设计模式(十)Strategy模式
Strategy模式,就是用来整体地替换算法,可以轻松地以不同的算法解决同一个问题。
还是根据一个示例程序来理解这种设计模式吧。先看一下示例程序的类图。
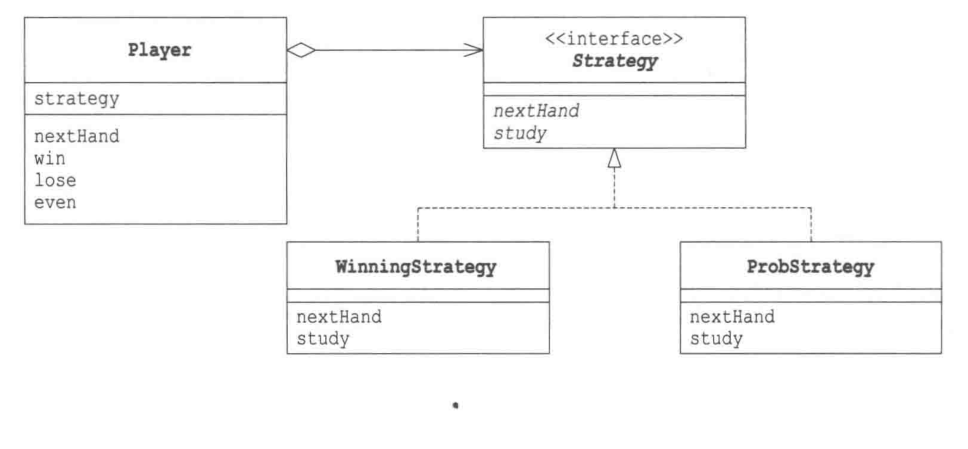
然后看示例程序代码。
1 package bigjunoba.bjtu.strategy; 2 3 public class Hand { 4 public static final int HANDVALUE_GUU = 0; // 表示石头的值 5 public static final int HANDVALUE_CHO = 1; // 表示剪刀的值 6 public static final int HANDVALUE_PAA = 2; // 表示布的值 7 public static final Hand[] hand = { // 表示猜拳中3种手势的实例 8 new Hand(HANDVALUE_GUU), 9 new Hand(HANDVALUE_CHO), 10 new Hand(HANDVALUE_PAA), 11 }; 12 private static final String[] name = { // 表示猜拳中手势所对应的字符串 13 "石头", "剪刀", "布", 14 }; 15 private int handvalue; // 表示猜拳中出的手势的值 16 private Hand(int handvalue) { 17 this.handvalue = handvalue; 18 } 19 public static Hand getHand(int handvalue) { // 根据手势的值获取其对应的实例 20 return hand[handvalue]; 21 } 22 public boolean isStrongerThan(Hand h) { // 如果this胜了h则返回true 23 return fight(h) == 1; 24 } 25 public boolean isWeakerThan(Hand h) { // 如果this输给了h则返回true 26 return fight(h) == -1; 27 } 28 private int fight(Hand h) { // 计分:平0, 胜1, 负-1 29 if (this == h) { 30 return 0; 31 } else if ((this.handvalue + 1) % 3 == h.handvalue) { 32 return 1; 33 } else { 34 return -1; 35 } 36 } 37 public String toString() { // 转换为手势值所对应的字符串 38 return name[handvalue]; 39 } 40 }
Hand类是用来表示猜拳中“手势”的类,首先创建了Hand类的实例,并将它们保存在hand数组中。getHand方法的作用是,将手势的值作为参数传递给getHand方法,它就会将手势的值对应的Hand类的实例返回。判断猜拳结果比较有意思,如果hand1赢了hand2,那么可以用hand1.isStrongerThan(hand2)来表示,反之如果hand1输了hand2,那么可以用hand1.isWeakerThan(hand2)来表示。fight方法是用来比较this和h的,如果this的手势值加1后是h的手势值,那么this获胜。例如this是石头(0),h是剪刀(1);或者this是剪刀(1)而h是布(2);或者this是布(2)而h是石头(0)。这里的取余是因为2加上1后除以3的余数正好是0,也就是石头。这里的Hand类被其他类使用,但是它不是strategy模式的一部分。
1 package bigjunoba.bjtu.strategy; 2 3 public interface Strategy { 4 public abstract Hand nextHand(); 5 public abstract void study(boolean win); 6 }
Strategy接口定义了猜拳策略的抽象方法接口。nextHand方法的作用是“获取下一局要出的手势”,study方法是学习“上一局的手势是否获胜了”。
1 package bigjunoba.bjtu.strategy; 2 3 import java.util.Random; 4 5 public class WinningStrategy implements Strategy { 6 private Random random; 7 private boolean won = false; 8 private Hand prevHand; 9 public WinningStrategy(int seed) { 10 random = new Random(seed); 11 } 12 public Hand nextHand() { 13 if (!won) { 14 prevHand = Hand.getHand(random.nextInt(3)); 15 } 16 return prevHand; 17 } 18 public void study(boolean win) { 19 won = win; 20 } 21 }
