JDK1.8线程池 ThreadPoolExecutor详解
线程属性#
private static final int COUNT_BITS = Integer.SIZE - 3; private static final int CAPACITY = (1 << COUNT_BITS) - 1;
- Integer.SIZE是32
- COUNT_BITS是29
- 容量CAPACITY是,二进制来看是00011111111111111111111111111111,29个1
线程状态#
// runState is stored in the high-order bits
private static final int RUNNING = -1 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int SHUTDOWN = 0 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int STOP = 1 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int TIDYING = 2 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int TERMINATED = 3 << COUNT_BITS;
对-1、0、1、2、3左移29位
- RUNNING, 10100000000000000000000000000000
- SHUTDOWN, 00000000000000000000000000000000
- STOP, 00100000000000000000000000000000
- TIDYING, 01000000000000000000000000000000
- TERMINATED,01100000000000000000000000000000
高三位存储的是线程状态,低29位存储的是线程的数量
装箱和开箱#
// Packing and unpacking ctl
private static int runStateOf(int c) { return c & ~CAPACITY; }
private static int workerCountOf(int c) { return c & CAPACITY; }
private static int ctlOf(int rs, int wc) { return rs | wc; }
- runStateOf,对CAPACITY取反,也就是11100000000000000000000000000000,置高3位为1,也就是参数 c 按照 & 操作判断线程状态
- workerCountOf,通过参数 c 按照 & 操作判断线程数量
- ctlOf,rs 按位或 wc,初始化的AtomicInteger,是 RUNNING | 0,还是RUNNING
按照new对象然后执行方法的顺序,先构造函数,execute执行方法,工作者worker,肃清队列purge,拒绝Handler等等
流程图#
示例代码
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>();
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 20, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, workQueue);
threadPoolExecutor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("task running...");
}
});
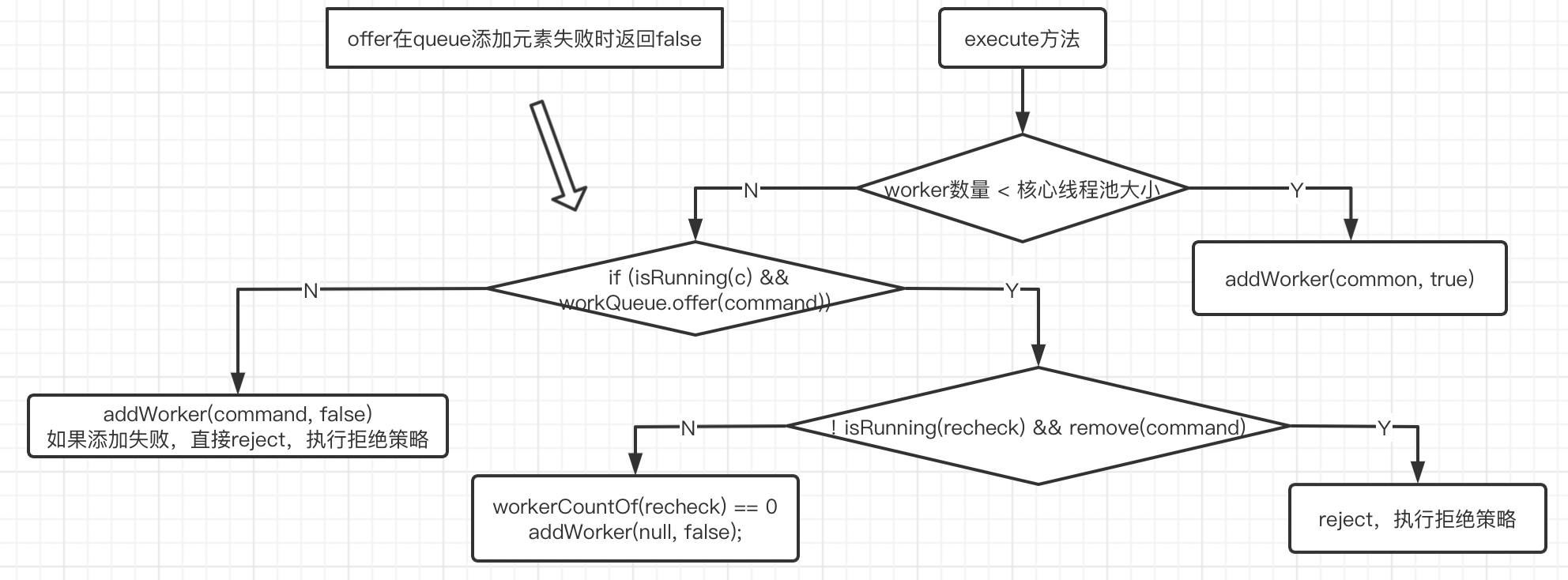
execute方法流程#
当worker数量 > 核心线程池数量时,如果入队成功,addWorker的core参数false,否则就拒绝
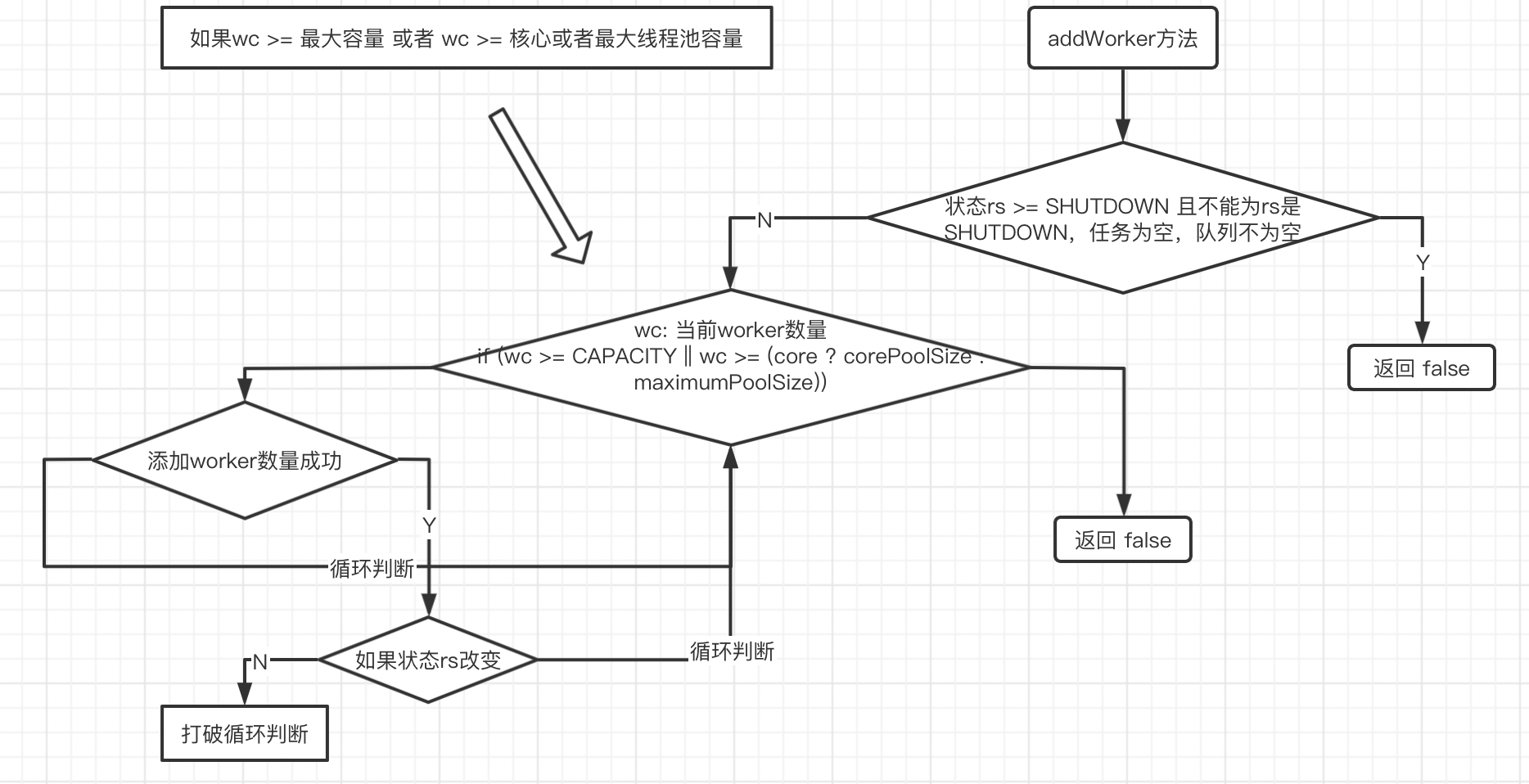
addWorker方法流程#
参数core为false的时候,在方法中判断数量大小的时候用maximumThreadPoolSize
构造函数 ThreadPoolExecutor#
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ?
