STL----stack
Stack
stack<T>容器适配器中的数据是以 LIFO 的方式组织的。
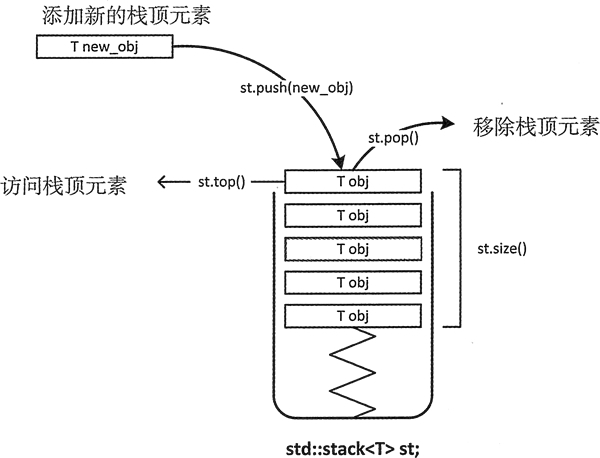
回顾一下之前所学的栈,栈是一种先进后出的数据结构,而实现方式需要创建多个结构体,通过链式的方式进行实现,这是标准的栈的思路,而在STL中栈可以以更为简单的方式实现。
头文件
头文件 #include<stack>
1.初始化
格式为:explicit stack (const container_type& ctnr = container_type());
我们以int类型作为参数为例进行创建,其创建方法与vector无异
stack<int> s;
stack<int> v(s);
vector<int> v(3,100);
stack<int,vector<int> > s(v); //注意,> >符号之间需要有一个空格隔开
2. stack容器内元素的访问
//由于栈(stack)本书就是一种后进先出的数据结构,在STL的stack中只能通过top()来访问栈顶元素
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
stack<int> st;
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
st.push(i); //push(i)用以把i压入栈,故此处依次入栈 1 2 3 4 5
}
printf("%d\n", st.top()); //top取栈顶元素
return 0;
}
3. stack常用函数实例解析
(1) push()
//push(x)将x入栈,时间复杂度为O(1)
(2) top()
//top()获得栈顶元素,时间复杂度为O(1)
(3) pop()
//pop()用以弹出栈顶元素,时间复杂度为O(1)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
stack<int> st;
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
st.push(i); //将 1 2 3 4 5 依次入栈
}
for(int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
st.pop(); //连续三次将栈顶元素出栈,即将5 4 3 依次出栈
}
printf("%d\n", st.top());
return 0;
}
(4) empty()
//empty()可以检测stack内是否为空,放回true为空,返回false为非空,时间复杂度为O(1)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
stack<int> st;
if(st.empty() == true) { //一开始栈内没有元素,因此栈空
printf("Empty\n");
} else {
printf("Not Empty\n");
}
st.push(1);
if(st.empty() == true) { //入栈"1"后,栈非空
printf("Empty");
} else {
printf("Not Empty\n");
}
return 0;
}
(5) size()
//size()返回stack内元素的个数,时间复杂度为O(1)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
stack<int> st;
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
st.push(i); //push(i)用以将i压入栈
}
printf("%d\n", st.size()); //栈内有5个元素
return 0;
}
因上求缘,果上努力~~~~ 作者:图神经网络,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/BlairGrowing/p/13493937.html


