Spring 学习-AOP
问题 :
- AOP 解决的问题是什么
- Spring AOP 的底层实现是什么
- Spring AOP 和 AspectJ 的区别是什么
概述
在软件业,AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
上面的概述可以知道,切面编程的实现可以在编译期或是动态代理的时候(即是运行时期)。我们需要知道的是 Spring 使用的是动态代理,即是在runtime进行切面编程,而 AspectJ 既可以在编译期就完成切面植入,也可以在运行期才完成植入。我们先确定下面几个叙述 :
- Spring AOP 并不是完成的AOP 解决方案,它只作用在被 Ioc Container 管理的 bean
- AspectJ 是完整的 AOP 解决方案
- AOP 的目的就是各个模块分离,降低耦合度
AspectJ AOP 切面编程的方式
AspectJ makes use of three different types of weaving:
- Compile-time weaving: The AspectJ compiler takes as input both the source code of our aspect and our application and produces a woven class files as output
- Post-compile weaving: This is also known as binary weaving. It is used to weave existing class files and JAR files with our aspects
- Load-time weaving: This is exactly like the former binary weaving, with a difference that weaving is postponed until a class loader loads the class files to the JVM
For more in-depth information on AspectJ itself, head on over to this article.
上面讲的是 AspectJ 可以使用的三种类型的植入。
Spring 方式下的 AOP
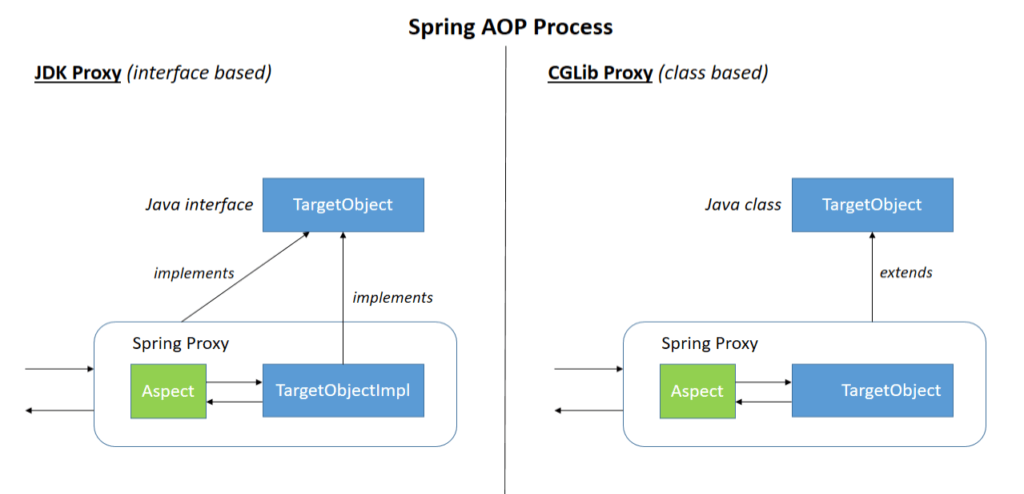
Spring 的AOP 用两种方式来实现,下面的图表示过程。
- JDK dynamic proxy – the preferred way for Spring AOP. Whenever the targeted object implements even one interface, then JDK dynamic proxy will be used
- CGLIB proxy – if the target object doesn’t implement an interface, then CGLIB proxy can be used
JDK 动态代理的方式下,需要targetObject 是一个接口,如果不是接口的话,那么就使用 CGLIB proxy
对比
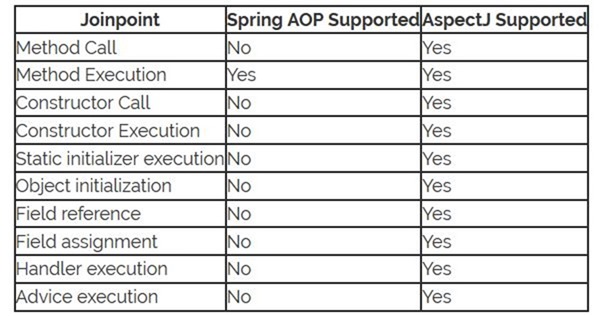
植入的节点对比
看下图。在某些节点的植入中,Spring 是无法做到的,例如方法调用调用,对象初始化等。
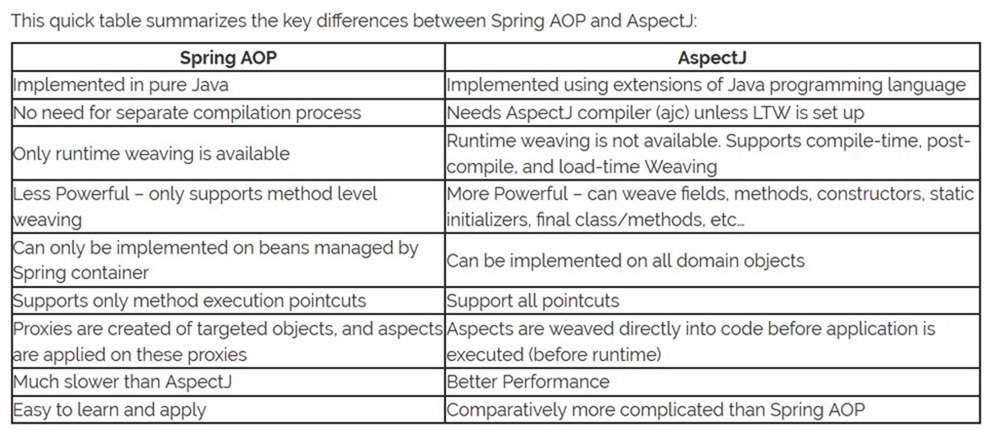
易用性对比
很显然 Spring 更加简单易用,因为它不用引入额外的编译器去编译代码,但是缺点也是明显,只使用它所管理的bean对象,而AspectJ需要引入编译器(ajc)和相关的包,除非AspectJ 使用的 post-compile 或是 load-time 植入。
性能对比
compile-time weaving is much faster than runtime weaving.
