多线程基础
线程的创建#
继承Thread#
public class MyThread extends Thread{ @Override public void run(){ for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } } } pulbic class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){ MyThread tt = new TestThread(); Thread t = new Thread(tt); t.start(); } }
实现Runnable接口#
public class MyThread implements Runnable{ @Override public void run(){ for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } } } pulbic class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){ MyThread tt = new TestThread(); Thread t = new Thread(tt); t.start(); } }
实现Callable接口#
public class TestRandomNum implements Callable<Integer>{ @Override public Integer call() throws Exception{ return new Random().nextInt(10);// 返回10以内的随机数 } } public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){ TestRandomNum trn = new TestRandomNum(); FutureTask ft = new FutureTask(trn); Thread t = new Thread(ft); t.start(); Object obj = ft.get(); System.out.println(obj); } }
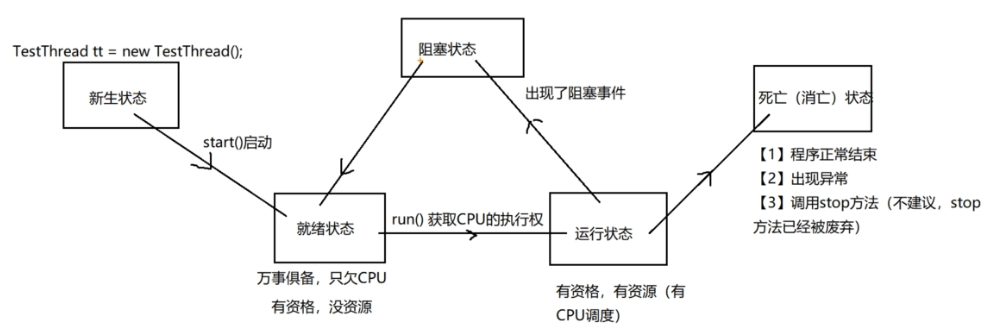
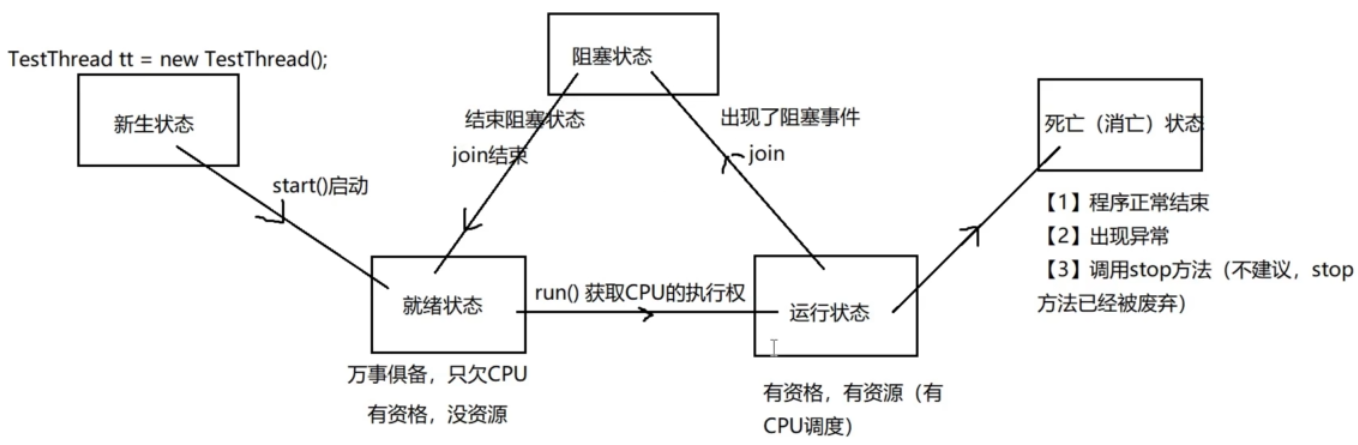
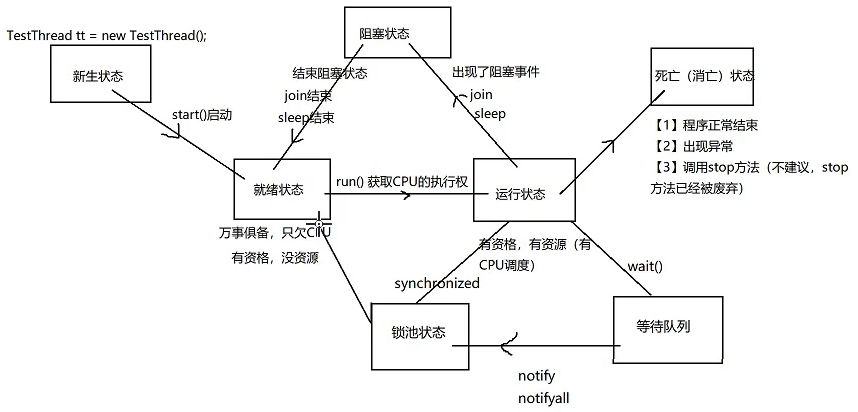
线程的生命周期#
五态模型#
线程常见方法#
start()#
启动当前线程,表面上调用start方法,实际在调用线程中的run方法
run()#
线程类 继承thread类 或者 实现Runnable接口的时候,都要重新实现run方法
run方法里面就是线程要执行的内容
currentThread()#
Thread类中的一个静态方法,获取当前正在执行的线程
setName()#
设置线程名字
getName()#
读取线程名字
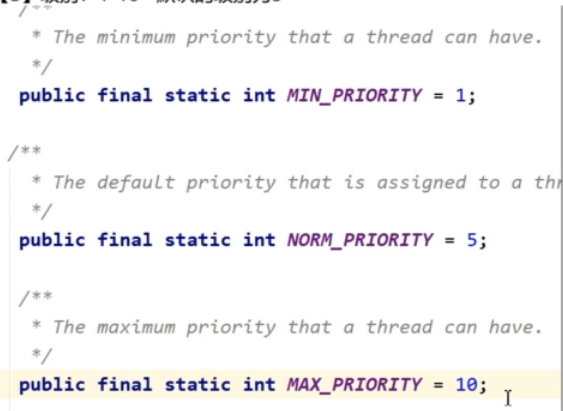
级别#
同优先级别的线程,采取的策略就是FCFS,使用时间片策略#
如果优先级别高,被CPU调度的概率就高
- 1,最小
- 5,普通
- 10,最大
设置优先级#
public class TestThread01 extends Thread{ @Override public void run(){ for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){ System.out.println(i); } } } public class TestThread02 extends Thread{ @Override public void run(){ for(int i = 20; i <= 30; i++){ System.out.println(i); } } } class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){ // 两个线程抢夺CPU, 可以通过设置优先级来调整 // 数字越小, 优先级越低 TestThread01 t1 = new TestThread01(); t1.setPriority(10); t1.start(); TestThread01 t2 = new TestThread02(); t1.setPriority(1); t2.start(); }
}
join方法#
当一个线程调用了join方法,这个线程会被先执行,结束后执行其他线程
必须先start,join才能生效
public class TestThread extends Thread{ public TestThread(String name){ super(name); } @Override public void run(){ for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){ System.out.println(i); } } } class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){ for(int i = 1; i <= 100; i++){ System.out.println("main..." + i); if(i == 6){ // 创建子线程: TestThread tt = new TestThread("子线程"); tt.start(); tt.join(); } } }
