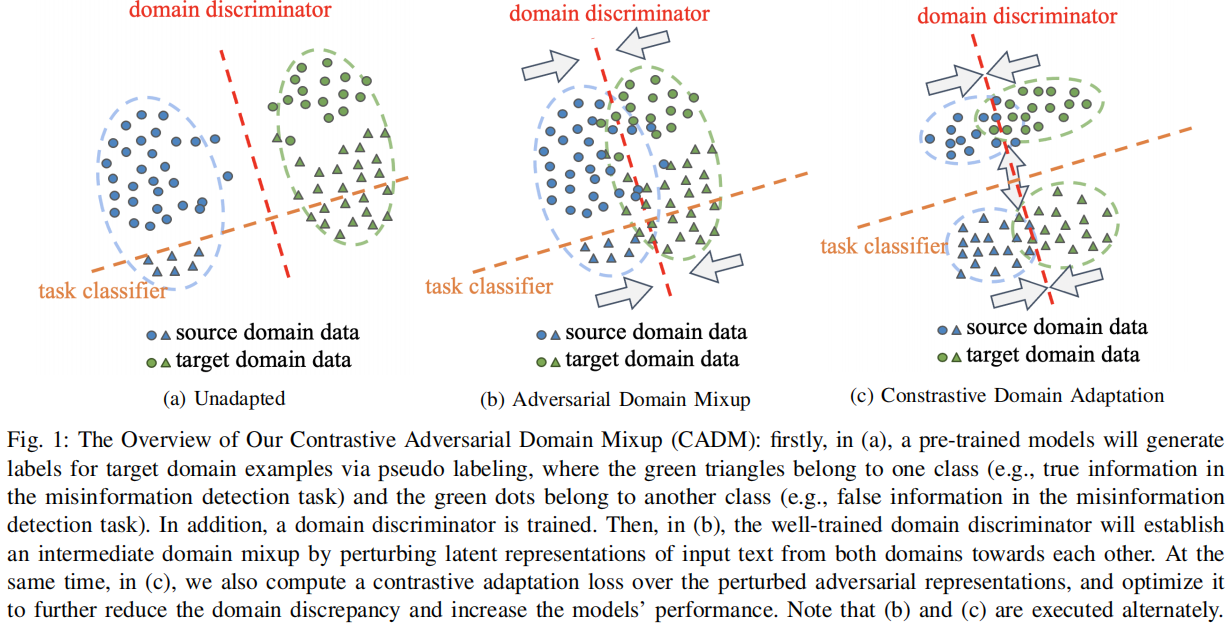
在训练好域鉴别器后,提出直接干扰来自源域表示和目标域表示到域鉴别器 fD 决策边界的距离,如 Figure 1b 所示。为此,来自两个域的扰动表示(即域对抗表示)可以变得更接近,表明域间隙减小。在此,从两个域生成的域对抗性表示在潜在特征空间中形成了一个平滑的中间域混合。
在数学上,通过求解一个优化问题,可以找到训练样本 x 的潜在表示 z 的最优扰动 δ∗:
A(fe,fD,x,yD,ϵ)=maxδ[l(fD(z+δ),yD)] s.t. ‖
注意,引入超参数 \epsilon 约束扰动 \delta,从而避免无穷大解。
最后,将 \text{Eq.3} 应用于合并训练集 \mathcal{X}^{\prime} 中的所有训练样本,得到对抗域混合 \mathcal{Z}^{\prime}:
\begin{aligned}\mathcal{Z}^{\prime} & =\left\{\boldsymbol{z}^{\prime} \mid \boldsymbol{z}^{\prime}=\boldsymbol{z}+\mathcal{A}\left(f_{e}, f_{D}, \boldsymbol{x}, y_{D}, \epsilon\right),\left(\boldsymbol{x}, y_{D}\right) \in \mathcal{X}^{\prime}\right\} \\& :=\mathcal{Z}_{s}^{\prime} \cup \mathcal{Z}_{t}^{\prime}\end{aligned}\quad\quad(4)
其中,\mathcal{Z}_{s}^{\prime} 是扰动的源域样本集,\mathcal{Z}_{t}^{\prime} 是扰动的目标域样本集。使用投影梯度下降(PGD)来近似 \text{Eq.3} 的解 [7],[8]。
4.3 Contrastive Domain Adaptation
受[6] 的启发,提出基于 \mathcal{Z}_{a d v} 的双重对比自适应损失,以进一步将源数据域的知识适应到目标数据域。目的:减少类内表示之间的域差异,增大类间表示之间的域差异。如 \text{Figure 1(c)} 所示,真实信息和虚假信息的表示之间的差异将被扩大。
错误信息检测任务的类感知损失如下:
\begin{aligned}\mathcal{L}_{\text {con }}\left(\mathcal{Z}^{\prime}\right) =&-\sum_{i=1}^{\left|\mathcal{Z}_{s}^{\prime}\right|} \sum_{j=1}^{\left|\mathcal{Z}_{t}^{\prime}\right|} \frac{\mathbb{1}\left(y_{s}^{(i)}=0, \hat{y}_{t}^{(j)}=0\right) k\left(\boldsymbol{z}_{s}^{(i)}, \boldsymbol{z}_{t}^{(j)}\right)}{\sum_{l=1}^{\left|\mathcal{Z}_{s}^{\prime}\right|} \sum_{m=1}^{\left|\mathcal{Z}_{t}^{\prime}\right|} \mathbb{1}\left(y_{s}^{(l)}=0, \hat{y}_{t}^{(m)}=0\right)} \\& -\sum_{i=1}^{\left|\mathcal{Z}_{s}^{\prime}\right|} \sum_{j=1}^{\left|\mathcal{Z}_{t}^{\prime}\right|} \frac{\mathbb{1}\left(y_{s}^{(i)}=1, \hat{y}_{t}^{(j)}=1\right) k\left(\boldsymbol{z}_{s}^{(i)}, \boldsymbol{z}_{t}^{(j)}\right)}{\sum_{l=1}^{\left|\mathcal{Z}_{s}^{\prime}\right|} \sum_{m=1}^{\left|\mathcal{Z}_{t}^{\prime}\right|} \mathbb{1}\