数据结构(十六)模式匹配算法--Brute Force算法和KMP算法
一、模式匹配
串的查找定位操作(也称为串的模式匹配操作)指的是在当前串(主串)中寻找子串(模式串)的过程。若在主串中找到了一个和模式串相同的子串,则查找成功;若在主串中找不到与模式串相同的子串,则查找失败。两种主要的模式匹配算法是Brute Force算法和KMP算法。
二、Brute Force算法
1.Brute Force算法也被称为朴素的模式匹配算法,是一种简单、直观的模式匹配算法。简单来说,就是对主串的每一个字符作为子串开头,与要匹配的字符串进行匹配。对主串做大循环,每个字符开头做次数为子串长度的小循环,直到匹配成功或全部遍历完成为止。
2.Brute Force算法的C语言代码实现:
/* 朴素的模式匹配法 */ int Index(String S, String T, int pos) { int i = pos; /* i用于主串S中当前位置下标值,若pos不为1,则从pos位置开始匹配 */ int j = 1; /* j用于子串T中当前位置下标值 */ while (i <= S[0] && j <= T[0]) /* 若i小于S的长度并且j小于T的长度时,循环继续 */ { if (S[i] == T[j]) /* 两字母相等则继续 */ { ++i; ++j; } else /* 指针后退重新开始匹配 */ { i = i-j+2; /* i退回到上次匹配首位的下一位 */ j = 1; /* j退回到子串T的首位 */ } } if (j > T[0]) return i-T[0]; else return 0; }
3.Brute Force算法的Java语言代码实现:
/*****************************朴素模式匹配算法*******************************************/ public int indexOf_BF(StrMatchingINF str, int begin) throws Exception { if ((this != null) && (str != null) && (str.strLength() > 0 && (this.strLength() >= str.strLength()))) { int i = begin; int j = 0; int slen = this.strLength(); // strLength()函数返回的数组下标最大值 int tlen = str.strLength(); while ((i < slen) && (j < tlen)) { if (this.charAt(i) == str.charAt(j)) { i++; j++; } else { i = i - j + 1; // 注意:i退回到主串上次匹配首位的下一位 j = 0; // j回退到子串的首位 } } if (j >= tlen) { // 全部匹配成功 return i - tlen; // 返回 子串在主串中的下标 } else { return 0; } } else { throw new Exception("主串为空或者子串为空或者子串长度大于主串长度"); } } // BF算法比较次数统计 public int indexOf_BFCount(StrMatchingINF str, int begin) throws Exception { int i = begin; int j = 0; int count = 0; int slen = this.strLength(); int tlen = str.strLength(); while ((i < slen) && (j < tlen)) { if (this.charAt(i) == str.charAt(j)) { i++; j++; } else { i = i - j + 1; // 注意:i退回到主串上次匹配首位的下一位 j = 0; // j回退到子串的首位 } count ++; } return count; } /***********************************************************************************/
4.Brute Froce模式匹配算法简单且易于理解,但在一些情况下,时间效率非常低,其原因是主串s和模式串t中已有多个字符比较相等时,只要后面遇到一个字符比较不相等,就需要将主串的比较位置i回退。
假设主串的长度为n,子串的长度为m,则模式匹配的BF算法在最好情况下的时间复杂度为O(m),即主串的前m个字符刚好等于模式串的m个字符。
BF算法在最坏情况下的时间复杂度为O(m x n):假设模式串的前m-1个字符串的相应字符序列比较总是相等,而模式串的第m个字符合主串的相应字符比较总是不相等时,此时,模式串的m个字符序列不许和主串相应字符序列一共比较n-m+1次,每次比较m个字符,总共需比较m x (n - m + 1)次,因此,其时间复杂度是O(m x n)。
例如1,主串s = “aaaab”,串长度n = 5,模式串t = “ab”,串长为m = 2。
每趟比较4次后匹配失败,i回到原位置加1,j返回到0,继续下一趟匹配,共计需要5 - 2 + 1 = 4趟,总共比较了4 x 2 = 8次。
例如2,主串s = “aaaaa”,串长度n = 5,模式串t = “ab”,串长为m = 2。
每趟比较4次后匹配失败,i回到原位置加1,j返回到0,继续下一趟匹配,共计需要5 - 2 + 1 = 4趟,这4趟是比较了4次,然而由于i继续加1,使得s的最后一位和t的第一位比较了一次,总共比较了4 x 2 + 1 = 9次。
三、KMP算法
1.KMP模式匹配算法也叫克努特-莫里斯-普拉特算法,可以大大避免重复遍历的情况。KMP算法的主要思想是,每当某趟匹配失败时,i指针不回退,而是利用已经得到的“部分匹配”的结果,将模式向右“滑动”尽可能远的一段距离后,继续进行比较。
