(Trie树)leetcode208: Implement Trie,79:Word Search,DFS与BFS(python实现),212:Word Search2

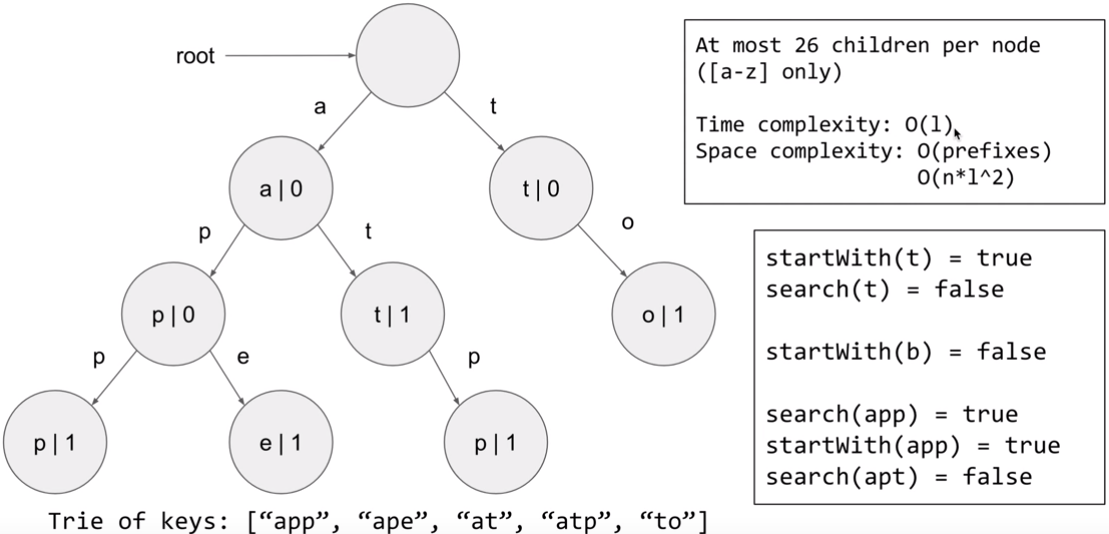
前缀树:查找字符串或其前缀。
一)数组实现,每个结点初始化有26个子结点,插入结点时,将该字母对应索引上创建结点。
class TrieNode{ public: TrieNode* child[26]; bool isWord; //构造函数初始化列表 TrieNode() : isWord(false){ for(auto& a: child) a = nullptr; } ~TrieNode(){ delete[] child; } }; class Trie { private: TrieNode* root; public: /** Initialize your data structure here. */ Trie() { root = new TrieNode(); } /** Inserts a word into the trie. */ void insert(string word) { TrieNode* p = root; for(char a: word){ int i = a - 'a'; if(!p->child[i]) //若某一字母对应索引的结点不存在 p->child[i] = new TrieNode(); p = p->child[i]; } p->isWord = true; } /** Returns if the word is in the trie. */ bool search(string word) { TrieNode* p = root; for(char a:word){ int i = a - 'a'; if(!p->child[i]) return false; p = p->child[i]; } return p->isWord; } /** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */ bool startsWith(string prefix) { TrieNode* p = root; for(char a: prefix){ int i = a - 'a'; if(!p->child[i]) return false; p = p->child[i]; } return true; } }; /** * Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such: * Trie* obj = new Trie(); * obj->insert(word); * bool param_2 = obj->search(word); * bool param_3 = obj->startsWith(prefix); */
class TrieNode{ public: vector<TrieNode*> child; bool isWord; //构造函数初始化列表 TrieNode() : isWord(false), child(26, nullptr){} ~TrieNode(){ for(auto& c:child) delete c; } }; class Trie { private: TrieNode* root; public: /** Initialize your data structure here. */ Trie() { root = new TrieNode(); } /** Inserts a word into the trie. */ void insert(string word) { TrieNode* p = root; for(char a: word){ int i = a - 'a'; if(!p->child[i]) //若某一字母对应索引的结点不存在 p->child[i] = new TrieNode(); p = p->child[i]; } p->isWord = true; } /** Returns if the word is in the trie. */ bool search(string word) { TrieNode* p = root; for(char a:word){ int i = a - 'a'; if(!p->child[i]) return false; p = p->child[i]; } return p->isWord; } /** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */ bool startsWith(string prefix) { TrieNode* p = root; for(char a: prefix){ int i = a - 'a'; if(!p->child[i]) return false; p = p->child[i]; } return true; } }; /**