编译时期完成植入的方式比运行时期完成植入的方式快得多了,可以理解为但我们生产一个class 的时候已经完成了植入,Spring 则是运行时完成植入,那么就有代理的创建等开销。
对比总结
Spring AOP 的使用
AOP 切面编程,那么我们必须要知道切哪里,切进去做什么,这是我们先要了解的几个名词。
- advice (通知) : 切进去做了什么动作
- PointCut(切点) : 在哪里切
- Introduction : 引入允许我们向现有的类添加新的方法或属性例如, 我们可以创建一个Auditable通知
类, 该类记录了对象最后一次修改时的状态。 这很简单, 只需一个方
法, setLastModified(Date), 和一个实例变量来保存这个状态。 然后, 这个新方法和
实例变量就可以被引入到现有的类中, 从而可以在无需修改这些现有的类的情况下, 让它们
具有新的行为和状态。
Spring切面可以应用5种类型的advice :
- 前置通知(Before) : 在目标方法被调用之前调用通知功能;
- 后置通知(After) : 在目标方法完成之后调用通知, 此时不会关心方法的输出是什么;
- 返回通知(After-returning) : 在目标方法成功执行之后调用通知;
- 异常通知(After-throwing) : 在目标方法抛出异常后调用通知;
- 环绕通知(Around) : 通知包裹了被通知的方法, 在被通知的方法调用之前和调用之后
执行自定义的行为。
Spring AOP 需要了解以下几点 :
- Spring通知是Java编写的
- Spring在运行时通知对象
- Spring只支持方法级别的连接点
Spring AOP 可以通过两种方式来实现 : chema-based configuration 和 @AspectJ style 注解 ,当使用@AspectJ注解时,spring使用了 AspectJ库的注解并且使用 AspectJ库对切点表达式进行解析和匹配,但AOP运行时并不使用 AspectJ的编译器和织入,仍然是使用纯粹的springAOP实现。
Spring 非常聪明,从上面知道使用Aspect需要特定的编译器和库,Spring使用了和它一样的注解,但是运行还是使用 springAOP 实现,为了可以使用@AspectJ 的一样的注解需要引入两个库(看下面的例子)
下面我们使用 @AspectJ style 注解的方式来使用 AOP .
开启@AspectJ支持,以便支持自动代理。关于自动代理看官方文档的叙述 :
To use @AspectJ aspects in a Spring configuration, you need to enable Spring support for configuring Spring AOP based on @AspectJ aspects and auto-proxying beans based on whether or not they are advised by those aspects. By auto-proxying, we mean that, if Spring determines that a bean is advised by one or more aspects, it automatically generates a proxy for that bean to intercept method invocations and ensures that advice is executed as needed.
例子使用的是spring boot ,下面为 build.gradle 文件 :
plugins {
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '2.1.3.RELEASE'
id 'java'
}
apply plugin: 'io.spring.dependency-management'
group = 'com.benjious'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
sourceCompatibility = '1.8'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
//AspectJ AOP 功能的支持
compile group: 'org.aspectj', name: 'aspectjrt', version: '1.9.2'
compile group: 'org.aspectj', name: 'aspectjweaver', version: '1.9.2'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}
定义切面
@Aspect
public class Audience {
@Pointcut(value = "within(com..aop..*)")
public void withInPointCut() {
}
@Pointcut(value = "execution(* *perform(..))")
public void methodPointCut() {
}
@Pointcut("withInPointCut() && methodPointCut()")
public void finalPointCut() {
}
@Before(value = "finalPointCut()")
public void beforeWatch(){
System.out.println("观看之前!");
}
@AfterReturning(value = "finalPointCut()")
public void afterWatch(){
System.out.println("观看之后把垃圾拿走");
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "finalPointCut()")
public void someThingTrouble(){
System.out.println("运行出现异常!!插入纪录");
}
@Around(value = "finalPointCut()")
public void aroundDo(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("观看之前!!");
joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("观看之后把垃圾拿走");
}
}
目标被切对象。
public interface Performance {
void perform() throws Exception;
}@Service
public class PerformanceImpl implements Performance {
@Override
public void perform() throws Exception {
System.out.println("进行表演当中!!!");
// System.out.println("我要扔出异常啦!!");
// throw new Exception();
}
}
这里开启@Aspect 注解支持和使其成为一个bean.
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class ConcertConfig {
@Bean
public Audience getAudience(){
return new Audience();
}
}总结
- AOP 表示切面编程,AOP的作用就是尽量减少侵入代码,使业务逻辑各个模块分离,Spring 中使用 动态代理和 CGLIB 来实现
- Spring 中如果需要代理的类继承了接口就使用动态代理,如果没使用接口,就使用CGLIB,Spring 在两者之间切换
- 动态代理的原理是使用反射生成一个继承Proxy 的类,利用这个类来调用实际类的方法,CGLIB 原理是生成一个继承该类的子类来完成代理工作,Cglib代理需要为每个目标类生成相应的子类。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号