WinningStrategy类实现了Strategy接口。这种猜拳策略是,如果上一局的手势赢了,则下一局的手势就与上局相同;如果上一局手势输了,那下一局就随机出手势。won字段中保存的是上一局猜拳的输赢结果,如果上一局赢了,那么won值为true,然后nextHand方法直接返回prevHand,study方法调用study(True)。
1 package bigjunoba.bjtu.strategy; 2 3 import java.util.Random; 4 5 public class ProbStrategy implements Strategy { 6 private Random random; 7 private int prevHandValue = 0; 8 private int currentHandValue = 0; 9 private int[][] history = { 10 { 1, 1, 1, }, 11 { 1, 1, 1, }, 12 { 1, 1, 1, }, 13 }; 14 public ProbStrategy(int seed) { 15 random = new Random(seed); 16 } 17 public Hand nextHand() { 18 int bet = random.nextInt(getSum(currentHandValue)); 19 int handvalue = 0; 20 if (bet < history[currentHandValue][0]) { 21 handvalue = 0; 22 } else if (bet < history[currentHandValue][0] + history[currentHandValue][1]) { 23 handvalue = 1; 24 } else { 25 handvalue = 2; 26 } 27 prevHandValue = currentHandValue; 28 currentHandValue = handvalue; 29 return Hand.getHand(handvalue); 30 } 31 private int getSum(int hv) { 32 int sum = 0; 33 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { 34 sum += history[hv][i]; 35 } 36 return sum; 37 } 38 public void study(boolean win) { 39 if (win) { 40 history[prevHandValue][currentHandValue]++; 41 } else { 42 history[prevHandValue][(currentHandValue + 1) % 3]++; 43 history[prevHandValue][(currentHandValue + 2) % 3]++; 44 } 45 } 46 }
ProbStrategy类是随机出手势,但是每种手势出现的概率会根据以前的猜拳结果而改变。这里的理解就是,假如上一局出的是石头,那么history【0】【0】表示两局分别出石头和石头时胜了的次数,同理history【0】【1】表示两局分别出石头和剪刀时胜了的次数,history【0】【2】表示两局分别出石头和布时胜了的次数。这三个的值假如是3/5/7的情况下,下一局就会以石头、剪刀和布的比率为3:5:7来决定,在0到15之间取一个随机数,如果随机数是0 1 2那么出石头,如果随机数在3 4 5 6 7 那么出剪刀,如果随机数是9 10 11 12 13 14 15那么出布。
1 package bigjunoba.bjtu.strategy; 2 3 public class Player { 4 private String name; 5 private Strategy strategy; 6 private int wincount; 7 private int losecount; 8 private int gamecount; 9 public Player(String name, Strategy strategy) { // 赋予姓名和策略 10 this.name = name; 11 this.strategy = strategy; 12 } 13 public Hand nextHand() { // 策略决定下一局要出的手势 14 return strategy.nextHand(); 15 } 16 public void win() { // 胜 17 strategy.study(true); 18 wincount++; 19 gamecount++; 20 } 21 public void lose() { // 负 22 strategy.study(false); 23 losecount++; 24 gamecount++; 25 } 26 public void even() { // 平 27 gamecount++; 28 } 29 public String toString() { 30 return "[" + name + ":" + gamecount + " games, " + wincount + " win, " + losecount + " lose" + "]"; 31 } 32 }
