二叉树 104,111, 226, 100
二叉树具有天然的递归结构。
1. 前序遍历
void preorder(TreeNode* node){ if(node){ cout<< node->val; preorder(node->left); preorder(node->right); } }
或这样写:
void preorder(TreeNode* node){
//递归终止条件 if( node==NULL ) return;
//递归过程 cout<< node->val; preorder(node->left); preorder(node->right); }
空是一颗二叉树。
2. 查找某个键值key
bool contain(Node* node, Key key){ //终止条件 if(node == NULL) return false; if(key==node->key) return true; if(contain(node->left, key) || contain(node->right, key)) return true; return false; }
3. 删除二叉树
void destroy(Node* node){ if(node == NULL) return; destroy(node->left); destroy(node->right); delete node; count--; }


/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) { //递归终止条件 if(root == NULL) return 0; //当前结点左子树最高的高度 int leftMaxDepth = maxDepth(root->left); int rightMaxDepth = maxDepth(root->right); return max(leftMaxDepth, rightMaxDepth)+1;
/*也可直接写为
return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right))+1;
*/ } };
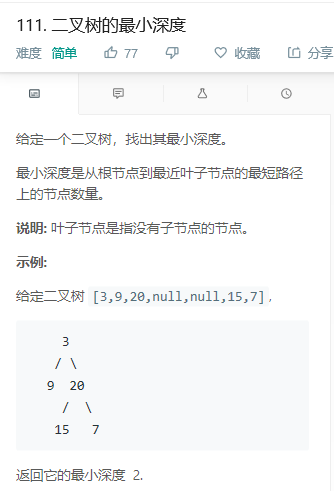
思路:DFS+递归
1)若当前结点若为空,则返回0;
2)若当前结点的左子树为空,则对右子树调用递归函数,并加1返回;
3)若当前结点的右子树为空,则对左子树调用递归函数,并加1返回;
4)若当前结点的左右子树都不为空,则对他们分别调用递归函数,并将二者的较小值加1返回。
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int minDepth(TreeNode* root) { if(root==NULL) return 0; if(root->left && root->right) return min(minDepth(root->right), minDepth(root->left))+1; else return max(minDepth(root->right), minDepth(root->left))+1; } };
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int minDepth(TreeNode* root) { if(root == NULL) return 0; if(root->left == NULL) return minDepth(root->right)+1; if(root->right == NULL) return minDepth(root->left)+1; return min(minDepth(root->left), minDepth(root->right))+1; } };

/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) { if(root == NULL) return NULL; invertTree(root->left); invertTree(root->right); swap(root->left, root->right); return root; } };

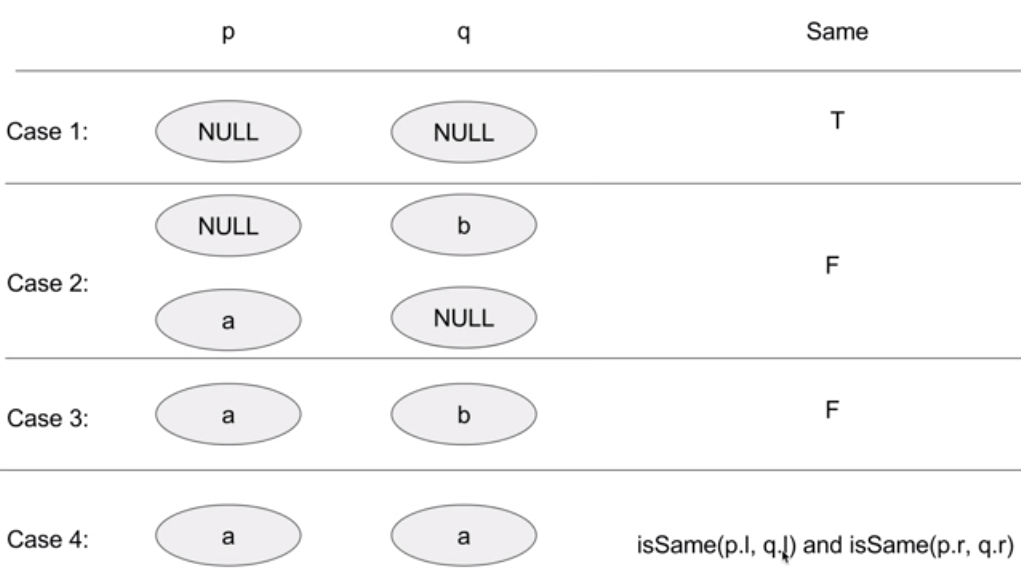
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) { if(!p && !q) return true; else if(!p && q) return false; else if(p && !q) return false; else{ if(p->val != q->val) return false; else return isSameTree(p->left, q->left) && isSameTree(p->right, q->right); } } };
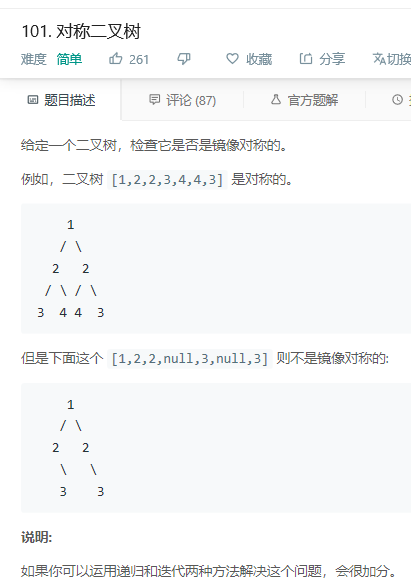
思路:判断二叉树是否是镜面对称的,比如有两个节点n1, n2,我们需要比较n1的左子节点的值和n2的右子节点的值是否相等,同时还要比较n1的右子节点的值和n2的左子结点的值是否相等,以此类推比较完所有的左右两个节点。
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) return true; return symmetric(root->left, root->right); } bool symmetric(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right){ if(!left && !right) return true; if(left && !right || !left && right || left->val != right->val) return false; return symmetric(left->left, right->right) && symmetric(left->right, right->left); } };



