LinkedList 源码解析(基于 JDK 1.8)
@
源码环境: JDK 1.8。
关键的算法用 gif 图进行描述。
如果大家对画图或者 gif 工具有建议,欢迎在评论区评论。
1 成员变量和 Node
链表节点是 Node,Node 包含 item,前一项 prev 和后一项 next。
LinkedList 是一个双向链表,保存头尾的 Node 节点以及链表大小 size。
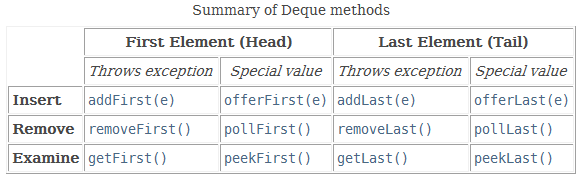
LinkedList 继承了 AbstractSequentialList,实现了 List, Deque, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable 接口。注意到Deque 是双端队列,也就是可以从头或尾插入,也可以从头或尾取出和删除的结构。下表是 Deque 的方法,在后面会分别描述。
要注意的是,在 LinkedList 中,add 和 offer 的方法基本一致,其他的方法可以认为满足下表。
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
transient int size = 0;
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;
...
private static class Node<E> { // Node 的结构:item,next 和 prev
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
}
2 构造器
一共两种构造器,对于参数为 Collection 的构造器,使用 addAll 加入。
public LinkedList() {
}
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
3 预备方法
在介绍插入、删除和获取之前,先介绍一些预备方法。由于是双向链表,在有对头尾操作两个方法的时候,只介绍头的方法。
为了简化思考,通常先假设用到的节点都不是 null,写出整个处理过程。
由于 null 没法使用 next/prev,在使用 node.next/node.prev 时要判断一下 node 是不是 null, 是 null 则对应一些特殊情况,一般会重置头结点或尾结点。
具体使用在下面会介绍。
3.1 linkFirst
linkFirst(E e)目的是将 e 包装的 newNode 插入头部。
将 e 包装到一个新的 Node 即 newNode 中,并将 e 的下一个节点指向原来的 first,并修改first 为 e,将 first 的前一个节点设为 newNode。