2.在朴素的模式匹配算法中,主串的i值是不断地回溯来完成的,KMP算法就是为了避免没有必要的回溯发生。
3.既然i值不回溯,也就是不可以变小,那么要考虑的变化就是j值了,通过观察可以发现,j值的变化与主串没有关系,而是拒绝域T串的结构中是否有重复的问题,也就是说,j值的多少取决于当前字符之前的串的前后缀的相似度。
4.把T串各个位置的j值变化定义为一个数组next,那么next的长度就是T串的长度,于是,可以得到下面的函数定义:
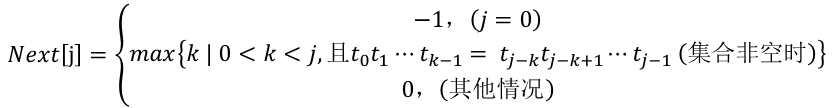
以模式串T = “abcabc”为例, 当j=0时,next[0]=-1; 当j=1时,next[1]=0; 当j=2时,等号左边最大为t0, 等号右边最大为t1, 由于t0不等于t1,所以next[2]=0; 当j=3时,等号左边最大为t0t1, 等号右边最大为t1t2, 由于t0不等于t2,所以next[3]=0; 当j=4时,等号左边最大为t0t1t2, 等号右边最大为t1t2t3, 由于t0等于t3, 所以next[4]=1; 当j=5时,等号左边最大为t0t1t2t3,等号右边最大为t1t2t3t4,由于t1等于t4,即有t0t1=t3t4,所以next[5]=next[4]+1=2;
以模式串T = “ababaaa”为例,
当j=0时,next[0]=-1; 当j=1时,子串为a, next[1]=0; 当j=2时,子串为ab, t0不等于t1,next[2]=0; 当j=3时,子串为aba, t0=t2=‘a’,next[3]=1; 当j=4时,子串为abab, t1=t3=‘b’,即有t0t1=t2t3, 则next[4]=next[3]+1=2; 当j=5时,子串为ababa, t2=t4=‘a’,即有t0t1t2=t2t3t4,则next[5]=next[4]+1=3;
当j=6时,子串为ababaa,t3不等于t5,则k=next[k]=next[3]=1;又因为t1不等于t5,则k=next[k]=next[1]=0;又因为t0等于t5,则next[6]=next[1]+1=1;
求解next[j]函数值的过程是一个递推过程:
初始时,next[0]=-1,next[1]=0;
若存在next[j]=k,则表明在模式串T中有“t0 t1... tk-1” = “tj-k tj-k+1 ... tj-1” (0<k<j),其中,k为满足等式的最大值。此时计算next[j+1]的值存在以下两种情况:
- 若tk = tj, 则表明在模式串中存在“t0 t1... tk-1 tk” = “tj-k tj-k+1 ... tj-1 tj” (0<k<j)并且不可能存在大于k的值满足上式,因此可以得到next[j+1]=next[j] + 1 = k + 1
- 若tk != tj,则表明在模式串中存在“t0 t1... tk-1 tk”不等于“tj-k tj-k+1 ... tj-1 tj” (0<k<j),此时可以把求next[j]的过程看成是一个模式匹配过程,整个模式串即是主串又是模式串。在当前匹配过程中,已有“t0 t1... tk-1” = “tj-k tj-k+1 ... tj-1”成立,则当tk不等于tj时,应将模式串T向右滑动值next[k]的位置,并把next[k]位置上的字符与主串中第j位置上的字符作比较。若此时next[k]的位置位置上的字符等于tj,则表明在“主串”T中第j+1个字符之前存在一个最大长度为next[k]的子串,使得t0~tnext[k] = tj-k~tj,因此有next[j+1]=next[k]+1。若此时此时next[k]的位置位置上的字符不等于tj,则将模式串T向右滑动继续匹配,直至某次比较有tk=tj,或某次比较有tk不等于tj且k=0,此时有next[j+1]=0
5.next[j]函数算法的Java语言代码实现
private int[] get_Next(StrMatchingINF T) throws Exception { int[] next = new int[T.strLength()]; int j = 1; int k = 0; next[0] = -1; next[1] = 0; while (j < T.strLength() - 1) { if (T.charAt(j) == T.charAt(k)) { next[j + 1] = k + 1; j++; k++; } else if (k == 0) { next[j + 1] = 0; j++; } else { k = next[k]; } } return next; }
四、改进的KMP算法
1.以上定义的next[j]函数在某些情况下还存在缺陷。例如,主串s=“bbbcbbbbbc”,模式串t=“bbbbc”,在匹配时,当i=3,j=3时,s3不等于t3,则j向右滑动next[j],接着还需要进行s3与t2,s3与t1,s3与t0的三次比较。实际上,因为模式串中的t0、t1、t2这三个字符与t3都相等,后三次比较结果与s3和t3的比较结果相同,因此,可以不必进行后三次的比较,而是直接将模式串向右滑动4个字符,比较s4与t0。
2.一般来说,若模式串t中存在tj=tk(k=next[j]),且si不等于tj时,则下一次si不必与tk进行比较,而直接与t next[k]进行比较,因此,修正next[j]函数为nextval[j]:
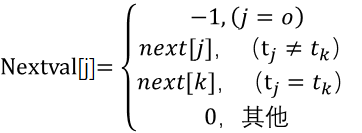
3.nextval[j]函数算法的Java语言代码实现
private int[] get_NextVal(StrMatchingINF T) throws Exception { int[] nextval = new int[T.strLength()]; int j = 1; int k = 0; nextval[0] = -1; while (j < T.strLength() - 1) { if (k == -1 || T.charAt(j) == T.charAt(k)) { j++; k++; if (T.charAt(j) != T.charAt(k)) { nextval[j] = k; } else { nextval[j] = nextval[k]; } } else { k = nextval[k]; } } return nextval; }
