AtCoder Beginner Contest 115 题解
题目链接:https://abc115.contest.atcoder.jp/
A Christmas Eve Eve Eve
题目:
Time limit : 2sec / Memory limit : 1024MB
Score : 100 points
Problem Statement
In some other world, today is December D-th.
Write a program that prints Christmas if D=25, Christmas Eve if D=24, Christmas Eve Eve if D=23 and Christmas Eve Eve Eve if D=22.
Constraints
- 22≤D≤25
- D is an integer.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
D
Output
Print the specified string (case-sensitive).
Sample Input 1
25
Sample Output 1
Christmas
Sample Input 2
22
Sample Output 2
Christmas Eve Eve Eve
Be sure to print spaces between the words.
题解:
没什么好说的。

1 #include <cstdio> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int main() 6 { 7 int d; 8 scanf("%d", &d); 9 if(d == 25) 10 printf("Christmas\n"); 11 else if(d == 24) 12 printf("Christmas Eve\n"); 13 else if(d == 23) 14 printf("Christmas Eve Eve\n"); 15 else if(d == 22) 16 printf("Christmas Eve Eve Eve\n"); 17 return 0; 18 }
B Christmas Eve Eve
题目:
Time limit : 2sec / Memory limit : 1024MB
Score : 200 points
Problem Statement
In some other world, today is the day before Christmas Eve.
Mr. Takaha is buying N items at a department store. The regular price of the i-th item (1≤i≤N) is pi yen (the currency of Japan).
He has a discount coupon, and can buy one item with the highest price for half the regular price. The remaining N−1 items cost their regular prices. What is the total amount he will pay?
Constraints
- 2≤N≤10
- 100≤pi≤10000
- pi is an even number.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N
p1
p2
:
pN
Output
Print the total amount Mr. Takaha will pay.
Sample Input 1
3
4980
7980
6980
Sample Output 1
15950
The 7980-yen item gets the discount and the total is 4980+7980⁄2+6980=15950 yen.
Note that outputs such as 15950.0 will be judged as Wrong Answer.
Sample Input 2
4
4320
4320
4320
4320
Sample Output 2
15120
Only one of the four items gets the discount and the total is 4320⁄2+4320+4320+4320=15120 yen.
题解:
没什么好说的。

1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 int n; 9 scanf("%d", &n); 10 int p[15], maxp = 0, sum = 0; 11 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) 12 { 13 scanf("%d", &p[i]); 14 maxp = max(maxp, p[i]); 15 sum += p[i]; 16 } 17 sum = sum - maxp + maxp / 2; 18 printf("%d\n", sum); 19 return 0; 20 }
C Christmas Eve
题目:
Time limit : 2sec / Memory limit : 1024MB
Score : 300 points
Problem Statement
In some other world, today is Christmas Eve.
There are N trees planted in Mr. Takaha's garden. The height of the i-th tree (1≤i≤N) is hi meters.
He decides to choose K trees from these trees and decorate them with electric lights. To make the scenery more beautiful, the heights of the decorated trees should be as close to each other as possible.
More specifically, let the height of the tallest decorated tree be hmax meters, and the height of the shortest decorated tree be hmin meters. The smaller the value hmax−hmin is, the better. What is the minimum possible value of hmax−hmin?
Constraints
- 2≤K<N≤105
- 1≤hi≤109
- hi is an integer.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N K
h1
h2
:
hN
Output
Print the minimum possible value of hmax−hmin.
Sample Input 1
5 3
10
15
11
14
12
Sample Output 1
2
If we decorate the first, third and fifth trees, hmax=12,hmin=10 so hmax−hmin=2. This is optimal.
Sample Input 2
5 3
5
7
5
7
7
Sample Output 2
0
If we decorate the second, fourth and fifth trees, hmax=7,hmin=7 so hmax−hmin=0. This is optimal.
There are not too many trees in these sample inputs, but note that there can be at most one hundred thousand trees (we just can't put a sample with a hundred thousand lines here).
题解:
最终的答案就是k个数中的最大高度-最小高度。要让答案尽可能的小,就要让这两个值尽可能接近。很容易想到排序一下,然后枚举第i个和第i+k-1个之间的差值(0≤i≤n-k),取最小值即可。