处理 null:根据前面的说明,这里用到了 f.prev ,先判断 f 是否为 null。如果 f 为 null,说明 e 是第一个插入的节点,所以 e 既是头结点也是尾结点。如果 f 非 null,则前一个节点为 newNode。
下面的图起始包含两个节点,然后在头部插入一个节点。
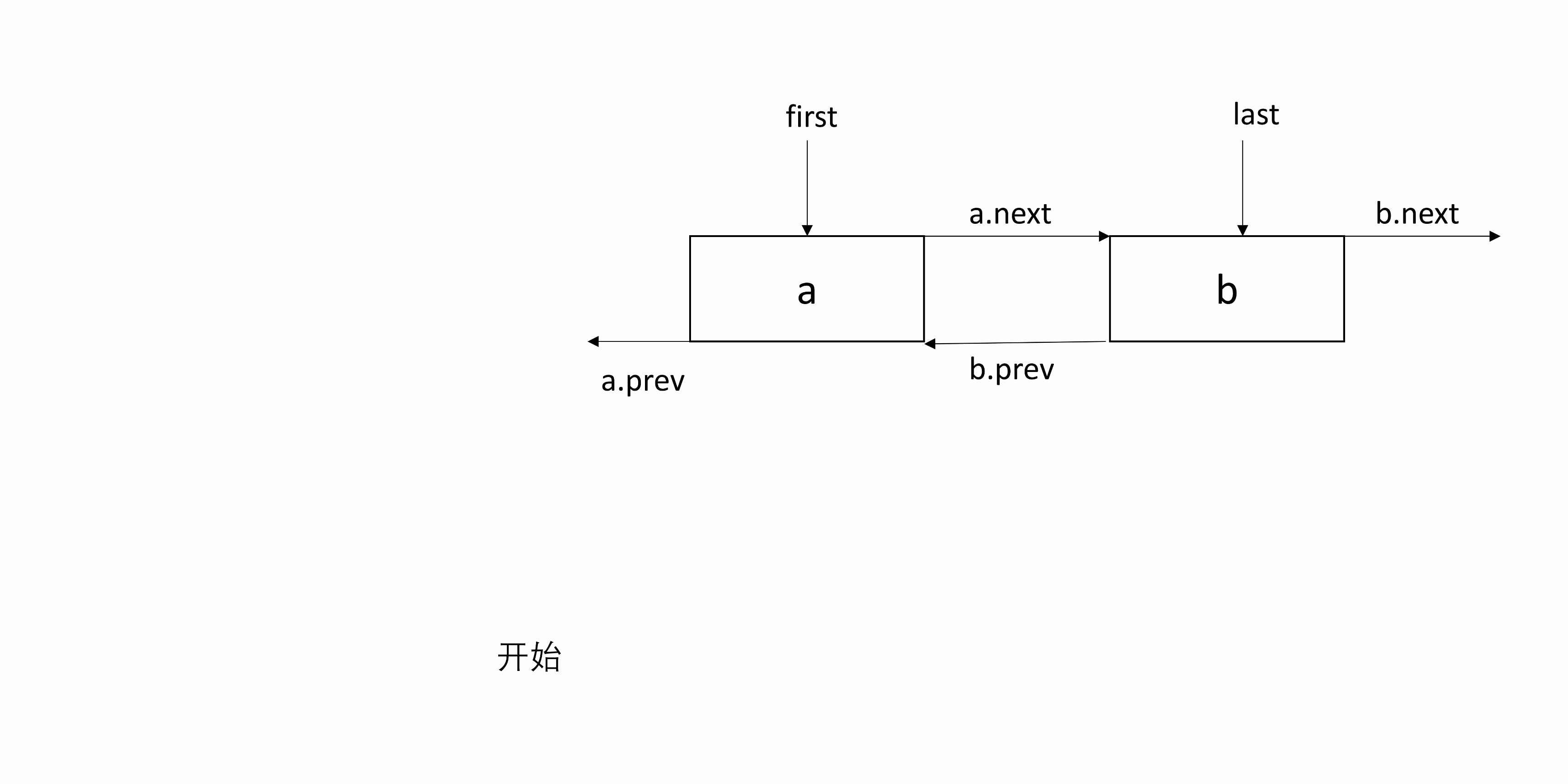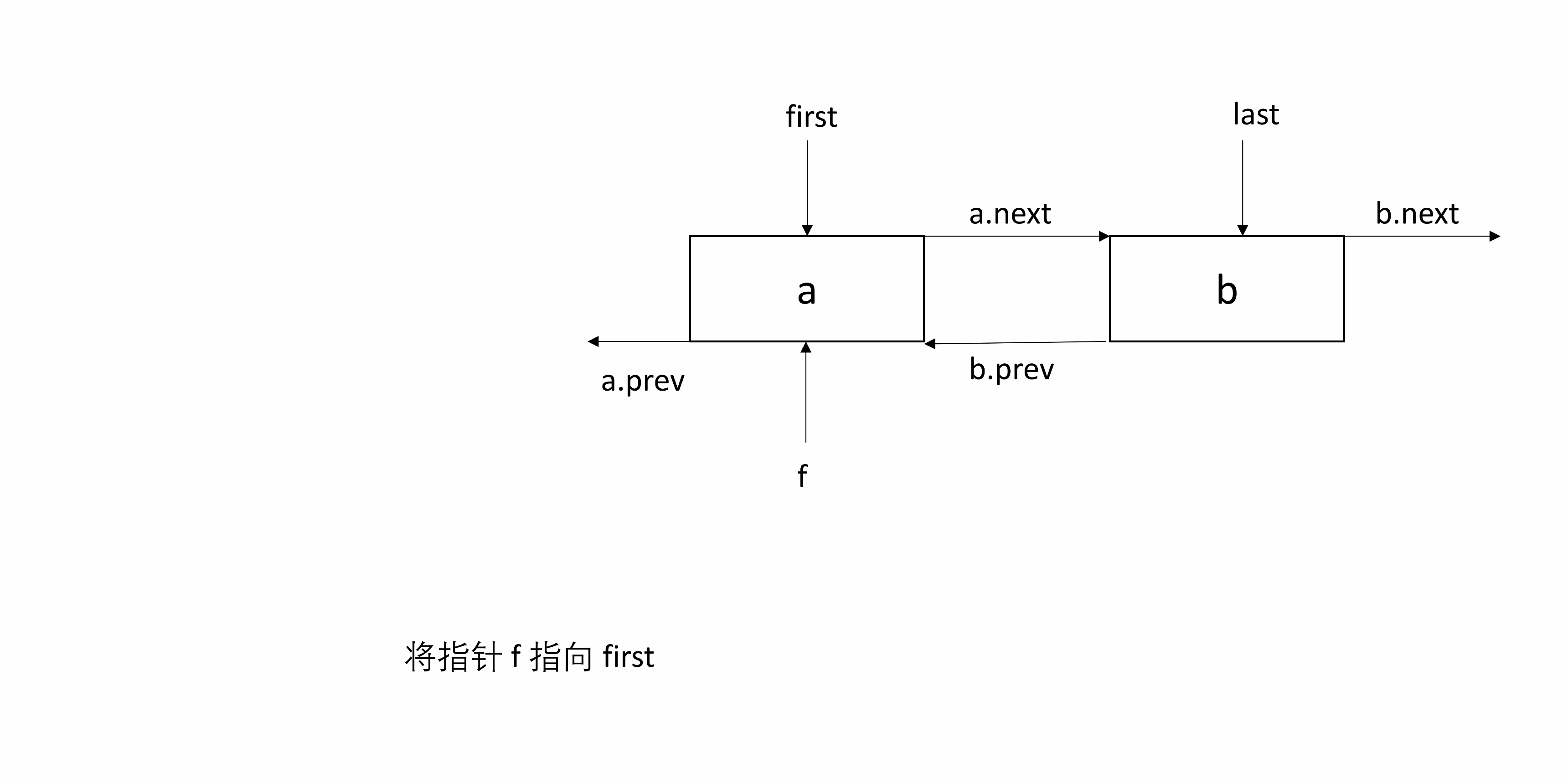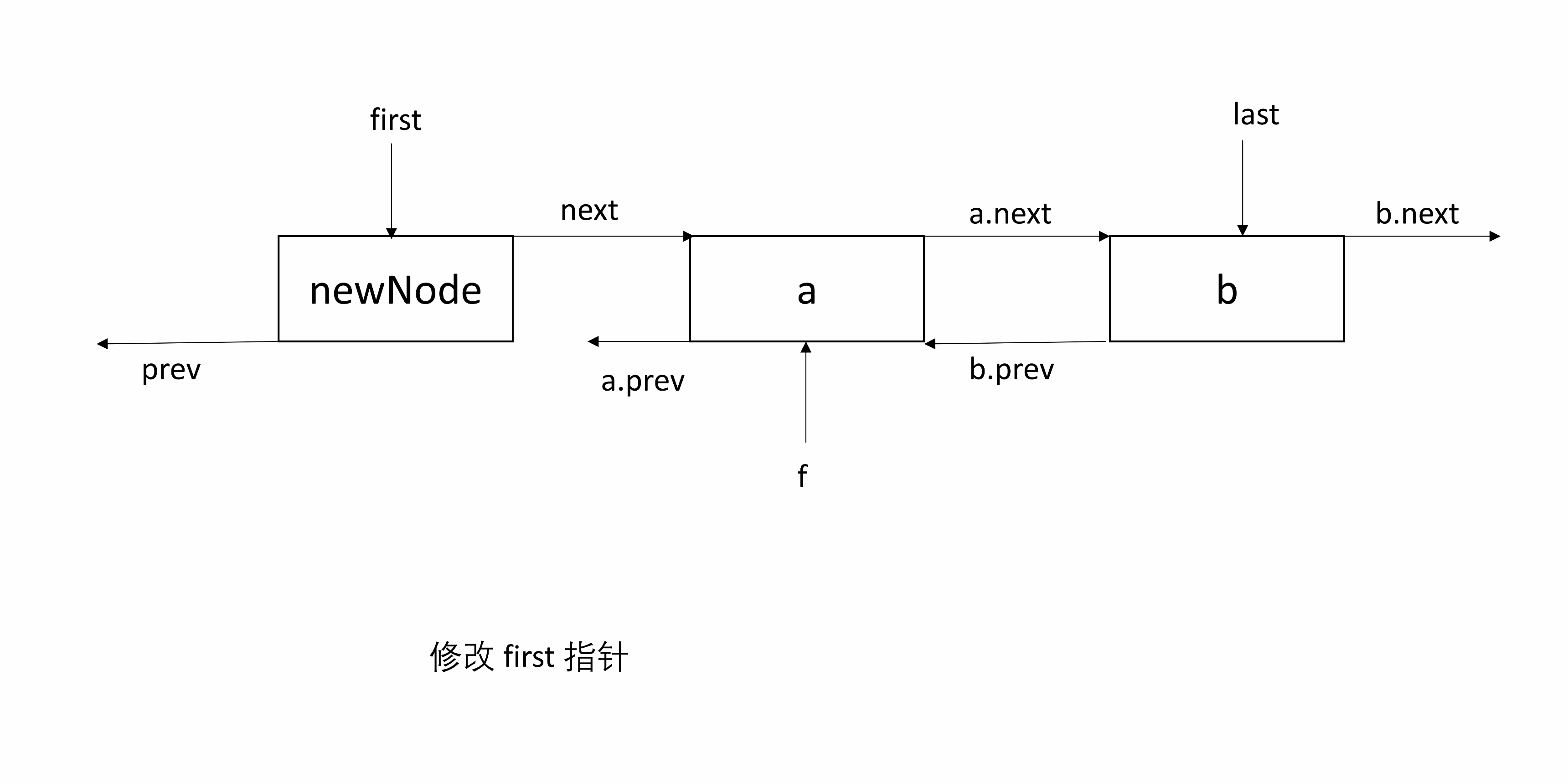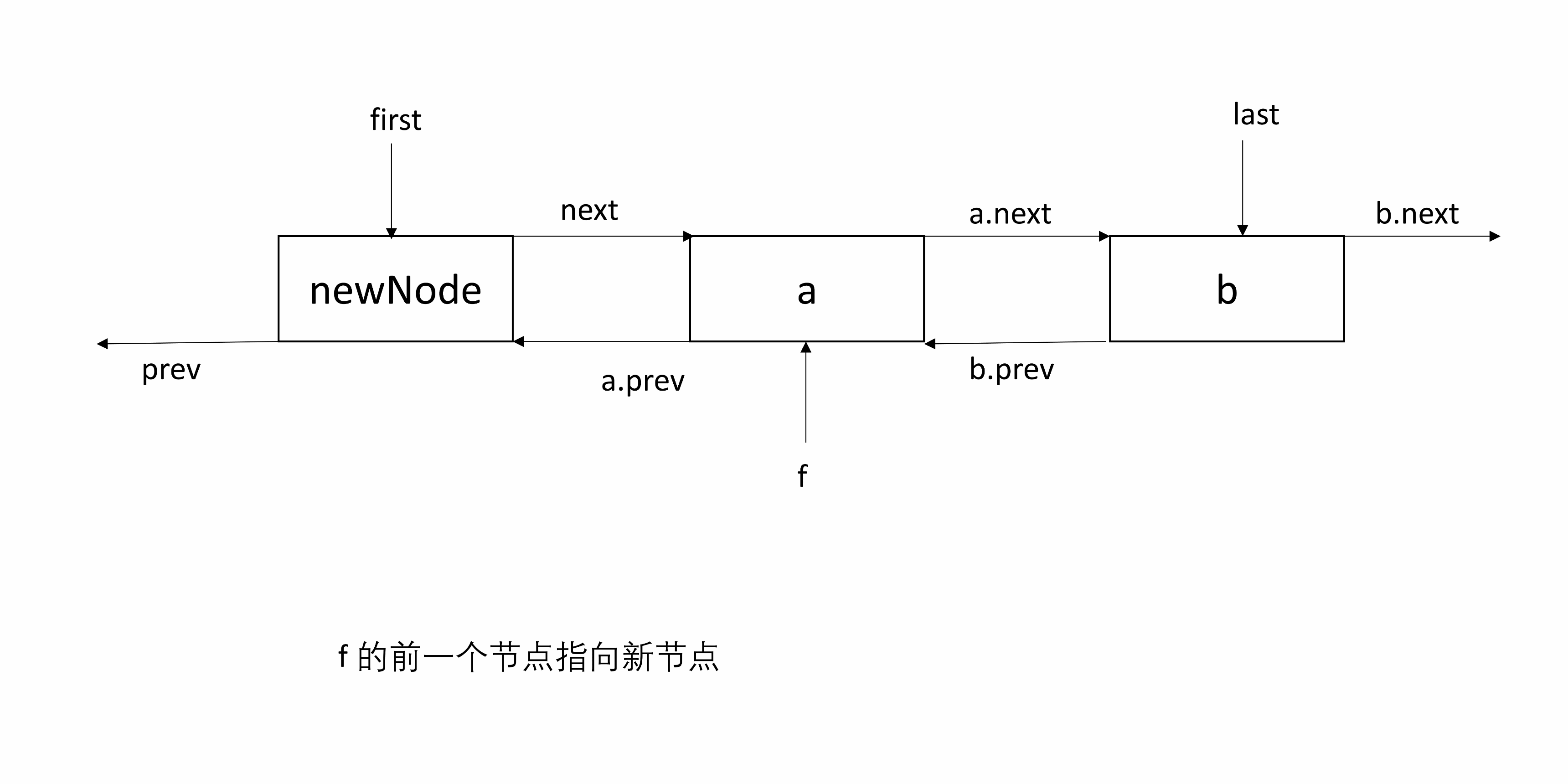
private void linkFirst(E e) { // 将 e 对应的节点插入头部
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);// 新节点.next = f
first = newNode;
if (f == null)// 头结点为空
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
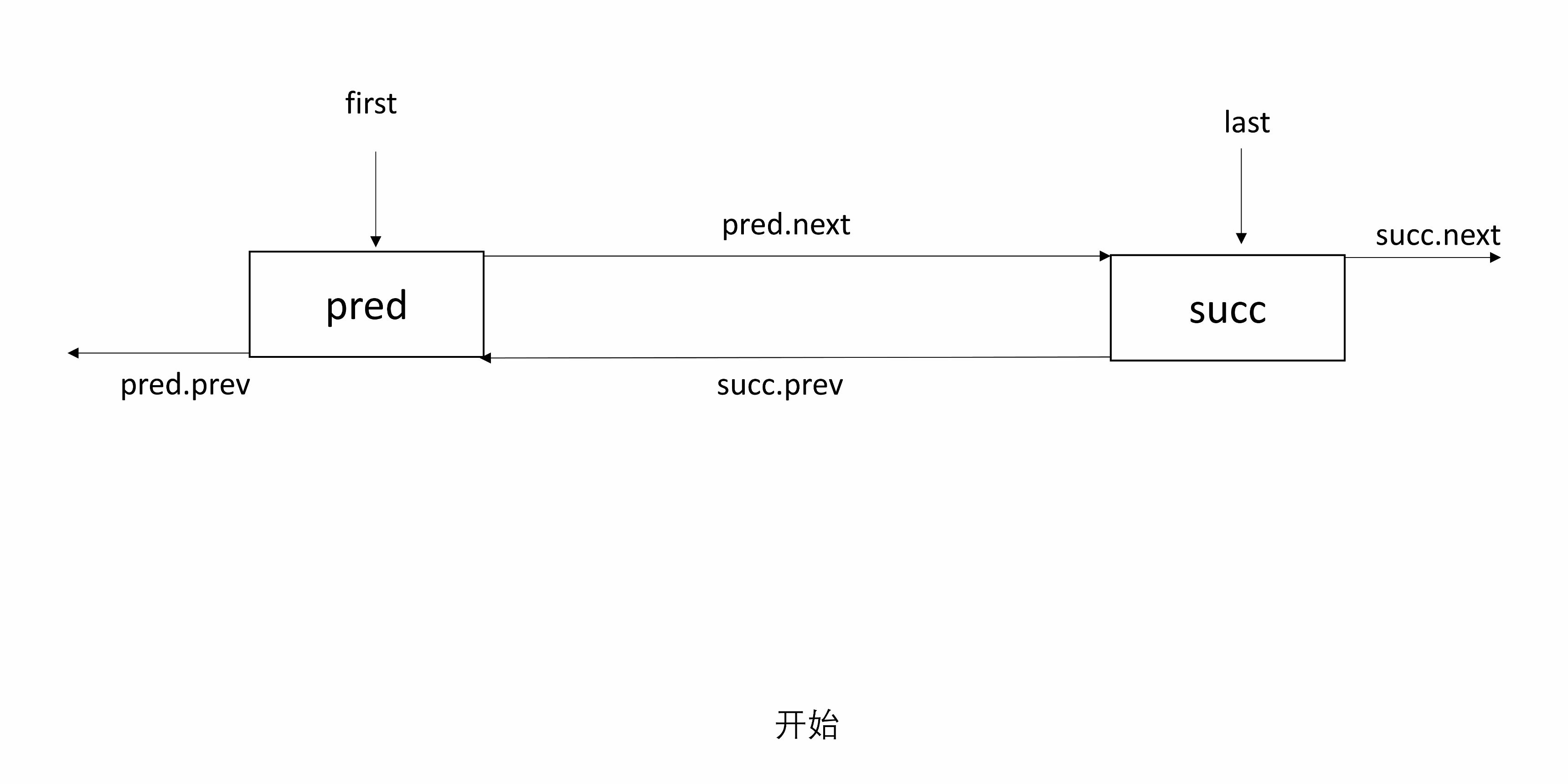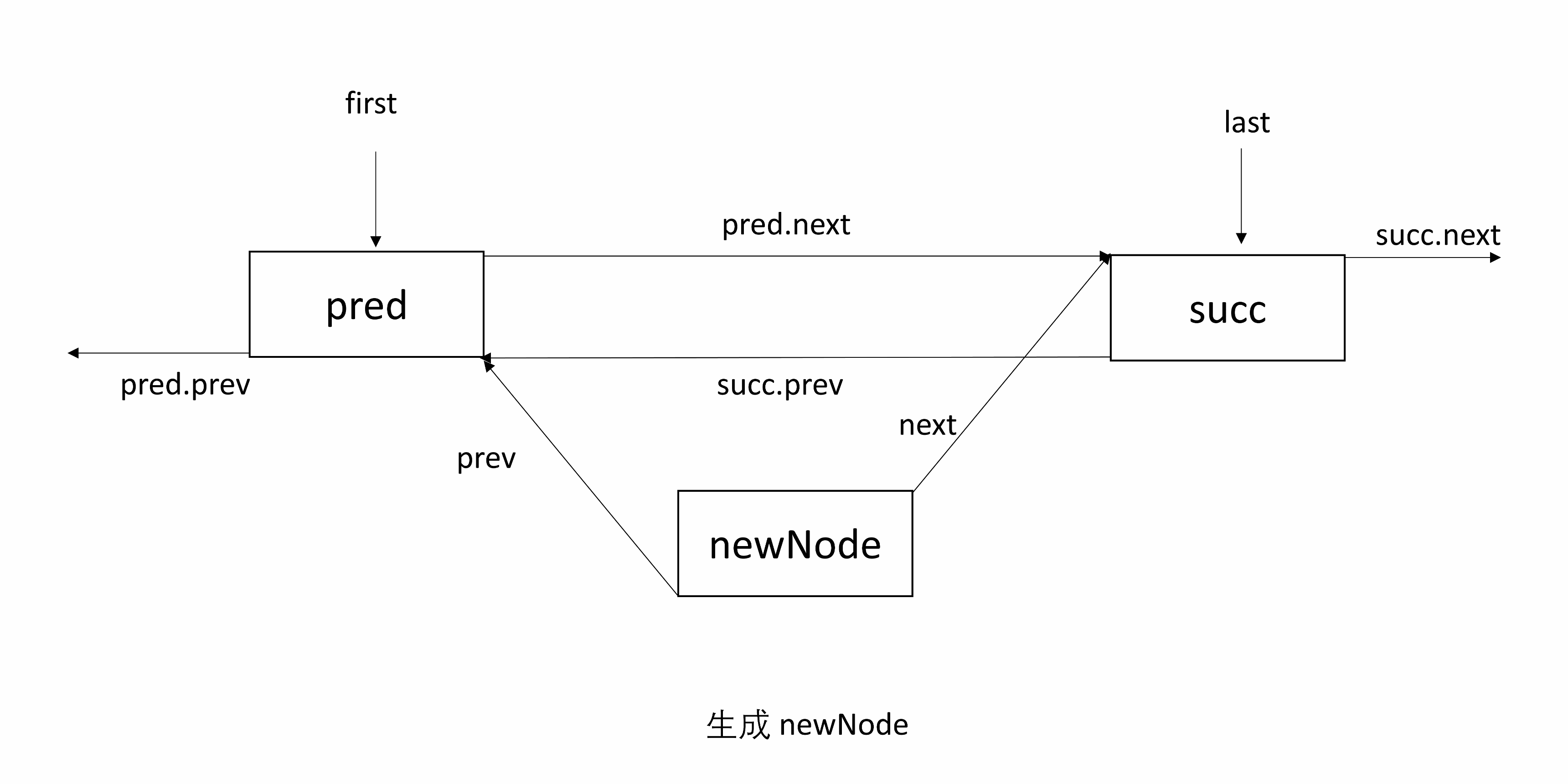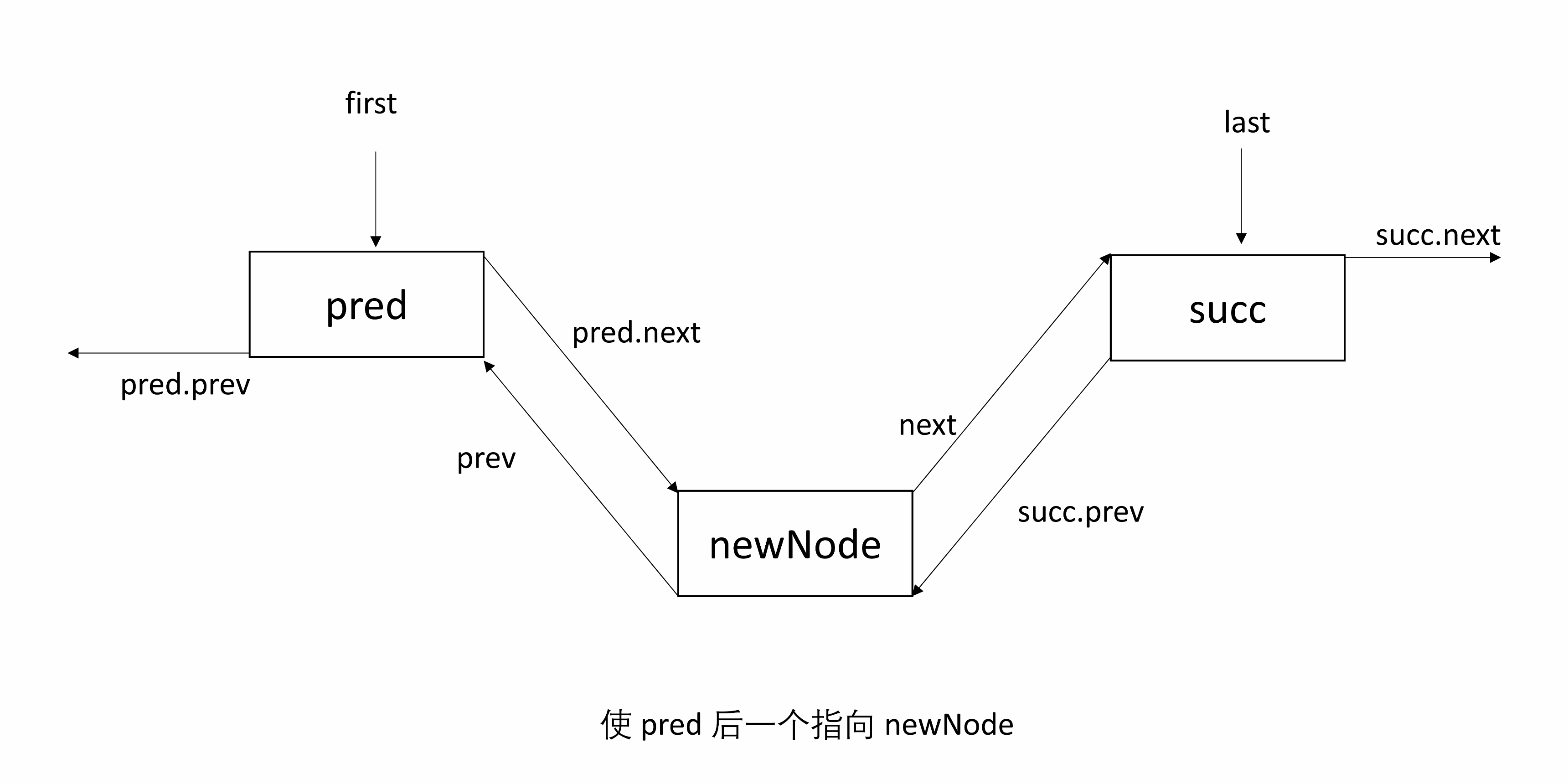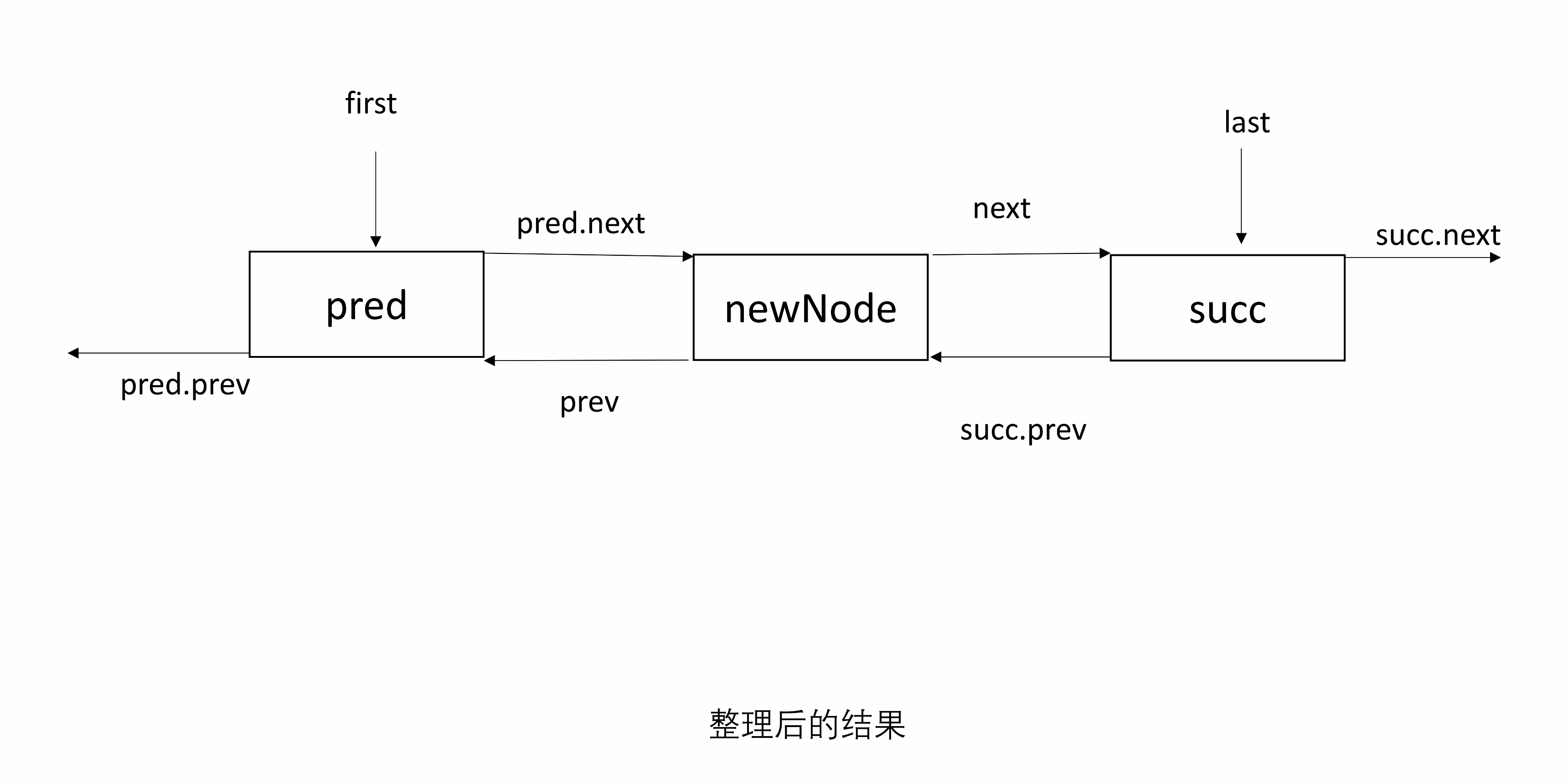
3.2 linkBefore
linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ)将 e 包装后的 newNode 插入到 succ 前。
首先找到 succ 前面的节点 pred,newNode 前一个为 pred ,后一个为 succ。修改 succ 前一个指向 newNode,然后 pred 后一个为 newNode。
处理 null:处理 pred 为 null 的情况,可以得知 succ 原来是 first 节点,所以 first 指向 newNode;若 pred 非 null,则 pred 下一个为 newNode。
下面的图初始有两个节点,succ 是尾结点。
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {// 将 e 对应的节点插入 succ 前
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null) // 此时 succ 为 first
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