left(y_{s}^{(l)}=1, \hat{y}_{t}^{(m)}=1\right)} \\& +\sum_{i=1}^{\left|\mathcal{Z}_{s}^{\prime}\right|} \sum_{j=1}^{\left|\mathcal{Z}_{s}^{\prime}\right|} \frac{\mathbb{1}\left(y_{s}^{(i)}=1, y_{s}^{(j)}=0\right) k\left(\boldsymbol{z}_{s}^{(i)}, \boldsymbol{z}_{s}^{(j)}\right)}{\sum_{l=1}^{\left|\mathcal{Z}_{s}^{\prime}\right|} \sum_{m=1}^{\left|\mathcal{Z}_{s}^{\prime}\right|} \mathbb{1}\left(y_{s}^{(l)}=1, y_{s}^{(m)}=0\right)} \\& +\sum_{i=1}^{\left|\mathcal{Z}_{t}^{\prime}\right|} \sum_{j=1}^{\left|\mathcal{Z}_{t}^{\prime}\right|} \frac{\mathbb{1}\left(\hat{y}_{t}^{(i)}=1, \hat{y}_{t}^{(j)}=0\right) k\left(\boldsymbol{z}_{t}^{(i)}, \boldsymbol{z}_{t}^{(j)}\right)}{\sum_{l=1}^{\left|\mathcal{Z}_{t}^{\prime}\right|} \sum_{m=1}^{\left|\mathcal{Z}_{t}^{\prime}\right|} \mathbb{1}\left(\hat{y}_{t}^{(l)}=1, \hat{y}_{t}^{(m)}=0\right)}\end{aligned}\quad\quad(5)
其中,径向基函数(RBF):k\left(z_{1}, z_{2}\right)=\exp \left[-\frac{\left\|\boldsymbol{z}_{1}-\boldsymbol{z}_{2}\right\|^{2}}{2 \sigma^{2}}\right],\hat{y}_{t} 为目标域样本的伪标签,z 表示 \text{CLS} 的表示。
4.4 Overall Contrastive Adaptation Loss
优化目标——交叉熵损失+比自适应损失:
\mathcal{L}_{\text {all }}=\mathcal{L}_{c e}(\boldsymbol{\mathcal { X }})+\lambda \mathcal{L}_{\text {con }}\left(\mathcal{Z}^{\prime}\right) \quad\quad(6)
其中,\mathcal{L}_{c e} 代表交叉熵损失函数。
5 Experiment
\text{source misinformation datasets}:\text{GossipCop}、\text{ LIAR}、\text{PHEME}
\text{target misinformation datasets(COVID)}:\text{Constraint}、\text{ANTiVax}
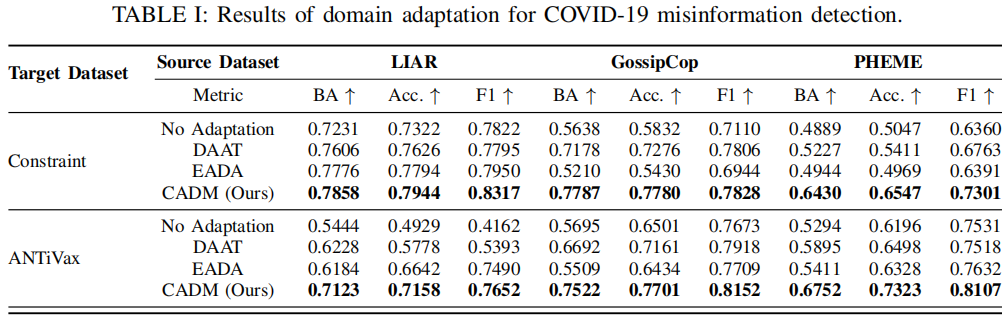
Results:
因上求缘,果上努力~~~~ 作者:别关注我了,私信我吧,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/BlairGrowing/p/17011593.html



【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Deepseek官网太卡,教你白嫖阿里云的Deepseek-R1满血版
· 2分钟学会 DeepSeek API,竟然比官方更好用!
· .NET 使用 DeepSeek R1 开发智能 AI 客户端
· DeepSeek本地性能调优
· 一文掌握DeepSeek本地部署+Page Assist浏览器插件+C#接口调用+局域网访问!全攻略