null :
AccessController.getContext();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
corePoolSize#
- the number of threads to keep in the pool, even if they are idle, unless {@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut} is set
- 池中要保留的线程数,即使它们处于空闲状态,除非设置了{@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut}
maximumPoolSize#
- the maximum number of threads to allow in the pool
- 池中允许的最大线程数
keepAliveTime#
- when the number of threads is greater than the core
- this is the maximum time that excess idle threads will wait for new tasks before terminating
- 当线程数大于内核数时,多余空闲线程在终止前等待新任务的最长时间
unit#
- the time unit for the {@code keepAliveTime} argument
- {keepAliveTime}参数的时间单位
workQueue#
- the queue to use for holding tasks before they are executed
- This queue will hold only the {@code Runnable} tasks submitted by the {@code execute} method
- 用于在任务完成之前保留任务的队列执行,此队列将仅包含{Runnable},由{execute}方法提交的任务
threadFactory#
- the factory to use when the executor creates a new thread
- 执行器创建新线程时要使用的工厂
handler#
- the handler to use when execution is blocked because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached
- 由于达到线程边界和队列容量而阻止执行时要使用的处理程序
Execute#
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int c = ctl.get();
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
reject(command);
}
}
该方法分三步进行:
第一步#
如果正在运行的线程少于corePoolSize,请尝试以给定命令作为第一个线程启动新线程任务
对addWorker的调用以原子方式检查运行状态和worker的数量,在添加了不应该添加的线程下通过返回false防止错误警报
第二步#
如果任务可以成功排队,进入此方法后,我们仍然需要再次检查是否应该添加线程
因为自上次检查以来,已存在的某些线程已死亡,或者池子已经关闭不再需要检查
所以我们重新检查状态,如果已停止,在有必要的情况下回滚入队或者如果任务执行结束,则启动新线程
第三步#
如果我们无法将任务排队,那么我们将尝试添加一个新线程。如果失败了,我们知道我们已经被关闭或饱和,所以拒绝这个任务
addWorker#
/*
* Methods for creating, running and cleaning up after workers
*/
private boolean addWorker(Runnable firstTask, boolean core) {
retry:
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get();
int rs = runStateOf(c);
// Check if queue empty only if necessary.