五、三种模式匹配算法的C语言代码实现(和Java实现有出入,数组下标为0的位置存储的是数组长度):
#include "string.h" #include "stdio.h" #include "stdlib.h" #include "io.h" #include "math.h" #include "time.h" #define OK 1 #define ERROR 0 #define TRUE 1 #define FALSE 0 #define MAXSIZE 100 /* 存储空间初始分配量 */ typedef int Status; /* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等 */ typedef int ElemType; /* ElemType类型根据实际情况而定,这里假设为int */ typedef char String[MAXSIZE+1]; /* 0号单元存放串的长度 */ /* 生成一个其值等于chars的串T */ Status StrAssign(String T,char *chars) { int i; if(strlen(chars)>MAXSIZE) return ERROR; else { T[0]=strlen(chars); for(i=1;i<=T[0];i++) T[i]=*(chars+i-1); return OK; } } Status ClearString(String S) { S[0]=0;/* 令串长为零 */ return OK; } /* 输出字符串T。 */ void StrPrint(String T) { int i; for(i=1;i<=T[0];i++) printf("%c",T[i]); printf("\n"); } /* 输出Next数组值。 */ void NextPrint(int next[],int length) { int i; for(i=1;i<=length;i++) printf("%d",next[i]); printf("\n"); } /* 返回串的元素个数 */ int StrLength(String S) { return S[0]; } /* 朴素的模式匹配法 */ int Index(String S, String T, int pos) { int i = pos; /* i用于主串S中当前位置下标值,若pos不为1,则从pos位置开始匹配 */ int j = 1; /* j用于子串T中当前位置下标值 */ while (i <= S[0] && j <= T[0]) /* 若i小于S的长度并且j小于T的长度时,循环继续 */ { if (S[i] == T[j]) /* 两字母相等则继续 */ { ++i; ++j; } else /* 指针后退重新开始匹配 */ { i = i-j+2; /* i退回到上次匹配首位的下一位 */ j = 1; /* j退回到子串T的首位 */ } } if (j > T[0]) return i-T[0]; else return 0; } /* 通过计算返回子串T的next数组。 */ void get_next(String T, int *next) { int i,j; i=1; j=0; next[1]=0; while (i<T[0]) /* 此处T[0]表示串T的长度 */ { if(j==0 || T[i]== T[j]) /* T[i]表示后缀的单个字符,T[j]表示前缀的单个字符 */ { ++i; ++j; next[i] = j; } else j= next[j]; /* 若字符不相同,则j值回溯 */ } } /* 返回子串T在主串S中第pos个字符之后的位置。若不存在,则函数返回值为0。 */ /* T非空,1≤pos≤StrLength(S)。 */ int Index_KMP(String S, String T, int pos) { int i = pos; /* i用于主串S中当前位置下标值,若pos不为1,则从pos位置开始匹配 */ int j = 1; /* j用于子串T中当前位置下标值 */ int next[255]; /* 定义一next数组 */ get_next(T, next); /* 对串T作分析,得到next数组 */ while (i <= S[0] && j <= T[0]) /* 若i小于S的长度并且j小于T的长度时,循环继续 */ { if (j==0 || S[i] == T[j]) /* 两字母相等则继续,与朴素算法增加了j=0判断 */ { ++i; ++j; } else /* 指针后退重新开始匹配 */ j = next[j];/* j退回合适的位置,i值不变 */ } if (j > T[0]) return i-T[0]; else return 0; } /* 求模式串T的next函数修正值并存入数组nextval */ void get_nextval(String T, int *nextval) { int i,j; i=1; j=0; nextval[1]=0; while (i<T[0]) /* 此处T[0]表示串T的长度 */ { if(j==0 || T[i]== T[j]) /* T[i]表示后缀的单个字符,T[j]表示前缀的单个字符 */ { ++i; ++j; if (T[i]!