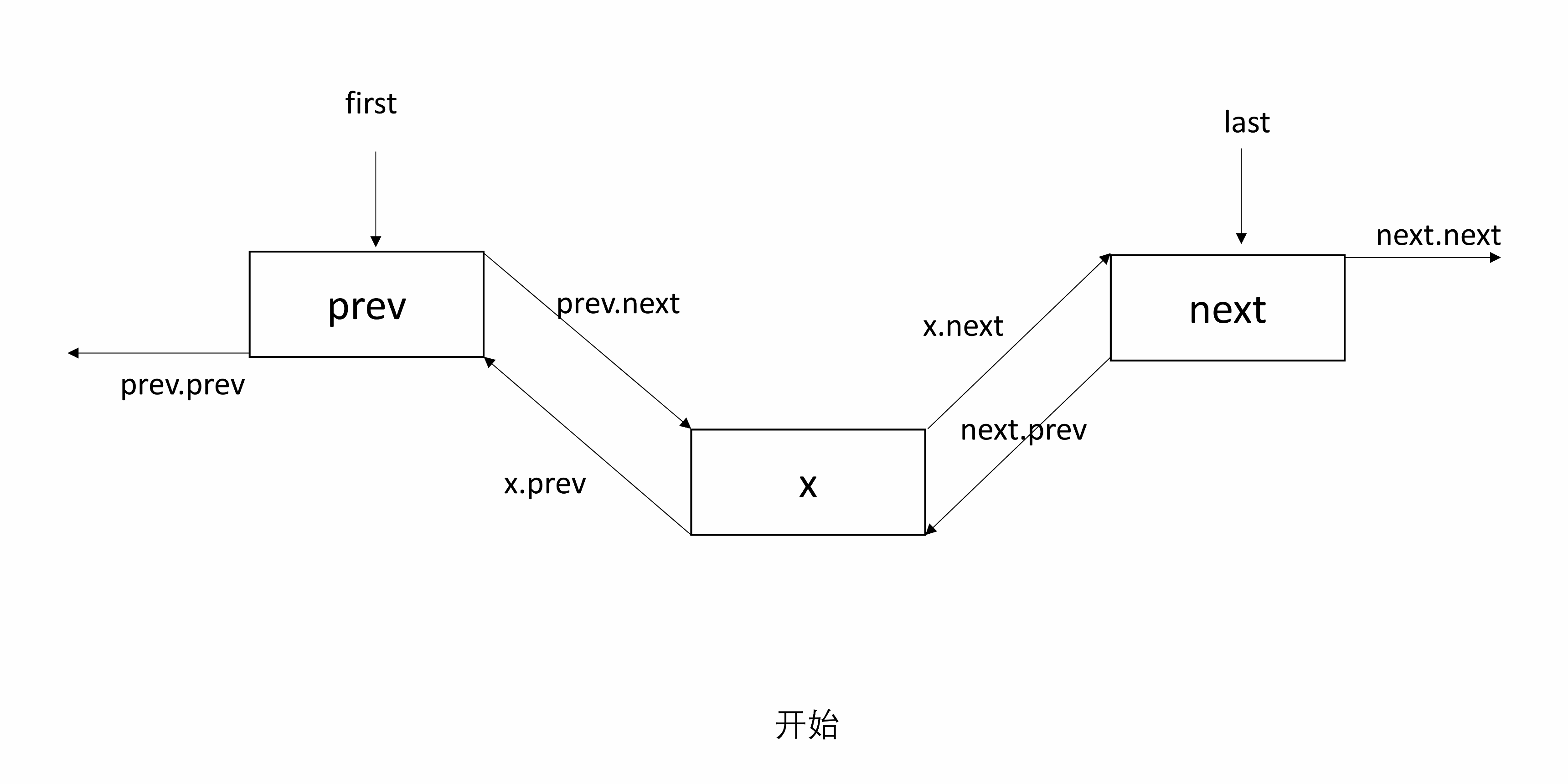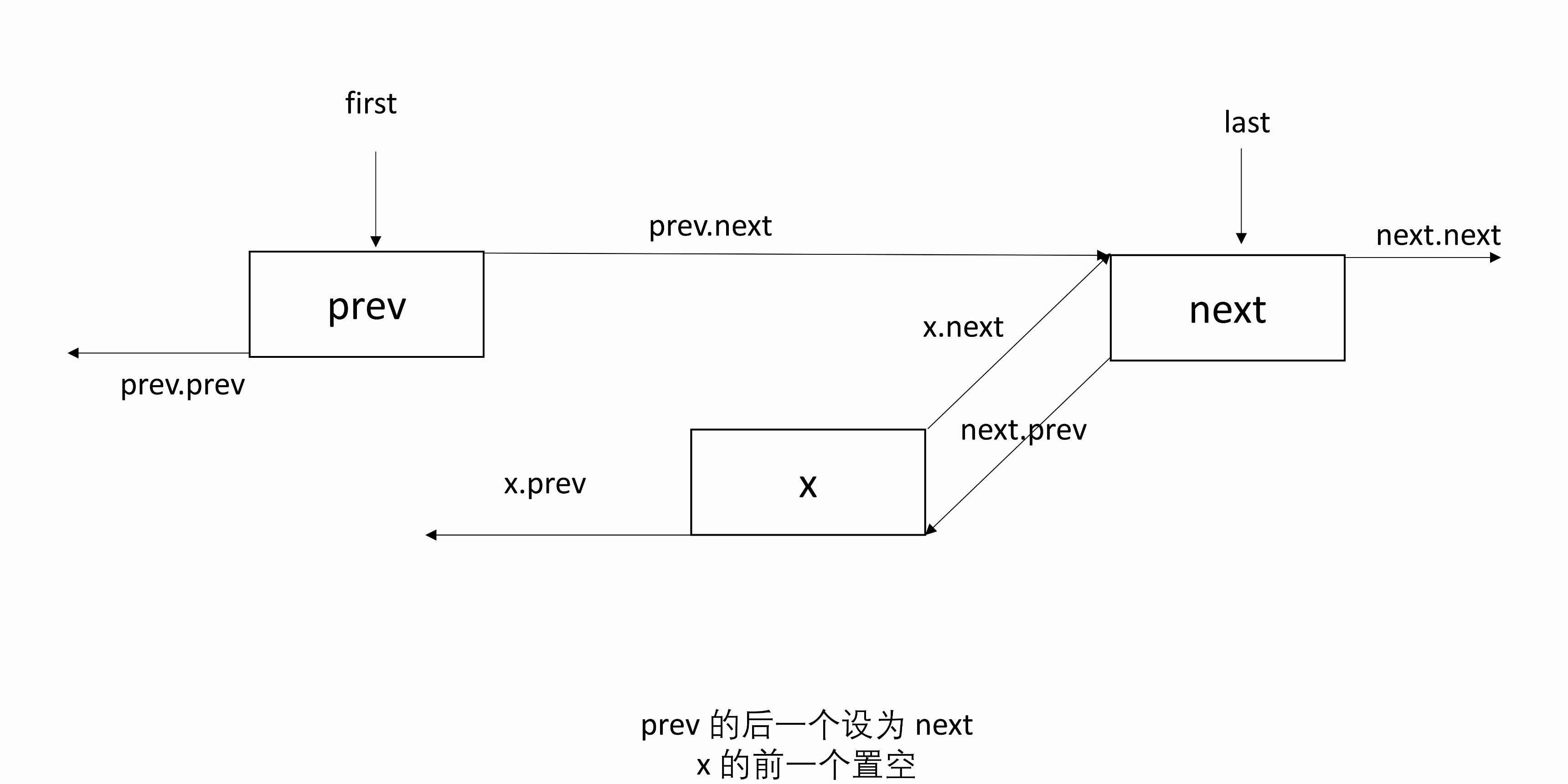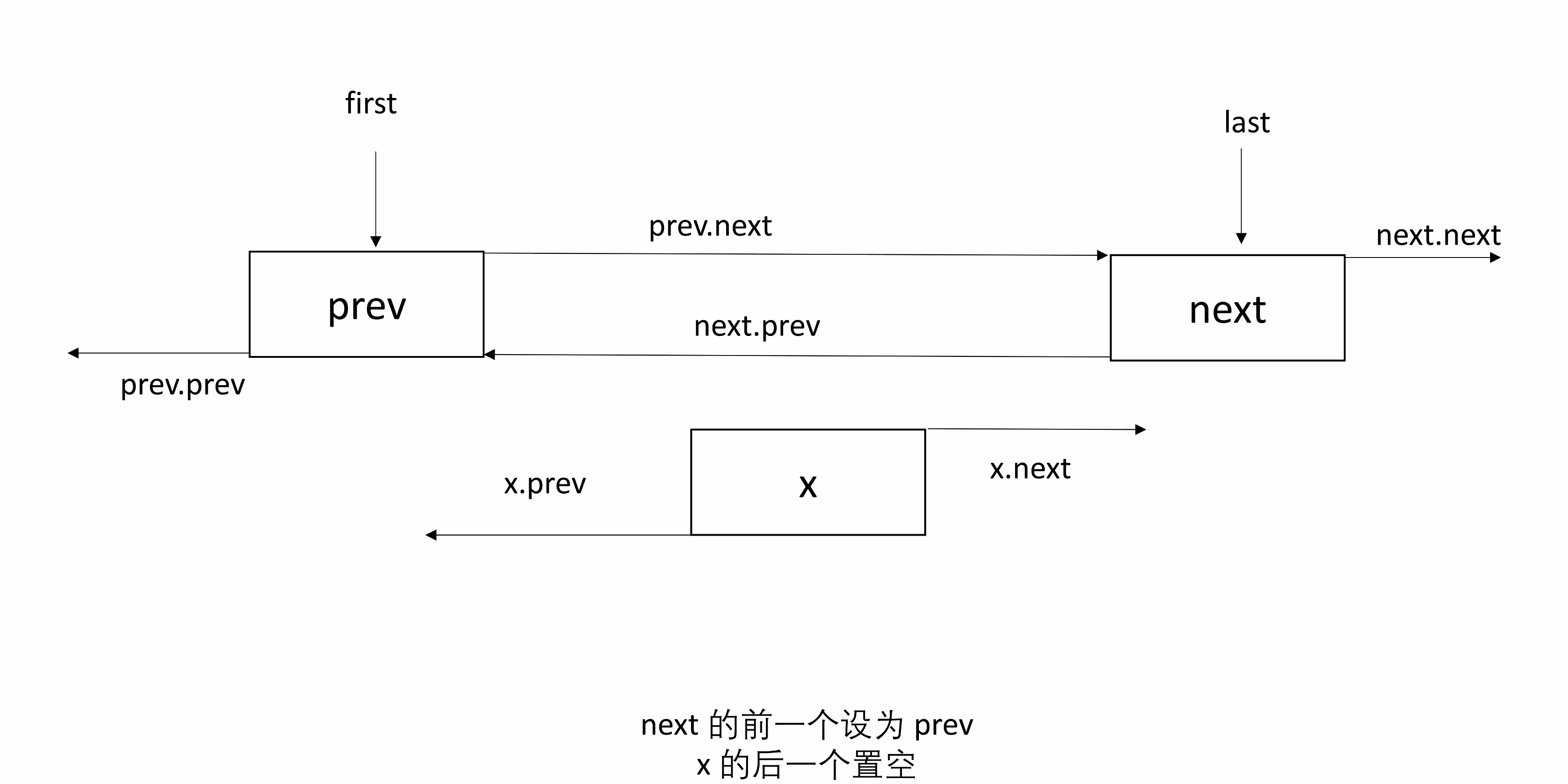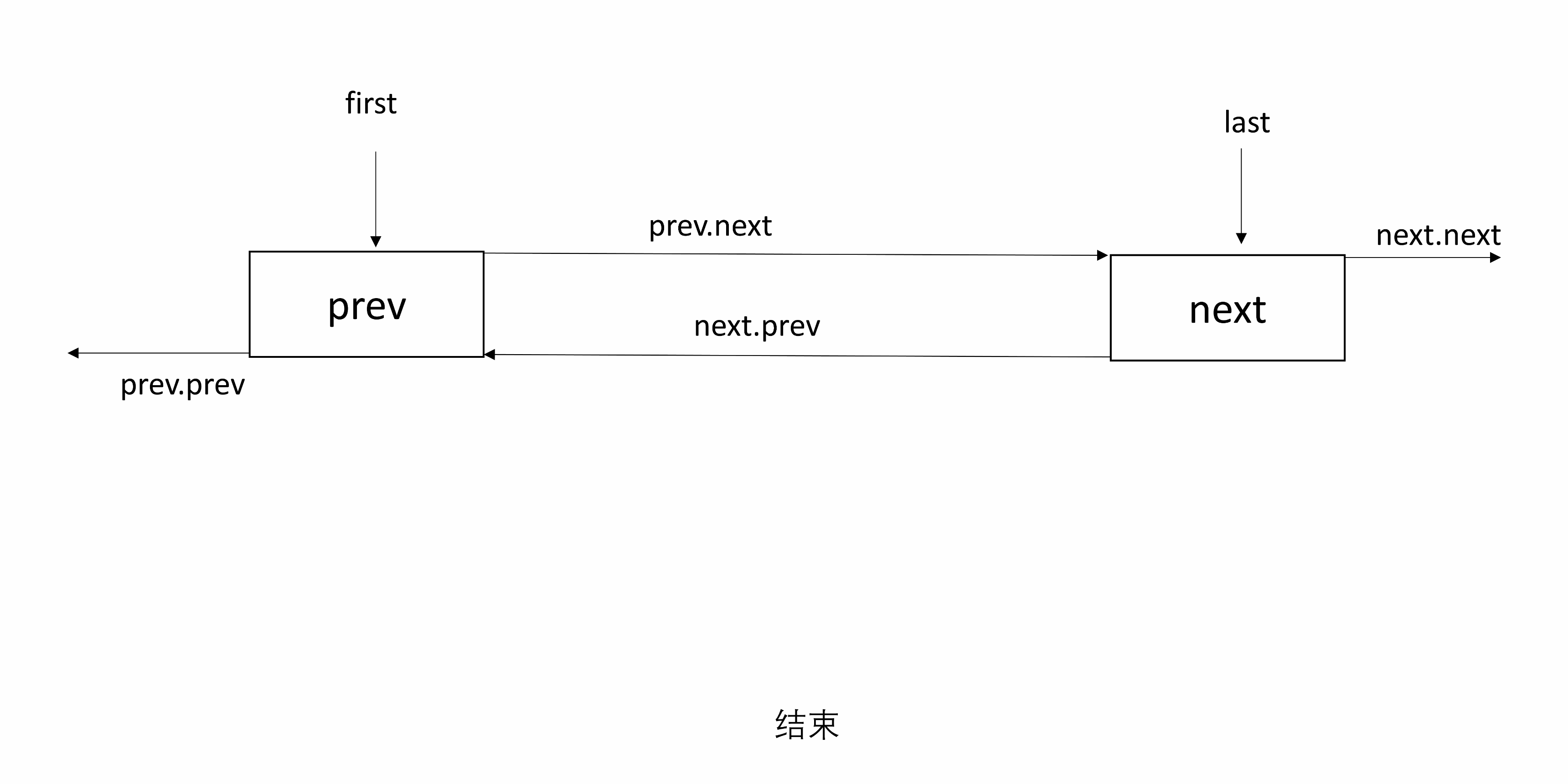
3.3 unlink
unlink(Node<E> x)将 x 从链表中取出,并断开和前后的连接。
需要找到 x 前后的节点,记为 prev 和 next,然后让 prev 下一个指向 next,next 前一个指向 prev,并且将 x 的 prev 和 next 置为 null。
处理 null:如果 prev 是 null,则 x 是 first,x 的前一个节点为 null,所以让 first 指向 next;否则 prev 下一个指向 next,且 x 前一个置 null。同理可知如果 next 是 null,则 x 是 last。
下图有三个节点,x是中间节点。
E unlink(Node<E> x) {// 将 x 从链表中取出,断开和前后的连接
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) { // 此时 x 为 first
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) { // 此时 x 为 last
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
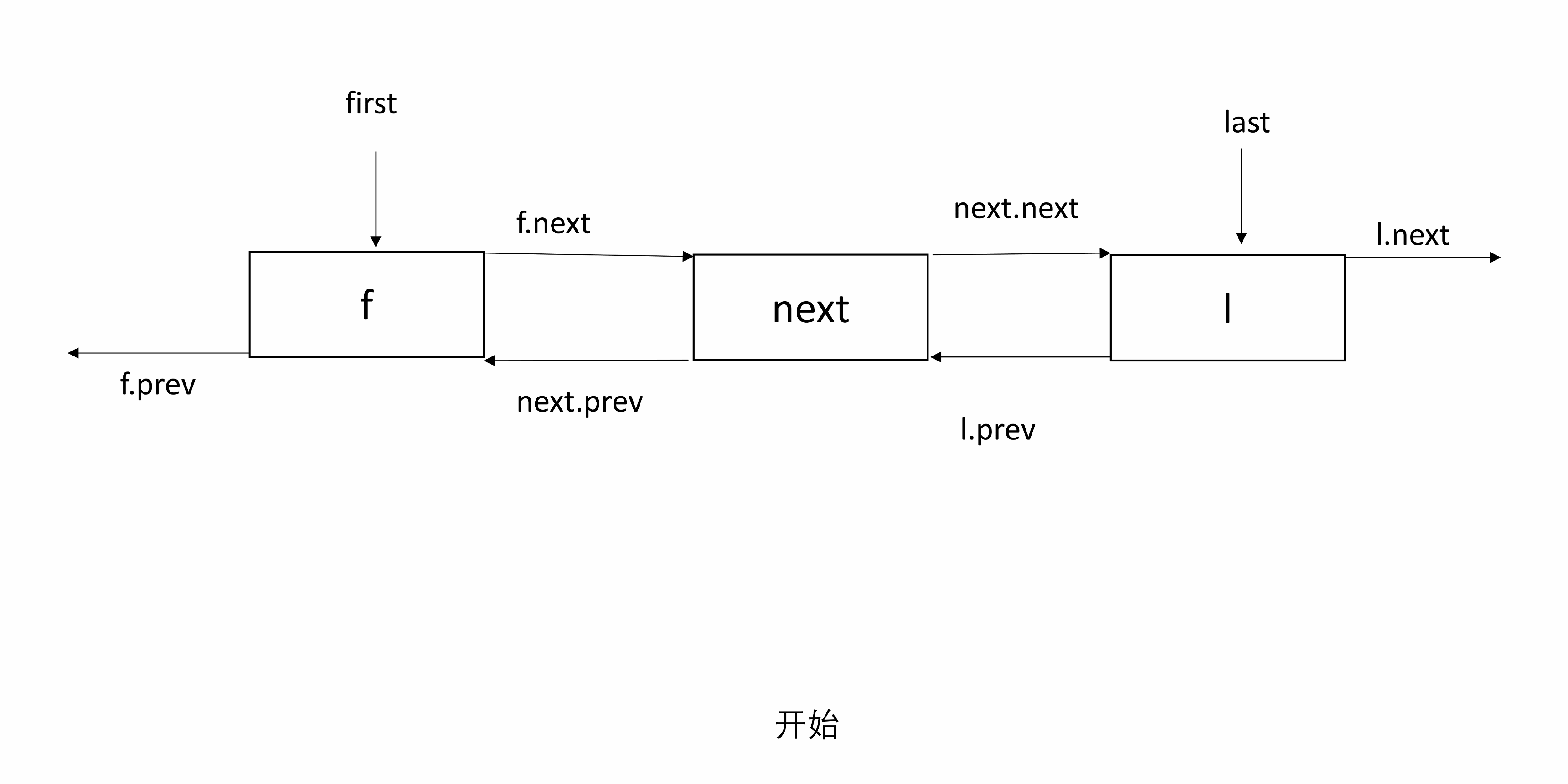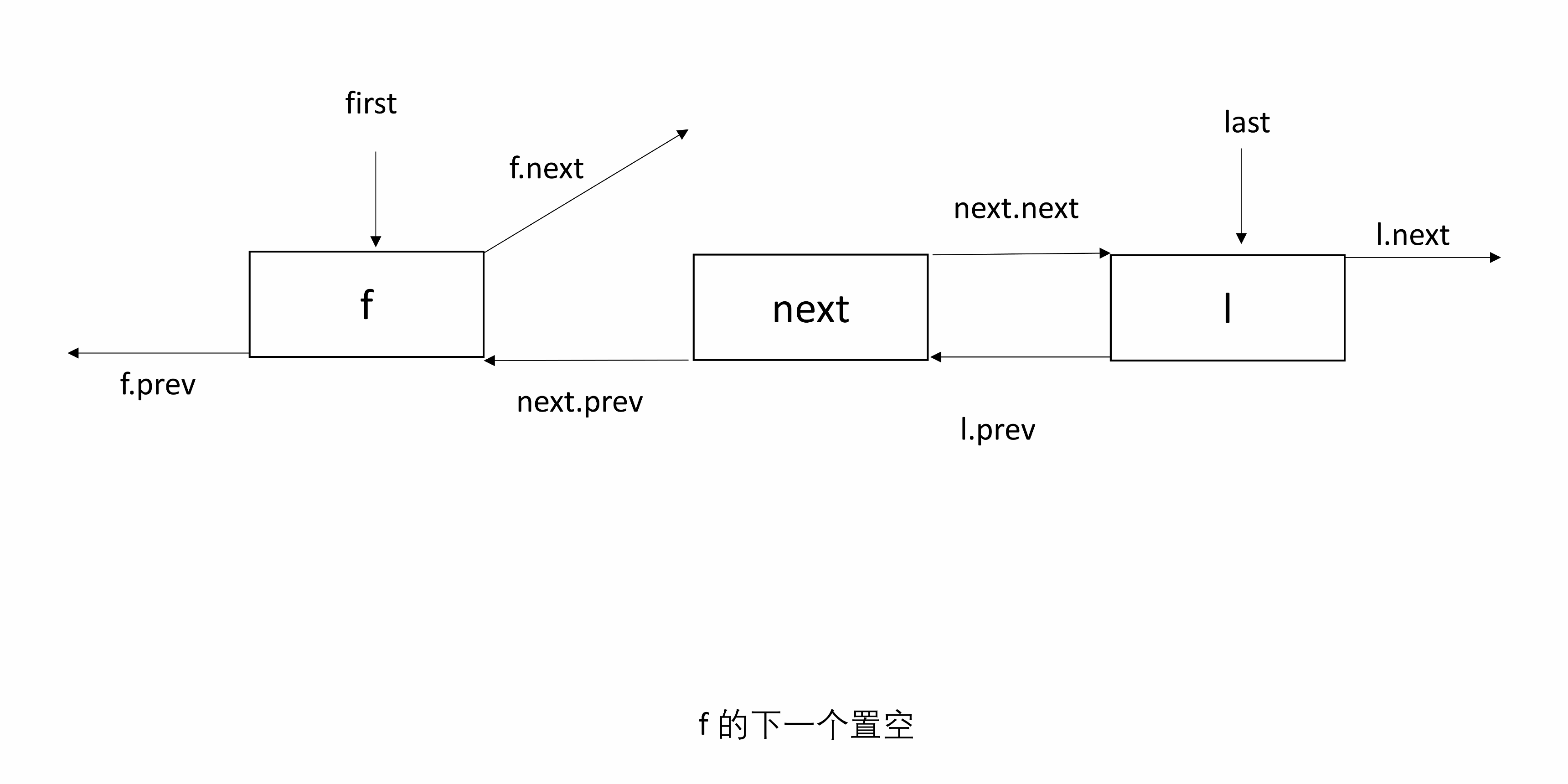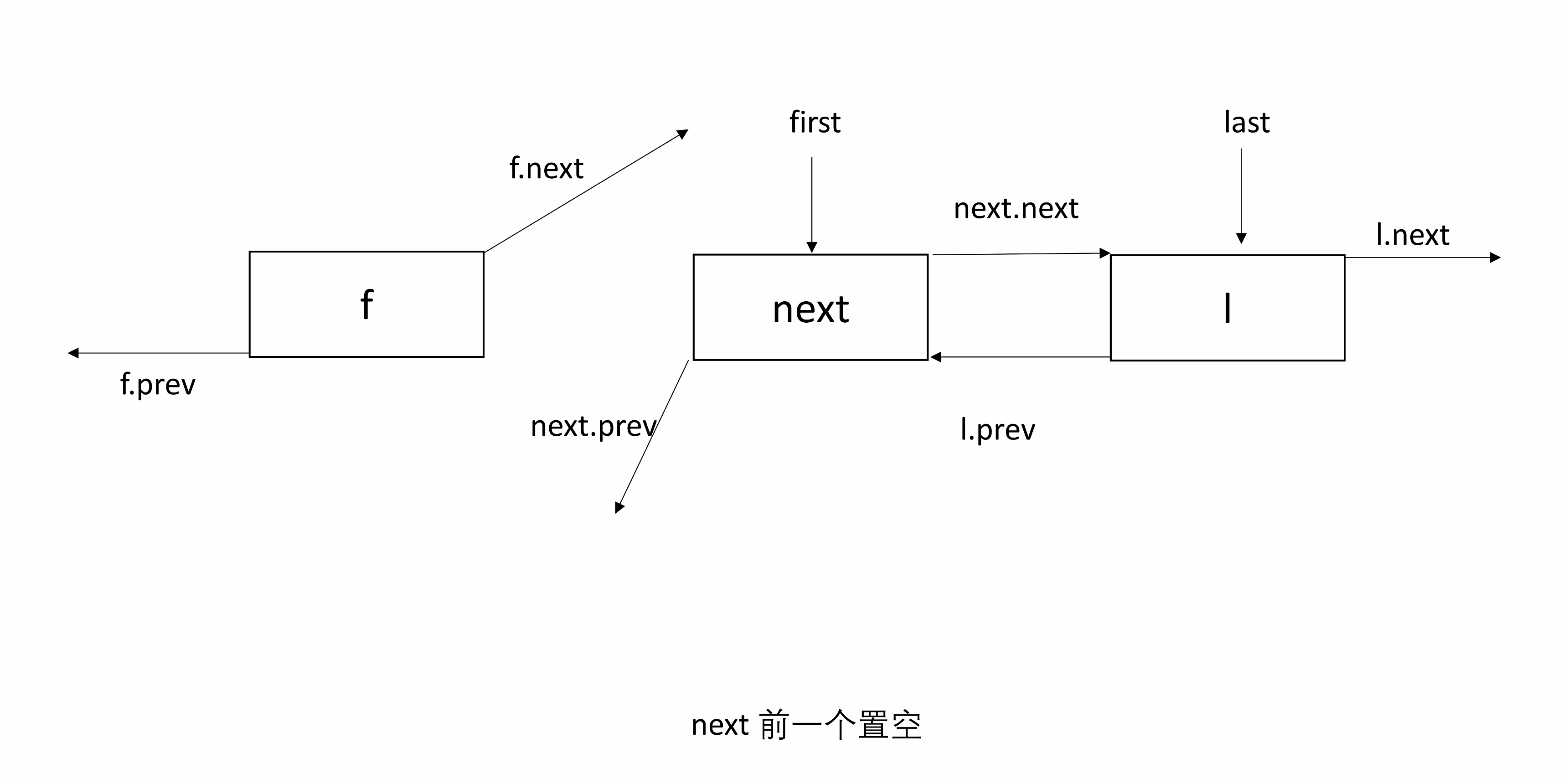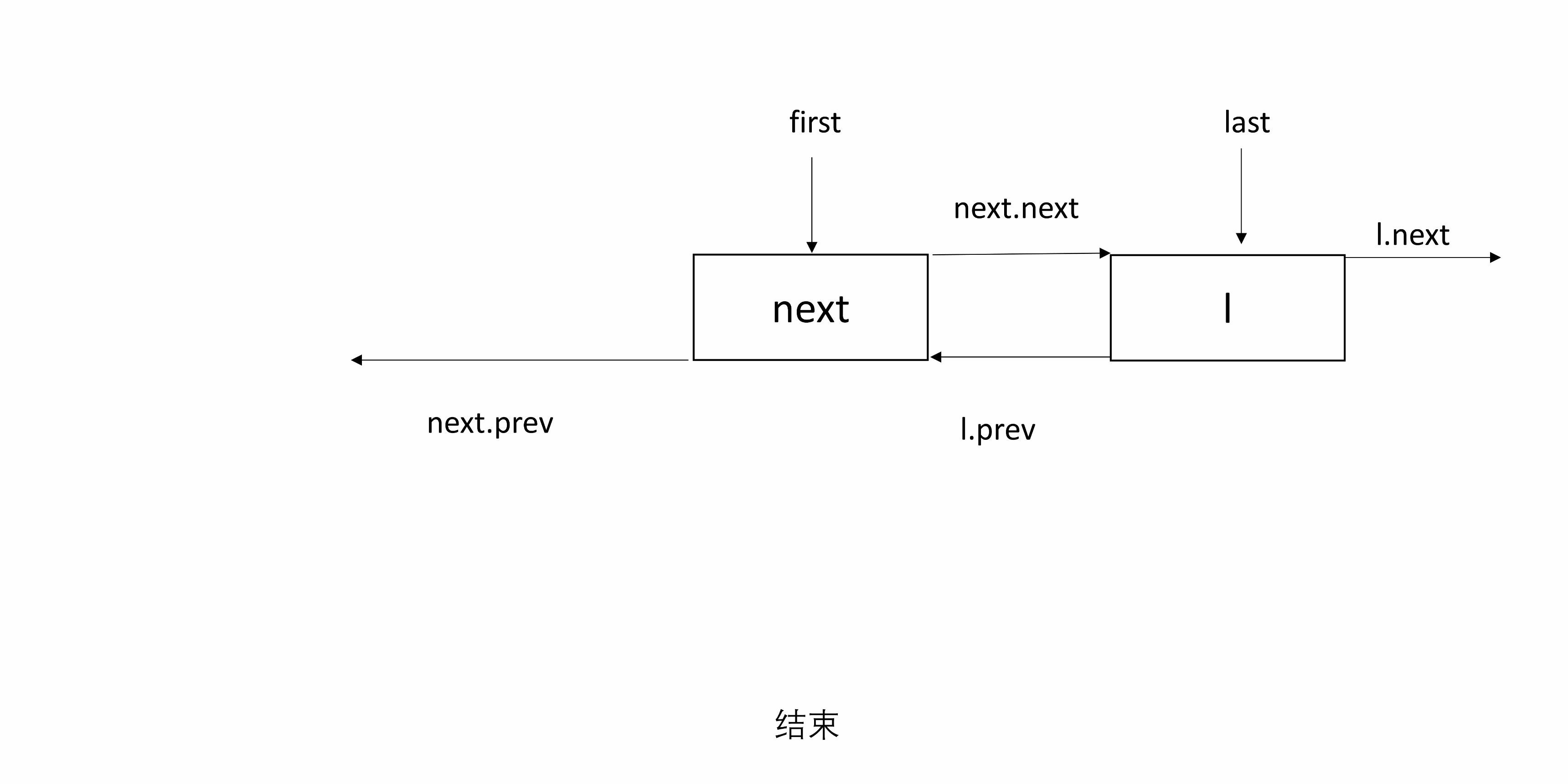
3.4 unlinkFirst
unlinkFirst(Node<E> f)表示 f 是头结点,将 f 和后续节点断开。
只需要找到 f 的下一个节点 next,并将其置为 first,将 f 的后一个和 next 的前一个置空。
处理 null:如果 next 为 null,则 f 既是头结点也是尾结点,也就是链表只有一个 Node,删除 f 后 last 为 null;否则,next 的前一个置为 null。
下图有三个节点,f 是头结点。
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) { // f 是头节点,将其取出并断开与后续节点的连接
