(Greedy approach)Find longest word in dictionary that is a subsequence of a given string
Find longest word in dictionary that is a subsequence of a given string

贪心算法:
1)将D按字符串的长度,从长到短排序。
2)从D[0]开始,尝试找到这个字符串(这里叫word)是S的子序列。
3)从word[0]开始,遍历S,尝试在S中找到这个字符;一旦找到,接着从当前位置的后面找word[1]是否在S中,以此类推。
// pch.cpp: 与预编译标头对应的源文件;编译成功所必需的 #include "pch.h" // 一般情况下,忽略此文件,但如果你使用的是预编译标头,请保留它。 #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<unordered_map> #include<iostream> #include<string> #include<assert.h> #include<set> using namespace std; struct length_more { bool operator()(const string& s1, const string& s2) { if (s1.length() == s2.length()) return true; return s1.length() > s2.length(); } }; /* 错误写法: string find(string MainWord, set<string, length_more> WordPool) { set<string>::iterator it; string res=""; //bool notBreak = true; //判断循环是否继续的标志 for (it = WordPool.begin(); it != WordPool.end(); ++it) { int i = 0; string word = *it; char w; for (int j = 0; j < word.length(); ++j) { for (;i < MainWord.length(); ++i ) { if (word[j] == MainWord[i]) { res += word[j]; w = word[j]; break; } } if (word[j] != w) break; else i = 0; } if (WordPool.count(res)) { break; } else { res.clear(); } } return res; } */ //正确: string find(string MainWord, set<string, length_more> WordPool) { set<string>::iterator it; string res = ""; for (it = WordPool.begin(); it != WordPool.end(); ++it) { int i = 0; string word = *it; bool flag = false; for (int j = 0; j < word.length(); ++j) { flag = false; for (;i < MainWord.length(); ++i) { if (word[j] == MainWord[i]) { res += word[j]; flag = true; break; } } if (!flag) break; } if (flag) return res; else res.clear(); } if(res.length()==0) return ""; } int main() { string MainWord = "abppplee"; set<string, length_more> WordPool; WordPool.insert("able"); WordPool.insert("ale"); WordPool.insert("apple"); WordPool.insert("bale"); WordPool.insert("kangaroo"); cout << find(MainWord, WordPool) << endl; //set<string>::iterator it; //for (it = WordPool.begin(); it != WordPool.end(); it++) // cout << (*it) << endl; return 0; }
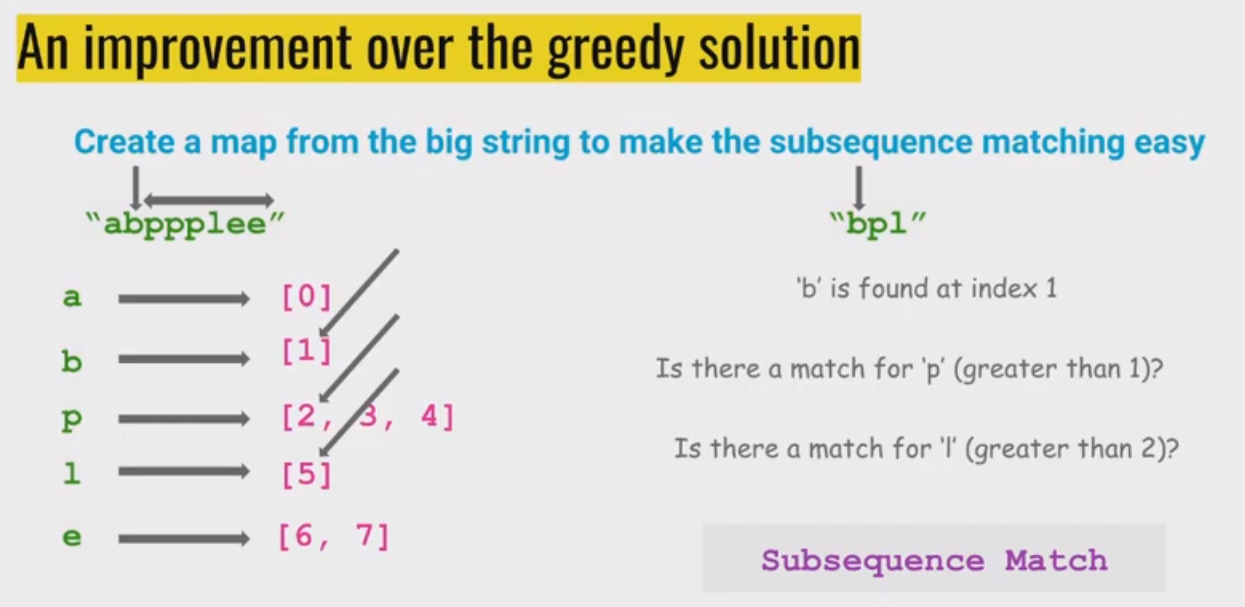
改进的贪心算法:将MainWord 插入到map中,记录每个元素对应得位置。感觉改进的这个更麻烦了,需要用到multimap来记录一个键值(字符)对应的多个位置,然后再用equal_range() 把这些位置给找到,循环遍历一遍:若找到比前一个字符索引大的,就看下一个字符,否则还要试这个字符的下一个索引位置。
// pch.cpp: 与预编译标头对应的源文件;编译成功所必需的 #include "pch.h" // 一般情况下,忽略此文件,但如果你使用的是预编译标头,请保留它。 #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<map> #include<iostream> #include<string> #include<assert.h> #include<set> using namespace std; struct more{ bool operator()(const string& s1, const string& s2) { if (s1.length() == s2.length()) return true; else return s1.length() > s2.length(); } }; string find(string MainWord, set<string, more> WordPool) { multimap<char, int> mp; int i = 0; string res=""; for (char a : MainWord) { mp.insert(make_pair(a, i)); ++i; } for (auto a : WordPool) { int k = -1; pair<multimap<char, int>::iterator, multimap<char, int>::iterator> it; bool flag; for (auto b : a) { flag = false; it = mp.equal_range(b); multimap<char, int>::iterator i = it.first; for ( ;i != it.second; ) { if (i->second > k) { k = i->second; res += i->first; flag = true; break; } else ++i; } } if (!flag) res.clear(); else return res; } if(res.length()==0) return ""; } int main() { string MainWord = "abppplee"; set<string, more> WordPool; WordPool.insert("able"); WordPool.insert("ale"); WordPool.insert("apple"); WordPool.insert("bale"); WordPool.insert("kangaroo"); cout << find(MainWord, WordPool) << endl; //set<string>::iterator it; //for (it = WordPool.begin(); it != WordPool.end(); it++) // cout << (*it) << endl; return 0; }
multimap:
http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/map/multimap/equal_range/


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号