Python中list的复制及深拷贝与浅拷贝探究
在Python中,经常要对一个list进行复制。对于复制,自然的就有深拷贝与浅拷贝问题。深拷贝与浅拷贝的区别在于,当从原本的list复制出新的list之后,修改其中的任意一个是否会对另一个造成影响,即这两个list在内存中是否储存在同一个区域,这也是区分深拷贝与浅拷贝的重要依据。接下来我们就针对Python中list复制的几种方法,来探究一下其是属于深拷贝还是浅拷贝。弄清楚这个问题,有助于我们在编程中规避错误,减少不必要的调试时间。
一、非拷贝方法——直接赋值
如果用=直接赋值,是非拷贝方法。这两个列表是等价的,修改其中任何一个列表都会影响到另一个列表。这也是Python作为动态语言与C这类静态语言在思想上的不同之处。
1 #!/usr/bin/env python3 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 4 old = [1, [1, 2, 3], 3] 5 new = old 6 print('Before:') 7 print(old) 8 print(new) 9 new[0] = 3 10 new[1][0] = 3 11 print('After:') 12 print(old) 13 print(new)
运行结果: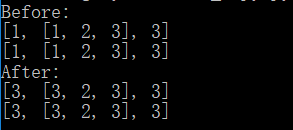
二、浅拷贝的几种方法
1.copy()方法
我们来看以下代码:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python3 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 4 old = [1, [1, 2, 3], 3] 5 new = old.copy() 6 print('Before:') 7 print(old) 8 print(new) 9 new[0] = 3 10 new[1][0] = 3 11 print('After:') 12 print(old) 13 print(new)
运行结果: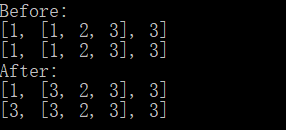
对于list的第一层,是实现了深拷贝,但对于嵌套的list,仍然是浅拷贝。这其实很好理解,内层的list保存的是地址,复制过去的时候是把地址复制过去了。嵌套的list在内存中指向的还是同一个。

2.使用列表生成式
使用列表生成式产生新列表也是一个浅拷贝方法,只对第一层实现深拷贝。
1 #!/usr/bin/env python3 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 4 old = [1, [1, 2, 3], 3] 5 new = [i for i in old] 6 print('Before:') 7 print(old) 8 print(new) 9 new[0] = 3 10 new[1][0] = 3 11 print('After:') 12 print(old) 13 print(new)
运行结果: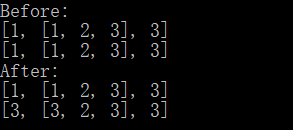
3.用for循环遍历
通过for循环遍历,将元素一个个添加到新列表中。这也是一个浅拷贝方法,只对第一层实现深拷贝。
1 #!/usr/bin/env python3 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 4 old = [1, [1, 2, 3], 3] 5 new = [] 6 for i in range(len(old)): 7 new.append(old[i]) 8 print('Before:') 9 print(old) 10 print(new) 11 new[0] = 3 12 new[1][0] = 3 13 print('After:') 14 print(old) 15 print(new)
运行结果: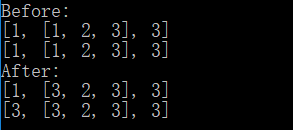
4.使用切片
通过使用[:]切片,可以浅拷贝整个列表。同样的,只对第一层实现深拷贝。
1 #!/usr/bin/env python3 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 4 old = [1, [1, 2, 3], 3] 5 new = old[:] 6 print('Before:') 7 print(old) 8 print(new) 9 new[0] = 3 10 new[1][0] = 3 11 print('After:') 12 print(old) 13 print(new)
运行结果: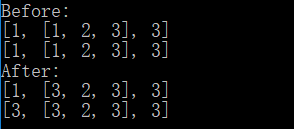
三、深拷贝的实现
如果用deepcopy()方法,则无论多少层,无论怎样的形式,得到的新列表都是和原来无关的,这是最安全最清爽最有效的方法。
使用时,要导入copy。
1 #!/usr/bin/env python3 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 4 import copy 5 6 old = [1, [1, 2, 3], 3] 7 new = copy.deepcopy(old) 8 print('Before:') 9 print(old) 10 print(new) 11 new[0] = 3 12 new[1][0] = 3 13 print('After:') 14 print(old) 15 print(new)
运行结果:
以上,就是对list的复制及深拷贝与浅拷贝探究。鉴于本人水平有限,文中有不妥之处,还请在评论中指出。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号