=T[j]) /* 若当前字符与前缀字符不同 */ nextval[i] = j; /* 则当前的j为nextval在i位置的值 */ else nextval[i] = nextval[j]; /* 如果与前缀字符相同,则将前缀字符的 */ /* nextval值赋值给nextval在i位置的值 */ } else j= nextval[j]; /* 若字符不相同,则j值回溯 */ } } int Index_KMP1(String S, String T, int pos) { int i = pos; /* i用于主串S中当前位置下标值,若pos不为1,则从pos位置开始匹配 */ int j = 1; /* j用于子串T中当前位置下标值 */ int next[255]; /* 定义一next数组 */ get_nextval(T, next); /* 对串T作分析,得到next数组 */ while (i <= S[0] && j <= T[0]) /* 若i小于S的长度并且j小于T的长度时,循环继续 */ { if (j==0 || S[i] == T[j]) /* 两字母相等则继续,与朴素算法增加了j=0判断 */ { ++i; ++j; } else /* 指针后退重新开始匹配 */ j = next[j];/* j退回合适的位置,i值不变 */ } if (j > T[0]) return i-T[0]; else return 0; } int main() { int i,*p; String s1,s2; StrAssign(s1,"abcdex"); printf("子串为: "); StrPrint(s1); i=StrLength(s1); p=(int*)malloc((i+1)*sizeof(int)); get_next(s1,p); printf("Next为: "); NextPrint(p,StrLength(s1)); printf("\n"); StrAssign(s1,"abcabx"); printf("子串为: "); StrPrint(s1); i=StrLength(s1); p=(int*)malloc((i+1)*sizeof(int)); get_next(s1,p); printf("Next为: "); NextPrint(p,StrLength(s1)); printf("\n"); StrAssign(s1,"ababaaaba"); printf("子串为: "); StrPrint(s1); i=StrLength(s1); p=(int*)malloc((i+1)*sizeof(int)); get_next(s1,p); printf("Next为: "); NextPrint(p,StrLength(s1)); printf("\n"); StrAssign(s1,"aaaaaaaab"); printf("子串为: "); StrPrint(s1); i=StrLength(s1); p=(int*)malloc((i+1)*sizeof(int)); get_next(s1,p); printf("Next为: "); NextPrint(p,StrLength(s1)); printf("\n"); StrAssign(s1,"ababaaaba"); printf(" 子串为: "); StrPrint(s1); i=StrLength(s1); p=(int*)malloc((i+1)*sizeof(int)); get_next(s1,p); printf(" Next为: "); NextPrint(p,StrLength(s1)); get_nextval(s1,p); printf("NextVal为: "); NextPrint(p,StrLength(s1)); printf("\n"); StrAssign(s1,"aaaaaaaab"); printf(" 子串为: "); StrPrint(s1); i=StrLength(s1); p=(int*)malloc((i+1)*sizeof(int)); get_next(s1,p); printf(" Next为: "); NextPrint(p,StrLength(s1)); get_nextval(s1,p); printf("NextVal为: "); NextPrint(p,StrLength(s1)); printf("\n"); StrAssign(s1,"00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001"); printf("主串为: "); StrPrint(s1); StrAssign(s2,"0000000001"); printf("子串为: "); StrPrint(s2); printf("\n"); printf("主串和子串在第%d个字符处首次匹配(朴素模式匹配算法)\n",Index(s1,s2,1)); printf("主串和子串在第%d个字符处首次匹配(KMP算法) \n",Index_KMP(s1,s2,1)); printf("主串和子串在第%d个字符处首次匹配(KMP改良算法) \n",Index_KMP1(s1,s2,1)); return 0; } 输出为: 子串为: abcdex Next为: 011111 子串为: abcabx Next为: 011123 子串为: ababaaaba Next为: 011234223 子串为: aaaaaaaab Next为: 012345678 子串为: ababaaaba Next为: 011234223 NextVal为: 010104210 子串为: aaaaaaaab Next为: 012345678 NextVal为: 000000008 主串为: 00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001 子串为: 0000000001 主串和子串在第41个字符处首次匹配(朴素模式匹配算法) 主串和子串在第41个字符处首次匹配(KMP算法) 主串和子串在第41个字符处首次匹配(KMP改良算法)
六、三种模式匹配算法即其各自的比较次数统计算法的Java语言代码实现:
- 接口类:
package bigjun.iplab.stringMatching; public interface StrMatchingINF { // 求顺序串的长度 public int strLength(); // 读取并返回串中的第index个字符值 public char charAt(int index) throws Exception; // Brute-Force模式匹配算法 public int indexOf_BF(StrMatchingINF str, int begin) throws Exception; // KMP模式匹配算法 public int indexOf_KMP(StrMatchingINF str, int begin) throws Exception; // 改进的KMP模式匹配算法 public int indexOf_ImprovedKMP(StrMatchingINF str, int begin) throws Exception; }
- 实现类:
package bigjun.iplab.stringMatching; public class StrMatching implements StrMatchingINF{ private char[] strElem; private int curlength; // 构造方法:以字符串常量构造串对象 public StrMatching(String str) { char[] tempCharArray = str.toCharArray(); strElem = tempCharArray; curlength = tempCharArray.length; } public int strLength() { return curlength; } public char charAt(int index) throws Exception { if ((index < 0) || (index >= curlength)) { throw new Exception("索引值超出范围,无法给出对应字符"); } return strElem[index]; } /*****************************朴素模式匹配算法*******************************************/ public int indexOf_BF(StrMatchingINF str, int begin) throws Exception { if ((this != null) && (str != null) && (str.strLength() > 0 && (this.strLength() >= str.strLength()))) { int i = begin; int j = 0; int slen = this.strLength(); // strLength()函数返回的数组下标最大值 int tlen = str.strLength(); while ((i < slen) && (j < tlen)) { if (this.charAt(i) == str.charAt(j)) { i++; j++; } else { i = i - j + 1; // 注意:i退回到主串上次匹配首位的下一位 j = 0; // j回退到子串的首位 } } if (j >= tlen) { // 全部匹配成功 return i - tlen; // 返回 子串在主串中的下标 } else { return -1; } } else { throw new Exception("主串为空或者子串为空或者子串长度大于主串长度"); } } // BF算法比较次数统计 public int indexOf_BFCount(StrMatchingINF str, int begin) throws Exception { int i = begin; int j = 0; int count = 0; int slen = this.strLength(); int tlen = str.strLength(); while ((i < slen) && (j < tlen)) { if (this.charAt(i) == str.charAt(j)) { i++; j++; } else { i = i - j + 1; // 注意:i退回到主串上次匹配首位的下一位 j = 0; // j回退到子串的首位 } count ++; if (j >= tlen) // 全部匹配成功 return count; // 返回 子串在主串中的下标 } return count; } /************************************KMP模式匹配算法***********************************************/ // KMP模式匹配算法 public int indexOf_KMP(StrMatchingINF str, int begin) throws Exception { int[] next = get_Next(str); int i = begin; int j = 0; while (i < this.strLength() && j < str.strLength()) { if (j == -1 || this.charAt(i) == str.charAt(j)) { i++; j++; } else { j = next[j]; } } if (j < str.strLength()) { return -1; } else { return (i - str.strLength()); } } private int[] get_Next(StrMatchingINF T) throws Exception { int[] next = new int[T.strLength()]; int j = 1; // 注意这里,只给定了数组下标为0和1的初始值,所以要令j从1开始,和get_Nextval()区分开 int k = 0; next[0] = -1; next[1] = 0; while (j < T.strLength() - 