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null) // f 为尾结点
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
3.5 其他
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
// size>>1 是 size/2,根据更靠前还是更靠后决定从头向后遍历还是从尾向前遍历
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;// 从头向后遍历
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;// 从尾向前遍历
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
public int indexOf(Object o) {// 两种情况,null 不能用 equals 处理,只能 ==。找不到返回 -1。
int index = 0;
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}
4 add 相关
4.1 add
一共有两个 add 方法,没有指定 index 会添加到最后,指定 index 的会在 index 处插入。
addFirst 和 addLast 方法,分别从头和尾加入。
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
4.2 addAll
addAll 方法同样有两个,对于单参数方法,调用另一个 addAll 将结果插入最后。
对于给定 index 的方法,找到 index 处的元素 succ,以及 succ 前一个元素 pred,将 c 中的元素 o 不断插入。
考虑到 null:如果 index 在边界处,succ 为 null,pred 为 last;否则 succ 为 index 处的元素, pred 是 succ 前一个。在插入 c 中元素的过程中,如果 pred 为 null,说明是从头插入,所以设置插入的新元素 newNode 为 first,否则 pred 的前指针指向 newNode,且 pred 重置为 newNode。最后,如果 succ 为 null,last 设置为 pred,否则 pred 下一个是 newNode,且 succ 前一个是 pred。
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {// 在最后插入 c 的元素