if (rs >= SHUTDOWN &&
! (rs == SHUTDOWN &&
firstTask == null &&
! workQueue.isEmpty()))
return false;
for (;;) {
int wc = workerCountOf(c);
if (wc >= CAPACITY ||
wc >= (core ? corePoolSize : maximumPoolSize))
return false;
if (compareAndIncrementWorkerCount(c))
break retry;
c = ctl.get(); // Re-read ctl
if (runStateOf(c) != rs)
continue retry;
// else CAS failed due to workerCount change; retry inner loop
}
}
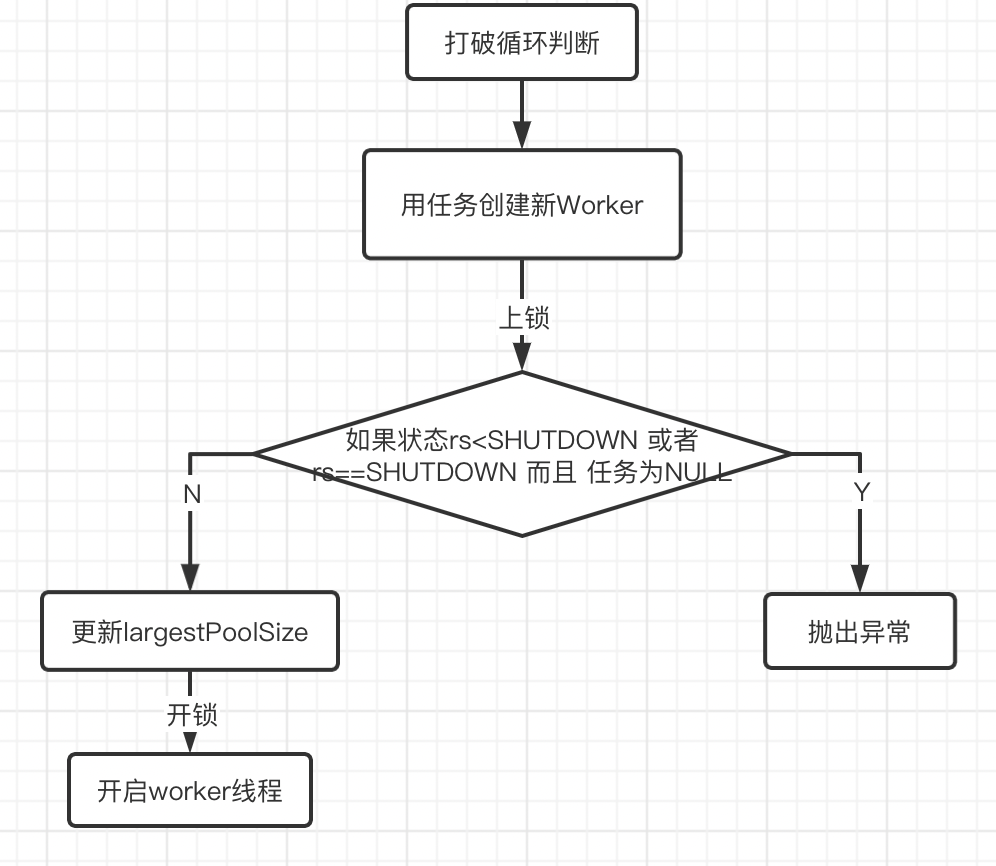
boolean workerStarted = false;
boolean workerAdded = false;
Worker w = null;
try {
w = new Worker(firstTask);
final Thread t = w.thread;
if (t != null) {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
// Recheck while holding lock.
// Back out on ThreadFactory failure or if
// shut down before lock acquired.
int rs = runStateOf(ctl.get());
if (rs < SHUTDOWN ||
(rs == SHUTDOWN && firstTask == null)) {
if (t.isAlive()) // precheck that t is startable
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
workers.add(w);
int s = workers.size();
if (s > largestPoolSize)
largestPoolSize = s;
workerAdded = true;
}
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
if (workerAdded) {
t.start();
workerStarted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (! workerStarted)
addWorkerFailed(w);
}
return workerStarted;
}
Purge 肃清#
public void purge() {
final BlockingQueue<Runnable> q = workQueue;
try {
Iterator<Runnable> it = q.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Runnable r = it.next();
if (r instanceof Future<?> && ((Future<?>)r).isCancelled())
it.remove();
}
} catch (ConcurrentModificationException fallThrough) {
// Take slow path if we encounter interference during traversal.
// Make copy for traversal and call remove for cancelled entries.
// The slow path is more likely to be O(N*N).
for (Object r : q.toArray())
if (r instanceof Future<?> && ((Future<?>)r).isCancelled())
q.remove(r);
}
tryTerminate(); // In case SHUTDOWN and now empty
}
尝试从工作队列中删除所有{@link Future}已取消的任务,这种方法可以作为一种有用的方法存储回收操作,这对功能性没有其他影响
取消的任务永远不会执行,但可能会在工作队列中累积,直到工作线程可以活动移除它们。相反,调用此方法会尝试删除它们
但是,如果存在其他线程的干扰,此方法可能无法删除任务
拒绝调用操作者#
CallerRunsPolicy#
public static class CallerRunsPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code CallerRunsPolicy}.