1) { if (T.charAt(j) == T.charAt(k)) { next[j + 1] = k + 1; j++; k++; } else if (k == 0) { next[j + 1] = 0; j++; } else { k = next[k]; } } return next; } public int indexOf_KMPCount(StrMatchingINF str, int begin) throws Exception { int[] next = get_Next(str); int count = 0; int i = begin; int j = 0; while (i < this.strLength() && j < str.strLength()) { if (j == -1 || this.charAt(i) == str.charAt(j)) { i++; j++; } else if (j == 0) { i++; } else { j=next[j]; } count++; } return count; } /*********************************改进的KMP模式匹配算法**********************************************/ public int indexOf_ImprovedKMP(StrMatchingINF str, int begin) throws Exception { int[] next = get_NextVal(str); int i = begin; int j = 0; while (i < this.strLength() && j < str.strLength()) { if (j == -1 || this.charAt(i) == str.charAt(j)) { i++; j++; } else { j = next[j]; } } if (j < str.strLength()) { return -1; } else { return (i - str.strLength()); } } private int[] get_NextVal(StrMatchingINF T) throws Exception { int[] nextval = new int[T.strLength()]; int j = 0; // 注意这里,只给定了数组下标为0的初始值,所以要令j从0开始,和get_Next()区分开 int k = -1; nextval[0] = -1; while (j < T.strLength() - 1) { if (k == -1 || T.charAt(j) == T.charAt(k)) { j++; k++; if (T.charAt(j) != T.charAt(k)) nextval[j] = k; else nextval[j] = nextval[k]; } else k = nextval[k]; } return nextval; } public int indexOf_ImprovedKMPCount(StrMatchingINF str, int begin) throws Exception { int[] next = get_NextVal(str); int i = begin; int j = 0; int count = 0; while (i < this.strLength() && j < str.strLength()) { if (j == -1 || this.charAt(i) == str.charAt(j)) { i++; j++; } else if (j == 0) { i++; }{ j = next[j]; } count++; } return count; } /***********************************************************************/ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { StrMatching str1 = new StrMatching("aaaaaaab"); StrMatching str2 = new StrMatching("aaaab"); System.out.println("采用BF算法, 主串和子串在主串数组下标为" + str1.indexOf_BF(str2, 0) + "的位置首次匹配成功"); System.out.println("采用KMP算法,主串和子串在主串数组下标为" + str1.indexOf_KMP(str2, 0) + "的位置首次匹配成功"); System.out.println("采用改进的KMP算法,主串和子串在主串数组下标为" + str1.indexOf_ImprovedKMP(str2, 0) + "的位置首次匹配成功"); System.out.println("采用BF算法, 比较次数为: " + str1.indexOf_BFCount(str2, 0)); System.out.println("采用KMP算法,比较次数为: " + str1.indexOf_KMPCount(str2, 0)); System.out.println("采用改进的KMP算法,比较次数为: " + str1.indexOf_ImprovedKMPCount(str2, 0)); System.out.println(); StrMatching str3 = new StrMatching("aaaaaaaa"); StrMatching str4 = new StrMatching("aaaab"); System.out.println("采用BF算法, 主串和子串在主串数组下标为" + str3.indexOf_BF(str4, 0) + "的位置首次匹配成功"); System.out.println("采用KMP算法,主串和子串在主串数组下标为" + str3.indexOf_KMP(str4, 