return addAll(size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { // 在 index 处插入 c 的元素
checkPositionIndex(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node<E> pred, succ;
if (index == size) { // 边界处 succ 为 null
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
4.3 offer
这里 offer 和相应的 add 方法一样。
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
5 remove
remove 有三个,无参数的删除头部元素,指定位置 index 则是删除 index 处的元素, 指定 Object 的元素则从头遍历来查找,找到则删除。
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
另外的四个方法,removeFirst 是删除头部元素,removeLast 删除尾部元素。 removeFirstOccurrence 表示从头到尾找到第一个删掉,removeLastOccurrence 表示从尾到头找到第一个删掉。
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
public E removeLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
return remove(o);
}
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
poll 相关的方法和 remove 基本一样,只是 poll 能返回 null,remove 碰到 null 则抛出异常。
public E poll() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
public E pollFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
public E pollLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l);
}
6 get/set
get 获取 index 位置的元素,getFirst 和 getLast 获取头尾元素,set 修改相应位置的元素。peek 和 get 基本一致,只是 get 不能处理 null。
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
public E getLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
public E peek() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
public E peekFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
public E peekLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : l.item;
}
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index);
Node<E> x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
x.item = element;
return oldVal;
}
7 迭代器
两种迭代器,迭代器 iterator,以及反向迭代器 descendingIterator,这两种都是 ListIterator。
LinkedList<Integer> linkedlist = new LinkedList<>();
Iterator<Integer> iterator = linkedlist.iterator(); // 迭代器
Iterator<Integer> descendingIterator = linkedlist.descendingIterator();// 反向迭代器
7.1 迭代器
debug 发现首先调用 AbstractSequentialList 的方法,然后是 AbstractList 的 listIterator。
public Iterator<E> iterator() {// AbstractSequentialList 的方法
return listIterator();
}
public ListIterator<E> listIterator() {// AbstractList 的方法
return listIterator(0);
}
后面的 listIterator 被 LinkedList 的方法重写,进入 LinkedList。这里的内部类 ListItr 和 ArrayList的 ListItr 基本一致。同样有 next 和 previous 的方法,不同在于这里的 next 和 lastReturned 都是 Node,找 next 和 previous 同样使用的是链表的操作,而不是用 int 类型的位置来查找。