二)vector容器实现,注意下构造函数和析构函数与数组的写法有差异。 * Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such: * Trie* obj = new Trie(); * obj->insert(word); * bool param_2 = obj->search(word); * bool param_3 = obj->startsWith(prefix); */
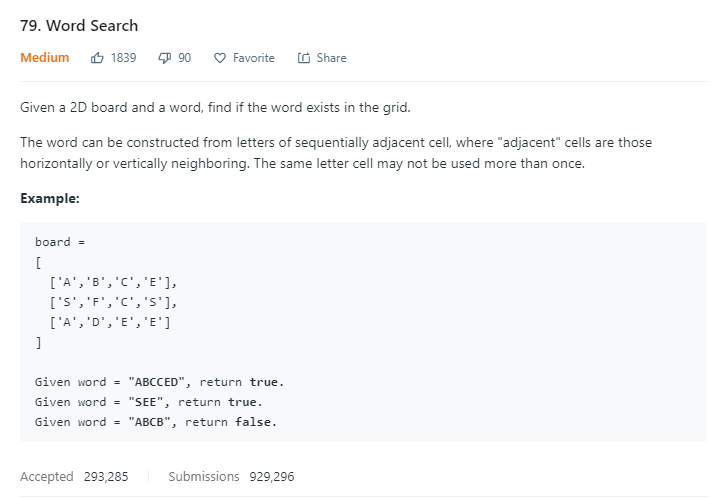
注意:同一个字符不能使用多次,即不能往回走。
思路:深度优先搜索,枚举每一个格子,将它作为根结点,来向上,向左,向右,向下寻找和word相同的字符。
伪代码:

class Solution { private: int w; int h; public: bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) { if(board.size()==0) return false; h = board.size(); w = board[0].size(); for(int i=0; i<w; i++){ for(int j=0; j<h; j++){ if(search(board, word, 0, i, j)) return true; } } return false; } bool search(vector<vector<char>>& board, const string& word, int d, int x, int y){ if(x<0 || x==w ||y<0 || y==h || word[d]!=board[y][x]) return false; //found the last char of the word if(d == word.length()-1) return true; //走过之后标记为不能走 char cur = board[y][x]; board[y][x]=0; bool found = search(board, word, d+1, x+1, y) || search(board, word, d+1, x, y+1) || search(board, word, d+1, x-1, y) || search(board, word, d+1, x, y-1); //递归结束后再标记回来 board[y][x] = cur; return found; } };
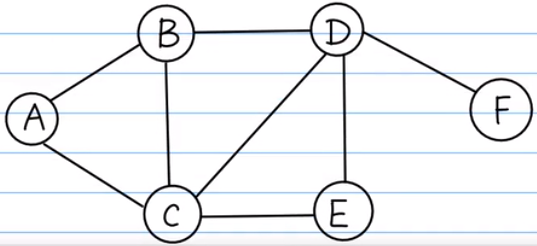
BFS:python实现,用队列先进先出实现。
#字典 graph ={ "A":["B","C"], "B":["A","C","D"], "C":["A","B","D","E"], "D":["B","C","E","F"], "E":["C", "D"], "F":["D"] }
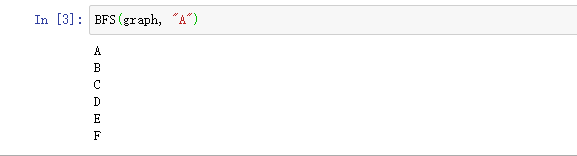
def BFS(graph, s): #s结点 queue = [] #数组来实现队列 queue.append(s) seen = set() #集合 seen.add(s) while(len(queue)): vertex = queue.pop(0) nodes = graph[vertex] for w in nodes: if w not in seen: queue.append(w) seen.add(w) print(vertex)
DFS: 用栈的后进先出来实现。
def DFS(graph, s): #s结点 stack = [] #数组来实现栈 stack.append(s) seen = set() seen.add(s) while(len(stack)): vertex = stack.pop() nodes = graph[vertex] for w in nodes: if w not in seen: stack.append(w) seen.add(w) print(vertex)

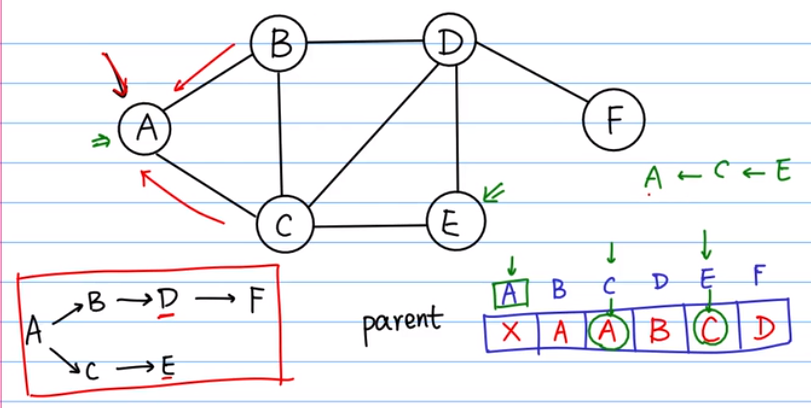
从A走到任一点的最短路径可以用这个图打印出来了。用映射表格来记录每一个结点的前一个结点。
问:从A到E的最短路径是哪一条?