0) + "的位置首次匹配成功"); System.out.println("采用改进的KMP算法,主串和子串在主串数组下标为" + str3.indexOf_ImprovedKMP(str4, 0) + "的位置首次匹配成功"); System.out.println("采用BF算法, 比较次数为: " + str3.indexOf_BFCount(str4, 0)); System.out.println("采用KMP算法,比较次数为: " + str3.indexOf_KMPCount(str4, 0)); System.out.println("采用改进的KMP算法,比较次数为: " + str3.indexOf_ImprovedKMPCount(str4, 0)); System.out.println(); StrMatching str5 = new StrMatching("00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001"); StrMatching str6 = new StrMatching("0000000001"); System.out.println("采用BF算法, 主串和子串在主串数组下标为" + str5.indexOf_BF(str6, 0) + "的位置首次匹配成功"); System.out.println("采用KMP算法,主串和子串在主串数组下标为" + str5.indexOf_KMP(str6, 0) + "的位置首次匹配成功"); System.out.println("采用改进的KMP算法,主串和子串在主串数组下标为" + str5.indexOf_ImprovedKMP(str6, 0) + "的位置首次匹配成功"); System.out.println("采用BF算法, 比较次数为: " + str5.indexOf_BFCount(str6, 0)); System.out.println("采用KMP算法,比较次数为: " + str5.indexOf_KMPCount(str6, 0)); System.out.println("采用改进的KMP算法,比较次数为: " + str5.indexOf_ImprovedKMPCount(str6, 0)); System.out.println(); StrMatching str7 = new StrMatching("bbbcbbbbc"); StrMatching str8 = new StrMatching("bbbbc"); System.out.println("采用BF算法, 主串和子串在主串数组下标为" + str7.indexOf_BF(str8, 0) + "的位置首次匹配成功"); System.out.println("采用KMP算法,主串和子串在主串数组下标为" + str7.indexOf_KMP(str8, 0) + "的位置首次匹配成功"); System.out.println("采用改进的KMP算法,主串和子串在主串数组下标为" + str7.indexOf_ImprovedKMP(str8, 0) + "的位置首次匹配成功"); /* i从0到4,每一趟的次数为:4 , 3 , 2 , 1 , 5 */ System.out.println("采用BF算法, 比较次数为: " + str7.indexOf_BFCount(str8, 0)); /* next[j] 为-1、0、1、2、3 */ /* i从0到4,每一趟的次数为:4 , 1 , 1 , 1 , 5 */ System.out.println("采用KMP算法,比较次数为: " + str7.indexOf_KMPCount(str8, 0)); /* nextval[j] 为-1、0、 0、0、3*/ /* 由于t0、t1、t2都与t3相等,却s3不等于t3,所以s3不等于t0、t1、t2,所以没有必要让s3和t0、t1、t2比较*/ /* i从0到4,每一趟的次数为:4 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 5 */ System.out.println("采用改进的KMP算法,比较次数为: " + str7.indexOf_ImprovedKMPCount(str8, 0)); } }
- 输出:
采用BF算法, 主串和子串在主串数组下标为3的位置首次匹配成功 采用KMP算法,主串和子串在主串数组下标为3的位置首次匹配成功 采用改进的KMP算法,主串和子串在主串数组下标为3的位置首次匹配成功 采用BF算法, 比较次数为: 20 采用KMP算法,比较次数为: 11 采用改进的KMP算法,比较次数为: 8 采用BF算法, 主串和子串在主串数组下标为-1的位置首次匹配成功 采用KMP算法,主串和子串在主串数组下标为-1的位置首次匹配成功 采用改进的KMP算法,主串和子串在主串数组下标为-1的位置首次匹配成功 采用BF算法, 比较次数为: 24 采用KMP算法,比较次数为: 12 采用改进的KMP算法,比较次数为: 8 采用BF算法, 主串和子串在主串数组下标为40的位置首次匹配成功 采用KMP算法,主串和子串在主串数组下标为40的位置首次匹配成功 采用改进的KMP算法,主串和子串在主串数组下标为40的位置首次匹配成功 采用BF算法, 比较次数为: 410 采用KMP算法,比较次数为: 90 采用改进的KMP算法,比较次数为: 50 采用BF算法, 主串和子串在主串数组下标为4的位置首次匹配成功 采用KMP算法,主串和子串在主串数组下标为4的位置首次匹配成功 采用改进的KMP算法,主串和子串在主串数组下标为4的位置首次匹配成功 采用BF算法, 比较次数为: 15 采用KMP算法,比较次数为: 12 采用改进的KMP算法,比较次数为: 9


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号