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> {
private Node<E> lastReturned;
private Node<E> next;
private int nextIndex;
private int expectedModCount = modCount;
ListItr(int index) { // 下一个的位置是 index
// assert isPositionIndex(index);
next = (index == size) ? null : node(index);
nextIndex = index;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return nextIndex < size;
}
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasNext())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next; // 记录下新的 lastReturned
next = next.next;// next 向后移动
nextIndex++;// index++
return lastReturned.item;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return nextIndex > 0;
}
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasPrevious())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
//如果 next 为 null,说明是 next 是 last 的下一个,这种情况下将 lastReturned 和 next 修改为 last。否则,修改为 next 的前一个。
lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev;
nextIndex--;
return lastReturned.item;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return nextIndex;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return nextIndex - 1;
}
public void remove() {
checkForComodification();
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next;
unlink(lastReturned);
if (next == lastReturned)
next = lastNext;
else
nextIndex--;
lastReturned = null;
expectedModCount++;
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
lastReturned.item = e; //修改 lastReturned 的 item
}
public void add(E e) {// 在 next 前插入,或者说是插入到 nextIndex 的位置。
checkForComodification();
lastReturned = null;
if (next == null)
linkLast(e);
else
linkBefore(e, next);
nextIndex++;
expectedModCount++;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
while (modCount == expectedModCount && nextIndex < size) {
action.accept(next.item);
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
}
checkForComodification();
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
7.2 反向迭代器
这里的反向迭代器就是上面的迭代器,只是将初始位置设为最后,然后将 next 的方法改成向前。
private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator<E> {
private final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size());// 初始位置在尾部。
public boolean hasNext() {
return itr.hasPrevious();
}
public E next() {
return itr.previous();// 向前。
}
public void remove() {
itr.remove();
}
}
下面是我的公众号,Java与大数据进阶,分享 Java 与大数据笔面试干货,欢迎关注




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号