Player类表示进猜拳游戏选手的类。nextHand方法的返回值就是策略的nextHand方法的返回值,也就是将自己的工作委托给了strategy。
1 package bigjunoba.bjtu.strategy; 2 3 public class Main { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 if (args.length != 2) { 6 System.out.println("Usage: java Main randomseed1 randomseed2"); 7 System.out.println("Example: java Main 314 15"); 8 System.exit(0); 9 } 10 int seed1 = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); 11 int seed2 = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); 12 Player player1 = new Player("Lianjiang", new WinningStrategy(seed1)); 13 Player player2 = new Player("Qiaoye", new ProbStrategy(seed2)); 14 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 15 Hand nextHand1 = player1.nextHand(); 16 Hand nextHand2 = player2.nextHand(); 17 if (nextHand1.isStrongerThan(nextHand2)) { 18 System.out.println("Winner:" + player1); 19 player1.win(); 20 player2.lose(); 21 } else if (nextHand2.isStrongerThan(nextHand1)) { 22 System.out.println("Winner:" + player2); 23 player1.lose(); 24 player2.win(); 25 } else { 26 System.out.println("Even..."); 27 player1.even(); 28 player2.even(); 29 } 30 } 31 System.out.println("Total result:"); 32 System.out.println(player1.toString()); 33 System.out.println(player2.toString()); 34 } 35 }
main类负责让电脑进行猜拳游戏。Lianjiang和Qiaoye分别使用不同的策略进行了100局比赛。这里必须输入两个数作为随机数的种子,关于这一方面,目前还是不太理解,等到理解了再来解释。
Even... Winner:[Qiaoye:1 games, 0 win, 0 lose] Winner:[Lianjiang:2 games, 0 win, 1 lose] Even... Winner:[Qiaoye:4 games, 1 win, 1 lose] Winner:[Lianjiang:5 games, 1 win, 2 lose] Even... Even... Winner:[Lianjiang:8 games, 2 win, 2 lose] Winner:[Lianjiang:9 games, 3 win, 2 lose] Winner:[Lianjiang:10 games, 4 win, 2 lose] Even... Winner:[Qiaoye:12 games, 2 win, 5 lose] Even... Winner:[Lianjiang:14 games, 5 win, 3 lose] Winner:[Qiaoye:15 games, 3 win, 6 lose] Winner:[Qiaoye:16 games, 4 win, 6 lose] Winner:[Lianjiang:17 games, 6 win, 5 lose] Winner:[Qiaoye:18 games, 5 win, 7 lose] Even... Total result: [Lianjiang:20 games, 7 win, 6 lose] [Qiaoye:20 games, 6 win, 7 lose]
输出结果如上,进行了20局的结果。
Strategy模式类图如下:
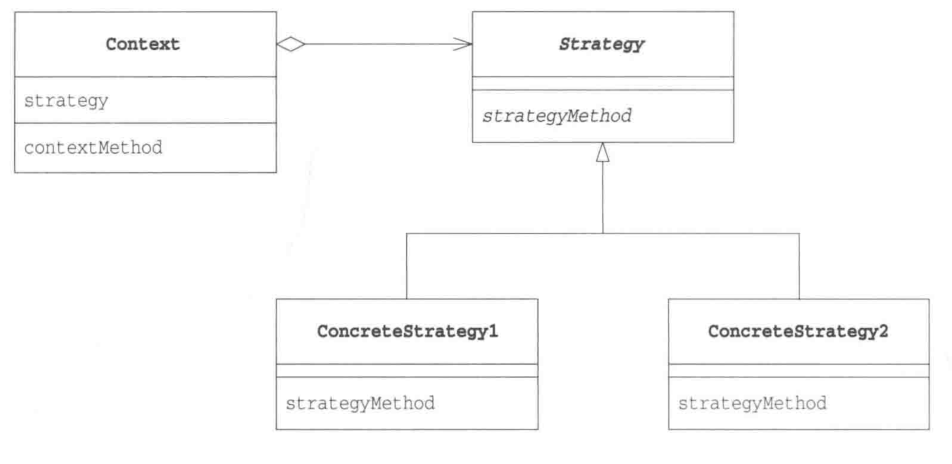
Strategy模式主要思想就是将算法与其他部分分离开,只定义了与算法相关的接口,然后在程序中以委托的方式来使用算法。使用委托这种弱关联关系可以很方便地整体替换算法,或者选择更好的算法在不同的环境下运行。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号