sleep方法#
人为阻塞
public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){ Thread.sleep(10);// ms System.out.println("....."); } }
setDaemon方法#
设置伴随线程,将子线程设置为主线程的伴随线程,主线程停止的时候,子线程也不继续执行了
public class Test{ public void run(String[] args){ for(int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++){ System.out.println("....."); } } } public class TestThread extends Thread{ public static void main(String[] args){ TestThread tt = new TestThread(); tt.setDaemon(true);// 设置伴随线程, 注意: 先设置, 再启动 tt.start(); for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){ System.out.println("main...." + i); } } }
stop方法#
public class Demo{ public static void main(String[] args){ for(int i = 1; i <= 100; i++){ if(i == 6){ Thread.currentThread().stop();// 过期方法, 不建议使用 } System.out.println(i); } } }
线程安全#
本质上是线程同步问题,需要加锁和同步监视器
public class MyThread implements Runnable{ int num = 0; @Override public void run(){ for(int i = 0; i <= 100; i++){ synchronized(this){ if(num > 0){ // coding } } } } }
synchronized关键字就是一个普通的排他锁(mutex)
synchronized就是对mutex=1的锁使用pv操作
public class MyThread implements Runnable{ int num = 0; @Override public void run(){ for(int i = 0; i <= 100; i++){ synchronized(this){ if(num > 0){ // coding } } } } }
尽量不要用String和Integer做同步监视器
建议使用final关键字修饰同步监视器(final只是锁定了地址值)
同步就是pv操作#
同步代码块可以发生CPU的切换,但是其他线程无法执行同步代码块
同步代码块--临界区#
同步方法#
public class MyThread implements Runnable{ int num = 0; @Override public static synchronized void do(){ for(int i = 0; i <= 100; i++){ if(num > 0){ // coding } } }
不要将run方法定义为同步方法
非静态同步方法同步监视器是this
静态同步方法同步监视器是字节码信息
同步方法的锁是this,同步代码块将线程挡在代码块之外,在方法内部
效率:同步代码块 > 同步方法
Lock锁#
lock是一个api,多态
public MyThreaqd implements Runnable{ int num = 0; Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); @Override public void run(){ for(int i = 1; i <= 100; i++){ lock.lock(); try{ if(num > 0){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }catch(Exception ex){ ex.printStackTrace(); }finally{ lock.unlock(); } } } }
使用顺序#
Lock > synchronized > 同步代码块
Lock和synchronized的区别#
- Lock是显式锁,synchronized是隐式锁
- Lock只有代码块锁,synchronized有代码块锁和方法锁
- 使用Lock锁,Jvm花费较少时间调度线程,性能更好,有更好的拓展性(提供更多原子类)
线程同步的缺点#
- 线程安全,效率低
- 线程不安全,效率高
可能造成死锁#
死锁,四个必要条件,两个充分条件
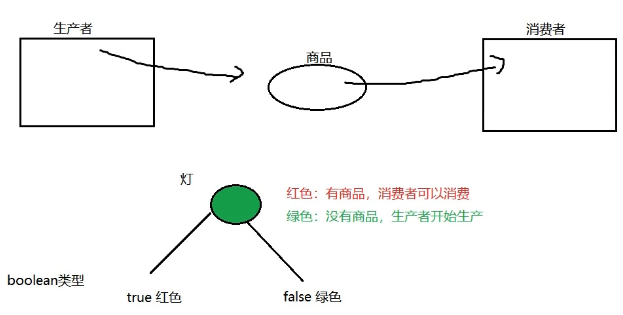
线程通信#
利用同步代码块解决数据错乱#
