客户端模式(Client Credentials Grant)
Tips:本篇已加入,.Net core 3.1 使用IdentityServer4 实现 OAuth2.0 --阅读目录 可点击查看更多相关文章。
前言
本篇会详细刨析客户端模式的流程图,罗列一下此模式的利弊,适用场景。最后会用代码进行实现,此外还会额外参杂一些相关知识的彩蛋。
流程图
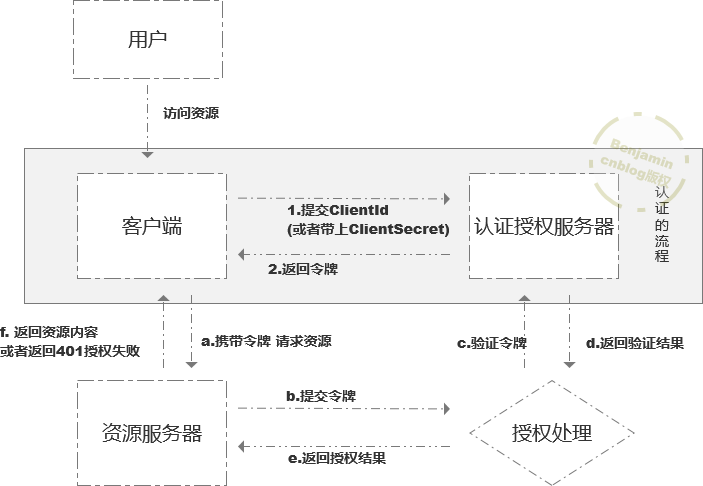
客户端模式(Client Credentials Grant) 是所有模式中最简单的模式,所以我会尽可能的把 一些细小的,可能后面文章也会涉及到的点,都归纳在此篇中。
对于一些名词解释,忘记的同学可以看一下之前一篇文章,打开传送门
业务场景:用户使用客户端模式去访问一个资源(我们可以理解成这个资源是查看数据)
上图是用户访问资源的整体流程,其实除了灰色的部分,认证的流程不一样,用户访问资源,资源服务器是否授权客户端资源都是一样的,所以之后的文章中我会只画出灰色的认证流程部分大家要注意一下。
用文字描述一下 客户端模式的流程就是:
|
1.客户端 访问授权服务器,提交clientid,或者clientSecret(密码可以提交也可以不提交,具体由代码控制) 2.授权服务器 校验clientid (和 clientSecret)是否可以通过身份认证,通过后返回 访问令牌(此令牌可以访问资源服务器) |
代码篇
我们按照官方文档的实现步骤,实现一遍代码。
官方实现的步骤如下:
|
如果是 使用IdentityServer4 4.x版本的话,就算按照以上步骤实现完,你会发现请求访问总是401。
|
要注意一下!!! ID4 4.x版本需要定义api的作用域,之前的版本作用域不定义的话都是默认与资源名称相同。 在这里我额外的加了一个步骤:
|
接下来 我们上手操作一遍:
先看一下目录结构:
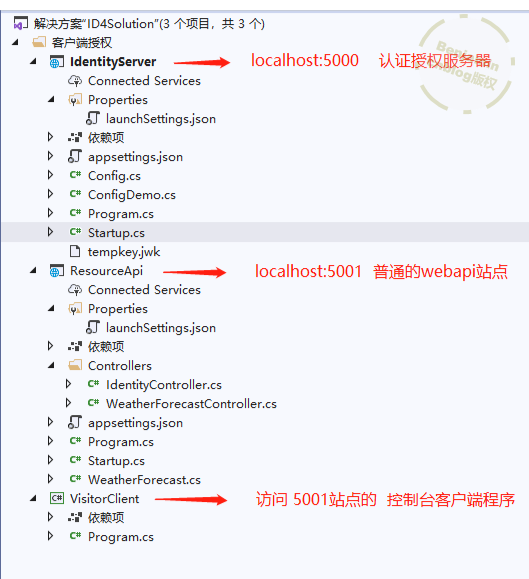
前面步骤说到的 定义api资源,定义作用域,定义客户端,我们全部写在 5000站点项目里的 Config文件。
大家想一下,我们要保护资源总要告诉认证授权服务器,保护资源的名称,哪些客户端可以看到(而客户端权限是作用在作用域上的,作用域又将api资源分组归类,那么这样也就定义了哪些客户端可以看到哪些api资源了)
public static class Config { /// <summary> /// Defining an API Resource /// </summary> public static IEnumerable<ApiResource> Apis => new List<ApiResource> { new ApiResource("api1", "My API") }; /// <summary> /// Defining the scope /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public static IEnumerable<ApiScope> ApiScopes => new ApiScope[] { new ApiScope("api1"), }; /// <summary> /// Defining the client /// </summary> public static IEnumerable<Client> Clients => new List<Client> { new Client { ClientId = "client", // no interactive user, use the clientid/secret for authentication AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.ClientCredentials, // secret for authentication ClientSecrets = { new Secret("secret".Sha256()) }, // scopes that client has access to AllowedScopes = { "api1" } } }; }
接下来要完成的步骤就是: Configuring IdentityServer 配置ID4 服务端
修改一下 IdentityServer项目中的 Startup 文件,为了让认证授权服务启动的时候能知道 资源相关的定义,并且启用一下 ID4中间件。
public class Startup { // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container. // For more information on how to configure your application, visit https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=398940 public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { //程序启动的时候加载 受保护的api资源,api作用域,客户端定义 var builder = services.AddIdentityServer()