1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 int n, k; 9 scanf("%d %d", &n, &k); 10 int h[100005]; 11 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) 12 scanf("%d", &h[i]); 13 sort(h, h + n); 14 int ans = 1e9; 15 for(int i = 0; i <= n - k; ++i) 16 ans = min(ans, h[i+k-1] - h[i]); 17 printf("%d\n", ans); 18 return 0; 19 }
D Christmas
题目:
Time limit : 2sec / Memory limit : 1024MB
Score : 400 points
Problem Statement
In some other world, today is Christmas.
Mr. Takaha decides to make a multi-dimensional burger in his party. A level-L burger (L is an integer greater than or equal to 0) is the following thing:
- A level-0 burger is a patty.
- A level-L burger (L≥1) is a bun, a level-(L−1) burger, a patty, another level-(L−1) burger and another bun, stacked vertically in this order from the bottom.
For example, a level-1 burger and a level-2 burger look like BPPPB and BBPPPBPBPPPBB (rotated 90 degrees), where B and P stands for a bun and a patty.
The burger Mr. Takaha will make is a level-N burger. Lunlun the Dachshund will eat X layers from the bottom of this burger (a layer is a patty or a bun). How many patties will she eat?
Constraints
- 1≤N≤50
- 1≤X≤( the total number of layers in a level-N burger )
- N and X are integers.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N X
Output
Print the number of patties in the bottom-most X layers from the bottom of a level-N burger.
Sample Input 1
2 7
Sample Output 1
4
There are 4 patties in the bottom-most 7 layers of a level-2 burger (BBPPPBPBPPPBB).
Sample Input 2
1 1
Sample Output 2
0
The bottom-most layer of a level-1 burger is a bun.
Sample Input 3
50 4321098765432109
Sample Output 3
2160549382716056
A level-50 burger is rather thick, to the extent that the number of its layers does not fit into a 32-bit integer.
题解:
题目中burger的定义是递归的定义,自然也想到用递归的方式去做。我们可以发现burger是对称的。那么就可以分段递归。nlen是每个burger的长度(高度),p记录的是每个burger含有的p的个数。这两个公式稍微推一下就可以得到,是一个等比数列的问题,这里不展开了。(事实上直接迭代也可以得到)
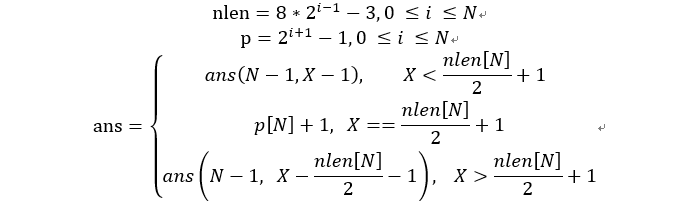
另外,我们可以发现X≤N的时候,ans=0;X≥nlen[N]的时候,ans=p[N]。由此可以写出代码。
注意输入输出的时候为了防止Compilation Error,用cin和cout较为妥当。

1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cmath> 3 #include <iostream> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 typedef unsigned long long ll; 8 9 ll p[55], nlen[55]; 10 11 ll solve(ll n, ll x) 12 { 13 if(x <= n) return 0; 14 if(x >= nlen[n] - 1) return p[n]; 15 if(x == nlen[n] / 2 + 1) return (p[n] / 2 + 1); 16 else if(x < nlen[n] / 2 + 1) 17 return solve(n - 1, x - 1); 18 else 19 return p[n] / 2 + 1 + solve(n - 1, x - nlen[n] / 2 - 1); 20 } 21 22 int main() 23 { 24 for(int i = 0; i <= 50; ++i) 25 { 26 p[i] = pow(2, i + 1) - 1; 27 nlen[i] = pow(2, i - 1) * 8 - 3; 28 } 29 ll n, x; 30 cin>>n>>x; 31 cout<<solve(n, x)<<endl; 32 return 0; 33 }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号