答:从点E出发,它的前一个结点是C,再找到A,结束。
映射可以用字典来写。
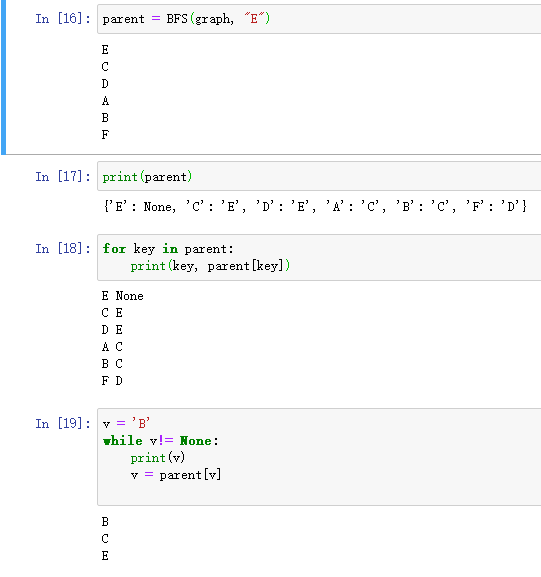
def BFS(graph, s): #s结点 queue = [] queue.append(s) seen = set() seen.add(s) parent = {s: None} #字典来实现映射 while(len(queue)): vertex = queue.pop(0) nodes = graph[vertex] for w in nodes: if w not in seen: queue.append(w) seen.add(w) parent[w] = vertex print(vertex) return parent

这道题是真心难,它用到了Trie树中的insert函数和深度优先搜索。先把words里的单词插入到Trie树中,其中Trie树里有个string变量叫str,用来存储当前是一个单词的字符串。然后使用两层for循环,在board里搜索Trie树的每个结点。
class Solution { public: struct TrieNode{ TrieNode* child[26]; string str; TrieNode(): str(""){ for(auto& a: child) a = nullptr; } ~TrieNode(){ delete[] child; } }; struct Trie{ TrieNode* root = new TrieNode(); void insert(string word){ TrieNode* p = root; for(char a:word){ int i = a -'a'; if(!p->child[i]) p->child[i] = new TrieNode(); p = p->child[i]; } p->str = word; } }; vector<string> findWords(vector<vector<char>>& board, vector<string>& words) { vector<string> res; int n = board.size(); int m = board[0].size(); if(n==0 || m==0 || words.empty()) return res; //记录是否访问过 vector<vector<bool>> visit(board.size(), vector<bool>(board[0].size(), false)); Trie T; for(auto& a:words) T.insert(a); for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){ for(int j=0; j<m; ++j){ if(T.root->child[board[i][j]-'a']) search(board, T.root->child[board[i][j]-'a'], i, j, visit, res); } } return res; } void search(vector<vector<char>>& board, TrieNode* p, int i, int j, vector<vector<bool>>& visit, vector<string>& res){ if(!p->str.empty()){ res.push_back(p->str); p->str.clear(); } int d[][2]={{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}}; visit[i][j] = true; for(auto& a:d){ int nx = a[0]+i, ny = a[1]+j; if(nx>=0 && nx<board.size() && ny>=0 && ny<board[0].size() && !visit[nx][ny] && p->child[board[nx][ny]-'a']) search(board, p->child[board[nx][ny]-'a'], nx, ny, visit, res); } visit[i][j] = false; } };
class Solution { public: /* * @param words: a set of words without duplicates * @return: all word squares */ struct TrieNode{ vector<TrieNode*> children; vector<int> index; TrieNode():children(26, nullptr){} }; TrieNode* buildTrie(vector<string>& words){ TrieNode* root = new TrieNode(); for(int i=0; i<words.size(); ++i){ TrieNode* t = root; //对于每一个单词遍历 for(int j=0; j<words[i].size(); ++j){ if(!t->children[words[i][j]-'a']) t->children[words[i][j]-'a'] = new TrieNode(); t = t->children[words[i][j]-'a']; t->index.push_back(i); //储存当前前缀的单词所在words中的索引 } } return root; } vector<vector<string>> wordSquares(vector<string> &words) { // write your code here vector<vector<string>> res; if(words.size()==0) return res; TrieNode* root = buildTrie(words); vector<string> out(words[0].size()); for(auto word: words){ out[0] = word; dfs(words, root, 1, out, res); } return res; } void dfs(vector<string> &words, TrieNode* root, int level, vector<string>& out, vector<vector<string>>& res){ string str = ""; //vector<string> out; // vector<vector<string>> res; if(level >= words[0].size()){ res.push_back(out); return; } for(int i=0; i<level; ++i) str += out[i][level]; TrieNode* p = root; for(int i=0; i<str.size(); ++i){ //在Trie树中找符合前缀的所有单词 if(!p->children[str[i]-'a']) return; p = p->children[str[i]-'a']; } for(int id : p->index){ //将符合前缀条件的单词放入out中 out[level] = words[id]; dfs(words, root, level+1, out, res); } } };
Word Squares:
解题步骤:
Store all words into a trie. Iterate through the words.
- For each word:
- create a new list. Add the word into the list.
- Search the trie for all the words that have the correct prefix. For each of these words:
- Add it to the list.
- Continue searching for the next prefix recursively.
- The recursion reaches its base case when the size of the list is equal to the length of a word. In this case, we've found a word square.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号