.AddDeveloperSigningCredential() // .AddInMemoryApiResources(Config.Apis) .AddInMemoryApiScopes(Config.ApiScopes) .AddInMemoryClients(Config.Clients); } // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline. public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env) { if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } app.UseRouting(); app.UseIdentityServer();//使用ID4中间件 app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => { endpoints.MapGet("/", async context => { await context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello World!"); }); }); } }
ID4 提供了 内存级别读取资源,作用域和客户端的方法 .AddInMemoryXXXXX() 上面案例中我们都是读取的 Config类中的写死的资源,当然也可以从配置文件中读取,
至此,认证授权的服务器全部完工。接下去我们写一个最基本的api,在ResourceApi中我们新增一个 IdentityController。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc; namespace ResourceApi.Controllers { [Authorize] public class IdentityController : Controller { [HttpGet] public IActionResult Get() { return new JsonResult(from c in User.Claims select new { c.Type, c.Value }); } } }
我们给 IdentityController 加一个 用户身份验证 标签 [Authorize] 这样进来的请求就需要经过 .netcore的 身份认证。
我们修改一下 ResourceApi的 Startup文件 :
|
public class Startup { public Startup(IConfiguration configuration) { Configuration = configuration; } public IConfiguration Configuration { get; } // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container. public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.AddMvc().AddNewtonsoftJson(options => { // 忽略循环引用 options.SerializerSettings.ReferenceLoopHandling = ReferenceLoopHandling.Ignore; // 不使用驼峰 options.SerializerSettings.ContractResolver = new DefaultContractResolver(); // 设置时间格式 options.SerializerSettings.DateFormatString = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"; // 如字段为null值,该字段不会返回到前端 // options.SerializerSettings.NullValueHandling = NullValueHandling.Ignore; }); //将认证服务注册到容器中,并且配置默认token的方案名为 Bearer services.AddAuthentication("Bearer") .AddJwtBearer("Bearer", options => { options.Authority = "http://localhost:5000";//授权服务器地址 options.RequireHttpsMetadata = false; options.Audience = "api1";//token能访问的 受众群体(这个定义要和授权服务器定义的资源名称一样) }); } // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline. public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env) { if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } app.UseHttpsRedirection(); app.UseAuthentication(); app.UseRouting(); app.UseAuthorization(); app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => { endpoints.MapControllerRoute( name: "default", pattern: "api/{controller}/{action}"); }); } }
