情感分析新手实践
Amazon Full Review 情感分析任务
input: Remark Text
output: Sentiment(\(\{-1, 0, 1\}\)) convert to \(\{0, 1, 2\}\) for calculating accuracy
Mark: 之前没有用 torch 做过 NLP,因此相当于一个 tutorial
数据准备工作
- 文本分词
NLP 需要将文本数据分词并转换为词汇表中的 id,这里使用transformers库中的BertTokenizer进行处理。
- 创建词汇表
需要完成的工作为
- 创建词汇表 Vocabulary, 用于将文本转换为数字,由于词汇数量巨大,并且测试集可能出现未知词汇,因此设置一个阈值,设置两个标记符号,一个是未知词汇,一个是填充符号。
- 同时在之后的 Embedding 中,词嵌入的输入是固定的,因此可以尝试将所有的句子 ids 的长度设置为相同的长度,不足的部分用填充符号填充。
- 创建 DataSet
主要是将文件读取入字典中,并在 getitem 方法中将文本数据转换为数字,同时将标签转换为数字。
模板如下
class MyDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, path, tokenizer=None, max_length=512, device="gpu"):
self.data = self.load_csv(path)
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
self.max_length = max_length
print(f"Loaded {len(self.data)} data from {path}")
def load_csv(self, path):
Data = {}
index = 0
try:
with open(path, "rt", encoding="utf-8") as f:
for line in f:
items = line.strip().split(",")
# convert labels
Data[index] = {
"subject": items[1],
"review": items[2],
"label": label,
}
index += 1
else:
continue
except IOError as e:
print(f"Error opening or reading the file: {path}. Error: {e}")
return Data
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
# 在这里进行数据处理
if idx < len(self.data) and idx >= 0:
item = self.data[idx]
# 编码处理
encoded_review = self.tokenizer.encode_plus(
item['review'],
add_special_tokens=True,
max_length=self.max_length,
return_token_type_ids=False,
padding="max_length",
truncation=True,
return_attention_mask=True,
return_tensors='pt',
)
item["ids"] = encoded_review["input_ids"].squeeze()
return item
- 划分数据集
可以直接在 dataset 中使用 subset 划分,但在创建 dataloader 时会存在索引问题,因此排列在预处理之前,出现问题的代码如下:
indices = list(range(len(train_data)))
np.random.shuffle(indices)
split = int(np.floor(0.8 * len(train_data)))
train_indices = indices[:split]
valid_indices = indices[split:]
train_data = Subset(train_data, train_indices)
valid_data = Subset(train_data, valid_indices)
需要注意的几个参数为batch_size, shuffle, drop_last, 其中shuffle表示是否打乱数据,drop_last表示是否丢弃最后一个 batch。
模型构建
1. Embedding + Pooling + Linear
- Embedding 层将输入的词汇 id 转换为词嵌入
- 然后使用 Pooling 层将词嵌入转换为句子向量
- 最后使用 Linear 层将句子向量转换为输出
class NBoW(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, num_class):
super(NBoW, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
self.fc = nn.Linear(embedding_dim, num_class)
def forward(self, ids):