public class ProducerThread extends Thread{ // 共享商品 private Product p; public ProducerThread(Product p) { this.p = p; } @Override public void run(){ for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){ synchronized(p){ if(i % 2 == 0){ p.setBrand(""); try{ Thread.sleep(100); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } p.setName(""); }else{ p.setBrand(""); try{ Thread.sleep(100); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } p.setName(""); } } } } } public class CustomerThread extends Thread{ // 共享商品 private Product p; public CustomerThread(Product p) { this.p = p; } @Override public void run(){ for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){ synchronized(p){ // coding } } } } public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){ Product p = new Product(); ProducerThread pt = new ProducerThread(); CustomerThread ct = new CustomerThread(); pt.start(); ct.start(); } }
利用同步方法解决问题#
public class Product{ public synchronized void setProduct(String brand, String name){ this.setBrand(brand); try{ Thread.sleep(100); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } this.setName(); } public synchronized void getProduct(){ // coding } } public class ProducerThread extends Thread{ // 共享商品 private Product p; public ProducerThread(Product p) { this.p = p; } @Override public void run(){ for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){ if(i % 2 == 0){ p.setProduct("", ""); } } } } public class CustomerThread extends Thread{ // 共享商品 private Product p; public CustomerThread(Product p) { this.p = p; } @Override public void run(){ for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){ p.getProduct(); } } } public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){ Product p = new Product(); ProducerThread pt = new ProducerThread(); CustomerThread ct = new CustomerThread(); pt.start(); ct.start(); } }
生产消费交替执行#
添加一个标志位
public class Product{ boolean flag = false; public synchronized void setProduct(String brand, String name){ if(flag == true){ try{ wait(); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } }else{ this.setBrand(brand); try{ Thread.sleep(100); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } this.setName(); flag = true; notify(); } } public synchronized void getProduct(){ if(!flag){ try{ wait(); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } // coding flag = false; notify(); } } public class ProducerThread extends Thread{ // 共享商品 private Product p; public ProducerThread(Product p) { this.p = p; } @Override public void run(){ for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){ if(i % 2 == 0){ p.setProduct("", ""); }else{ p.setProduct("", ""); } } } } public class CustomerThread extends Thread{ // 共享商品 private Product p; public CustomerThread(Product p) { this.p = p; } @Override public void run(){ for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){ p.getProduct(); } } } public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){ Product p = new Product(); ProducerThread pt = new ProducerThread(); CustomerThread ct = new CustomerThread(); pt.start(); ct.start(); } }
锁池#
synchronized
等待池#
wait(),notify(),notifyAll()
当一个线程调用了某个对象的wait方法,该线程进入该对象的等待池(并已将锁释放)
如果之后,其他线程调用了notify或者notifyAll
该等待池中的线程会唤起,进入对象的锁池获取该锁,获得锁成功,线程沿着wait方法的路径继续执行
Lock锁情况下的线程通信#
public class Product{ boolean flag = false; Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); Condition produceCondition = lock.newCondition(); Condition consumeCondition = lock.newCondition(); public void setProduct(String brand, String name){ lock.lock(); try{ if(flag == true){ try{ // 生产者阻塞, 生产者进入等待队列中 produceCondition.await(); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } }else{ this.setBrand(brand); try{ Thread.sleep(100); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } this.setName(); flag = true; consumeCondition.signal(); }finally{ lock.unlock(); } } public void getProduct(){ lock.lock(); try{ if(!flag){ try{ consumeCondition.await(); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } // coding flag = false; produceCondition.signal(); }finally{ lock.unlock(); } } } public class ProducerThread extends Thread{ // 共享商品 private Product p; public ProducerThread(Product p) { this.p = p; } @Override public void run(){ for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){ if(i % 2 == 0){ p.setProduct("", ""); }else{ p.setProduct("", ""); } } } } public class CustomerThread extends Thread{ // 共享商品 private Product p; public CustomerThread(Product p) { this.p = p; } @Override public void run(){ for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){ p.getProduct(); } } } public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args){ Product p = new Product(); ProducerThread pt = new ProducerThread(); CustomerThread ct = new CustomerThread(); pt.start(); ct.start(); } }
Condition是在jdk1.5之后出现的,用来替代传统的await和notify
可以使用多个锁池和多个锁
作者:BigBender
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/BigBender/p/14422873.html
版权:本作品采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际」许可协议进行许可。








【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!