*/
public CallerRunsPolicy() { }
/**
* Executes task r in the caller's thread, unless the executor
* has been shut down, in which case the task is discarded.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
r.run();
}
}
}
直接在{@code execute}方法的调用线程中执行被拒绝任务,除非执行器已关闭,在这种情况下,任务被丢弃
AbortPolicy#
public static class AbortPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates an {@code AbortPolicy}.
*/
public AbortPolicy() { }
/**
* Always throws RejectedExecutionException.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException always
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Task " + r.toString() +
" rejected from " +
e.toString());
}
}
用于抛出{@code RejectedExecutionException}
DiscardPolicy#
public static class DiscardPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code DiscardPolicy}.
*/
public DiscardPolicy() { }
/**
* Does nothing, which has the effect of discarding task r.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
}
}
被拒绝任务的处理程序,以静默方式丢弃被拒绝的任务
DiscardOldestPolicy#
public static class DiscardOldestPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code DiscardOldestPolicy} for the given executor.
*/
public DiscardOldestPolicy() { }
/**
* Obtains and ignores the next task that the executor
* would otherwise execute, if one is immediately available,
* and then retries execution of task r, unless the executor
* is shut down, in which case task r is instead discarded.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
e.getQueue().poll();
e.execute(r);
}
}
}
用于丢弃最旧的未处理任务请求,然后重试{@code execute},除非执行器被关闭,在这种情况下,任务被丢弃
Worker#
private final class Worker
extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
implements Runnable
{
/**
* This class will never be serialized, but we provide a
* serialVersionUID to suppress a javac warning.
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6138294804551838833L;
/** Thread this worker is running in. Null if factory fails. */
final Thread thread;
/** Initial task to run. Possibly null. */
Runnable firstTask;
/** Per-thread task counter */
volatile long completedTasks;
/**
* Creates with given first task and thread from ThreadFactory.
* @param firstTask the first task (null if none)
*/
Worker(Runnable firstTask) {
setState(-1); // inhibit interrupts until runWorker
this.firstTask = firstTask;
this.thread = getThreadFactory().newThread(this);
}
/** Delegates main run loop to outer runWorker */
public void run() {
runWorker(this);
}
// Lock methods
//
// The value 0 represents the unlocked state.
// The value 1 represents the locked state.
protected boolean isHeldExclusively() {
return getState() != 0;
}
protected boolean tryAcquire(int unused) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected boolean tryRelease(int unused) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
setState(0);
return true;
}
public void lock() { acquire(1); }
public boolean tryLock() { return tryAcquire(1); }
public void unlock() { release(1); }
public boolean isLocked() { return isHeldExclusively(); }
void interruptIfStarted() {
Thread t;
if (getState() >= 0 && (t = thread) != null && !t.isInterrupted()) {
try {
t.interrupt();
} catch (SecurityException ignore) {
}
}
}
}
Worker类继承了AQS,实现了Runnable接口,用来创建新线程来执行任务
runWorker#
final void runWorker(Worker w) {
Thread wt = Thread.currentThread();
Runnable task = w.firstTask;
w.firstTask = null;
w.unlock(); // allow interrupts
boolean completedAbruptly = true;
try {
while (task != null || (task = getTask()) != null) {
w.lock();
// If pool is stopping, ensure thread is interrupted;
// if not, ensure thread is not interrupted. This
// requires a recheck in second case to deal with
// shutdownNow race while clearing interrupt
if ((runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP) ||
(Thread.interrupted() &&
runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP))) &&
!wt.isInterrupted())
wt.interrupt();
try {
beforeExecute(wt, task);
Throwable thrown = null;
try {
task.run();
} catch (RuntimeException x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Error x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Throwable x) {
thrown = x; throw new Error(x);
} finally {
afterExecute(task, thrown);
}
} finally {
task = null;
w.completedTasks++;
w.unlock();
}
}
completedAbruptly = false;
} finally {
processWorkerExit(w, completedAbruptly);
}
}
runWorker方法在当前传入的任务为null时,从队列中获取任务执行
作者:BigBender
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/BigBender/p/15256137.html
版权:本作品采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际」许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!
2020-09-11 二元拉格朗日中值定理
2020-09-11 单位列向量