到这里,授权服务器代码也好了,资源api服务也好了。剩下的就是 客户端代码了,我们看一下 VisitorClient这个控制台应用:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // discover endpoints from metadata var client = new HttpClient(); var disco = client.GetDiscoveryDocumentAsync("http://localhost:5000").Result;//IdentityModel.Client 中对client的扩展 if (disco.IsError) { Console.WriteLine(disco.Error); return; } // request token client的扩展方法 使用 客户端模式 请求token var tokenResponse = client.RequestClientCredentialsTokenAsync(new ClientCredentialsTokenRequest { Address = disco.TokenEndpoint, ClientId = "client", ClientSecret = "secret", Scope = "api1" }).Result; if (tokenResponse.IsError) { Console.WriteLine(tokenResponse.Error); return; } Console.WriteLine(tokenResponse.Json); // call api client.SetBearerToken(tokenResponse.AccessToken); var response = client.GetAsync("http://localhost:5001/api/Identity/Get").Result; if (!response.IsSuccessStatusCode) { Console.WriteLine(response.StatusCode); } else { var content = response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().Result; Console.WriteLine(JArray.Parse(content)); } Console.ReadLine(); } }
运行下来获取token 没问题,但是访问 5001 api报错了

我们虽然是按照 文档去实现的,却总还是磕磕盼盼,这其实是好事情,我们看一下错误原因,有助于我们更加了解ID4
{StatusCode: 401, ReasonPhrase: 'Unauthorized', Version: 1.1, Content: System.Net.Http.HttpConnectionResponseContent, Headers:
{
Date: Wed, 23 Sep 2020 06:47:44 GMT
Server: Kestrel
WWW-Authenticate: Bearer error="invalid_token", error_description="The audience 'empty' is invalid"
Content-Length: 0
}}
报错原因是这样的,经过分析token是没问题的,但是无效,最后想了好久,The audience 'empty' is invalid 还记不记得之前我说过 ID4 4.x版本多了一个 scope的定义,
其实我们定义api资源的时候也要告诉授权服务器,这个api的scope,我们需要改一下 5000站点里 Config文件里的定义api字段那段代码。
/// <summary> /// Defining an API Resource /// </summary> public static IEnumerable<ApiResource> Apis => new List<ApiResource> { new ApiResource("api1", "My API") { Scopes = { new string("api1") } } };
把作用域给加上,然后我们再运行一下 VisitorClient控制台程序。
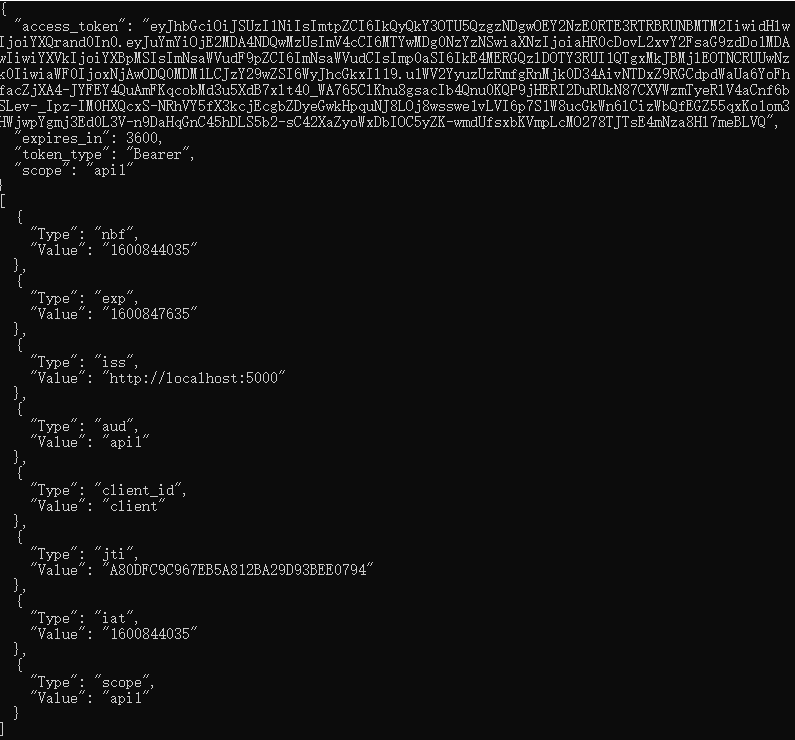
大功告成 !!
我们成功访问了被保护的api并输出了 User.Claims 的信息。
总结
这篇文章 从授权的流程到代码,完整的输出了一个 客户端模式的验证案例,
代码之后会完整的上传 github,如果我忘记了 可以留言里提醒我一下,
那么就这么结束了吗?并没有,里面还有一写概念,比如最终输出的 User.Claims 是个啥,token是怎么获取到的(我们现在只知道 配了一点东西,然后用了client的扩展方法)等等等。
我会再写一篇 补充篇 在那里完善,敬请期待~(●'◡'●)
| 如果觉得本篇随笔对你有帮助,请点击右下方的 【推荐👍】,或者给作者 【打赏】,感谢大家的支持,这将成为作者继续写作的动力。 |