# ids = [batch size, seq len]
embedded = self.embedding(ids)
# embedded = [batch size, seq len, embedding dim]
pooled = torch.mean(embedded, dim=1)
# pooled = [batch size, embedding dim]
pred = self.fc(pooled)
# pred = [batch size, output dim], 输出由于loss是CE, 不需要softmax
return pred
2. LSTM
模型结构如下:
- Embedding 层将输入的词汇 id 转换为词嵌入
- LSTM 层将词嵌入转换为句子向量
- Linear 层将句子向量转换为输出
同时防止过拟合,使用了 Dropout 层。以dropout_rate的概率,在训练时将输入的某些元素置为 0,以防止过拟合。
class LSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim,
n_layers, bidirectional, dropout_rate) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(
embedding_dim,
hidden_dim,
n_layers,
bidirectional=bidirectional,
dropout=dropout_rate,
batch_first=True,
)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim * 2 if bidirectional else hidden_dim, output_dim)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout_rate)
def forward(self, ids):
# ids = [batch size, seq len]
# length = [batch size]
embedded = self.dropout(self.embedding(ids))
# embedded = [batch size, seq len, embedding dim]
output, (hidden, cell) = self.lstm(embedded)
# hidden = [n layers * n directions, batch size, hidden dim]
# cell = [n layers * n directions, batch size, hidden dim]
# output = [batch size, seq len, hidden dim * n directions]
if self.lstm.bidirectional:
hidden = self.dropout(torch.cat([hidden[-1], hidden[-2]], dim=-1))
# hidden = [batch size, hidden dim * 2]
else:
hidden = self.dropout(hidden[-1])
# hidden = [batch size, hidden dim]
prediction = self.fc(hidden)
# prediction = [batch size, output dim]
return prediction
模型训练
使用(torch.argmax(predict, dim=1) == label).float().mean().item()计算准确率。
在第一种模型中,batch_size=512, epoch=3,在第二种模型中,batch_size=128, epoch=3。
训练过程中使用,Adam优化器,CrossEntropyLoss损失函数。
然而由于没有考虑到数据平衡性问题,因此在训练过程中,准确率并不高,可以考虑使用WeightedRandomSampler解决数据不平衡问题。
| Embedding | LSTM |
|---|---|
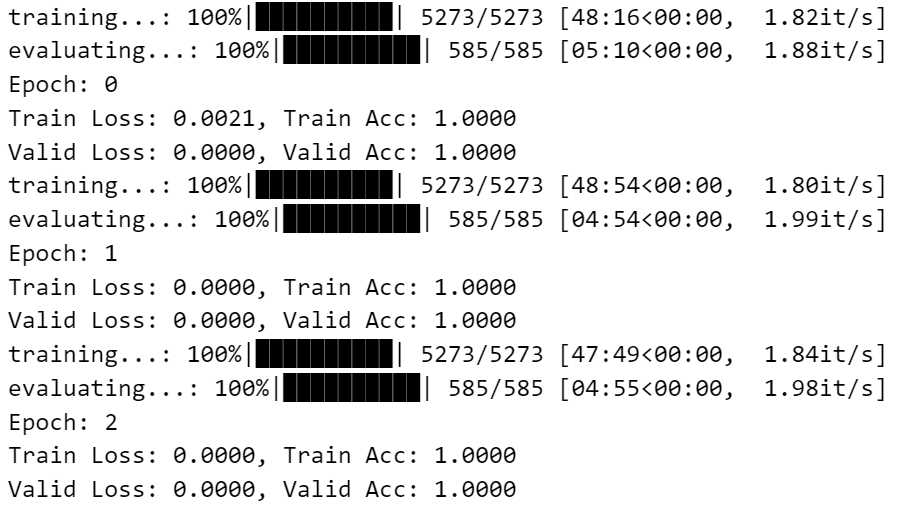 |
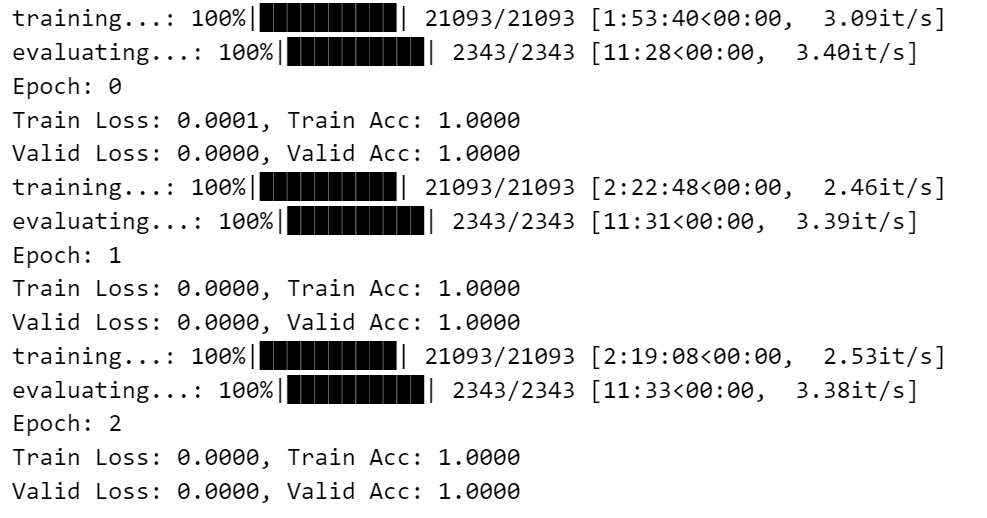 |
模型接口
要注意的是最终结果的计算,由于预处理时已经将 label 转换为 idx,因此获得结果时只需套torch.argmax获取 idx 即可。
def predict_sentiment(text, model, tokenizer, device):
model.eval()
encoded_review = tokenizer.encode_plus(
text,
add_special_tokens=True,
max_length=512,
return_token_type_ids=False,
padding="max_length",
truncation=True,
return_attention_mask=True,
return_tensors='pt',
)
ids = encoded_review["input_ids"].to(device)
prediction = model(ids)
return torch.argmax(prediction).item()

